WVU EXPH 240: Endocrine & Blood and Lymphatic System
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
337 Terms
The system (and its hormones) that influence nearly every cell, organ, and organ system in the body
endocrine system
Hormone: Thyroid-stimulation hromone (TSH)
Function: stimulates secretion from thyroid gland
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
Hormone: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Function: stimulates secretion from adrenal cortex
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
Hormone: Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Function: initiates growth of ovarian follicle; stimulates secretion of estrogen in females and spem production in males
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
Hormone: Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
Function: affects skin pigmentation
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
Hormone: Growth hormone (ADH)
Function: Influences growth
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
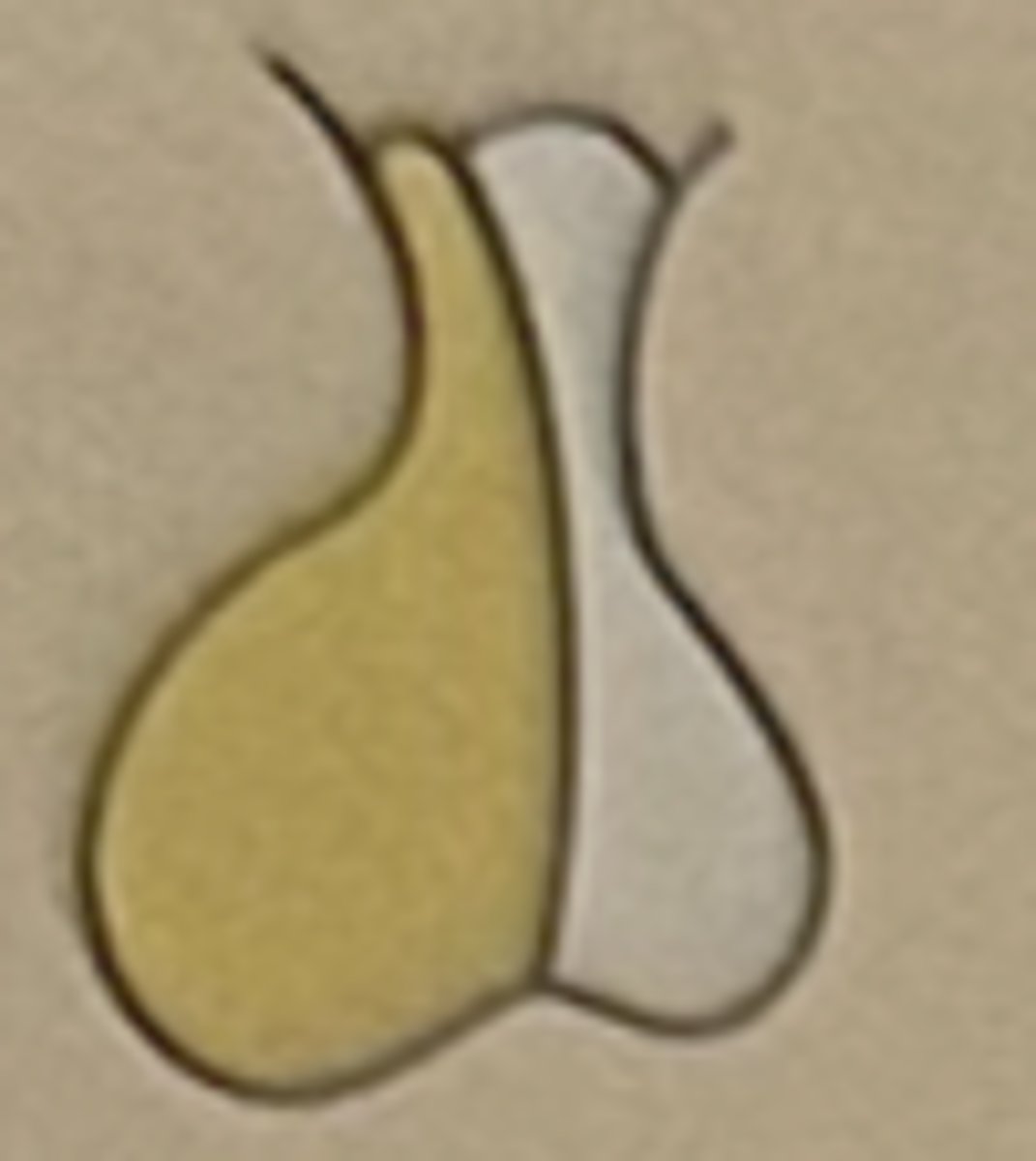
Hormone: Prolactin (PRL)
Function: Stimulates breast development and milk secretion
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
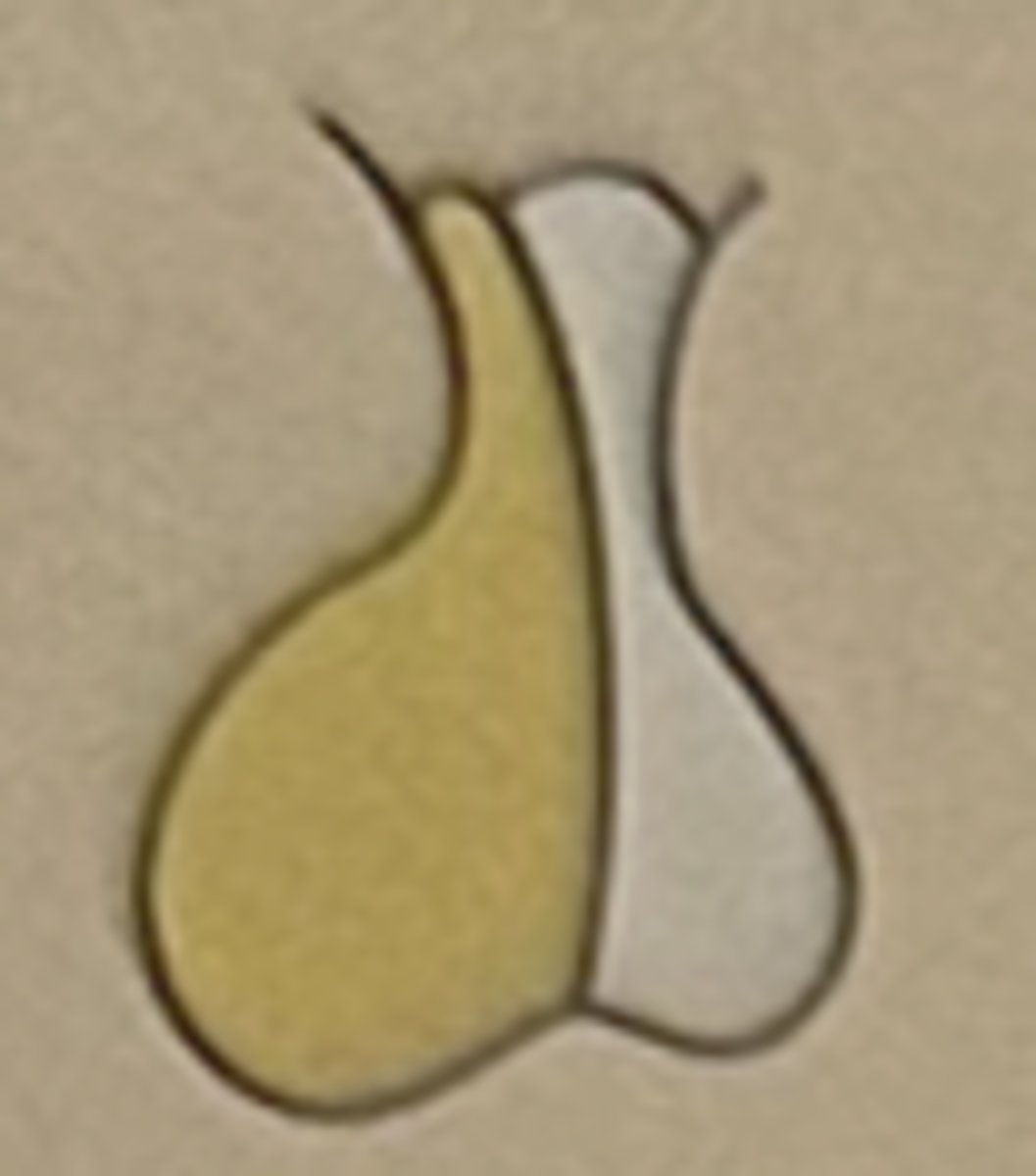
Hormone: Antidiuertic hormone (ADH)
Function: influences the absorption of water by kidney tubules
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
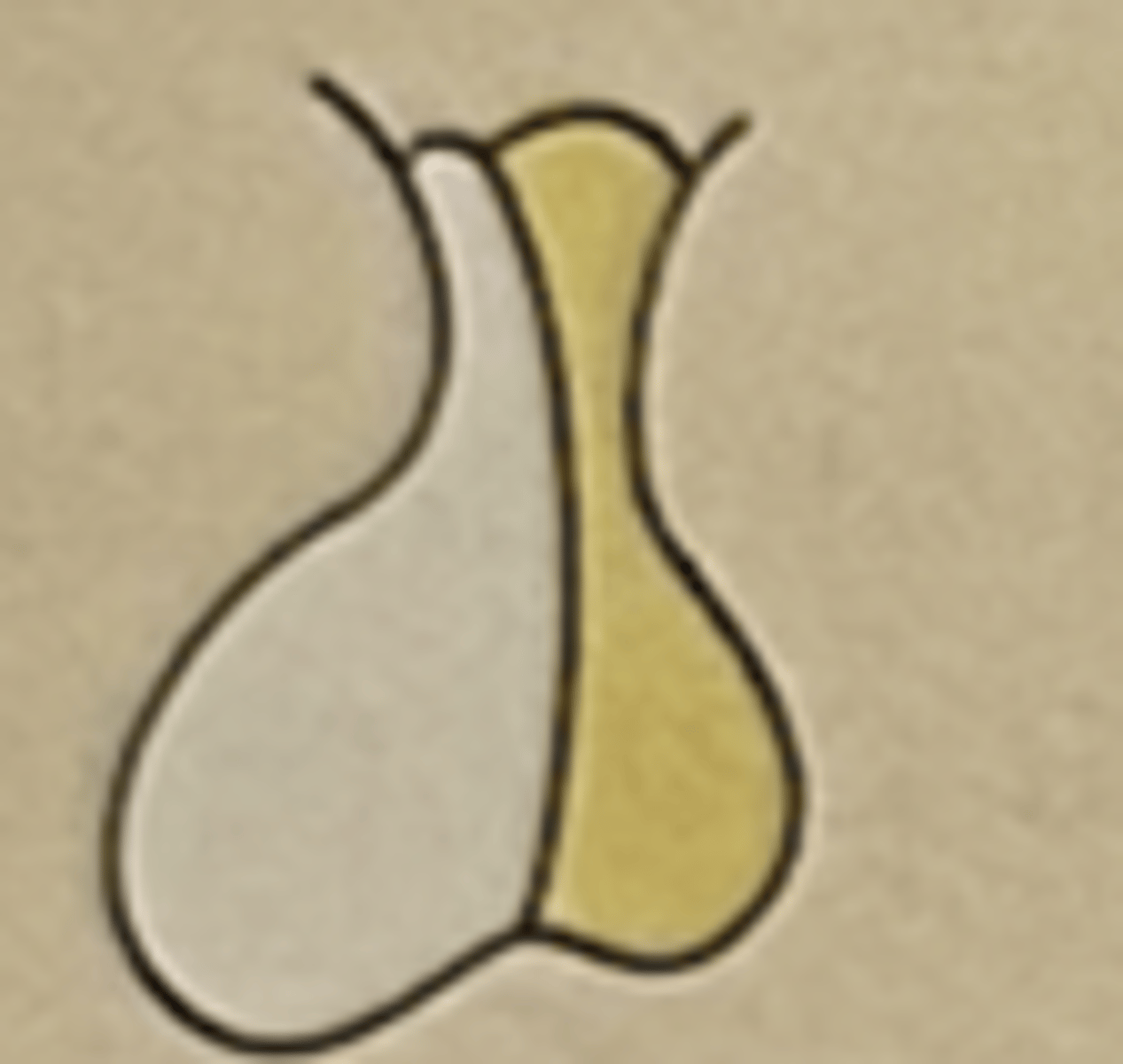
Hormone: Oxytocin (OXT)
Function: influences uterine contraction
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
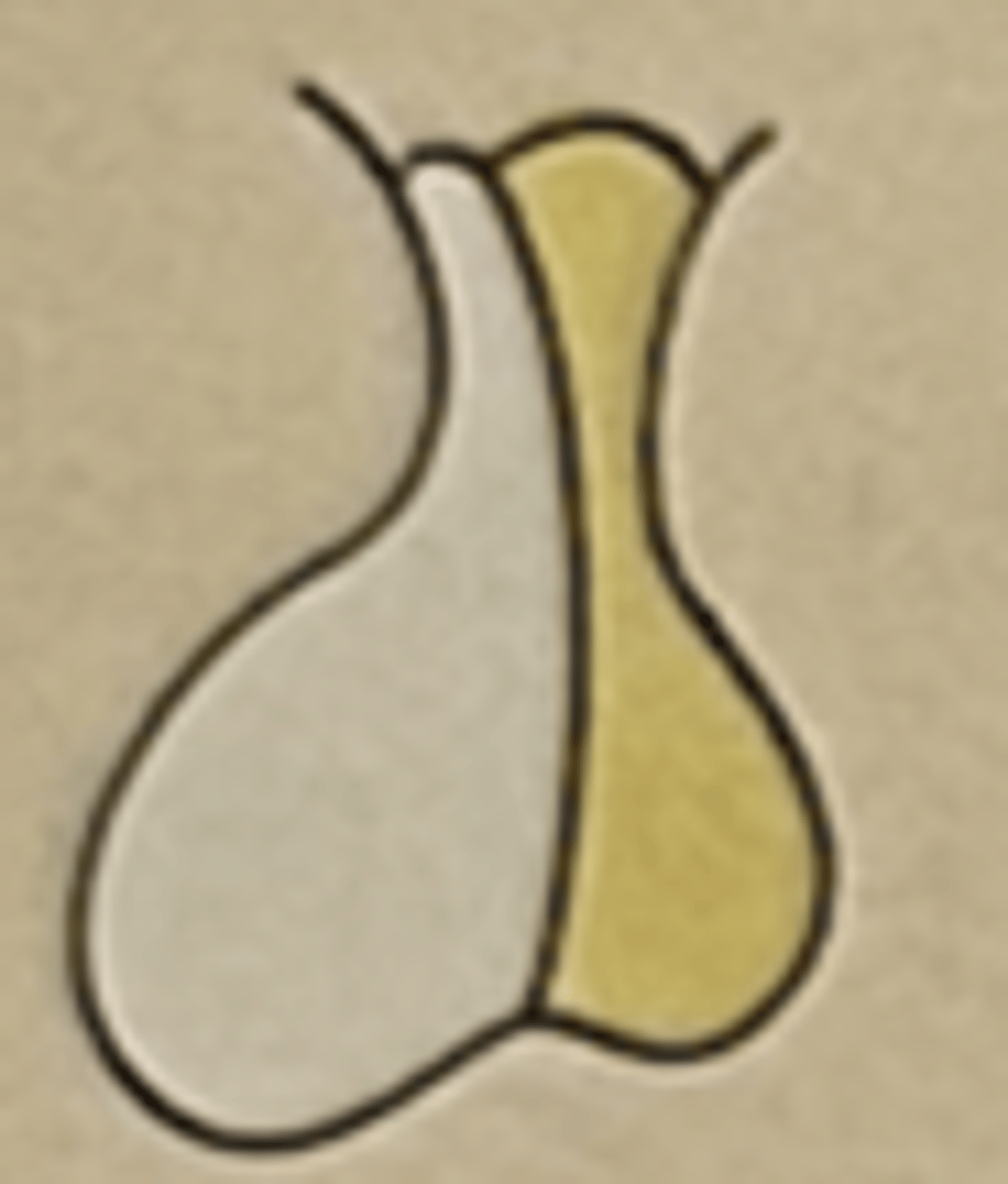
Hormone: melatonin
Function: involved with circadian rhythm
Pineal body

Hormone: serotonin
Function: constricts blood vessels and acts as a neurotransmitter
Pineal body

Hormone: Triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4)
Function: regulate metabolism
Thryoid gland
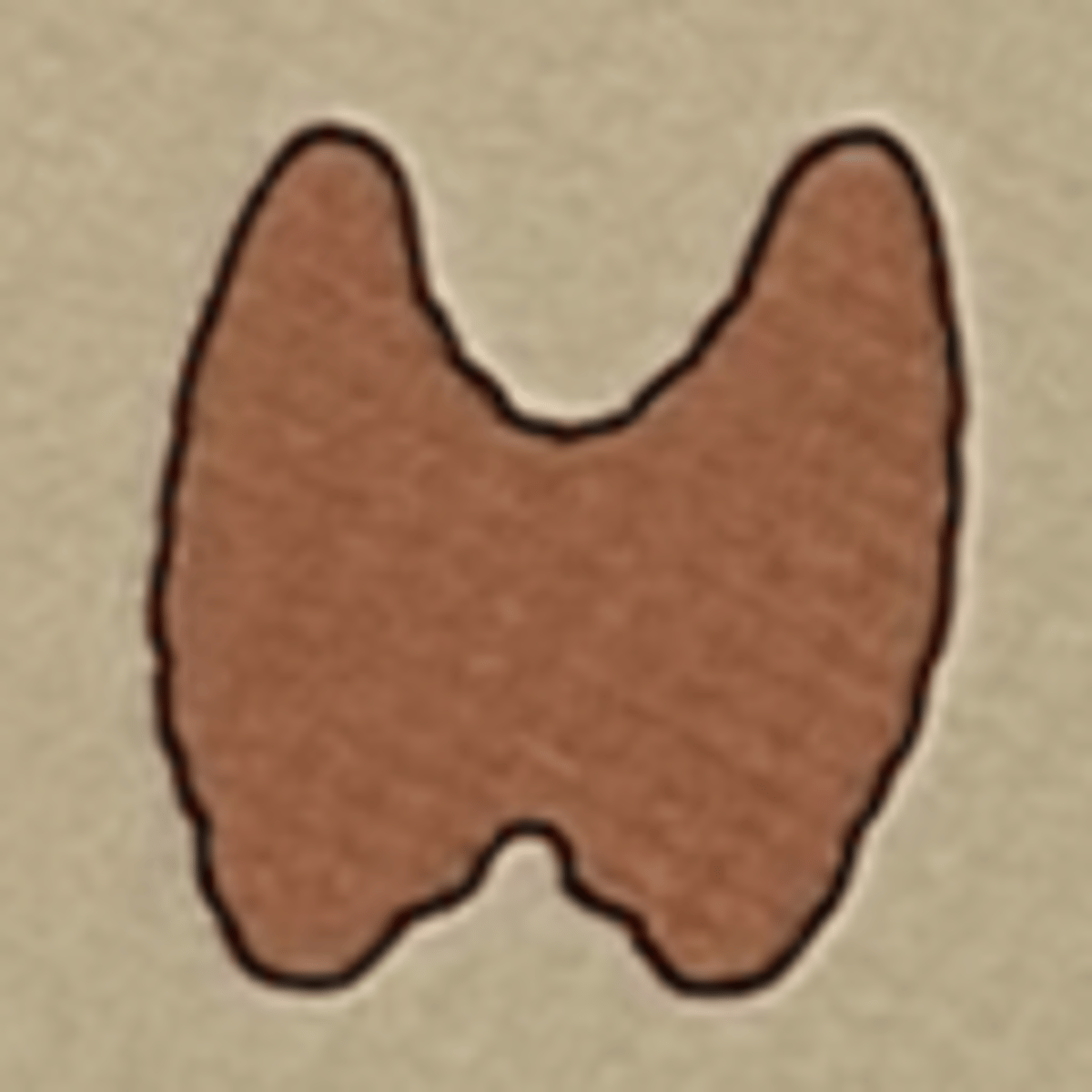
Hormone: Calcitonin
Function: regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism
Thyroid gland
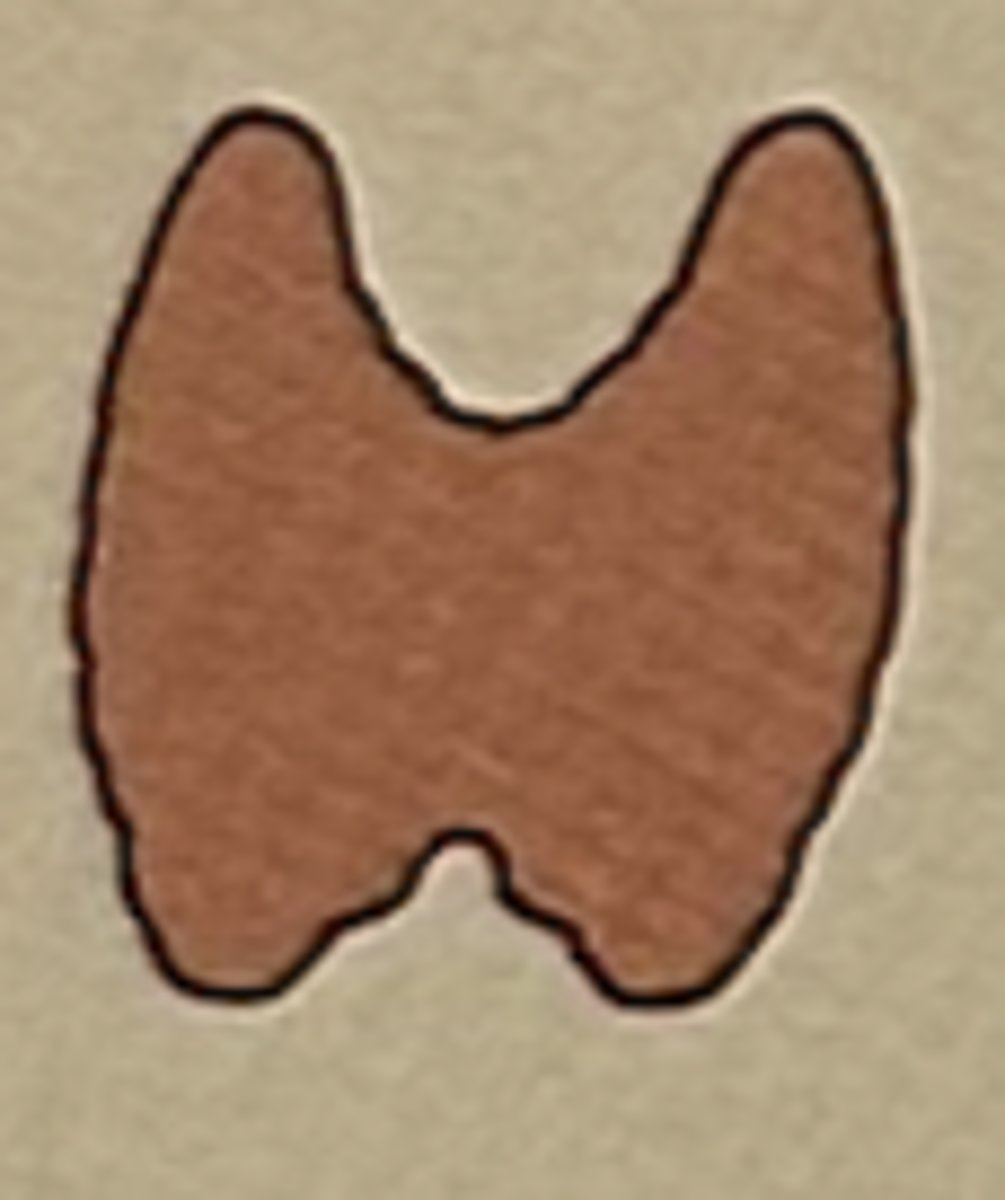
Hormone: parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Function: regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism
Parathyroid glands
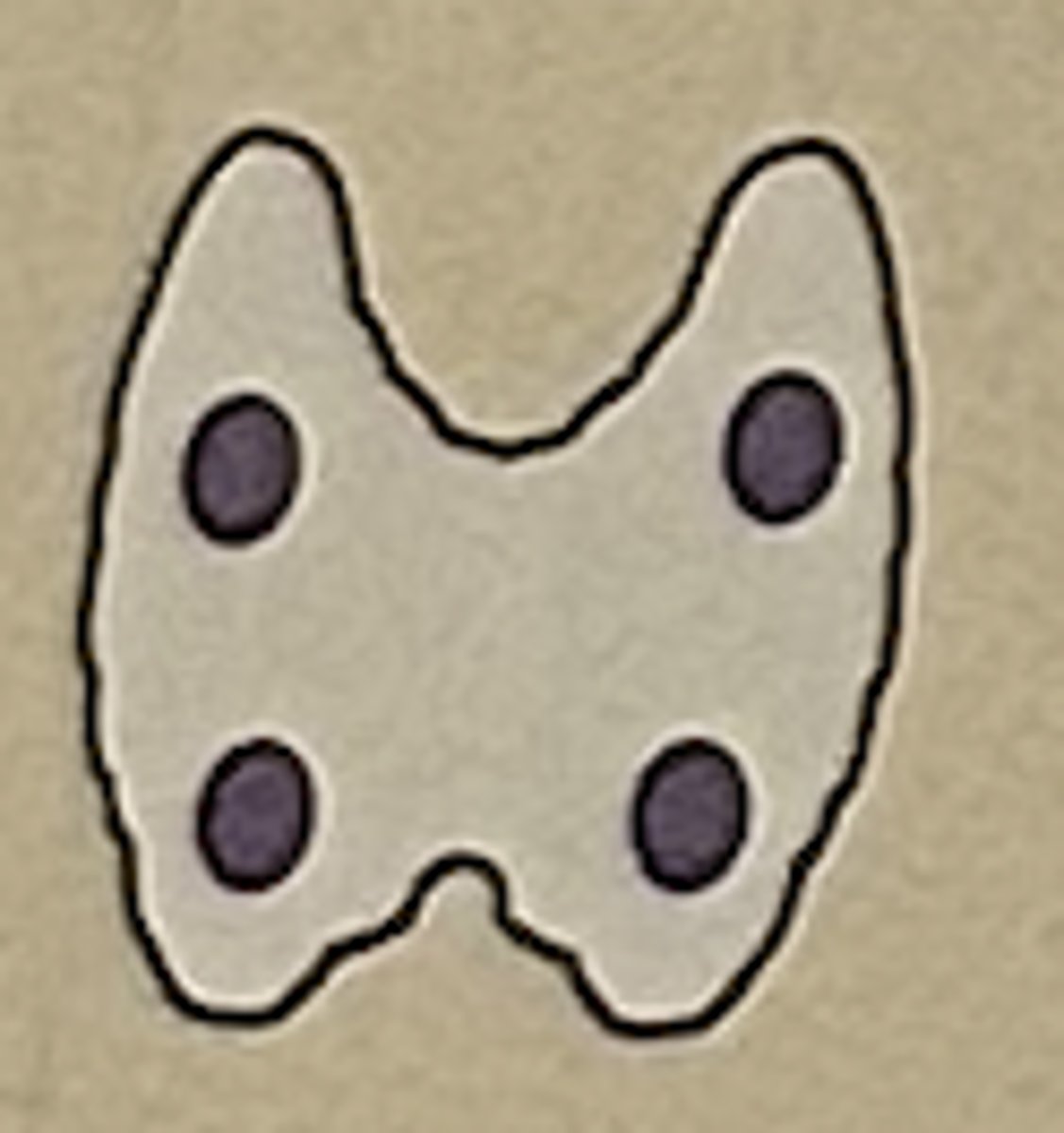
Hormone: insulin, glucagon
Function: regulates carbohydrate/sugar metabolism
Pancreas (islets of Langerhans)
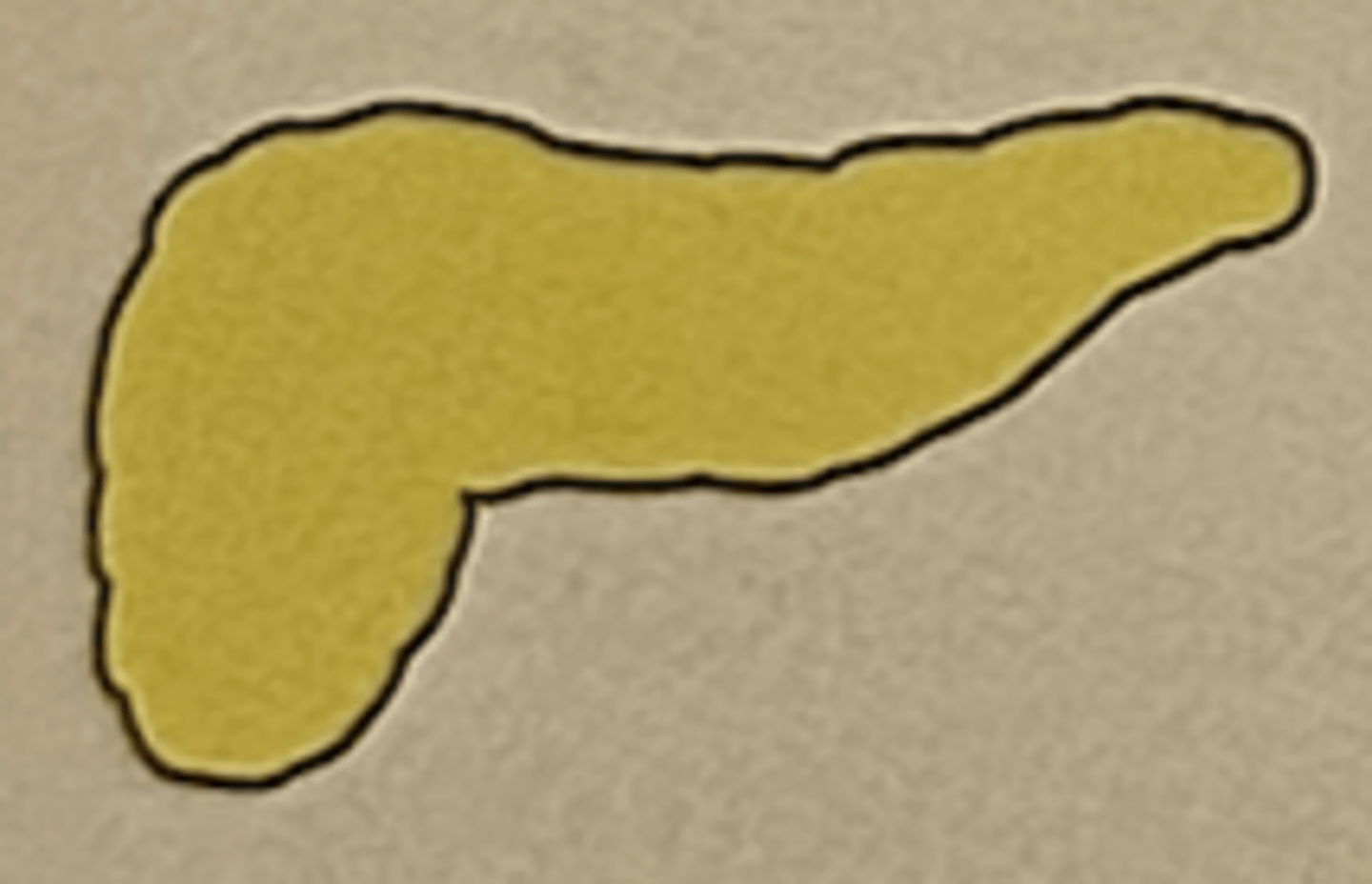
Hormone: Thymosin
Function: regulates immune response
Thymus gland

Hormone: Steriod hormones- glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens
Function: regulate carbohydrate metabolism and salt and water balance; androgens affect male sex characteristics
Adrenal glands (supraenal glands)
Hormone: epinephrine, norepinephrine
Function: affect sympathetic nervous system in stress response
Adrenal glands (suprarenal glands)

Hormone: estrogen, progesterone
Function: responsible for the development of female secondary sex characteristics and the regulation of reproduction
Ovaries
Hormone: Testosterone
Function: affects masculinization and reproduction
Testes
aden/o
gland
adren/o
adrenal gland
adrenal/o
adrenal gland
andr/o
male
crin/o
to secrete
dips/o
thirst
gluc/o
glucose (sugar)
glucos/o
glucose (sugar)
glyc/o
glucose (sugar)
hormon/o
hormone (an urging on)
ket/o
ketone bodies
keton/o
ketone bodies
pancreat/o
pancreas
thym/o
thymus gland
thyr/o
thyroid gland (shield)
thyroid/o
thyroid gland (shield)
located on the superior surface of each kidney; the puter adrenal cortex secretes steroid hormones, and the inner adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine; also called supradrenal glands
adrenal glands
located on the superior surface of each kidney; the puter adrenal cortex secretes steroid hormones, and the inner adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine; also called adrenal glands
suprarenal glands
hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex
steroid hormones
hormones that regulate carbohydrate metabolism and have anti-inflammatory effects; cortisol is the most significant glucocorticoid
glucocorticoids
hormones that maintain salt and water balance
mineralocorticoid
hormones that influence development and maintenance of male sex characteristics, for example, facial hair, deep voice
androgens
hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla that affect the sympathetic nervous system in stress response
catecholamines
hormone that is secreted in response to fear or physical injury; also called adrenaline
epinephrine
hormone that is secreted in response to fear or physical injury; also called epinephrine
adrenaline
hormone that is secreted in response to hypotension (low blood pressure) and physical stress
norepinephrine
located on both sides of the uterus in the female pelvis; secrete estrogen and progesterone
ovaries
hormone that is responsible for the development of female secondar sex characteristics
estrogen
hormone that regulates uterine conditions during pregnancy
progesterone
endocrine tissue within the pancreas (the organ located behind the stomach, in front of the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae); secretes insulin and glucagon; also called pancreatic islets
islets of Langerhans of the pancreas
a hormone secreted by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans that is responsible for regulating the metabolism of glucose (insulin=island)
insulin
a hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans that regulates carbohydrate metabolism by raising blood sugar
glucagon
two paired glands located on the posterior aspect of the thyroid gland in the neck; secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH)
parathyroid glands
hormone that regulates calcium and phosphrous metabolism
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
located in the center of the brain; secretes melatonin and serotonin
pineal gland
hormone that is involved with circadian rhythm (24-hour cycle); affects the onset of puberty
melatonin
hormone that constricts blood vessels and acts as a neurotransmitter
serotonin
located at the base of the brain; considered the master gland as it secretes hormones that regulate the function of other glands, such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, ovariesm and testicles; the anterior pituitary secretes thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocortiocotropic hormone, melanocyte-stimulating hormone, growth hormone, and prolactin; the posterior pituitary releases antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin
pituitary gland
hypophysis
anterior lobe of the pituitary gland; also called adenohypophysis
anterior pituitary
anterior lobe of the pituitary gland; also called anterior pituitary
adenohypophysis
hormone that stimulates secretion from thyroid gland
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
hormone that stimulates secretion from adrenal cortex
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
hormone that initiates the growth of ovarian follicle; stimulates the secretion of estrogen in females and the production of sperm in males
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
hormone that causes ovulation; stimulates the secretion of progesterone by the corpus luteum; causes the secretion of testosterone in the testes
luteinizing hormone (LH)
hormone that affects skin pigmentation
melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
hormone that influences growth
growth hormone (GH)
hormone that stimulates breast development and milk production during pregnancy; also called lactogenic hormone
prolactin (PRL)
hormone that stimulates breast development and milk production during pregnancy; also called prolactin
lactogenic hormone
posterior lobe of the pituitary gland; also called neurohypophysis
posterior pituitary
posterior lobe of the pituitary gland; also called posterior pituitary
neurohypophysis
hormone released by the posterior pituitary that influences the absorption of water by kidney tubules; also called vasopressin
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
hormone released by the posterior pituitary that influences the absorption of water by kiney tubules; also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
vasopressin (VP)
hormone released by the posterior pituitary that influences uterine contraction
oxytocin (OXT)
located on both sides within the scrotum in the male; secrete testosterone
testes
affects masculinization and reproduction
testosterone
located in the mediastinum (partition between the lungs) anterior to and above the heart; secretes thymosin
thymus
hormone that regulates immune response
hymosin
located in front of the neck; secretes triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and calcitonin
thyroid
thyroid hormone similar to thyroxine but having greater potency; regulates metabolism
triiodothyronine (T3)
thyroid hormone that regulates metabolism
thyroxine (T4)
hormone that regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism
calcitonin
protrusion of one or both eyeballs, often because of thyroid dysfunction or a tumor behind the eyeball; also called exophyhalmus
exophthalmos
protusion of one or both eyeballs, often becuase of thyroid dysfunction or a tumpr behind the eyeball; also called exophthalmos
exophthalmus
glucose (sugar) in the urine; also called glycosuria
glucosuria
glucose (sugar) in the urine; also called glucosuria
glycosuria
shaggy; an excessive growth of hair, especially in unusual places (e.g., a woman with a beard)
hirsutism
an abnormally high level of calcium in the blood
hypercalcemia
an abnormally low level of calcium in the blood
hypocalcemia
an abnormally high level of glucose in the blood
hyperglycemia
an abnormally low level of glucose in the blood
hypoglycemia
an abnormally high level of potassium in the blood (kalium= potassium)
hyperkalemia
deficient level of potassium in the blood
hypokalemia
abnormally increased secretion
hypersecretion
abnormally decreased secretion
hyposecretion
presence of an abnormal amount of ketone bodies (acetone, beta-hydroxybutyric acid, and acetoacetic acid) in the blood and urine indicating an abnormal metabolism of carbohydrates, such as in uncontrolled diabetes and starvation (keto=alter); also called ketoacidosis and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
ketosis
presence of an abnormal amount of ketone bodies (acetone, beta-hydroxybutyric acid, and acetoacetic acid) in the blood and urine indicating an abnormal metabolism of carbohydrates, such as in uncontrolled diabetes and starvation (keto=alter); also called ketosis and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
ketoacidosis
presence of an abnormal amount of ketone bodies (acetone, beta-hydroxybutyric acid, and acetoacetic acid) in the blood and urine indicating an abnormal metabolism of carbohydrates, such as in uncontrolled diabetes and starvation (keto=alter); also called ketosis and ketoacidosis
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
all chemical processes in the body that result in growth, generation of energy, elimination of waste, and other body functions
metabolism
excessive thirst
polydipsia