Physics I Exam 2 Ch 4-6 Terms
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Newton’s First Law
An object at a constant velocity stays at this velocity until or unless acted upon by an external force.
Newton’s Second Law
F=ma
Newton’s Third Law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Gravitational Force equation
F=GM1M2/r2

What does a Newton (N) equal?
kg(m/s2)
Circumference of a circle
2πr
What are the 4 Fundamental Forces
Gravity
Strong Force
Weak Force
Electromagnetic Force
Describe the fundamental force gravity
The weakest force, for massive objects (planets)
Describe the fundamental force strong force
the bond that holds atoms together
Describe the fundamental force weak force
electroweak force that governs particle decay
Describe the fundamental force electromagnetic force
governs electricity and magnetism
What are the specific types of mechanical/gravitational forces
Normal Force Fn=mg
Gravitational Force for planets M1M2/r2
Frictional Force μFn
Tension Force F=ma
What is the equation for Normal force?
Fn=ma
Frictional Force equation
μFn
What does μ equal
coefficient of friction
What is a constant?
Something that doesn’t change (eg gravitational constant)
What is inertia?
The natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at a constant velocity. The mass of an object is a quantitative measure of inertia.
Inertial Reference frame
The frame of reference that is moving
Free body diagram
represents the object and the forces that act on it
Tension
opposite force
A system in equilibrium has no net force
True
A system not in equilibrium has net force
True
Kinetic Energy
KE= ½ mv2
Potential Energy
PE=mgh
Total Energy
KE+PE
If total energy =0, what is the equation
KE+PE=0
KE=-PE
Work
W=F⋅s
W= |F||s|cosθ
What does the s equal in the Work equation?
W=F⋅s
W= |F||s|cosθ
s=path length
What does the θ equal in the Work equation?
W=F⋅s
W= |F||s|cosθ
θ= angle between the force vector and the path (displacement vector)
Is a dot product a vector or scalar?
Always a scalar
What is a dot product?
a⋅b= axbx+ ayby
What is the Kinetic Force equation
FKE= ½ mvf2 - ½ mvo2
Work is not a change in Kinetic Energy
False
Momentum equation
p=mv
Total Work/Energy equation
ΔEtotal=(½ mvf2+mghf) - ((½ mvo2+mgho)
Gravitational Potential Energy
the energy that an object has by virtue of its position. For an object near the surface of the earth.
Gravitational Potential Energy equation
Wgravity=mg(ho-hf)
What does a Joule equal?
J= N x m (Force times mass)
Power equation
Work/t = (F⋅s)/t = ΔE/t
Conservation of Energy
Initial Energy = Final Energy
acceleration equation
Δv/Δt
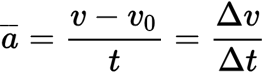
The 4 kinematic equations

centripetal force equation
Fc= mv2/r
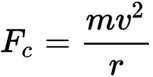
centripetal acceleration
a= v2/r