AP Psych Neuron Notes
Neurons are specialized brain cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the nervous system. They receive, process, and send information to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
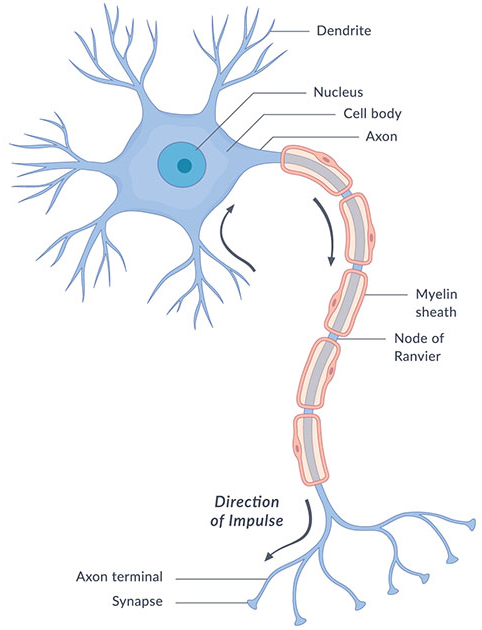
Dendrites = receive incoming information
Myelin sheath = fatty tissue that insulates the axon, speeding up transmission
Glial cells (Schwann cells) = non-neuronal cells in the CNS that form the myelin sheath
Cell body (soma) = contains the nucleus
Nucleus = makes decisions to fire or not to fire
Node of Ranvier = space between the myelin sheath
Axon = longest part of the neuron which the electrical message travels the length of
Axon terminal buds = sends message to the next neuron
Neuron Firing Process
Resting potential (state of being/HOMEOSTASIS) = not firing as a negative charge
Sodium on the outside (positively charged)
Potassium on the inside (negatively charged)
Polarization = at resting potential
Sodium on the outside (positively charged)
Potassium on the inside (negatively charged)
Action potential = “nerve impulse” that causes the neuron to fire (electrical message sent down the axon)
Reuptake = the process where a neuron reabsorbs a neurotransmitter it previously released into the synapse after the neurotransmitter has performed its function
“All-or-nothing” principal = fires down completely or not at all
Threshold = minimum level of electrical stimulation required to trigger an action potential
Intensity = same strength/power of the message the entire length of the axon
Depolarization = when message begins, Sodium (Na+) ions come in and depolarize (neutralize) the section of the axon
When “opposites” are no longer away from each other
This happens with action potential like a domino effect
Refractory Period = Potassium (K+) ions are pushed out and the neuron “pauses to reload”
The period of time after firing that the neuron is focused on resetting, and therefore is unable to fire again
Action Potential
Stimulus arrives
Sodium channels open and sodium ions rush in
Potassium channels open and potassium ions rush out
The first sodium channels close, but channels further down open causing the process to travel down the length of the axon
Synapse
Reuptake = the process by which neurotransimtters, after transmitting their signals, are absorbed back into the neuron that orginally released them
Neurotransmitters = chemical substances that cross synapses to carry on the message
Synapse = open space between two neurons of which neurotransmitters will cross
Receptor cells = specific points on dendrites of neurons that receive specific types of neurotrasmitters