Prokaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotes are the most basic living organisms. These were the first cells that appeared on Earth.
%%Pro:%% Before
%%Karyotic:%% Nucleus
Animals and plants, along with other eukaryotes, have a nucleus where DNA is stored in the cell. Prokaryotes do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, but they do have a general area in the cell where the DNA resides.
There are two basic types of prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea.
Archaea are the more ancient group and, as a result, tend to live in extreme environments – salty lakes, the bottom of the ocean, and very hot environments.
Bacteria are found everywhere – in your body, on your skin, on practically every surface and place on Earth.
Prokaryotes can be both helpful and harmful to other living organisms.
Cell Theory
The Cell Theory applies to all living things and has three principles:
Every living thing is made of cells.
Cells come from existing cells.
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function.
Structure
The function of a cell usually determines its structure.
- All cells must have a cell membrane. Cell membranes surround the cell and serve as a barrier to the outside environment.
- All cells must have genetic material (DNA).
- All cells must have ribosomes. Ribosomes are used to produce proteins.
- All cells have cytoplasm. Cytoplasm fills the free spaces in the cell, holding the parts of a cell in place.
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, unlike prokaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotes have a cell wall for protection, keeping shape, and preventing the cell from bursting. Some eukaryotes have cell walls, but not all.
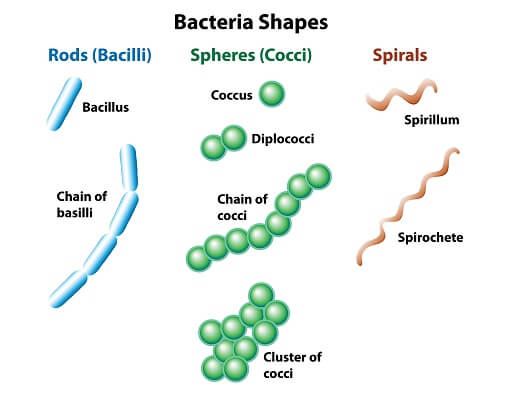
Common Shapes of Prokaryotic Cells
Cocci
Bacilli
Spirilli
 Edited: 05 October 2022
Edited: 05 October 2022