Jawetz Chapter 5-6
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the difference between nitrogen fixation and ammonification?
Nitrogen fixation is the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen gas (N₂) to ammonia (NH₃).
Ammonification is the conversion of organic nitrogen (e.g., from dead organisms or waste) into ammonia, usually by decomposers.
It is the process of propagating organisms by providing proper environmental conditions.
Cultivation
Which organisms generally require cultivation for detailed study?
Parasites, bacteria, and viruses.
What method of reproduction do bacteria use?
Binary fission, a type of asexual reproduction
Name three factors that must be controlled during bacterial growth.
pH, temperature, and nutrients (also acceptable: aeration, salt concentration, ionic strength).
Why is controlling ionic strength important in bacterial cultivation?
Because ionic strength affects osmotic balance and enzyme activity, which are critical for survival and replication.
What six elements make up most of the dry weight of microorganisms?
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur.
Name four essential inorganic ions needed by microorganisms.
Potassium, sodium, magnesium, and calcium (also acceptable: iron, chloride).
What molecule provides energy for forming anhydride bonds?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
In prokaryotes, where does the proton motive force occur?
Across the cytoplasmic membrane
What are the two components of the proton motive force?
A pH gradient and an electrical (charge) gradient.
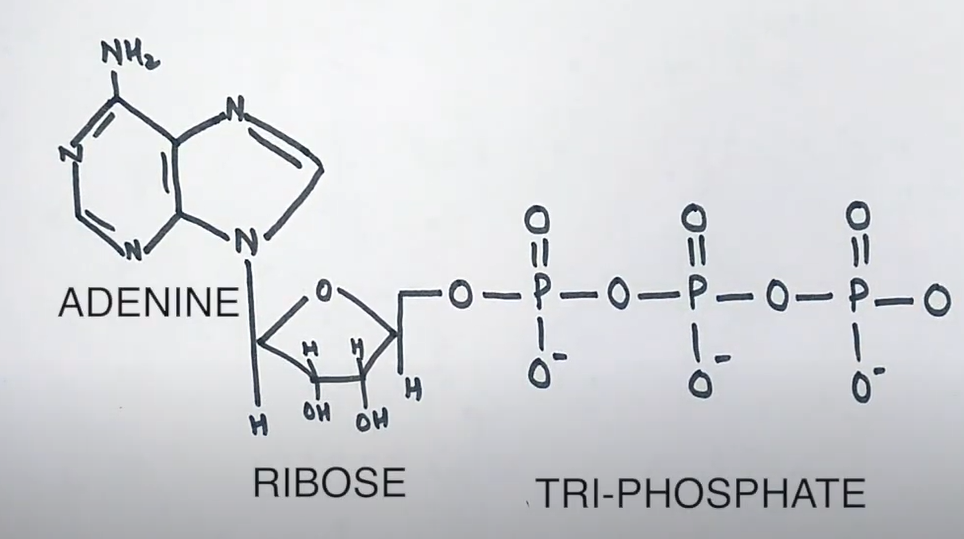
If a microorganism lacked ATP, how might it still power cellular functions using the proton motive force?
It could generate the proton motive force using environmental energy or reverse the usual flow by hydrolyzing existing ATP to drive proton pumping
For the most part, the organic matter is in macromolecules formed by the introduction of ________________ between building blocks.
anhydride bonds
The charge on the___________ of the bacterial membrane is more positive than the charge on the ___________.
outside; inside