Transpiration
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are the 4 reasons that water is needed?
For photosynthesis
Thermoregulation (evaporation from leaves cools a plant)
Minerals and glucose in water for growth
Pressure of water in cells and vessels help for the support
What is the structure of xylem?
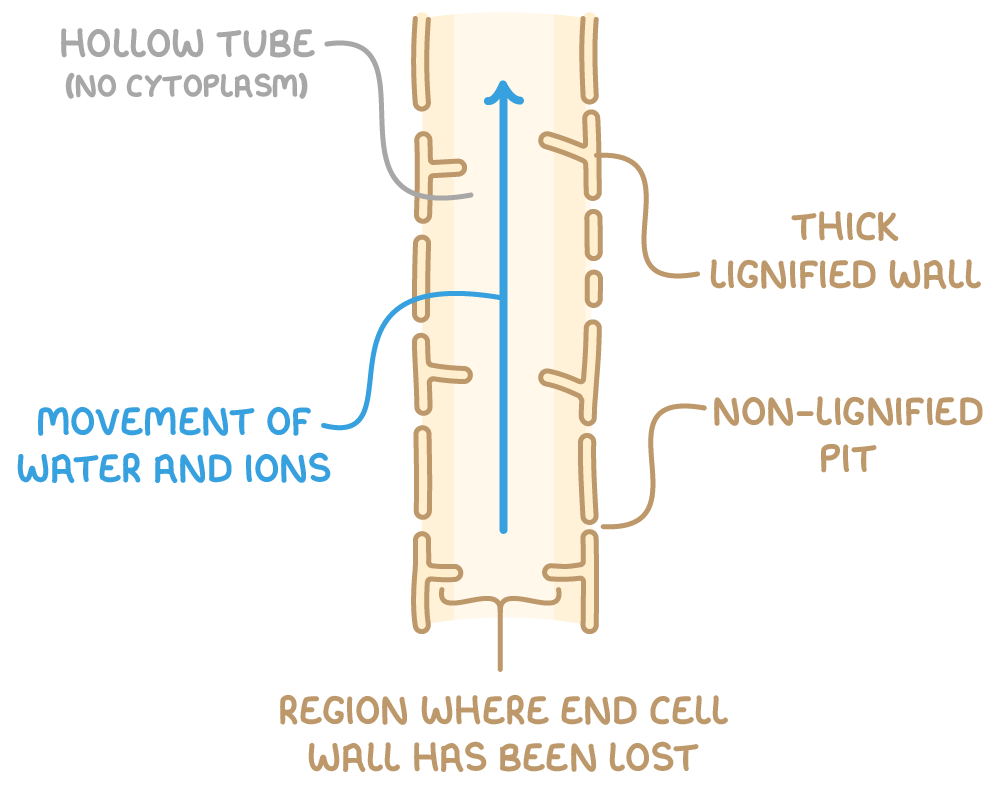
How do xylem’s work?
Xylem’s are originally non-lignified (still made out of cellulose). As it grows older, xylem becomes lignified (made out of wood)
How do xylem’s form?
Xylem vessels are formed from xylem cells that fuse together. Then the end cell walls are lost to form one continous
What are pits?
Small holes to allow water to move laterally
What is going on in root hair cells?
NO3 uses active transport and H2O uses osmosis from hypotonic to hypertonic
What does a root hair cell look like?
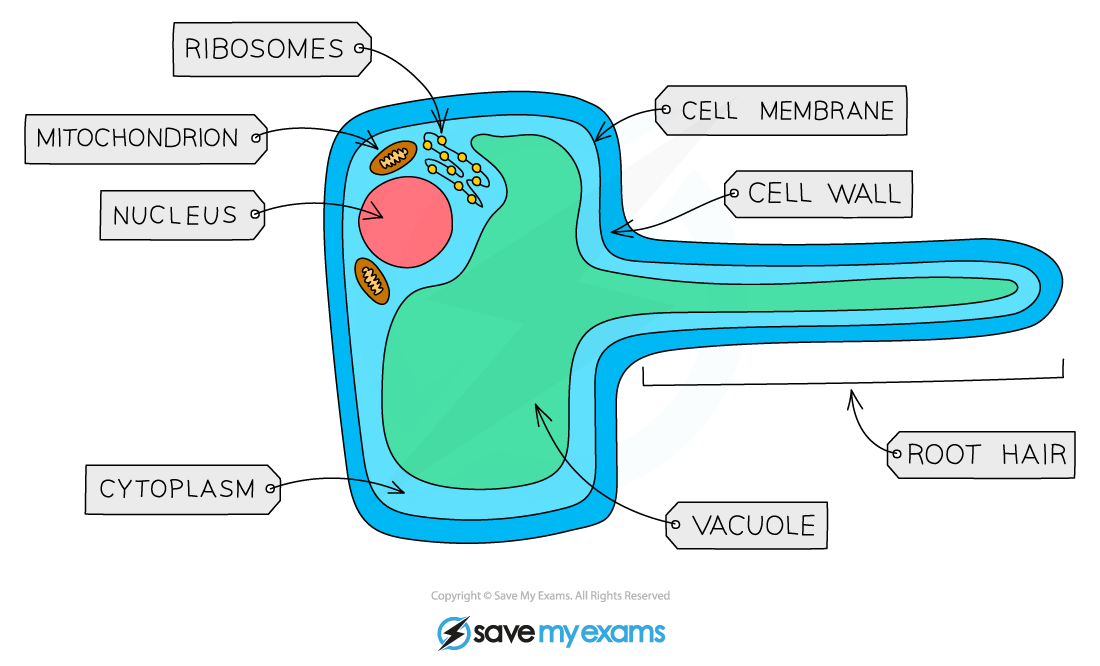
What are the adaptations of a root hair cell?
Thin cell wall and cell membrane for short diffusion difference
Protrusion to increase SA to speed up diffusion
Many mitochondria to speed diffusion
Roots anchor plants in the soil it is growing in
Water is transported through root tissue via two pathways. What are they called?
Symplastic pathway and Apoplastic pathway
How is the symplastic pathway used?
This transports water via plasmodesmata. There is a decreasing water potential gradient (next cell will be more hypertonic) from the root to the xylem so water travels via osmosis.
How is the apoplastic pathway used?
This moves water through the cell walls and intercellular spaces. Water molecules stick to one another due to the cohesive properties of water, creating a continuous flow of water.
What needs to happen in apoplastic pathway?
Water needs to pass through at least one membrane
How is the vacuolar pathway used?
Water enters by osmosis and moves within and through vacuoles.
What is the Caspian strip?
This is a waterproof layer made of suberin that is formed in the endodermis of the vascular bundle.
How does the Caspian strip work?
It forces water to move through the symplastic pathway, therefore filtering all potentially toxic substance from getting into the xylem as they will then have travel through a selectively permeable membrane
Name the structures of a leaf
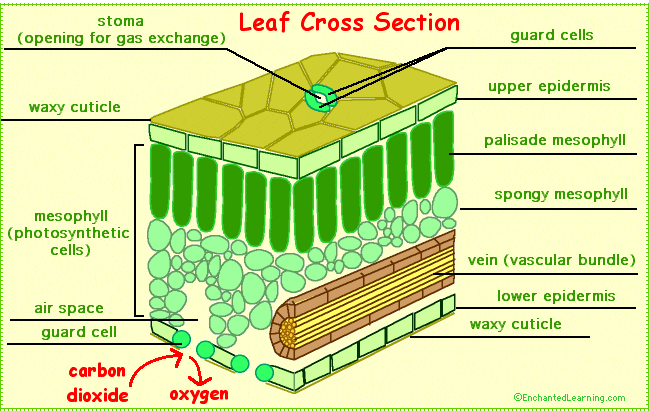
How does transportation work throughout the plant?
Roots to lower xylem, it is hypertonic in the soil. It travels to lower xylem with enough pressure from osmosis.
Lower xylem to Upper xylem. It moves to upper xylem by cohesion due to tension.
Upper xylem to leaves. Water moves by osmosis.
Water leaves out by transpiration. (Hypertonic)
What is cohesion and adhesion?
Cohesion is the hydrogen bonding between water molecules
Adhesion is when water molecules and xylem cell wall molecules bond together.
What is the cohesion-adhesion theory?
Water evaporated from spongy mesophyll and water vapour diffuses out of the stomata
Loss of water from the mesophyll layer lowers the water potential so must move into them from adjacent cells via osmosis
Water moves by osmosis from the xylem to the spongey mesophyll cells down a water potential gradient
Because water is cohesive (because it is polar) water lost at the top of the xylem vessels pull on water molecule further down the xylem.
This, along with adhesion and capillarity, creates a tension on the water in the xylem vessels.
Lost water is replaced in the xylem from the roots