Economics Unit 1 flashcards
1/25
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
economics:
study of how society allocates scarce resources among unlimited wants and needs
microeconomics examines
how producers and consumers interact in individual markets
macroeconomics examines
the factors that affect the economy as a whole
the economic decision rule
if the benefits are greater than the costs; do it
if the costs are greater than the benefits; dont do it
cost benefit analysis is the process of
weighing up strengths and weaknesses of a policy, choice, or action, and then coming up with a judgement/decision
opportunity cost
the next best thing is sacrificied or given up as a result of a choice
trade off
anything that is given off as the result of a choice
free goods
something that is so abundant that it is not scarce and it can be considered free
economic goods
something that is scarce and has competition for it is known as an economic good
incentive
something that motivates an individual to act a certain way
the three parts of the basic economic problem
WHAT should be produced and how much?
HOW should things be produced?
for whom (WHO) should things be produced
societies often answer the basic economic with three solutions
Planned (command) economy
Free market economy
Mixed market economy
resources are seperated into four categories (factors of production)
Land
Labour
Capital
Entrepreneurship
The Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) is a
graph which shows the tradeoff between the production of two different items
the PPC easily illustrates the concepts of
scarcity, choice, opportunity cost, and efficiency
the PPC demonstrates
the maximum combinations of two types of output that can occur in an economy if all resources are being used efficiently and technology is fixed
the law of increasing opportunity cost is when
increasing the quantities of one good can only be accomplished by sacrificing ever-increasing quantities of another good
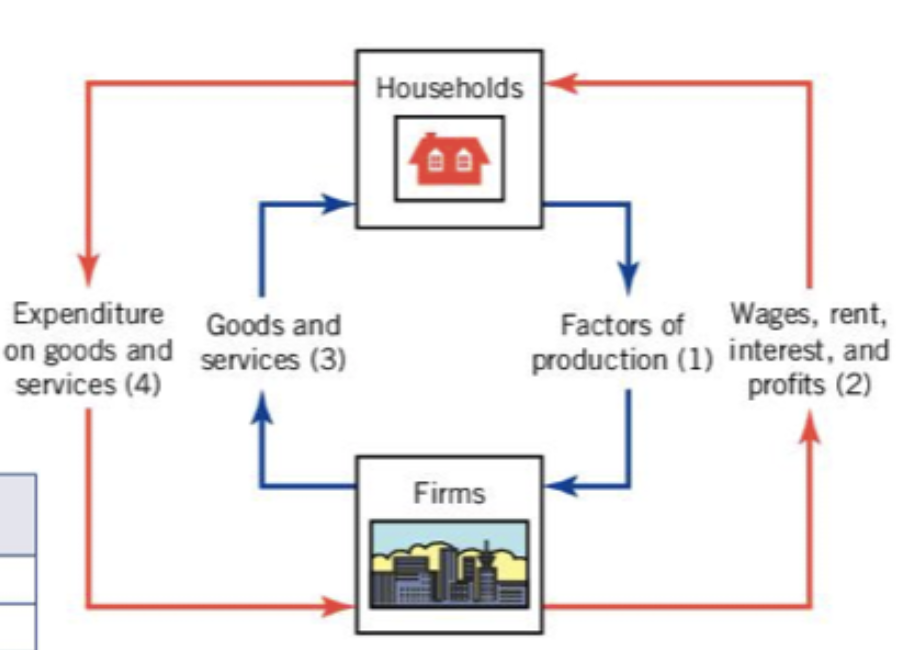
the economy can be illustrated by the
circular flow model, in which households supply the factors of production and firms provide payments to the factor
not all money stays in the domestic consumer economy, some money leaves the economy through
leakages
leakages can be
governments taking money from consumers in the form of taxes
consumers saving some of their income in financial institutions
households and businesses spendingmoney on imports, sending the money to foreign producers
money can also enter the economy in form of
injections
injections can be
government spending on public services, infrastructure and salaries
the financial sector investing money into firms
foreign households purchasing exports, injecting money into the economy
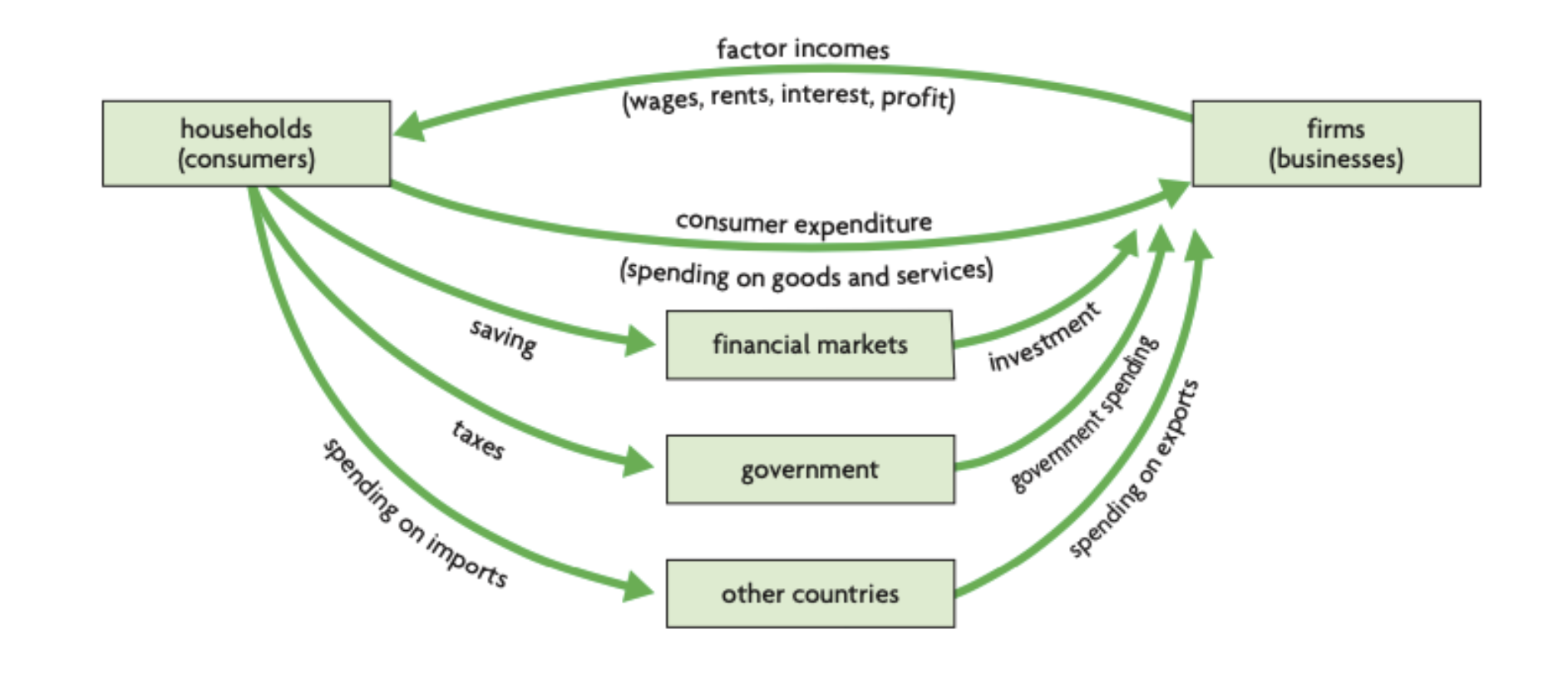
this a diagram displaying
the circular flow of income with leakages and injections
the ceteris paribus assumption is when economists assume
“all other things being equal”