Technologies and disorders
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:36 AM on 9/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two main types of hearing loss?
1. sensorineural hearing loss
2. conductive hearing loss
2
New cards
What is sensorineural hearing loss? What causes it?
Damage to the delicate structures of the inner ear and/or its associated nerves.
It is caused by:
* exposure to loud noise
* age
* illness such as measles, mumps and meningitis
* genetic disorder
It is caused by:
* exposure to loud noise
* age
* illness such as measles, mumps and meningitis
* genetic disorder
3
New cards
What is conductive hearing loss? What causes it?
Mechanical disruption to the middle ear
\
It is caused by:
* middle-ear infection
* perforated eardrum
* damage to the middle ear bones
* a benign growth in the middle ear
\
It is caused by:
* middle-ear infection
* perforated eardrum
* damage to the middle ear bones
* a benign growth in the middle ear
4
New cards
Name few treatments for hearing disorders
1. Cochlear implants
2. Cone conduction implants (BAHA)
3. Hearing aids
5
New cards
what is cochlear implant? How does it work?
Electronic devices that are used to give hearing to those who are profoundly deaf. The electrode is surgically inserted into the cochlea, a part of your inner ear. The implant stimulates the hearing nerve to provide sound signals directly to your brain. It helps people who have a sensorineural hearing loss
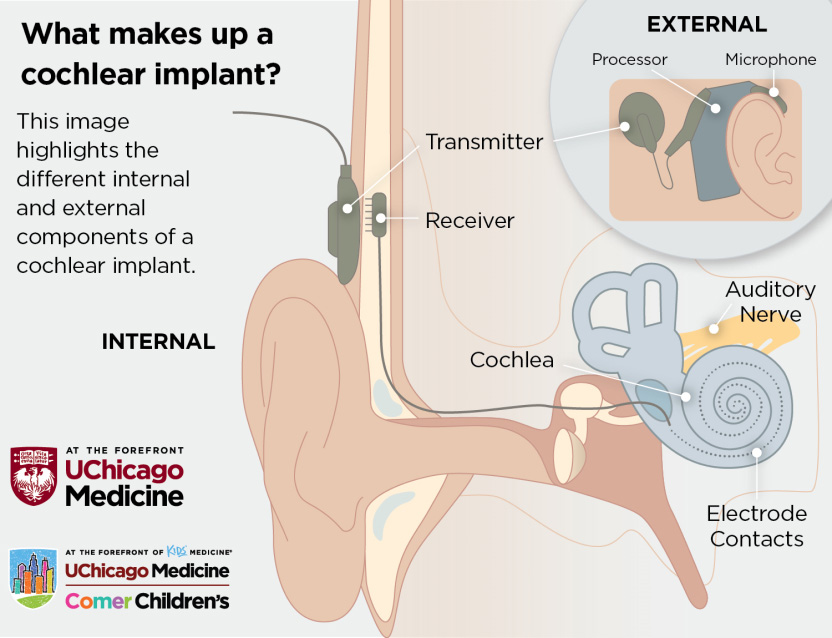
6
New cards
what is bone conduction implants? How does it work?
BAHA transmits sound vibrations through the bone. The sound processor converts the sound picked up by its microphone into vibrations. The sound processor then transmits the vibrations through the bones of the skull to the cochlear of the inner ear. It would help a person who is deaf due to damaged middle ear bones.
7
New cards
what is hearing aids? How does it work?
Hearing aids amplify sounds as they enter the outer ear. It helps people who have a loss of sensitivity in the cochlea.
8
New cards
What are the limitations of bone conduction implants?
* Local infection following the operations
* Loss of the osseointegrated fixture as a result of trauma
* Chronic pain
* Expensive
Satisfaction rate of 100%
* Loss of the osseointegrated fixture as a result of trauma
* Chronic pain
* Expensive
Satisfaction rate of 100%
9
New cards
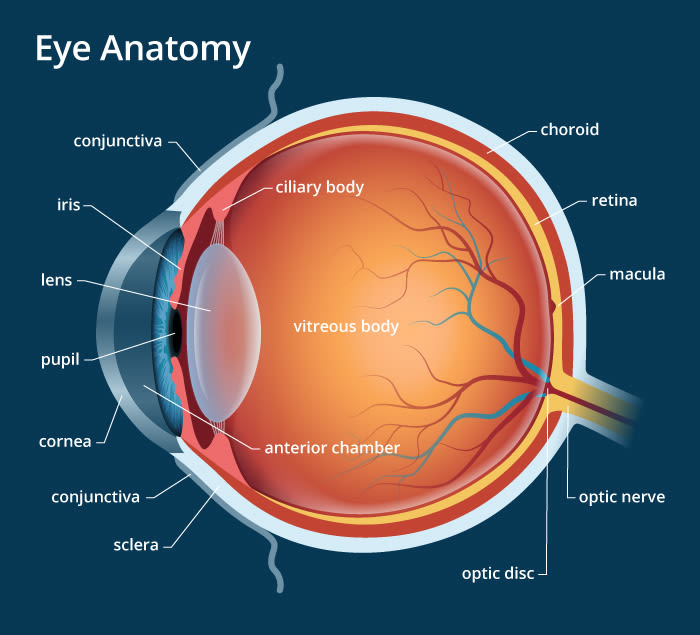
What causes eye disorders?
1. Myopia- short sightedness (can see close)
2. Hyperopia- long sightedness (can see far)
3. Astigmatism- blurry vision
4. Cataracts- cloudy vision
5. Glaucoma- Vision is lost
6. Detached retina- seeing floaters, sudden flashes of light or shadow in the field of vision
7. Macular degeneration- loss of sharpness in vision
10
New cards
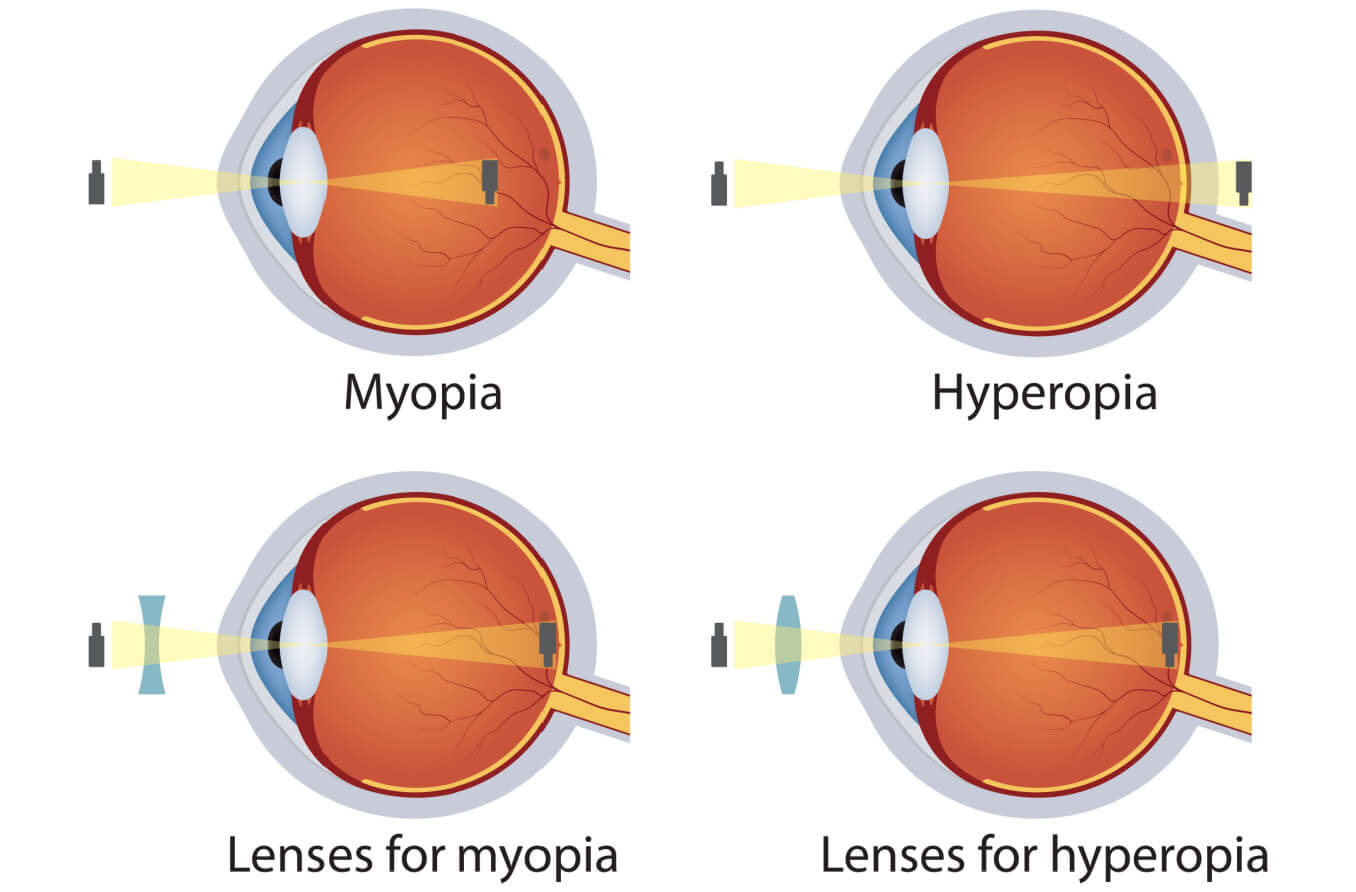
What causes myopia and hyperopia?
The focal point not forming on the retina
11
New cards
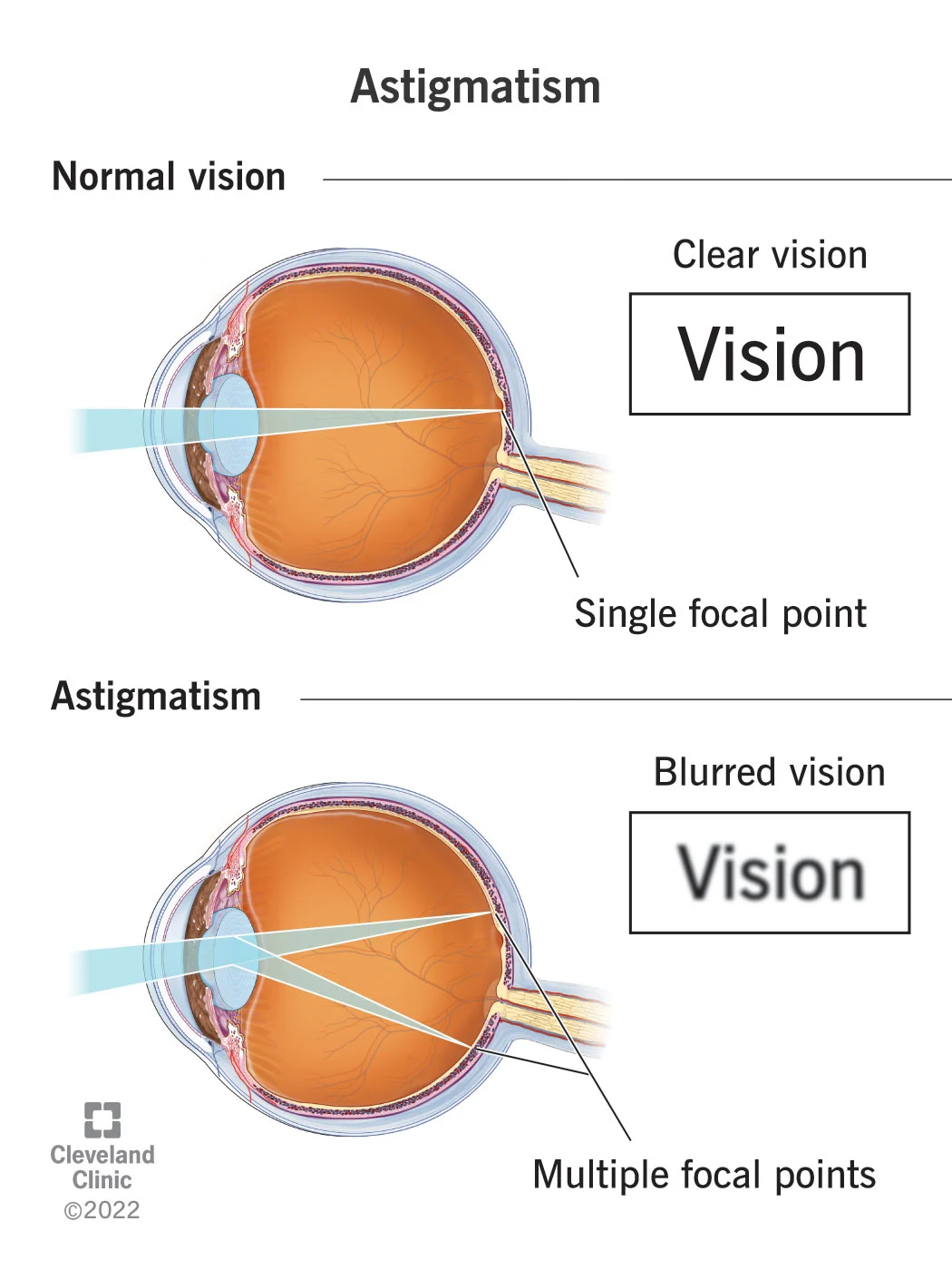
What causes astigmatism?
Astigmatism happens when your cornea or lens has a different shape than normal. The shape makes light bend differently as it enters your eye, causing many refractive errors. Thus resulting in blurry vision
12
New cards
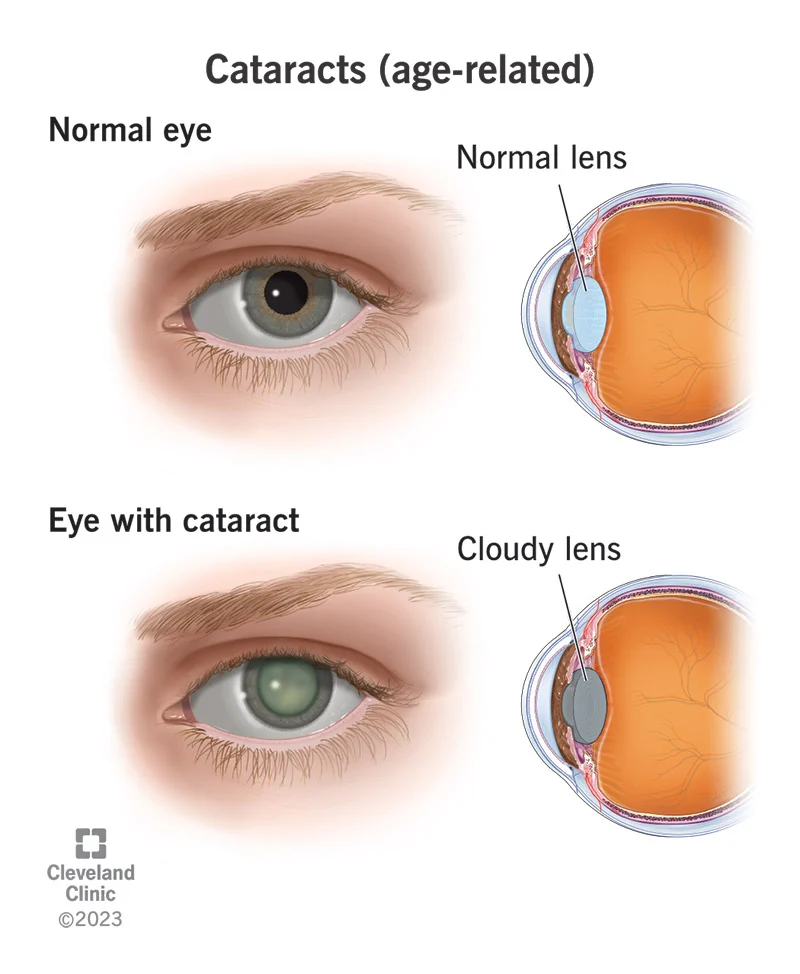
What causes cataracts?
As an individual ages the proteins in the lens of the eye start to break down and clump together. This clump makes a cloudy area on the lens — known as a cataract.
13
New cards
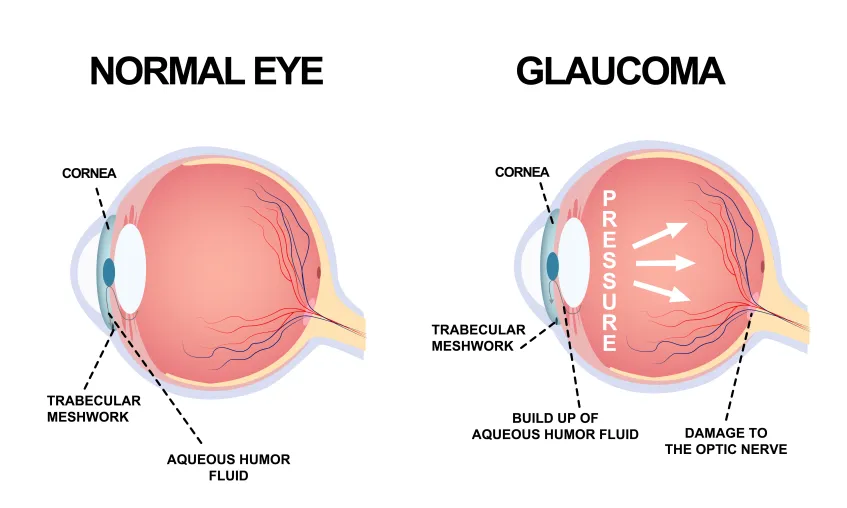
What causes Glaucoma?
A build up of pressure in the eye damages the optic nerve and the blood vessels that carry blood to the retina. This causes a blockage in the drainage channel that drains fluid from the aqueous humour.
14
New cards
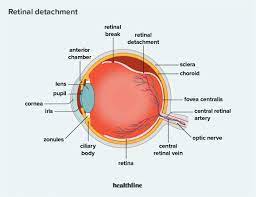
What causes detached retina?
Aging or an eye injury causes the retina to begin separating from the sclera which contains the blood vessels that provide necessary oxygen and nutrients.
15
New cards
What causes muscular degeneration?
Degradation of the retina
16
New cards
Name few treatments for eye disorders
1. Spectacles and contact lenses- for myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism
2. Laser eye surgery
17
New cards
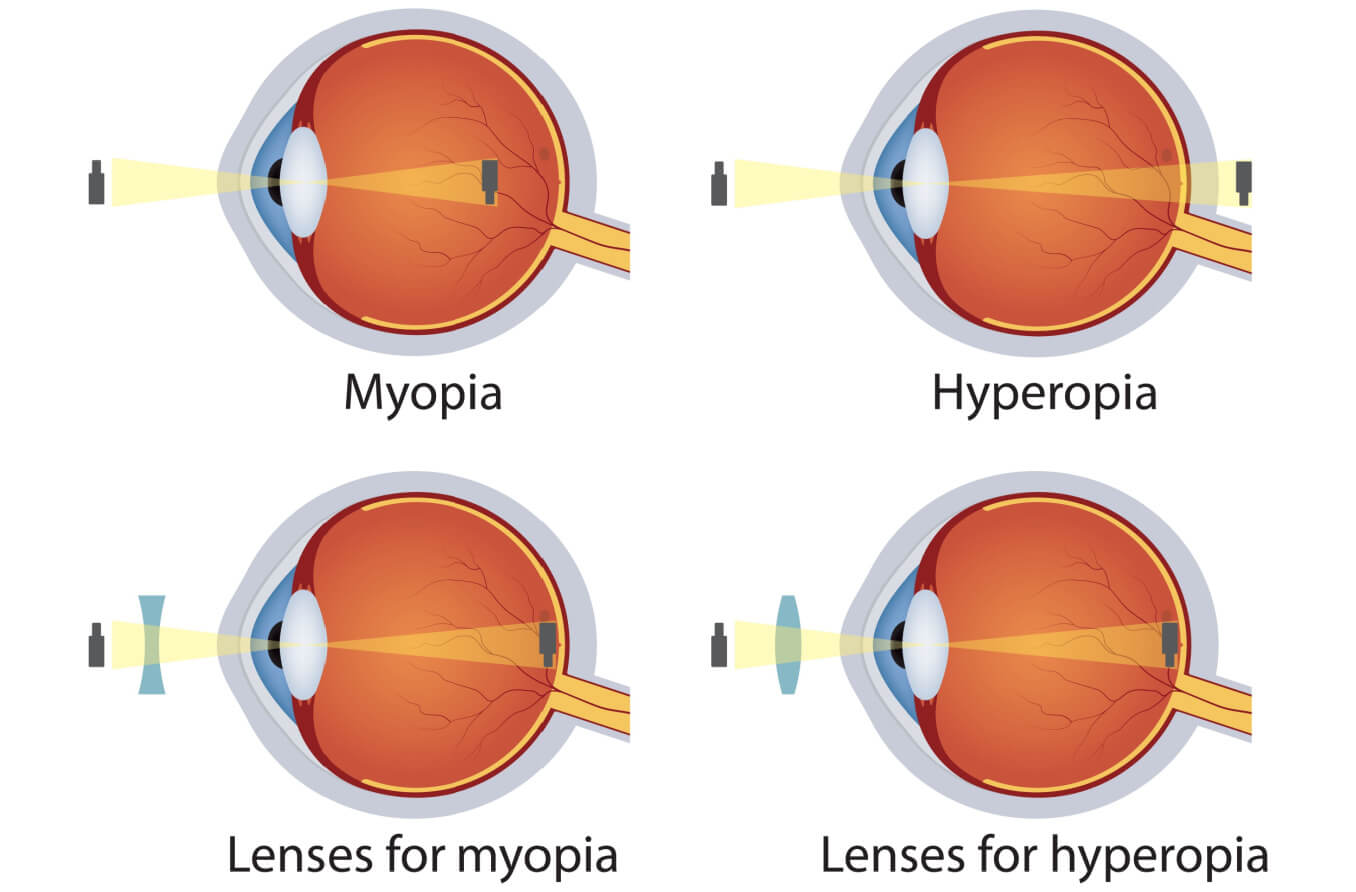
what is spectacles and contact lenses? How does it work?
Spectacles and contact lenses correct the vision of people with hyperopia, myopia and/or astigmatism by reflecting the light entering the eye in a way that is complementary to the defect in the eye.
18
New cards
what is LASIK? How does it work?
LASIK stands for laser assisted in situ keratomileusis.
1. A small circular flap is created in the cornea using a precise metal blade or a laser.
2. The flap is then folded back to reveal a layer of the cornea called the stroma.
3. A laser is then used to vaporise materials in the corneal stroma in order to reshape the cornea to correct it from the refractive error in the eye
4. Finally the flap is replaced and allowed to heal.
1. A small circular flap is created in the cornea using a precise metal blade or a laser.
2. The flap is then folded back to reveal a layer of the cornea called the stroma.
3. A laser is then used to vaporise materials in the corneal stroma in order to reshape the cornea to correct it from the refractive error in the eye
4. Finally the flap is replaced and allowed to heal.
19
New cards
What are the limitations of laser eye surgery?
* Subconjunctival haemorrhage
* Dry eyes
* Follow-up over/under correction surgery
* Glasses or contact lenses
* Chronic physical pain
* Glares during the day
* Inflammation at the interface between the flap and the underlying stroma
satisfaction rate of 95%-98%
* Dry eyes
* Follow-up over/under correction surgery
* Glasses or contact lenses
* Chronic physical pain
* Glares during the day
* Inflammation at the interface between the flap and the underlying stroma
satisfaction rate of 95%-98%
20
New cards
Name few causes of kidney diseases
1. Glomerulonephritis- inflammation of kidney nephrons
2. Diabetic nephropathy- damage to kidney tissue resulting from type I or Type II diabetes
3. Hypertension- High blood pressure which can lead to hardening of kidney tissue
4. Polycystic kidney disease- cysts in the kidneys
21
New cards
Name few symptoms for kidney diseases
* Itchiness
* Swelling in hands, feet and face
* Ammonia breath
* Changes in the colour or appearance of urine
* nausea
* Bad taste in the mouth
* Swelling in hands, feet and face
* Ammonia breath
* Changes in the colour or appearance of urine
* nausea
* Bad taste in the mouth
22
New cards
Name few treatments for kidney diseases
1. Dialysis
2. Kidney transplant
23
New cards
what is Dialysis? How does it work?
Dialysis is a process where the blood is artificially filtered to remove the waste. The most common type of dialysis is haemodialysis in which the blood is removed from the body and circulated through a dialyze.