Social Studies Grade 7 Alberta (vocabulary & pictures)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
settlement
Establishing settlers in a new region as a way to take control of it.

Ethnocentric
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.

Imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.

citizenship
Being a member of a country with rights, responsibilities, and duties.

pluralism
A condition in which several distinct ethnic, religious, or cultural groups are present and tolerated within a society.
Seven Years War
In May 1756 Britain declared war on France marking the official beginning of the seven years war between them.
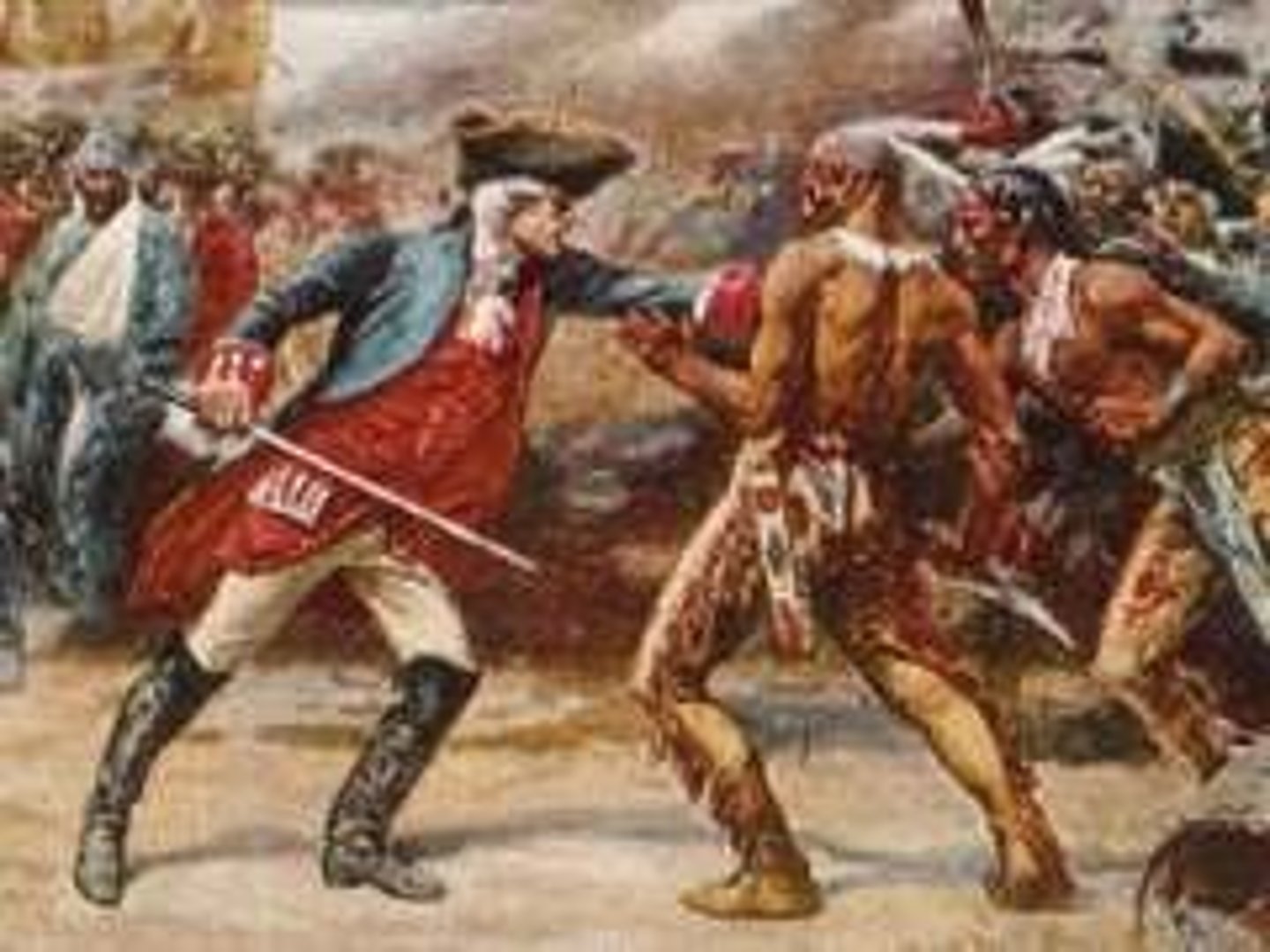

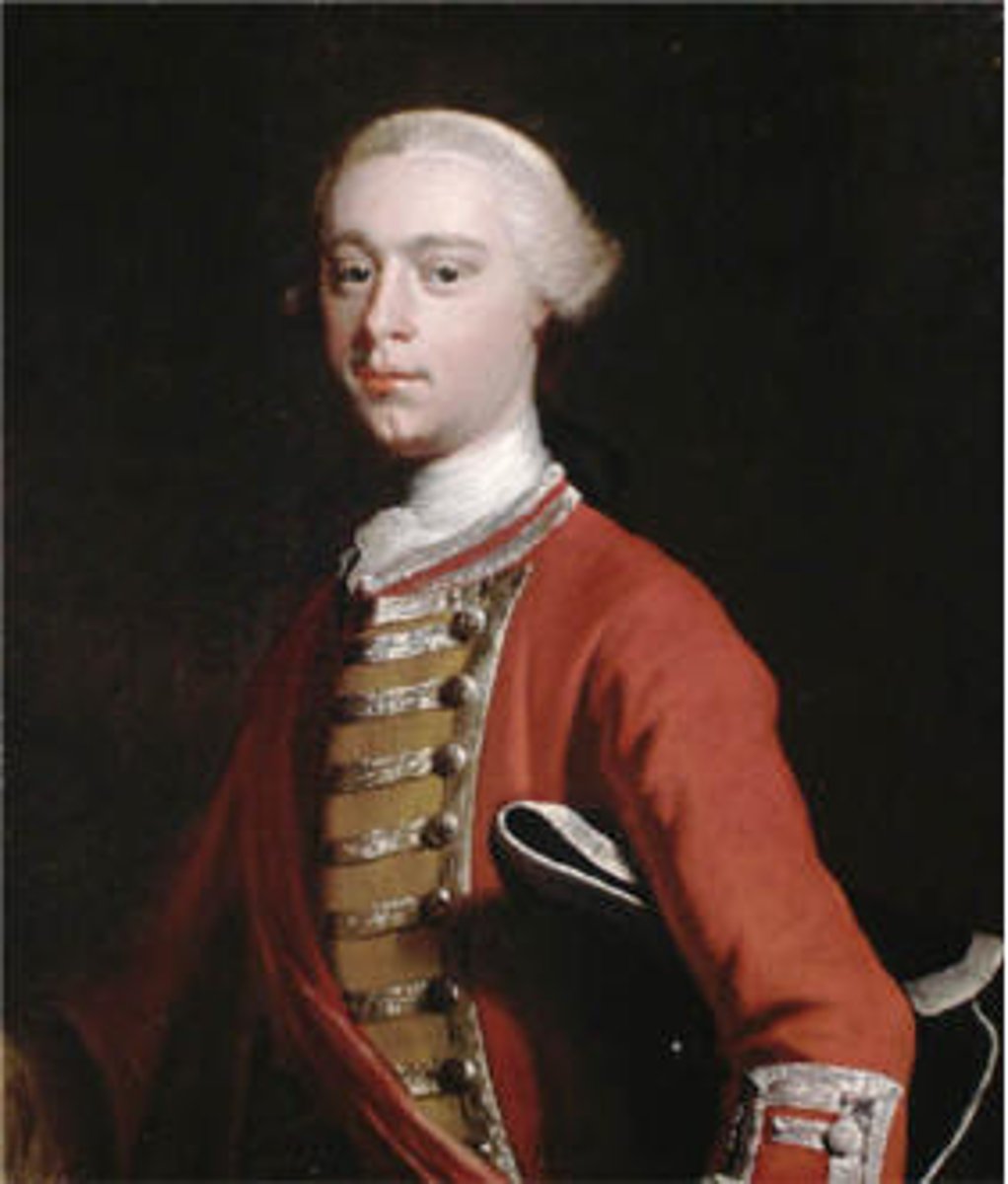
James Wolfe
A top General at 30 years old. With Pitt's new generals Britain scored its first major victory capturing the fort at Louisbourg. Then they took Fort Duquesne. These and other victories led the Iroquois to join the British. Other victories set the stage to attack Quebec.

Treaty of Paris
After losing Quebec the French couldn't protect their other North American property so they lost Montreal. Britain and France made the Treaty of Paris. The French surrendered.

Consensus
agreement by everyone

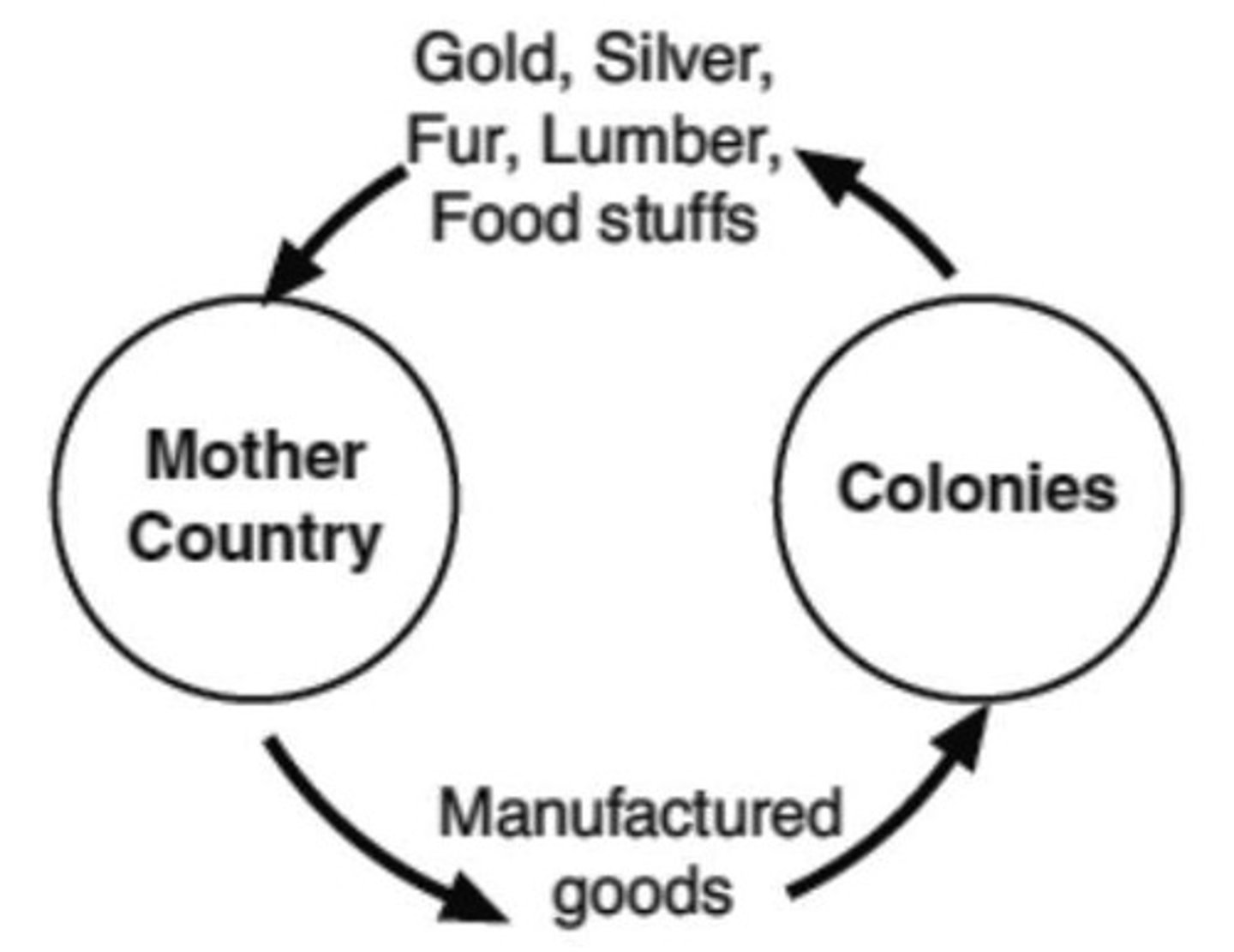
Mercantilism
A regulated economic system that made a country rich from its colonies.
Governor
Represented the king, controlled the military, and looked after the defense of the colony. He also dealt with "external relations," such as trade with First Nations.

Intendant
The chief administrator of the colony. He worked to keep the colony in good order and to make it less dependent on France for meeting its basic needs. He also kept his eye out for new ways to exploit the colony for the benefit of France.

Bishop
He represented the Catholic Church. The Catholic Church played an important role in the colony. It provided moral guidance and founded schools, hospitals, and orphanages.

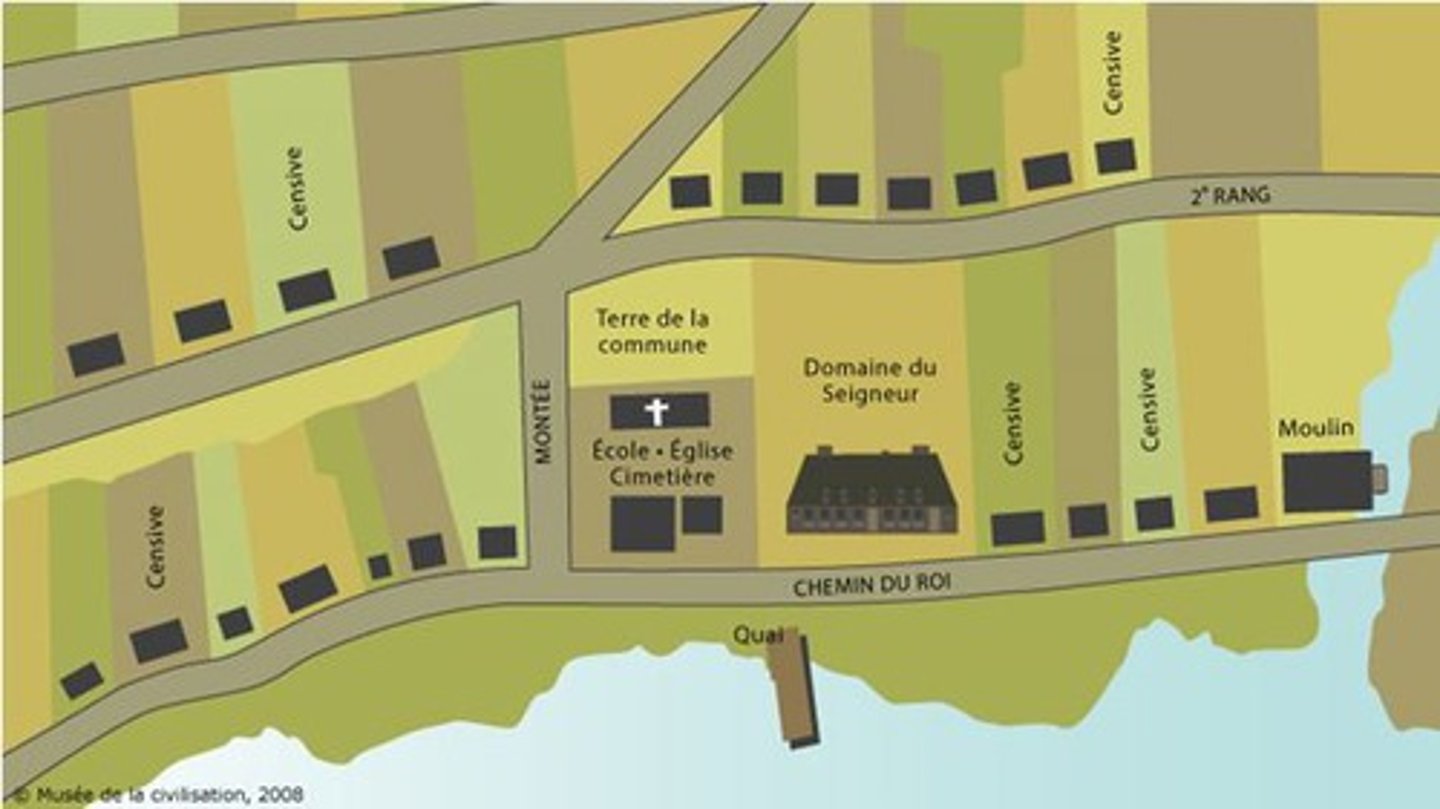
Habitants
farmers who lived on seigneuries; had to clear the land, plant crops, build a house, and give a few days' labour to the seigneur each year.

Seigneur
Landlords who received the land as grants from the King of France.

Seigneury
Large plots of land owned by seigneurs.
coureurs de bois
means "runner of the woods." The term comes from the way some men in New France engaged in the fur trade -by "running into the forest" to seek and trade with First Nations.
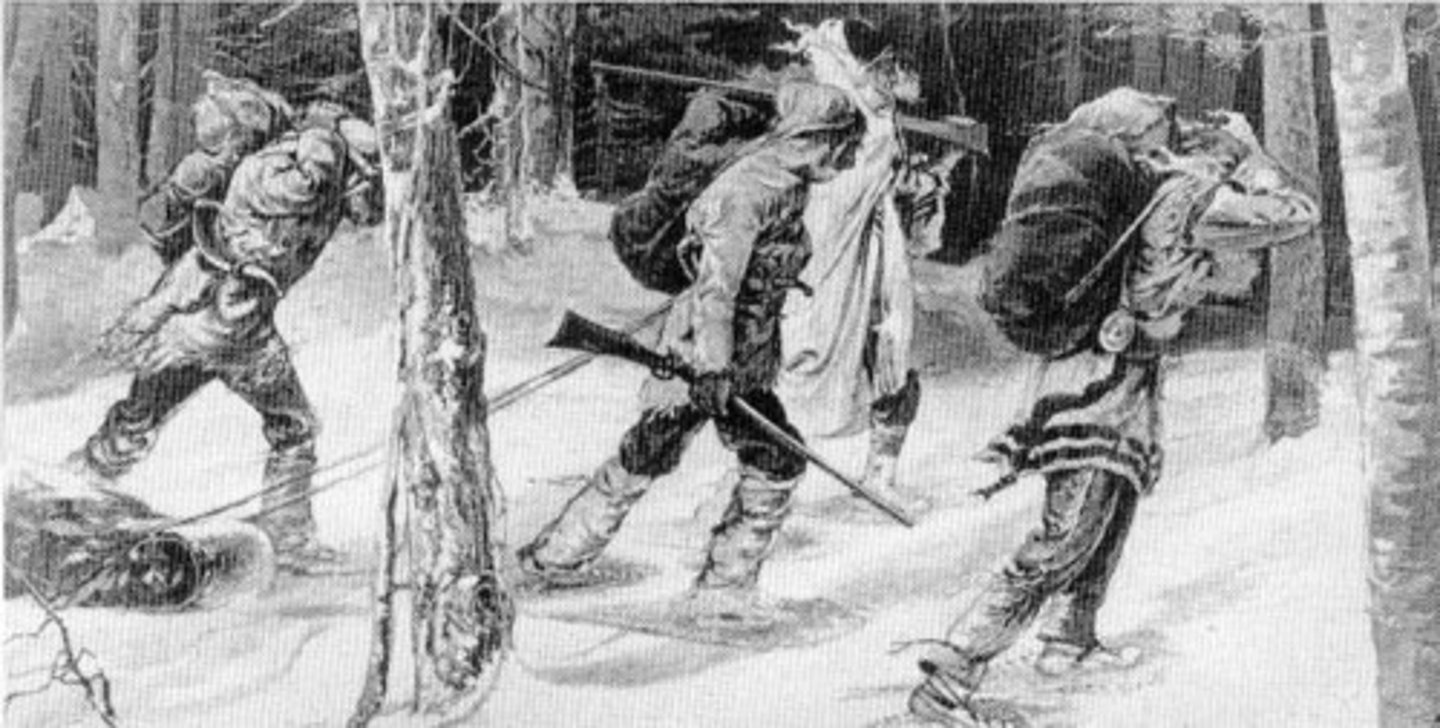

Voyageur
Means "traveller." They were men from New France who travelled between the fur merchants of Montréal and the fur trade posts of the Great Lakes and eventually further west.

Competition
The rivalry among sellers trying to achieve such goals as increasing profits.

Métis
Children that had First Nations mothers and French fathers.

Francophone
A person whose first language is French.

Canadien
A descendant of the settlers of New France.

The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC)
British fur trading company started 1670

The North West Company (NWC)
French fur trade company

Colonization
The process of one country establishing domination over territory in another country or region.

Oath of allegiance
The oath that the British required of the Acadians.

Deportation
The process of forcing someone to leave a place, especially a country.

The Great Deportation
The removal of eleven thousand Acadians from Acadia by Britain, starting in 1755.

Elected Assembly
Representatives elected by voters. In British colonies, elected assemblies could advise, but not direct, the governors and councils appointed by Britain.

Treaty of Paris
The 1763 agreement between Britain and France that ended the Seven Years' War, in which France gave up nearly all its claims in North America in favour of Guadeloupe.

Loyalists
Colonists who remained loyal to the British during the American Revolution.

Representative government
Citizens elect representatives to an assembly and the assembly speaks for citizens.

Immigration
The process of people establishing homes and citizenship in a country that is not their native country.
Reserves
An area of land set aside by treaty (agreement) for the use of First Nations.

Assimilation
The process of becoming part of a different cultural group. (not your own)

Immigrant
A person intending to establish a home and citizenship in a country that is not their native country.

Democracy
A system of government in which citizens elect those who rule them.

Colonial government
A government established in a colony and controlled by an imperial power such as Britain.

Political deadlock
The inability to decide on a course of action because of disagreement among equally powerful decision-makers.

Tariffs
Taxes on imports or exports.

Representation by Population
(rep-by-pop)
A form of proportional representation in government; areas with higher populations have more elected officials in government.

Head tax
The fee that Chinese immigrants were required to pay after 1885 in order to enter Canada.

The Famous Five
Five Alberta women demanded recognition for women as "persons" in Canadian law.

suffrage
The right to vote in political elections.

Bilingualism
The ability to speak two languages.
Indigenous peoples
First Nations, Métis and Inuit peoples.

Urbanization
An increase in the number of people living in cities and the expansion of cities into rural areas.

First Nations
A term that is used to describe Indigenous peoples of Canada who are ethnically NOT Métis or Inuit. The original people of the land.
imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.
filles du roi
Daughters of the king; Women sent from Europe to marry colonists.

North-west mounted police (NWMP) (mounties)
The government established the northwest mounted police in 1873. The NWMP was both a police force and a paramilitary organization. It's first task was to drive out the whisky traders and regain control over the entire North West Territories.

Québec Act
In 1774 Britain passed a law that allowed Québec to keep the Catholic faith and gave the church more freedom. French was allowed as a language and French law was used in Québec.

National Policy
Policies put in place by the government of John A. MacDonald.
1. Tariffs to protect Canadian producers and products.
2. Building the railway to the Pacific.
3. Immigration policies aimed at populating Western Canada.

Royal Proclamation
Also called Treaty of Paris, signed in 1763. France gave up control of North American colony to England. French language and religion rights taken away. Land was given to Aboriginal people.

Council of Elders
Groups of respected people that chose and advised Mi'kmaq leaders.

Grand Council
A council for all seven districts of the Mi'kmaq Nation.

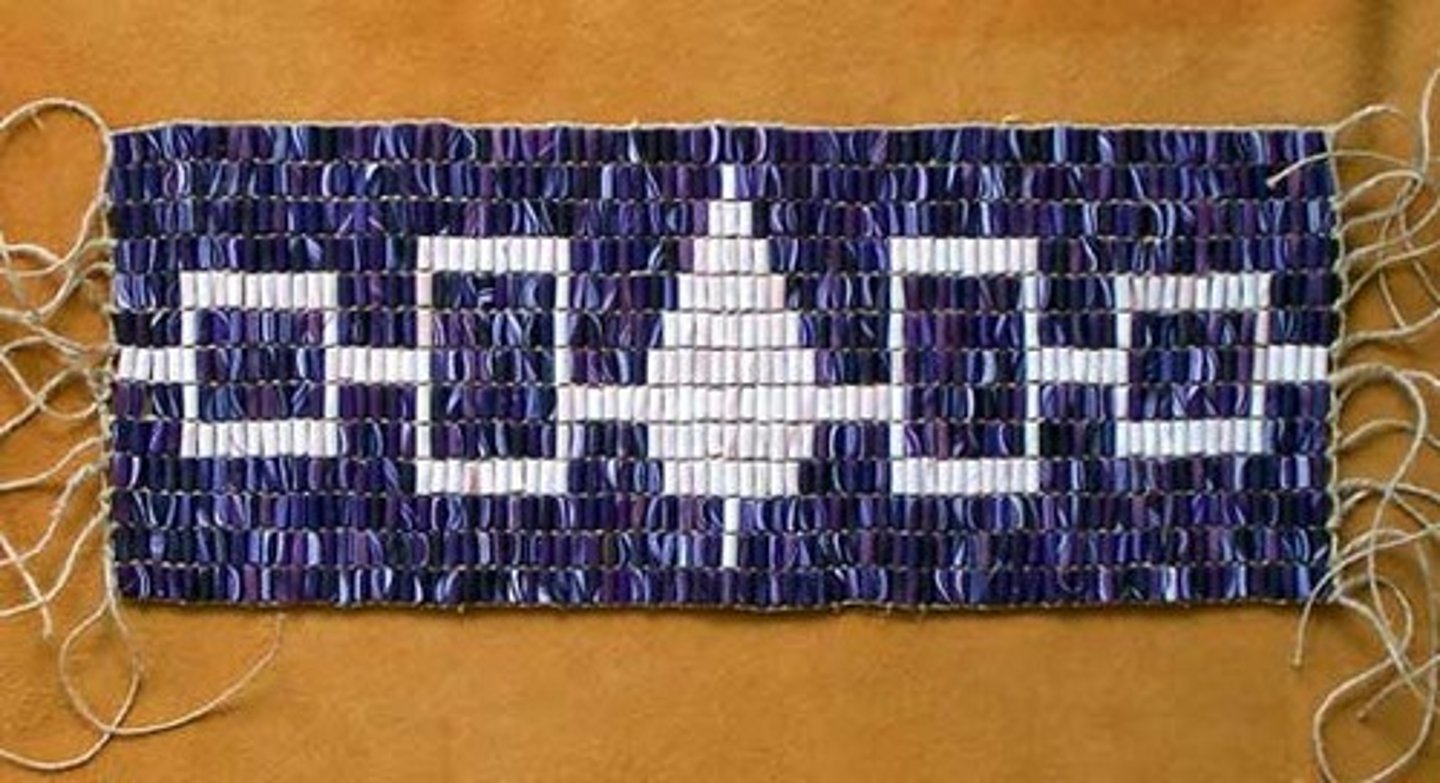
Wampum Belt
Shell beads woven into belts or strings used to record treaties and other agreements among different nations.

Clan Mothers
Female leaders of clans in Haudenosaunee society.

Great Law of Peace
The constitution of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy that guaranteed certain rights and freedoms including freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and the rights of the individual and guided all aspects of governance and society.

Alliance
An agreement among a group of nations to act together to support each other's interests.

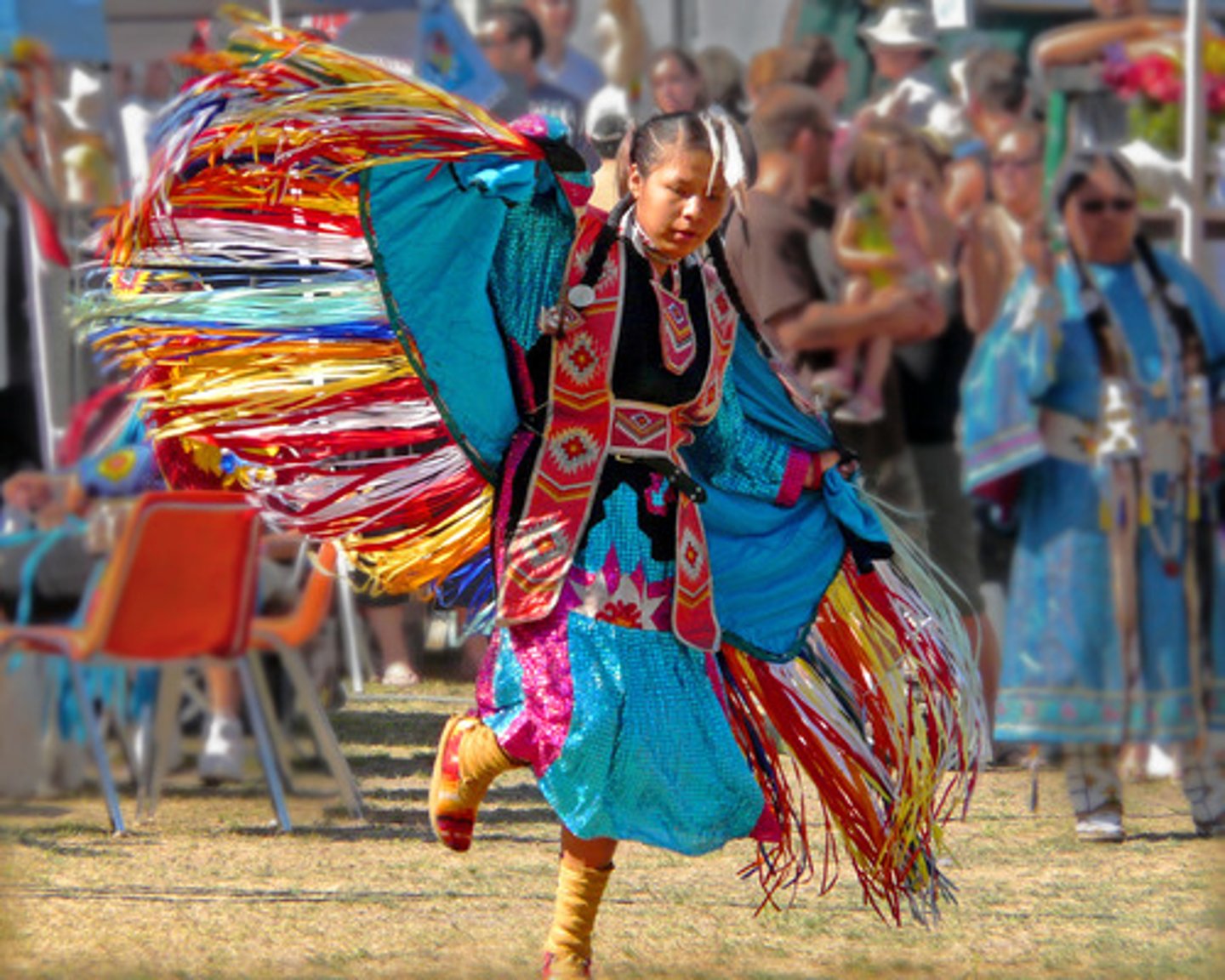
Pow-wow
A gathering of First Nations peoples to celebrate their cultures.

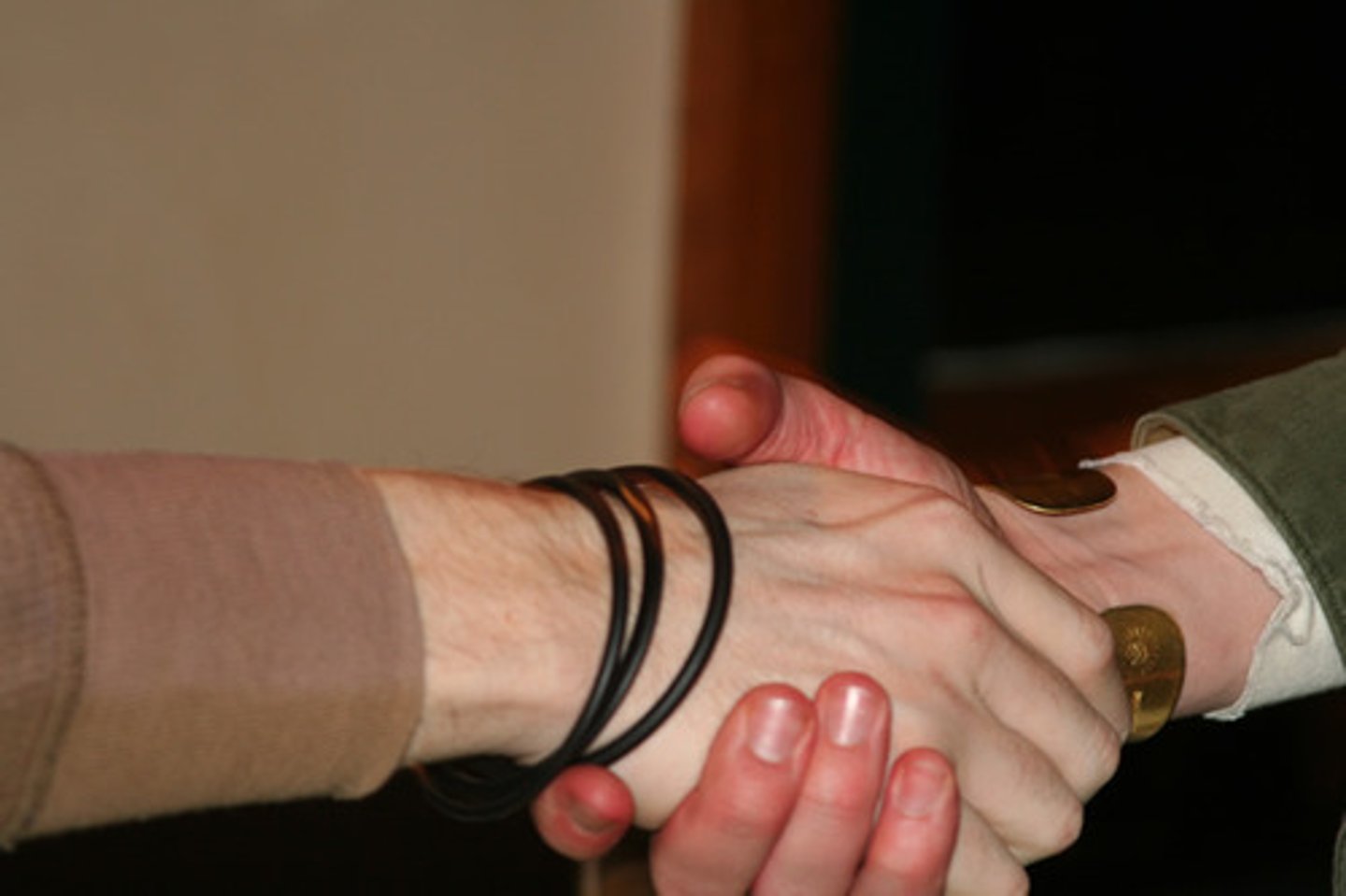
Coexistence
Two or more peoples of diverse cultures living together peacefully.

Immunity
The ability of the body to fight off infection.

epidemic
The infection of a large population by a disease.

Dowry
Money a woman brings to a marriage; an old custom.
Middleman
A go-between person; connects the buyer and seller.

Strategic position
A place whose physical location makes it important or valuable, often for military reasons.

prejudice
A negative generalization about a group of people based on uninformed judgments.
genocide
A policy to eliminate people of a particular cultural identity.

bilingual / officially bilingual
Having rights in law that establish equality between two languages.

The Maritimes
The Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island.
Decisive battle
A battle producing lasting change.

Retaliate
to get revenge

Tithe
A payment to support a church, usually based on one-tenth of a person's income.

Bicultural society
Giving official recognition to two cultures.

Revolution
An overthrow of a government or social system with another taking it's place.

Refugee
A person who seeks protection in another country to escape danger in their own country.
Lineage
ancestry or family line
Petition
To ask for something in a formal way.

Royal Commission
An official investigation established by the government. (the Crown)

Demographic change
A change in the characteristics of a population, such as rates of growth, birth, death and migration.

Reformers
Someone who seeks to change — to reform —established rules and arrangements in society.

Rebellion
A challenge to the authority of a recognized government.

Delegate
A representative who votes according to the preferences of his or her constituency.
Constitution
The official set of rules about how a country is governed.

Provisional government
A temporary government formed when no other authority can establish legitimate control.

Compromise
A course of action that balances the conflicting priorities of many groups or stakeholders.

Collective Identity
The shared identity of a group of people, especially because of a common language and culture.

Biculturalism
When an individual identifies equally with two or more cultures.

Strategic Position
A place whose physical location makes it important or valuable, often for military reasons.

Maneuver
to steer

Sponsor
A person or organization that contributes to a project or activity by paying for it.

Scurvy
A disease resulting from lack of Vitamin C that causes internal bleeding.

Smallpox
A disease that causes the skin to break out, accompanied by a high fever.
Human Rights
every person has these

Settlement
A place where people live permanently, such as a village.

Monopoly
The complete control of a resource by a single country.

Charter
A set of rules and privileges granted to a company by a king or queen.

Epidemic
The infection of a large population by disease.

Pemmican
A food made from dried meat, pounded and mixed with berries and fats.
