AdU Building Utilities 1 Plumbing
1/358
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1 Plumbing (Ar. Chun September 6, 2025)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
359 Terms
is the art and science of installing pipes, fixtures and other apparatus to convey and supply water in buildings and to dispose and discharge waste water and other liquids, gases and other substances out of buildings in a safe, orderly healthy and sanitary way to ensure health and sanitation of life and property
Plumbing
a title given to a person skilled in the field of sanitation.
Plumber
refers to an individual who worked in the sanitary field in ancient Rome.
Plumbarius
meant lead, A metal used as plumbing material by the Romans, preferred for its twin properties of malleability and resistant to acid
Plumbum
Around 2,500 BC, the Egyptians used _____ pipes in their irrigation and sewerage systems.
copper
had been established as evidenced by their skillful planning in their network of canals.
science of hydraulics
were built to convey water from sources to houses.
Aqueducts
Bath of Diocletian
a bath that could accommodate 3,200 bathers at one time. These baths were lines with ceramic tiles.
The quality of plumbing declined after the fall of the
Roman Empire in 476AD
a type of water closet was developed.
In 1500's
were introduced in the mid 1800's
Septic tanks
a modern sewerage system began operating in
London in the 1860's
includes the water supply distributing pipes; the fixture and fixture traps; the soil, waste and vent pipes; the building drain and building sewer; the storm water drainage, with their devices, appurtenances and connections within the building and outside the building within the property line.
plumbing system
Plumbing has two main objectives:
To supply water to different parts of the building
To remove and discharge human waste and other substances out of the building into the public sewer or septic tank
A system in plumbing which provides and distributes water to the different parts of the building or structure, for purposes such as drinking, cleaning, washing, culinary use, etc.; it includes the water distributing pipes, control devices, equipment, etc
Water Supply System
All the piping within public or private premises which conveys sewage, rainwater or other liquid wastes to a point of disposal.
Drainage System
are installed by the plumber to remove wastewater and water-borne wastes from the plumbing fixtures and appliances, and to provide circulation of air within the drainage piping.
Sanitary Drainage and Vent Piping System
Pipes installed to remove the wastewater and water-borne wastes from plumbing fixtures and convey these to the sanitary sewer and other point of disposal.
Sanitary Drainage Pipes
A system of pipes, fittings and other devices installed for the purpose of providing circulation of air and creating balanced atmospheric condition within the system thereby preventing siphonage and backpressure.
Ventilation System
A pipe that conveys the discharge of water closets or similar fixtures containing fecal matter, with or without the discharge of other fixtures to the sewer.
Soil Pipe
A pipe that conveys only liquid waste free of fecal matter.
Waste Pipe
the most basic and fundamental component of life on earth.
Water
become the central issue in protecting our water resources.is a great source for supplying our water needs, but it is also one that is susceptible to contamination.
Ground water
Much of the human body is water, the most abundant chemical in our body as well as in our diet.
Nourishment
Water is a nearly ideal medium for the dissolution and transport of organic waste, and its high heat storage capacity makes the attainment of comfortable temperatures for bathing easy. Much larger quantities of water are used for cleaning than for nourishment.
Cleansing and Hygiene
Largely through its association with cleaning, water acquired a ceremonial significance that remains particularly evident in religious services.
Ceremonial Uses
Waterways had been developed for this purpose to allow the passage of water vessels and to be able to transport large quantities of goods as well as people
Transportation Uses
Water has a remarkable cooling potential: it stores heat readily, removes large quantities of heat when it evaporates, and vaporizes readily at temperatures commonly found at the human skin surface
Cooling Medium
In almost any landscaping application, indoors or out, water becomes a center of interest. Our association of water with nourishing, cleansing, and cooling make a very powerful design element which is a fact recognized by landscape designers throughout history.
Ornamental Element
Water is an essential element in fire protection. The vast quantities of water potentially required for firefighting must be delivered quickly; the result is pipes of enormous sizes regulated by very large valves. Despite its size and guarantee of at least partial exposure in public places, a fire protection water supply system is rarely treated as a visually integral design element.
Protective Uses
Uses of Fresh Water
• Agricultural
• Industrial
• Household
• Recreation
• Others
Water Pollution / Crisis
• Population Growth
• Industrialization
• Rapid Urbanization
• Climate Change
• Depletion of Aquifers
Advantage:
• Obtained from roofs and watersheds.
• It is soft pure and good on places where there is an abundant rainfall
Disadvantage:
• Hard to store for a long time as it will be a breeding place for mosquitoes
• Bad for places that receives a little amount of rainfall
Rainfall
Advantage:
• Obtained from ponds, lakes, rivers
• Easiness of procurements and good for locality near such bodies of water
Disadvantage:
• Dangerous since it contains large amounts of bacteria, organic and inorganic substances
Natural Surface
Advantage:
• Obtained from below ground surface by means of mechanical and manual equipments
• More water can be obtained depending by equipments used and locality
Disadvantage:
• Because of various organic matter and chemical elements present, it requires treatment in various nature such as sedimentation, chemical, filtration, aerations
Underground Water
That portion of the rainwater which was percolated into the earth to form underground deposits called
aquifers
A mixture of surface run-off and groundwater, surface sources include rivers, lakes, ponds and impounding reservoir.
Surface Water
Average Daily Consumption per Fixture.
Water Closet 4 to 5 gals.
Lavatory 2 gals.
Bathtub 30 gals.
Shower 10 to 40 gals.
Clothes washer 40 gals.
Garden hose 150 gals.
particles of matters that are suspended in the water are allowed to stay in a container so that they will settle in the bottom, then drawing the water out, leaving these sediments in the container
Sedimentation
water are given chemical treatments to kill the harmful bacteria present and to cure the turbid taste or mud taste, remove clay, salts, iron etc. commonly used chemical is chlorine
Chemical Treatments
water is filtered on various processes, so as to remove the particles of vegetable matter present in the water, most commonly used materials are sand and gravel
Filtration
raw water is made to pass on pipes of tiny sieves and exposed to air of fine mist
Aeration
removes suspended matters from water by allowing time and the inactivity of water to do the work
Sedimentation
a chemical such as Alum (hydrated aluminum sulfate) is added to turbulent water
Coagulation
removes iron and manganese and decrease its corrosiveness; much of the water surface is exposed to air
Aeration (Oxidation)
water treatment process that destroys bacteria and other microorganisms through an infusion of ozone, a gas produced by subjecting oxygen molecules to high electrical voltages.
Ozonation
a very common treatment for removing suspended particles, bacteria and color
Filtration
Chlorine, Chloramine, Chlorine Dioxide, Iodine
Disinfection
water is heated to allow condensation, as water vapor encounters cooler surface, it condenses
Distillation
fluoride may help in minimizing tooth decay but excessive amounts are toxic and caused mottled teeth thus it’s levels must be carefully monitored
Fluoridation
control of concentration of elements in corroding supply and discharge lines
Corrosion Control
Algae growths, the most prevalent nuisance, can usually be controlled by applying copper sulfate (blue stone or vitriol) to the water body.
Nuisance Control
Adsorption is a mechanism of contaminant removal making use of the adsorption phenomenon, the act of physical adhesion of molecules or colloids to the surface of the medium w/o chemical reaction.
Adsorption
Exposure to UV radiation is used in small scale water supplies. Water is exposed to the rays after filtration because particles of sediment in water might shield the bacteria.
Ultraviolet Irradiation
done by heating seawater then pumping water into a low-pressure tank, where the water vapor is condensed and removed as pure water. The remaining liquid (brine).
Water Desalination
Water Storage
• Groundwater
• Soil Moisture
• Wetlands
• Ponds and Tanks
• Dams and Reservoirs
are carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide methane, oxygen and nitrogenous and organic compounds
Entrained Gases
are calcium, magnesium sodium, iron and manganese and other carbonates and silicates, alkyl benzene sulfate from detergents and synthetic organic from insecticides and pesticides
Dissolved Minerals
such as bacteria, algae, fungi, silt, protozoa, and other colloidal matters making the water colored and acidic
Suspended and Colloidal Materials
by entrainment of radioactive substances from mining or processing ores, by wastes from industrial use of radioactive materials
Radioactive Materials
Wells that are supplying water for public use should be located at a minimum distance of ______ from residential areas
100 meter radius
There should be no concrete sanitary sewers existing within
15 meter radius of the well
No outdoor privy, cesspools, septic tank or drain fields shall be located within
45 meter radius from the well
water is distributed from normal water pressure coming from public water main for use in low rise buildings
Up feed System
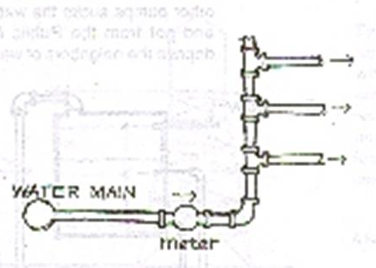
Up feed System
water pressure is distributed from air pressure coming from suction tank for use in all tall buildings which cannot be reached by normal water pressure.
Pneumatic Tank
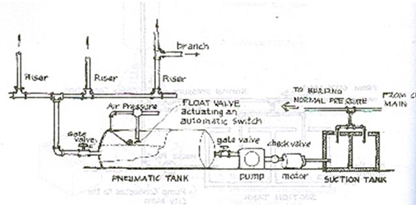
Pneumatic Tank
by gravity from overhead tanks and are suspended either by structural frames or on the roof decks.
Down feed System
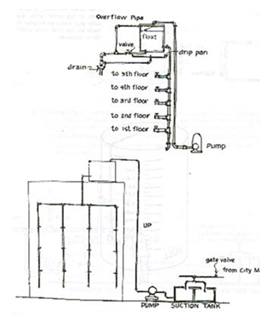
Down feed System
from the rain
Storm Water
waste from laundries, wash basins, sinks etc.
Grey Water
human waste and urine
Black Water
➢ Smaller in size than the soil pipe
➢ It receives the discharges of any fixture except the water closet
➢ It has two types:
▪ Direct Waste
▪ Indirect Waste
WASTE PIPE
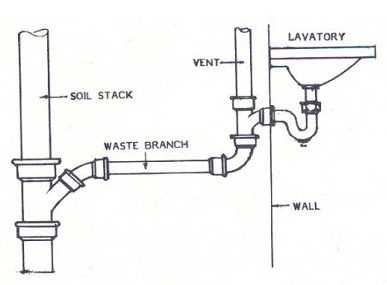
Direct Waste
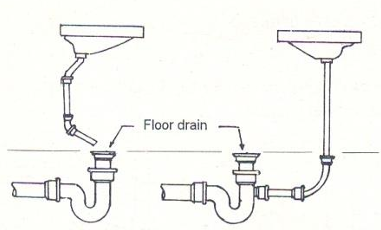
Indirect Waste
A pipe that receives and conveys discharges of water closet, with or without the discharge from other fixtures
SOIL PIPE
➢ Is the portion of the plumbing system that receives the discharges of all soil and waste stacks within the building
➢ Referred to as the “Collection Line of a Plumbing System”
➢ It can be installed underground or maybe suspended below the floor or inside the ceiling
HOUSE DRAIN
is defined as a device installed in the house drain immediately inside the foundation wall of the building.
House Trap
consists of a running trap installed under the basement floor to protect it from freezing.
Area Drain
a receptacle used to receive water to be drained from the floor into the plumbing system.
Floor Drain
a receptacle used to catch surface water drained from the cemented courts, driveways and yards
Yard Catch Basin
a device designed to convey waste from garage, wash rack, grease pits and repair floors into the house drain
Garage Catch Basin
this is more prevalent in large kitchens serving hotels, dining rooms, clubhouses, and restaurants
Grease Basin
➢ That portion of the horizontal drainage system which starts from the outer face of the building and terminate at the main sewer in the street or septic tank
➢ It is sometimes called “Building Sewer”
HOUSE SEWER
➢ The unit of the plumbing system that conveys rain or storm water to a suitable terminal.
➢ Storm water is normally discharged into street gutter conveyed by public drain system and carried to some natural drainage terminals like canals, rivers, lakes and the like.
STORM DRAIN
➢ Ventilation of a plumbing system is the portion of the drainage pipe installation designed to maintain a balance atmospheric pressure inside the system to prevent various plumbing problems.
VENTILATION
for the admission of air and the discharging of gasses, soil and waste stacks are extended through roofs, and a system if air vents, largey paralleling the drainage system is also provided
Vents
It serves as the terminal for the main vent and other vents of the plumbing system
Main Soil and Waste Vent
It is the portion of the vent pipe system which serves as a terminal of the smallest forms of units and grouped fixture trap ventilation. It also serves as a relief vent for any back pressure.
Main Vent
Also known as the back vent, it is the portion of the vent pipe system which serves a single trap. It should be connected close to the fixture trap as possible, it should be located underneath and back of the fixture and it must be connected to the main vent above the overflow line of the fixture
Individual Vent
This is the portion of the vent pipe which ventilates two fixture traps. Usually used in apartments arranged back to back
Unit Vent
This is employed where two or more fixture traps are installed on a horizontal soil or waste branch. The use of circuit vent generally reduces the cost of the plumbing installation
Circuit or Loop Vent
It is installed to ventilate the soil and waste pipe and the connecting branches other than the fixture traps. Relief vent is provided when waste branches are circuit vented
Relief Vent
On a long vertical soil pipe, a relief vent is installed at 3 to 5 floor intervals. In this case, the relief vent is referred to as the Yoke or by-pass ventilation
Yoke or By-Pass Ventilation
Refers to the vertical pipe of the plumbing system used as ventilation of the plumbing, installation and fixture traps which at the same time receives and convey liquid waste discharge from the fixtures.
Wet Ventilation
It is used on fixtures in a room away from any partitions. Common to beauty parlors, barber shops and dental clinics and surgical rooms
Looped Vent
Can be attributed to inadequate ventilation of the trap and the subsequent minus and plus pressures inside the system.
Trap Seal Loss
It is the result of the minus pressure in the drainage system. When a large amount of water flows rapidly through the trap, self siphoning is automatically developed and the water content of the trap is absolutely discharged.
Siphonage
This condition is caused by a plus pressure which blows the water out of the fixture.
Back Pressure
This process is a minor problem and less probable to drain water inside the trap. Evaporation happens only on floor drains not regularly used to admit water but is exposed to extreme temperature
Evaporation