Mendel’s Principles & Meiosis: Genetics, Inheritance, and Diversity
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Mendel's Law of Segregation
An organism inherits two copies of each gene, one from each parent, but only one copy is passed to each offspring.
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment
Genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other.
Dominant trait
Traits that are displayed in hybrid individuals.
Recessive trait
Traits that are masked by dominant traits.
Genotype
The genetic composition of an organism.
Phenotype
An organism's observable characteristics.
Probability
Chance that an event will have a particular outcome.
Homunculus
The belief that sperm contained fully formed 'little people'.
Like begets like
The belief that offspring are like their parents.
Everything from the egg
The belief that females controlled all traits.
Paternal heredity
The belief that males control all traits.
Blending inheritance
The belief that offspring were the average between both parents.
Inheritance of acquired characters
The belief that changes happening to parents could be passed on to offspring.
Pangenesis
The idea that particles called 'gemmules' carry the traits we inherit.
Gregor Johann Mendel
Considered the father of genetics.
True breeding
Traits that consistently produce offspring with the same traits.
Monoecious
Having male and female reproductive organs in one flower.
Short generation times
The time it takes for an organism to reach maturity and reproduce.
Mendel's Notation System
P: parent generation of true breeding plants.
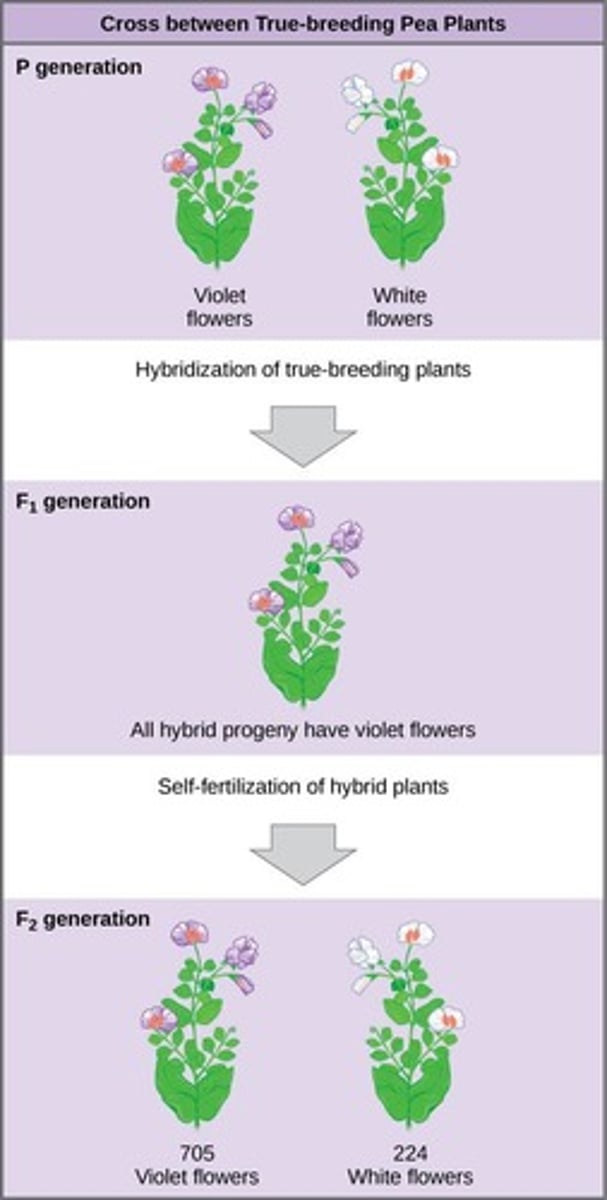
P
Parent generation of true breeding plants.
F1
First filial generation of offspring from a cross between parents.
F2
Second filial generation of offspring produced by crossing two F1 individuals with each other.
Self cross
Crossing a plant with itself (selfing).
Single-Factor Cross
An experiment where the experimenter follows only a single trait.
Monohybrids
Offspring of P cross if parents differ in one trait.
3:1 F2 ratio
The ratio observed in F2 generation from a formal monohybrid cross, where approximately three quarters of the plants had one trait and one quarter had another.
Dominant
Some versions of a trait that mask other versions of a trait.
Recessive
Other versions of a trait that are masked by dominant versions.
Trait
A characteristic such as flower color, eye color, etc.
Alleles
Specific versions of a 'hereditary particle' (today = versions of a gene).
Homozygote
When both alleles for the same trait are the same, e.g., PP (homozygous dominant) or pp (homozygous recessive).
Heterozygote
When alleles for the same trait differ, e.g., Pp (heterozygous).
Zygote
First diploid cell produced by fertilization.
Gene
The location in a DNA strand that encodes information causing a trait.
Reciprocal cross
A formal mating cross where a previous cross is repeated, but the parental roles are reversed.
Wildtype allele
The most common allele in a population, referred to as the 'normal allele.'
Mutant allele
A rare allele in a population, reasoned to be the most recently formed allele by mutation, referred to as the 'non-normal allele.'
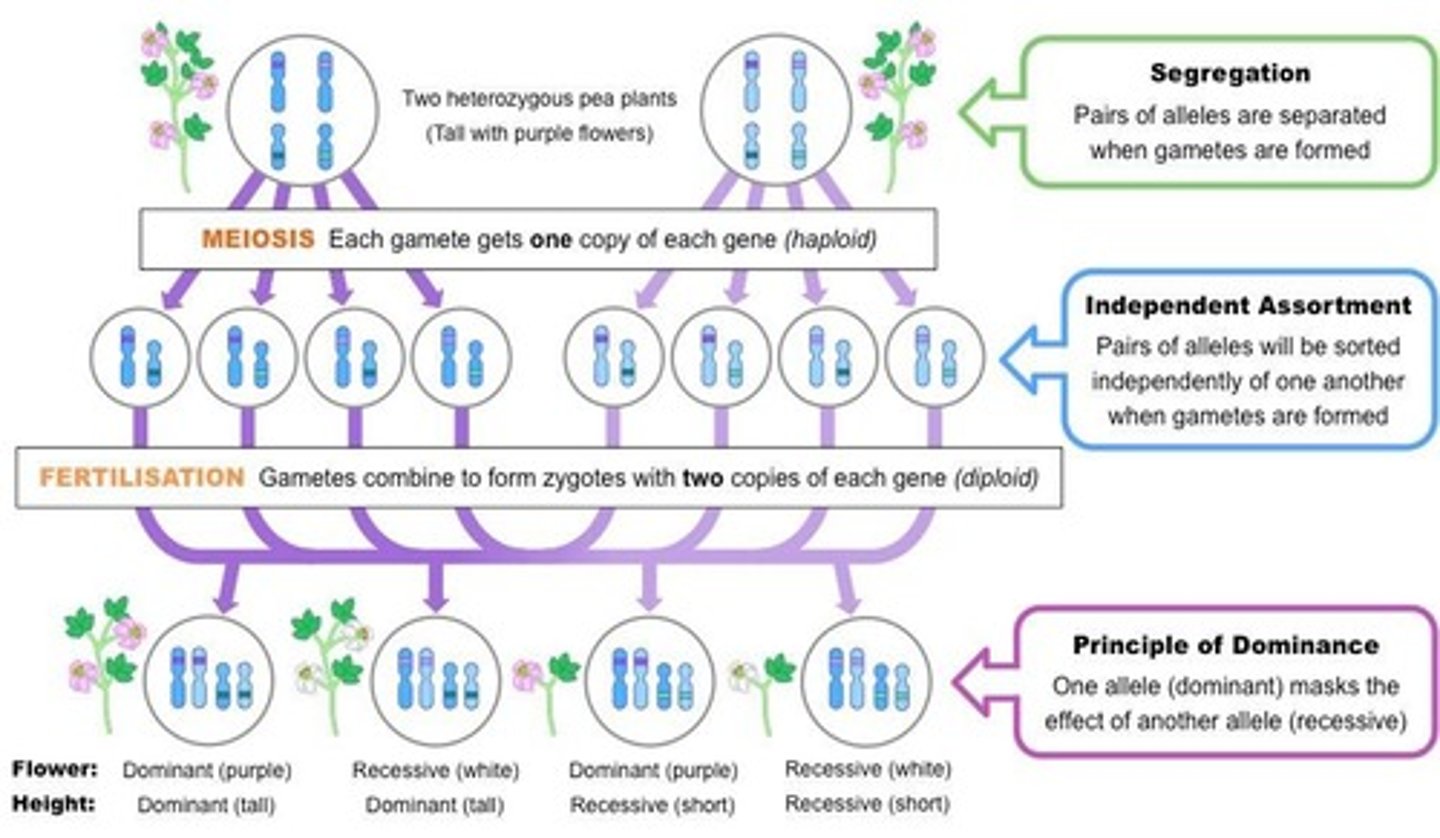
Mendel's First Law
The Law of Segregation.
Law of Segregation
Two alleles segregate from each other during the transmission from parent to offspring, meaning only one of the two gene copies present in an organism is distributed to each gamete.
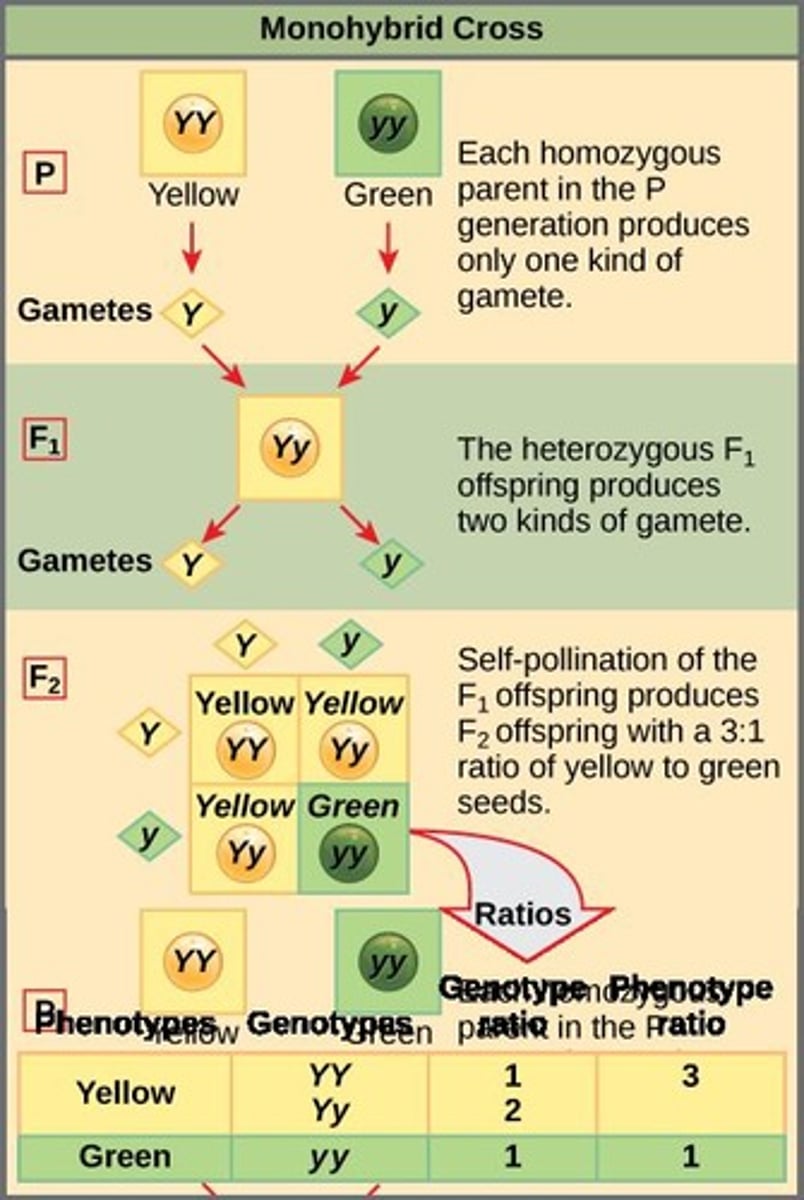
Punnett Squares
A tool used to predict the probability of genetic crosses.
Monohybrid Cross
A cross between pea plants that are true-breeding for the dominant yellow phenotype and plants with the recessive green phenotype, producing F1 heterozygotes with a yellow phenotype.
True-breeding
A kind of breeding in which the parents with a particular phenotype produce offspring only with the same phenotype.
Mendel's Second Law
The Law of Independent Assortment.
Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles of different genes assort independently of each other during gamete formation, meaning the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene.
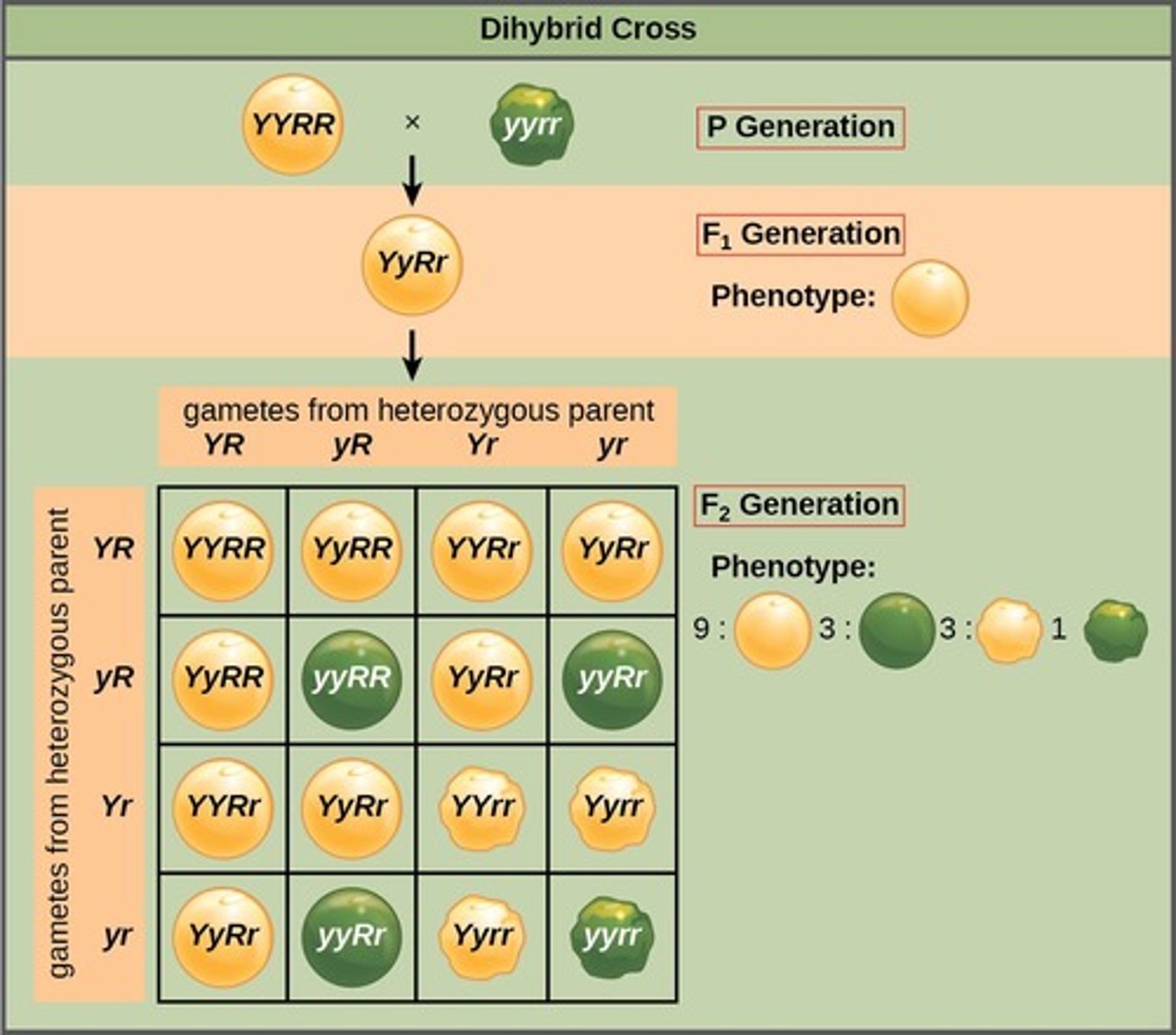
Dihybrid Cross
A cross involving two different traits, such as seed shape (round or wrinkled) and seed color (yellow or green) in pea plants.
3:1 ratio
The ratio observed in monohybrid crosses, indicating that traits are inherited independently from one another.
Segregation
The process by which alleles for one trait are separated during gamete formation.
Recombination
The process by which alleles for different traits are mixed during gamete formation.
Gamete
A reproductive cell (egg or sperm) that carries one allele for each gene.
F1 generation
The first generation of offspring from a cross, typically heterozygous for the traits being studied.
F2 generation
The second generation of offspring, produced by crossing individuals from the F1 generation.
Pea plants
The organism used by Mendel in his experiments to study inheritance patterns.
Allele
Different forms of a gene that can exist at a specific locus on a chromosome.

P generation
The parental generation in a genetic cross, typically true-breeding for specific traits.
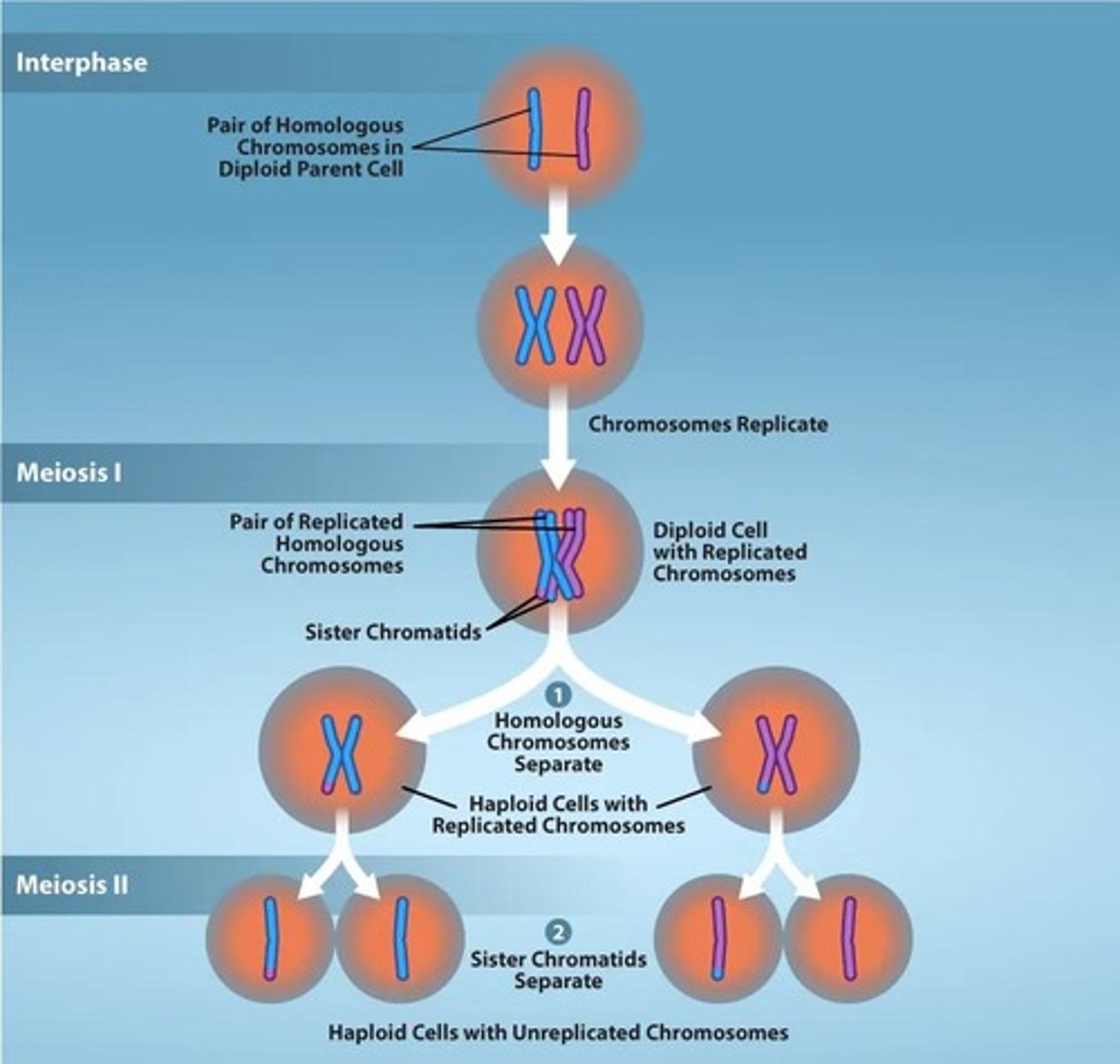
Meiosis
A type of cell division used in sexual reproduction that reduces the chromosome number of the parent cell by half.
Ploidy
Describes the number of sets of chromosomes present in an organism or cell.
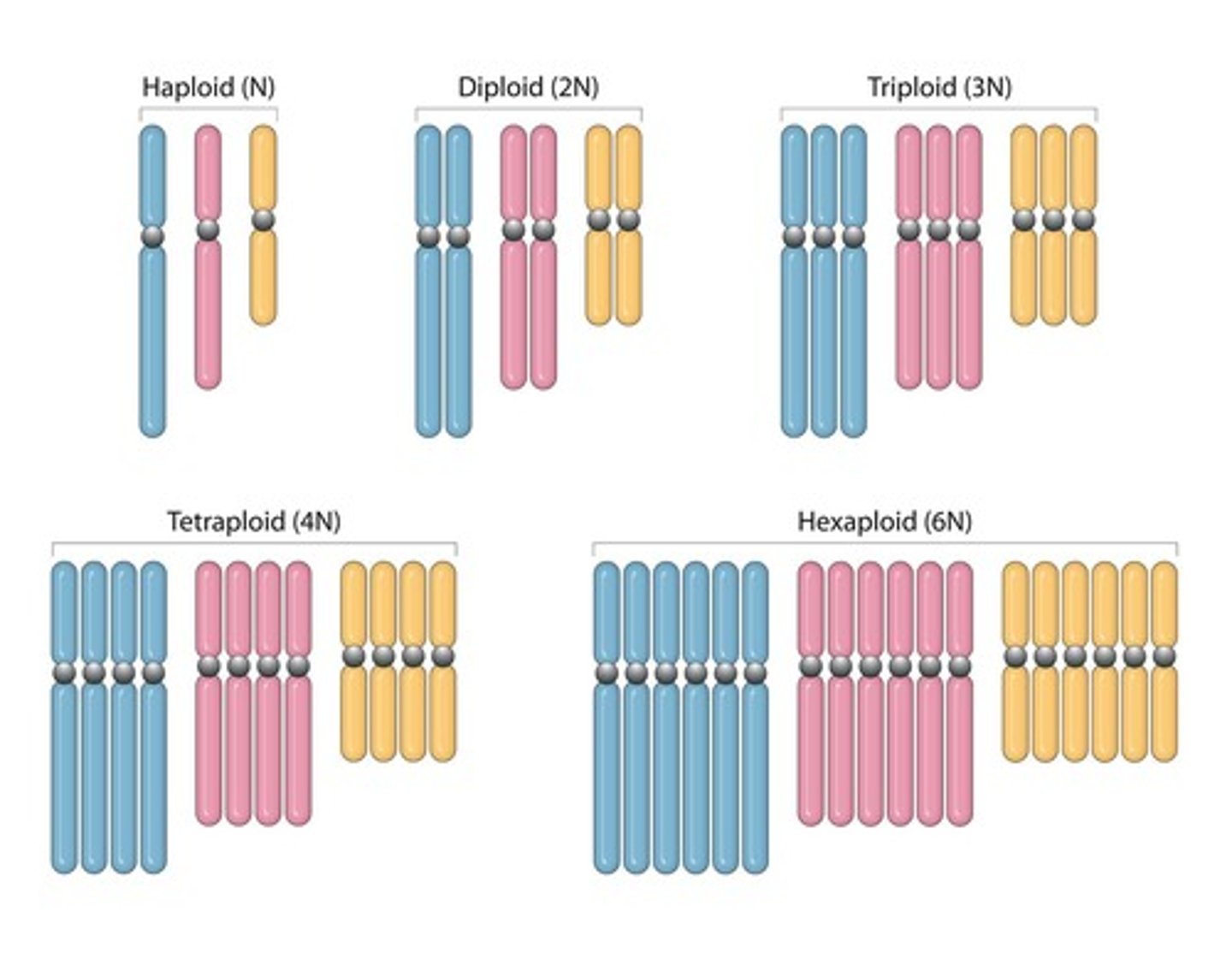
Haploid (n)
A single set of chromosomes.
Diploid (2n)
Two sets of chromosomes.
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that contain the same genes but may have different versions of those genes (different alleles) and are thus not identical.
Sister chromatids
Replicated chromosomes that are identical.
Gametes
Haploid cells (sperm and egg) produced through meiosis.
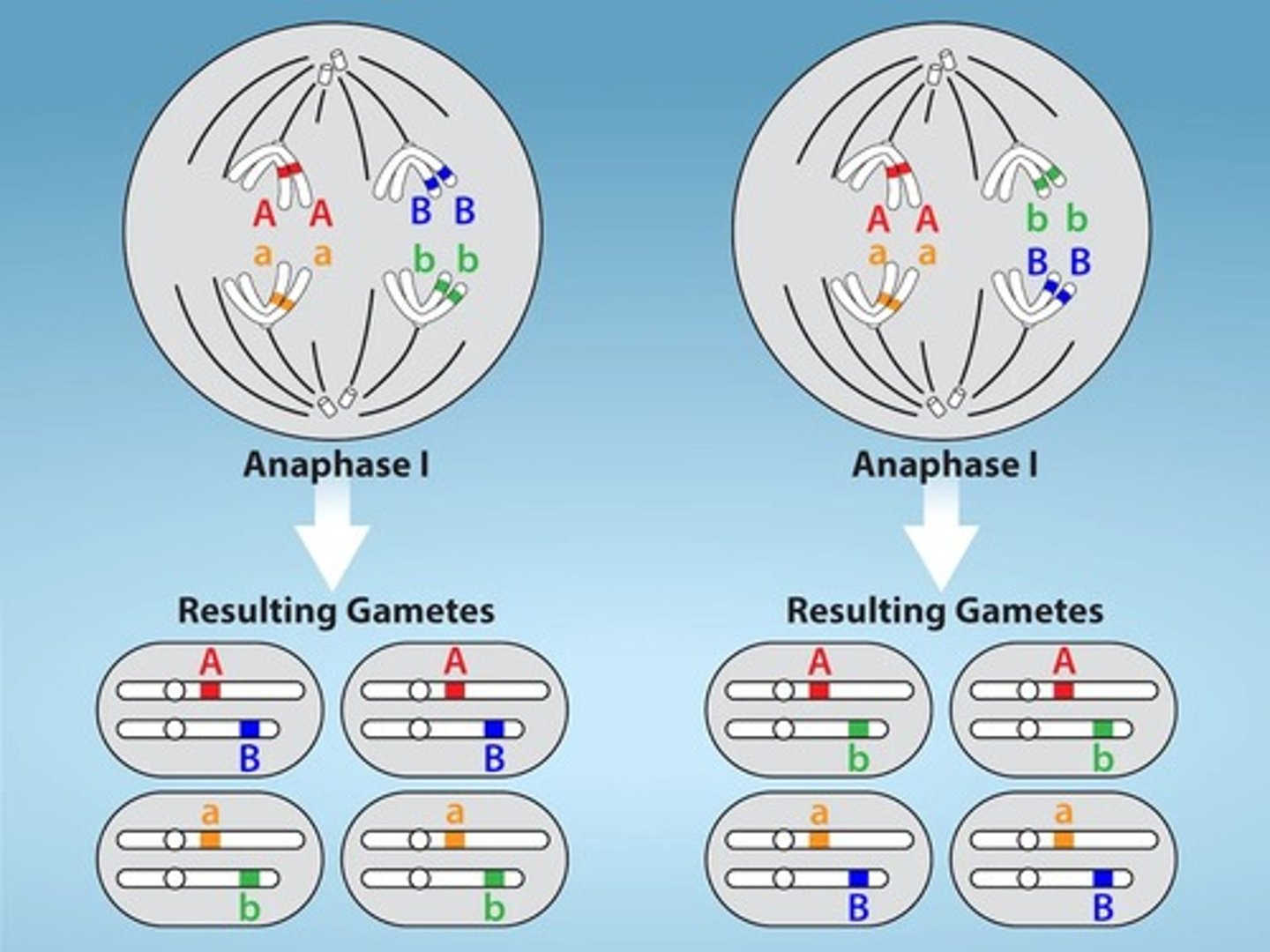
Independent assortment
The random lining up of tetrads at the metaphase plate, resulting in daughter cells with a unique mix of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
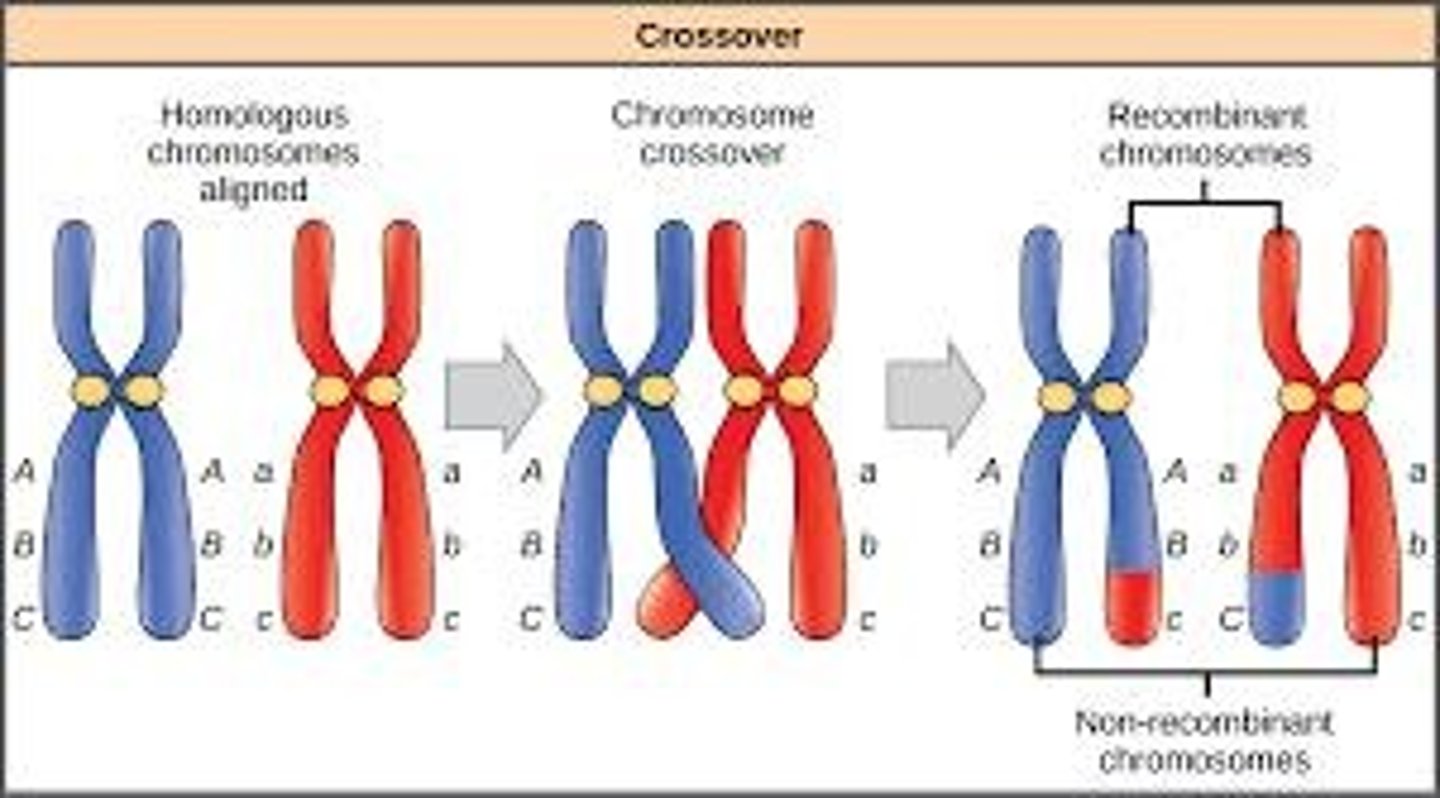
Crossing over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis I, generating unique gene combinations.
Somatic cells
Cells in the body other than sperm and egg cells; they are diploid (2n).
Reduction in ploidy
The decrease in chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n) during meiosis I.
Meiosis I
The first meiotic division where homologous chromosomes pair up, exchange genetic material, and separate.
Meiosis II
The second meiotic division where sister chromatids separate, resulting in haploid daughter cells.
Genetic diversity
Increased variation in genetic traits due to the mixing of chromosomes from two individuals during sexual reproduction.
Tetrads
Homologous chromosomes that have paired up during meiosis.
Recombinant chromosomes
Chromosomes that have undergone crossing over and contain a mix of maternal and paternal genes.
Non-recombinant chromosomes
Chromosomes that have not undergone crossing over and are identical to the parental chromosomes.
Fertilization
The process by which gametes combine to form a new diploid organism.
Genetic recombination
The process of producing new combinations of alleles through crossing over and independent assortment.
1n
Indicates a haploid cell with a single set of chromosomes.
2n
Indicates a diploid cell with two sets of chromosomes.
Chromosome replication
Occurs in the S phase of interphase, making identical sister chromatids that remain attached at the centromere.
Synapsis
The pairing of homologous chromosomes held together by the synaptonemal complex.
Chiasmata
Visible structures at crossover points where segments of chromosomes are exchanged.
Tetrad
The four chromatids held together by chiasmata during crossing over.
Prophase I
Stage in meiosis where spindle fiber microtubules attach to kinetochore proteins at the centromeres and the nuclear membrane breaks down.
Prometaphase I
Stage in meiosis where homologous chromosomes are attached to spindle microtubules and the nuclear envelope completely disappears.
Metaphase I
Stage in meiosis where homologous chromosomes are arranged at the cell equator with kinetochores facing opposite poles, creating genetic variation.
Segregation of homologous chromosomes
The process in meiosis I that leads to a reduction in ploidy.
Haploid cells
Cells that contain half the number of chromosomes (1n) compared to diploid cells.
Diploid
A cell or organism that has two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Nonsister chromatids
Chromatids from different homologous chromosomes that participate in crossing over.
Kinetochore
A protein structure on the chromosome where spindle fibers attach during cell division.
Nuclear membrane breakdown
The process in which the nuclear envelope disintegrates, allowing chromosomes to interact with spindle fibers.
Chromosome alignment
The arrangement of chromosomes along the metaphase plate during metaphase I.
Maternal and paternal chromatids
Chromatids that originate from the mother and father, respectively, and can assort independently during meiosis.
Daughter cells
The resulting cells from the division process of meiosis, which are genetically unique.
Offspring fitness
The ability of offspring to survive and reproduce, which can be enhanced by genetic diversity.
Anaphase I
The stage in meiosis I where microtubules pull tetrads apart and chiasmata are broken, but sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere.
Telophase I
The stage where separated chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and, if cytokinesis occurs, nuclei do not reform.
Cytokinesis
The process of separating cytoplasmic contents into daughter cells; in animal cells, it occurs via a cleavage furrow, while in plant cells, a cell plate forms.
Prophase II
The stage in meiosis II where events depend on species-specific differences, and chromosomes may recondense if they decondensed in telophase I.
Prometaphase II
The stage where nuclear envelopes disappear, the spindle is fully formed, and each sister chromatid forms a kinetochore that attaches to microtubules from opposite poles.
Metaphase II
The stage in meiosis II where sister chromatids align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase II
The stage in meiosis II where sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles.
Recombinant Chromatids
Chromatids that have undergone crossing over, resulting in new combinations of genes.