biology Exam 3
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
The stages of mitosis
arrange a cells chromosomes spatially so they can be duplicated and divide
5 phases of mitosis
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
cytokinesis
cleavage of the cell into equal halves
Mitosis makes cells that..
are genetically identical to each other
Overview of Meiosis
meiosis is a form of nuclear division that leads to the production of gametes (in animals).
Gametes
egg and sperm cells
Gametes are
haploid
Adult body cells (somatic cells)
are diploid, containing 2 sets of chromosomes
Sexual Reproduction
includes the fusion of gametes (fertilization) to produce diploid zygote.
sexual reproduction & meiosis =
genetic diversity
Prophase 1
Difference in mitosis:
-homologous become closely associated in Synapsis
-Crossing over
Crossing Over
genetic recombination between non-sister chromatids
Metaphase 1
- microtubules from opposite poles attach to each homologue
- homologues are aligned at the metaphase plate side-by-side
- the orientation of each pair of homologous on the spindle is random
Each gene arrangement results in..
a different gamete
Meiosis II resembles a
mitotic division
Prophase II (Meiosis)
nuclear envelope dissolves and spindles apparatus form
Metaphase II (Meiosis)
chromosomes align on metaphase plate
Anaphase II (Meiosis)
sister chromatids separated from each other
Telophase II (Meiosis)
nuclear envelope re-forms; cytokinesis follow
no crossing over in
meiosis
Trait
particular form of a character (ex.: red flowers)
Recessive
masked in phenotype when heterozygous
Character
observable physical feature (ex. floral color)
Dominant
fully expressed in phenotype
Gene
units of inheritance, segment of DNA that codes for a protein
Allele
Different forms of a gene
Phenotype
physical expression of the organism (ex: red or white flower)
Genotype
The composition of alleles of an organism
genetics
study of heredity and variation
Heredity
continuity of biological traits from one generation to the next
Variation
difference among individuals of the same species (due to environment and genetic components.
dominant allele
fully expressed in phenotype; masks recessive allele; ex. S= Spherical
recessive allele
masked in phenotype when heterozygous (genotype); ex. s= wrinkled
Types of genotypes
homozygous, heterozygous
Homozygous
having two identical alleles for a given character
SS= homozygous dominant for smooth seeds
ss= homozygous recessive for wrinkled seeds
Heterozygous
having two different alleles for a trait
-Ss
heredity
inheritance from parents to offspring
Variation
differences among offspring
F1 generation
First filial generation - offspring produced by crossing 2 true breeding strains
F2 generation
offspring results from the self-fertilization of F1 plants
the terms ratio, frequency, percent, and proportion
are all parts of a whole
Mendel's Law of Segregation
during gamete formation, alleles separate so that each gamete receives only one allele for each gene.
monohybrid cross
cross between two individuals regarding only one gene locus of interest; only have 2 variations
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles governing different traits assort independently of each other during meiosis
-your genotype for one character does not determine a second character
-came from work with dihybrid crosses
dihybrid cross
a cross between two individuals that differ in two traits
(ex. RrYy)
In meiosis
MANY gametes are made in individuals
-
MANY gametes are released into the environment, with all possible genotypes from an individual.
-
ONE egg will be fertilized by one sperm
mitosis, meiosis, and mendelian genetics are
at an individual level
population genetics
the study of genetic variation and its causes within population
Darwin
Evolution is descent with modification
Evolution
Genetic changes through time.
1. species accumulate difference
2. descendants differ from their ancestors
3. new species arise from existing ones
natural selection
Proposed by darwin's as the first mechanism of change.
1. individual have inherited characteristics
2. they produce more surviving offspring
3. the population includes more individuals with these specific characteristics
4. population evolves and is better adapted to its present environment
Gene variation in nature
measure levels of genetic variation at different loci
Locus
the place on a chromosome where a gene is located
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
single base change in DNA used to look at many loci at once.
-happens from mutation (error)
Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection
Different survival & reproduction; genetically-based variation leads to evolutionary change
-variation results of pre-existing differences
Genetic Variation
we can use genetic markers to identify groups of genetically similar humans
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
The original proportions of the genotypes in a population will remain constant from generation to generation as long as 5 assumptions are met.
Gene Pool
sum of all alleles in a population
genetic variation within populations
-An allele's frequency = number of copies of allele in pop/sum of all alleles in the population
-allele frequencies range from 0 to 1
-Sum of all allele frequencies at a locus = 1
Allele Frequencies equation
p+q = 1
p= frequency of dominant allele
q= frequency of recessive allele
Genotype frequencies equation
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
The Anthropocene
We are in it right now.
-marked by human activity
-climate change in the atmosphere
-change identified in sediments
(stratigraphic signature)
Hardy-Weinberg assumptions
1. No Mutation takes place
2. No genes are transferred to or from another sources (no movement)
3. Random mating is occuring
4. The population size in very large
5. No selection occurs (no change)
Forces of Evolution
1. mutation
2. gene flow (migration)
3. non-random mating
4. genetic drift
5. selection (change)
Mutation
A change in a cell's DNA.
- mutation rates are generally so low they have little effect on hardy-weinberg proportions of common alleles
- ultimate source of genetic variation
Gene Flow
A movement of alleles from one population to another.
-powerful agent of change
-tends to homogenize allele frequencies
Non-Random Mating
mating with specific genotypes.
-shifts genotype frequencies
-assortative mating- "likes mates with like"
Genetic Drift
Random fluctuations in allele frequencies over time.
-important in small populations
founder effect (genetic drift)
few individuals found new population
bottleneck effect (genetic drift)
drastic reduction in population, and gene pool size
What causes extinction of species?
H- habitat loss/destruction
I- Invasive species
P- pollution
P- Human Population
O- Over-harvesting; Poaching
Natural Selection
environmental conditions determine which individuals in a population produce the most offspring.
3 conditions for natural selection to occur:
1. variation must exist among individuals in a population
2. variation must be genetically inherited
3. variation among individuals must result in differences in the number of offspring surviving
Fitness
genetic contribution of a genotype to the next generation relative to other genotypes.
Fitness is a combination of:
1. survival: how long does an organism live
2. mating success: how often it mates
3. number of offspring per mating that survive
How is fitness measured?
one way is via mean # surviving offspring in the next generation
3 kinds of natural selection
stabilizing selection,
directional selection,
disruptive selection
stabilizing selection
Selection may favor average individuals for a phenotypic character = stabilizing selection
-mean stays the same, tails pull in
(ex. human birth weight)
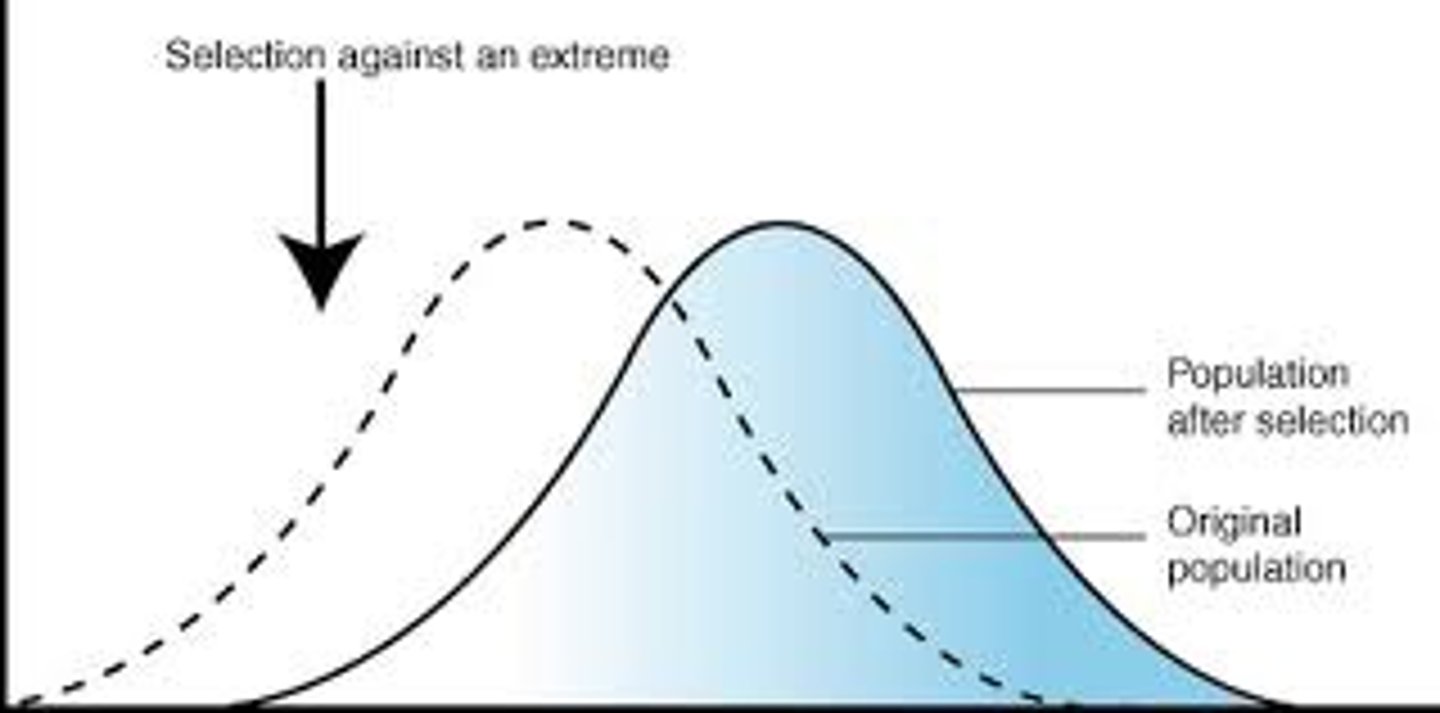
directional selection
Selection may favor individuals at one extreme for phenotypic character = directional selection
-mean shifts toward one direction
(ex. cliff swallows after bad weather - surviving birds were larger than dead birds)
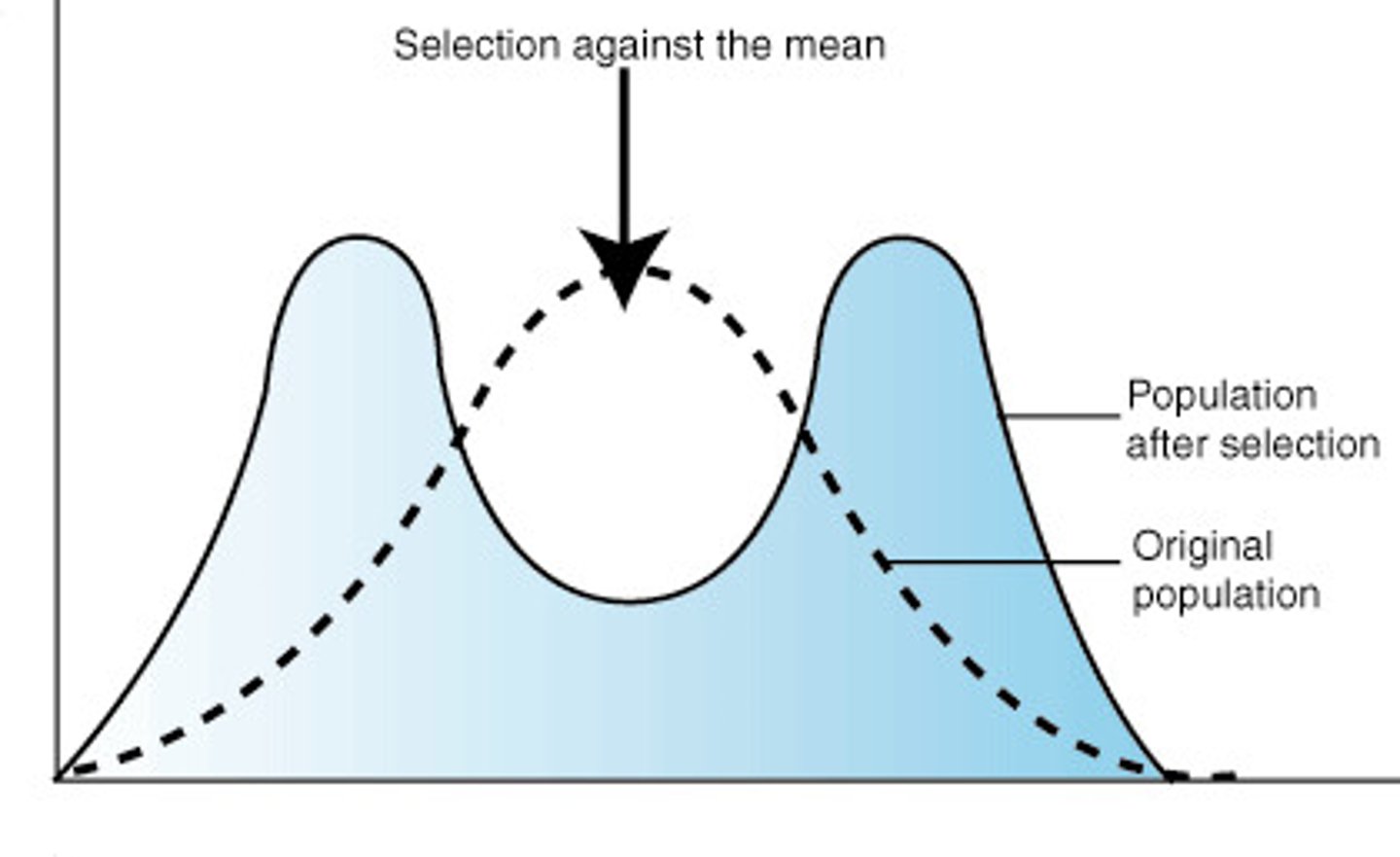
disruptive selection
Selection may favor individuals at both extremes = disruptive selection
- mean stays the same but shape of curve changes
-rarest form of selection
stabilizing selection dia.
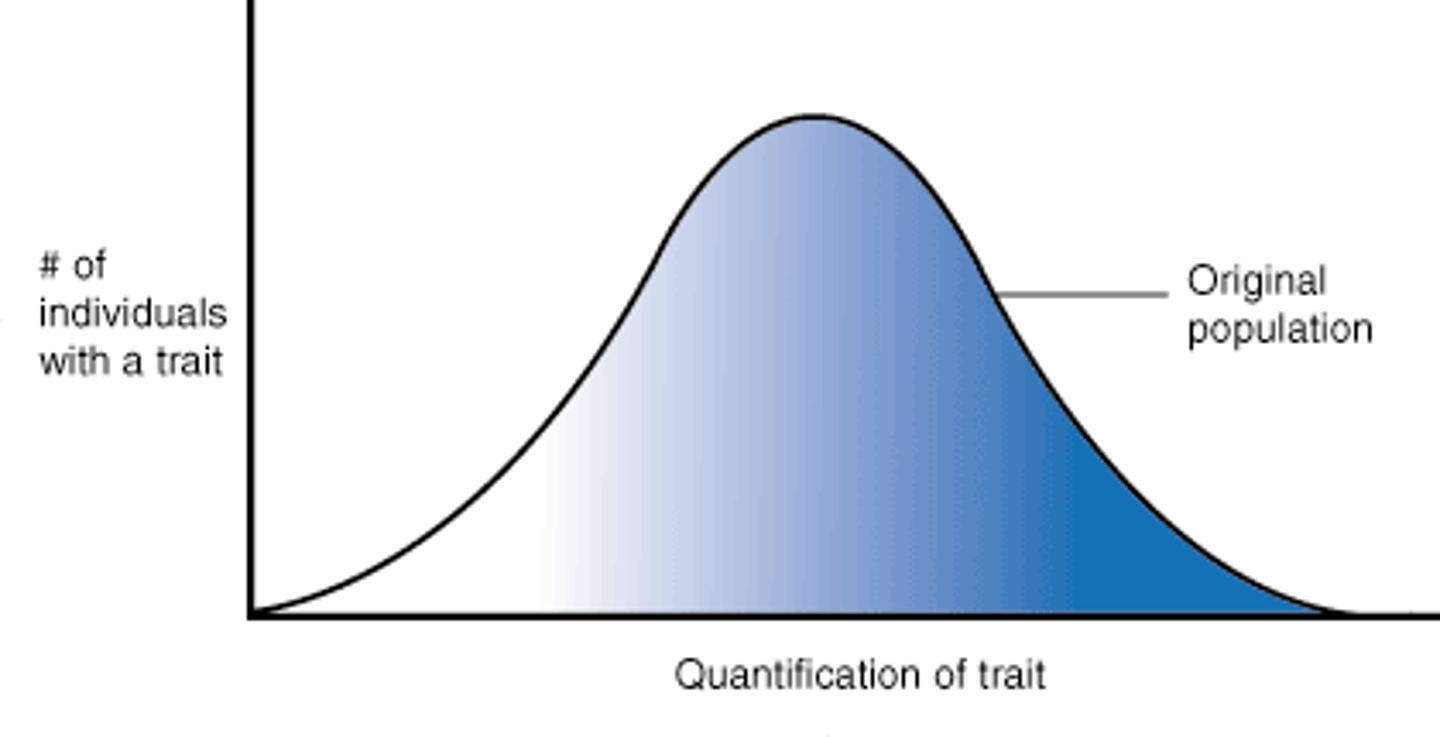
directional selection dia.
disruptive selection dia.