Ch.15 Modern and Nuclear Physics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Hadrons
Particles that are affected by strong nuclear force, and contain quarks.
Protons and Neutrons.
Leptons
Are one of the classes of "fundamental particles" and are affected by weak nuclear force... Cannot be broken down. Electrons, Positrons, Neutrinos, Anti-neutrinos.
Proton quark composition
up up down
Neutron quark composition
up down down
Up, Top, and Charm quark charge
+2/3e
Down, Bottom, and Strange quark charge
-1/3e
The strange quark is strange because-
it lives longer than we would expect.
1. Charge is -1/3e with strangeness -1.
2. Antistrange is 1/3e Charge with strangeness 1
3. Other quarks have strangeness of 0
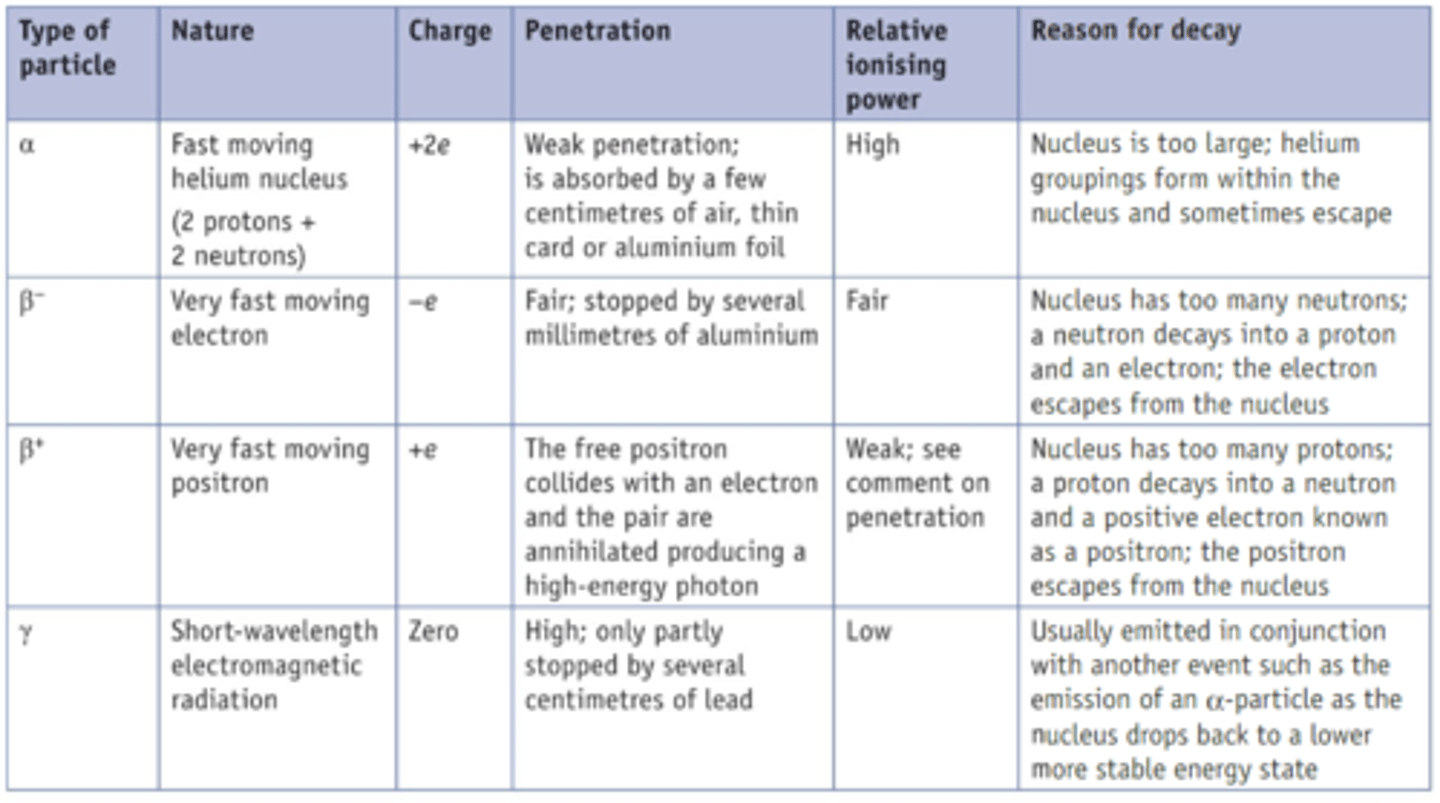
beta negative decay
Radioactive decay
decay of neutron into a proton
emission of an e- and an antineutrino.
A down quark decays to an up quark
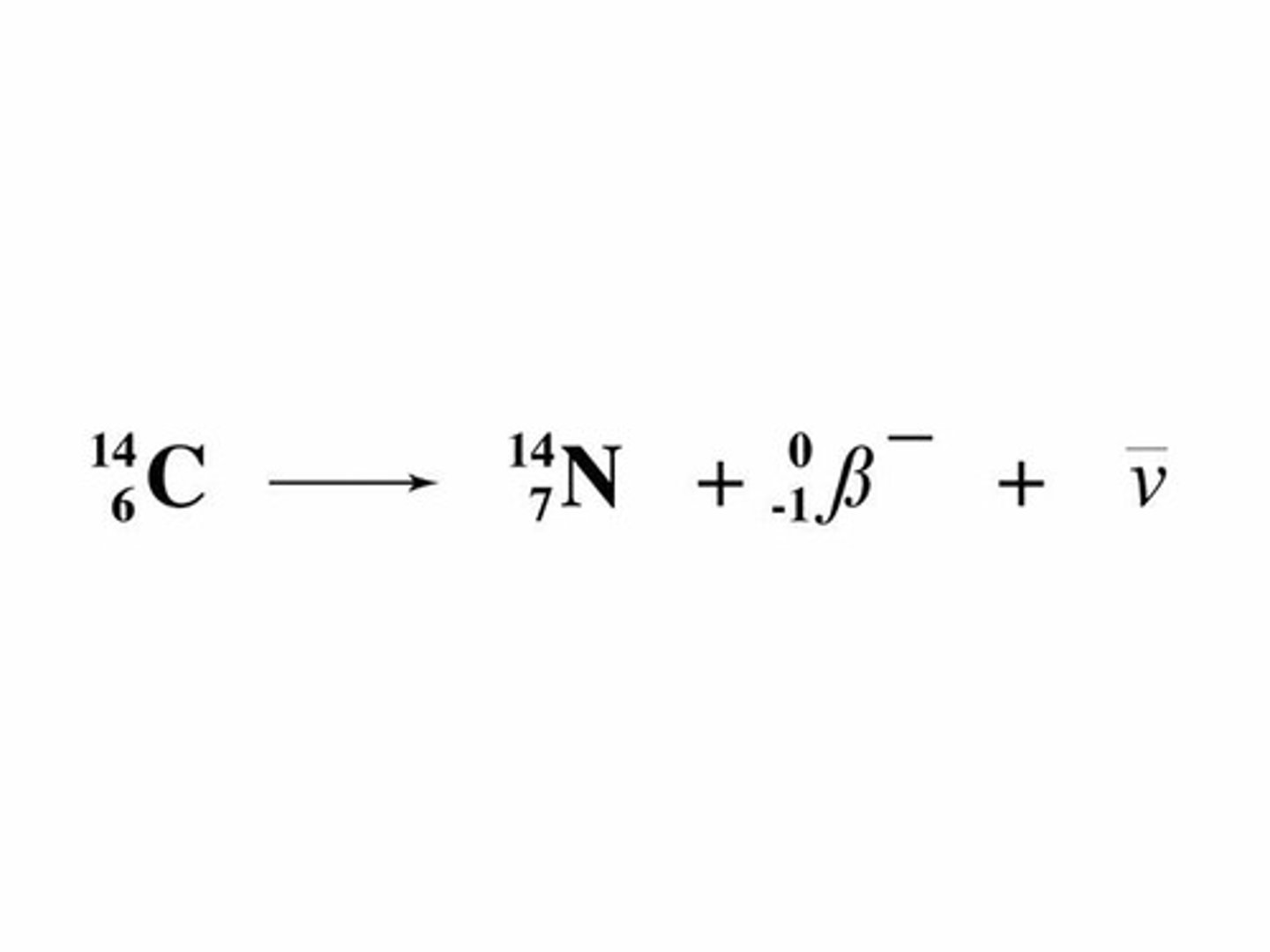
Beta positive decay
Proton decays into a neutron and a beta positive particle and a neutrino.
An up quark decays to a down quark
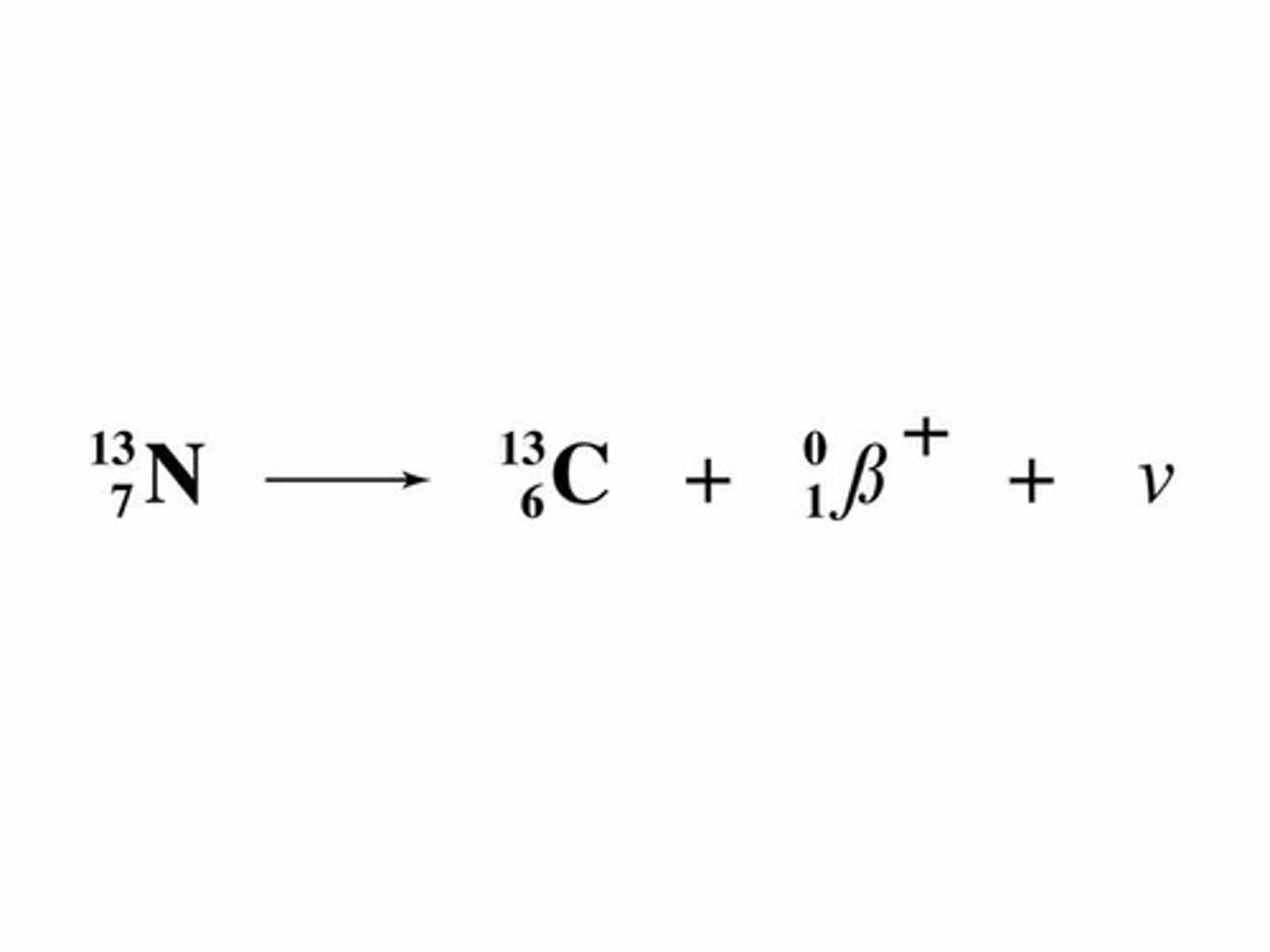
Ionization radiation through an electric field.
1. B- Particle attracted to positive plate.
2. B+ Particle attracted to negative plate.
3. Alpha +2 Particle attracted to negative plate, but a longer arc than B+
4. Gamma particle no attraction... straight through
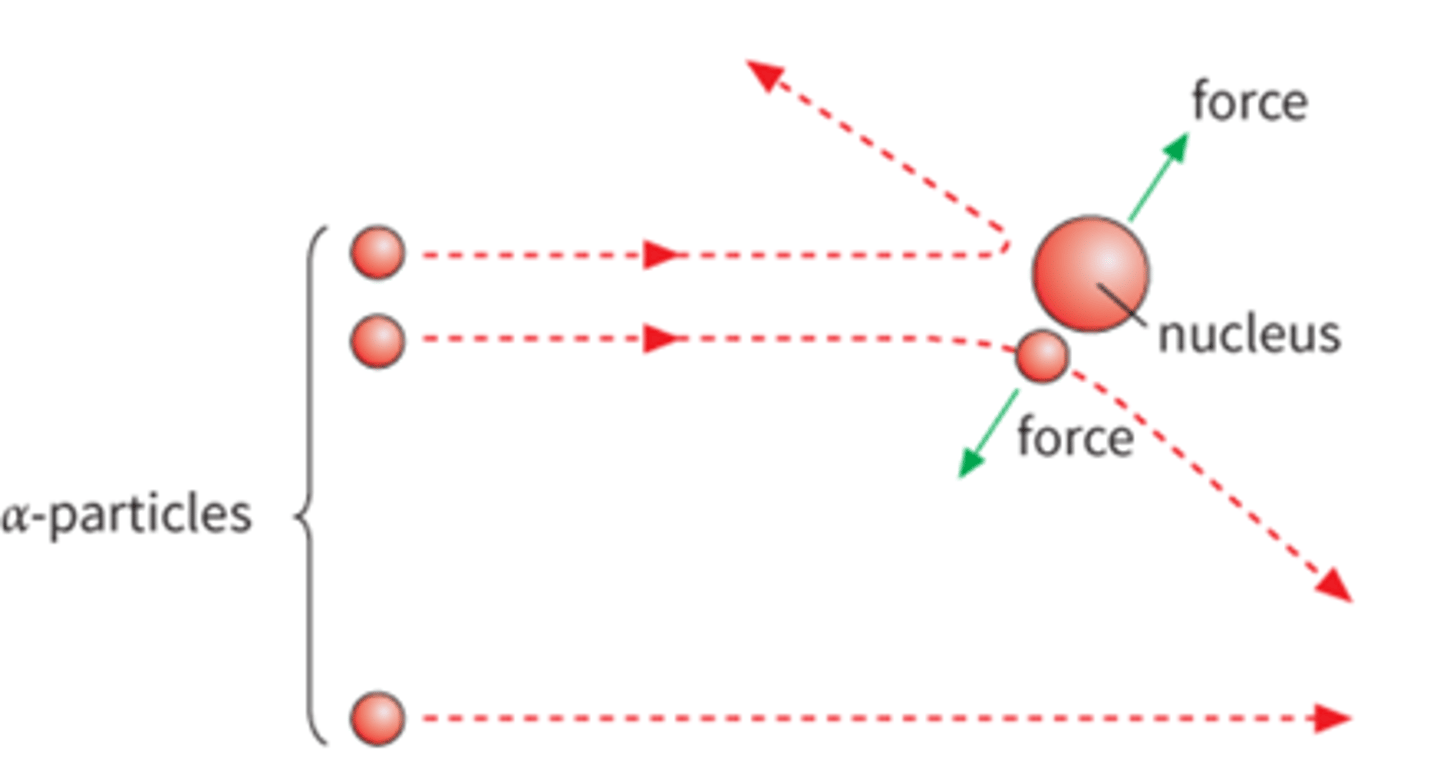
Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment
1. Most particles go straight through with no deflection... means
most of the atom is empty space.
2. With small deflections (less than 90 degrees)… means it is
near a positive particle
3. Very few particles have a deflection of greater than 90
degrees... means there is a very small, dense, positively
charged center called the nucleus.
Alpha particle radiation.
Parent nucleus emits a Helium nucleus and a smaller daughter particle.
+2e Charge
Slowest
Highest Ionization
Penetrates up to a few cm of air or paper
Reduces nucleon number by 4
Reduces Proton number by 2
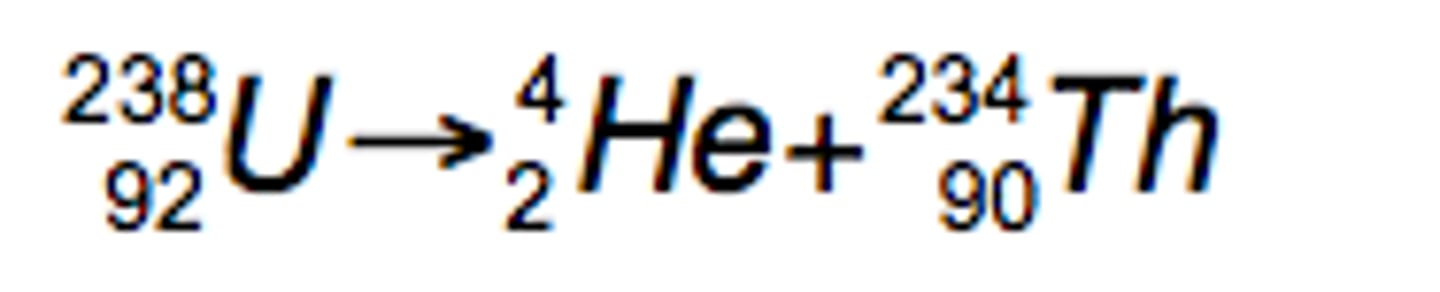
gamma radiation
EM radiation emitted during radioactive decay and having an extremely short wavelength and high energy
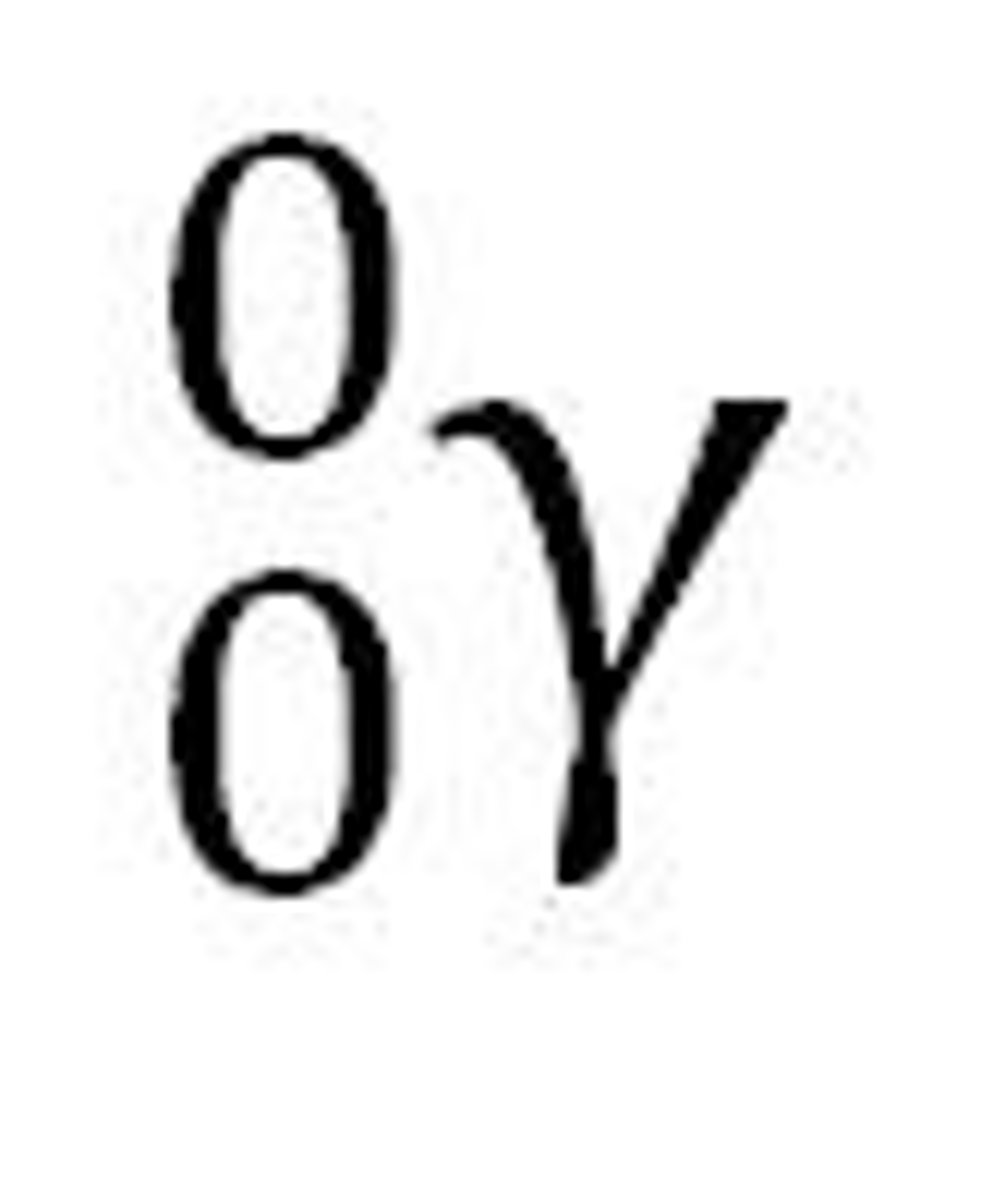
Antineutrino
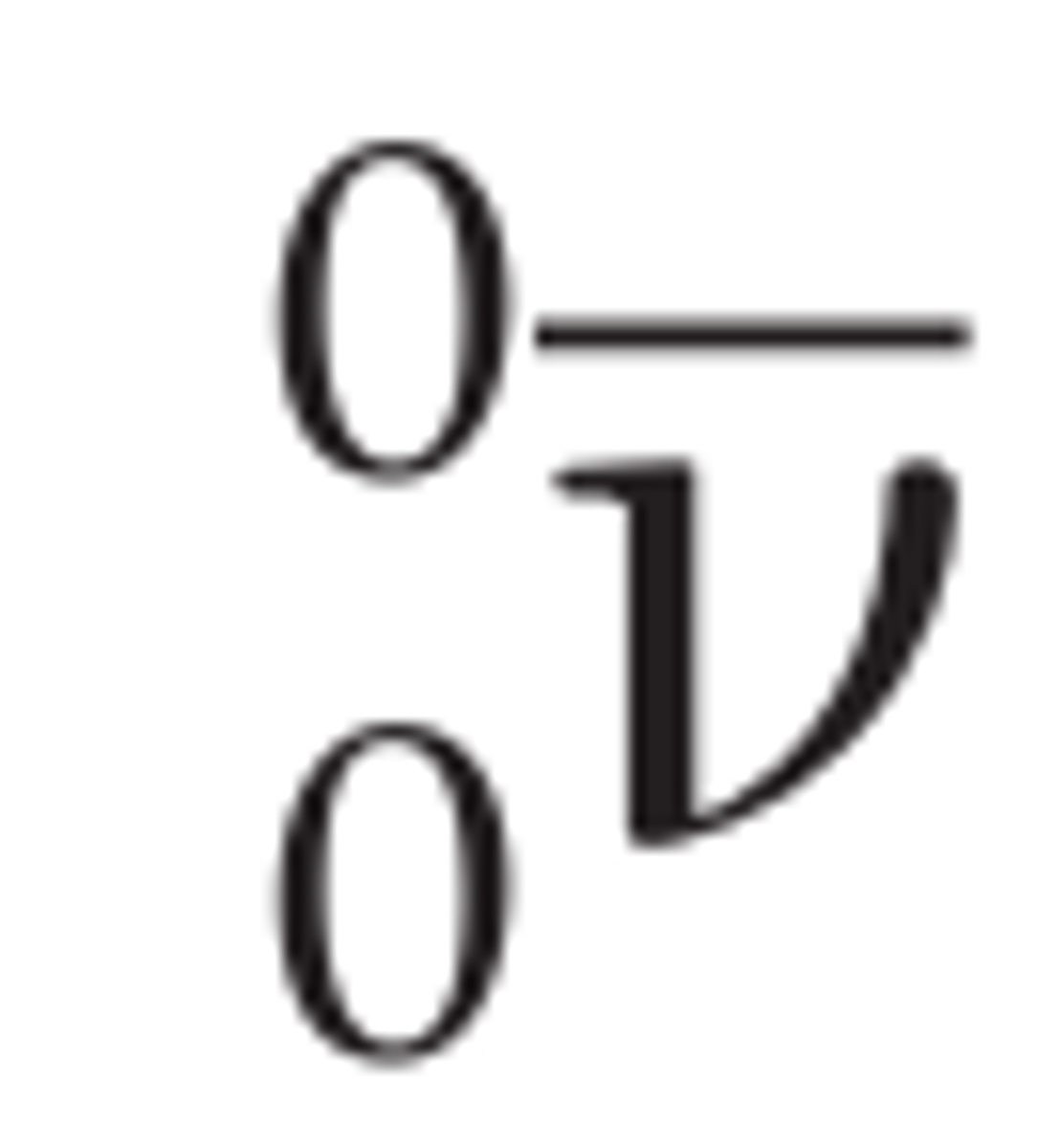
Neutrino
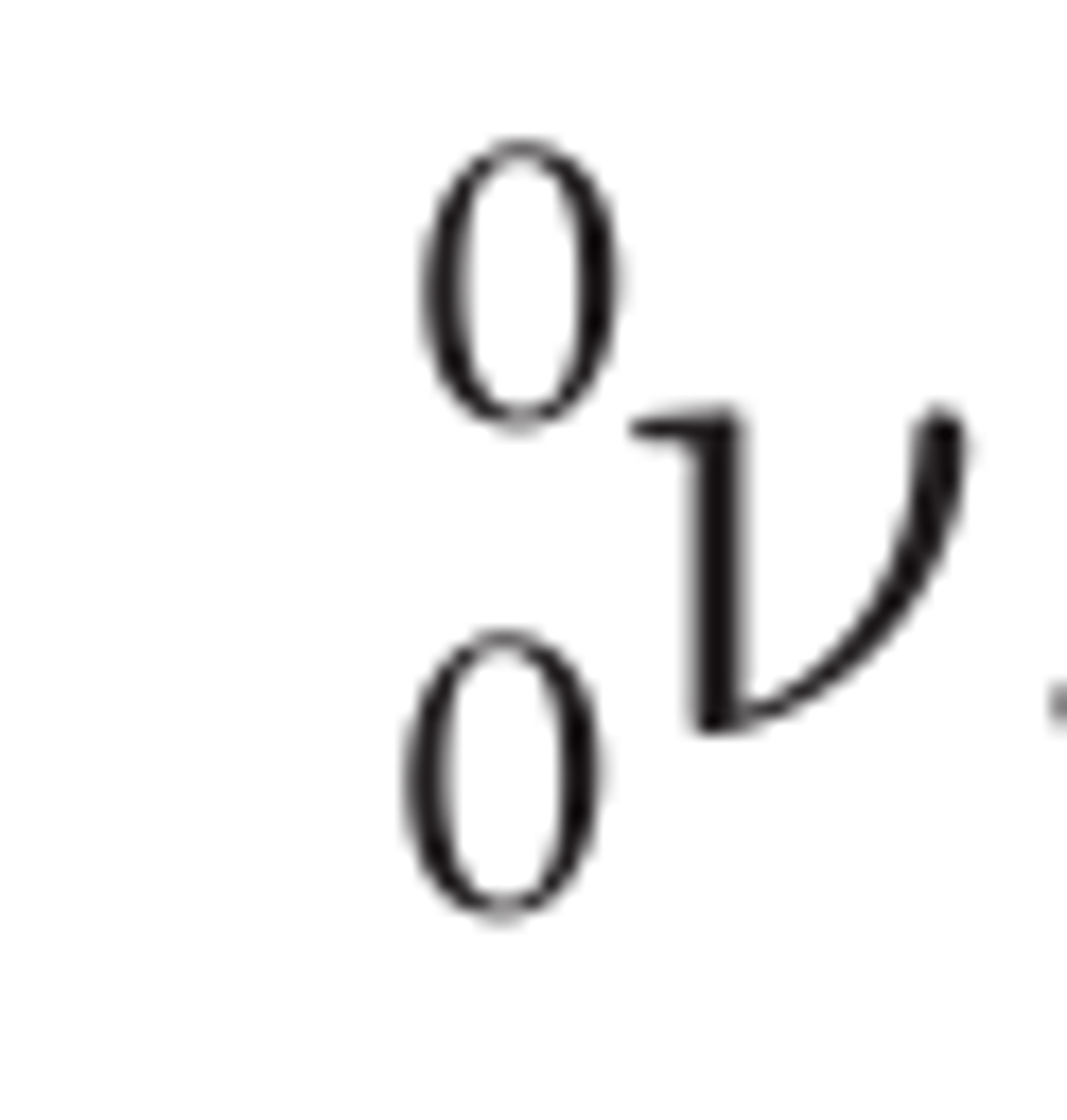
Types of Radiation
Baryon
A hadron consisting of three quarks.
Ex... uuu, uud, udd,...
Meson
A hadron consisting of a quark and an antiquark.
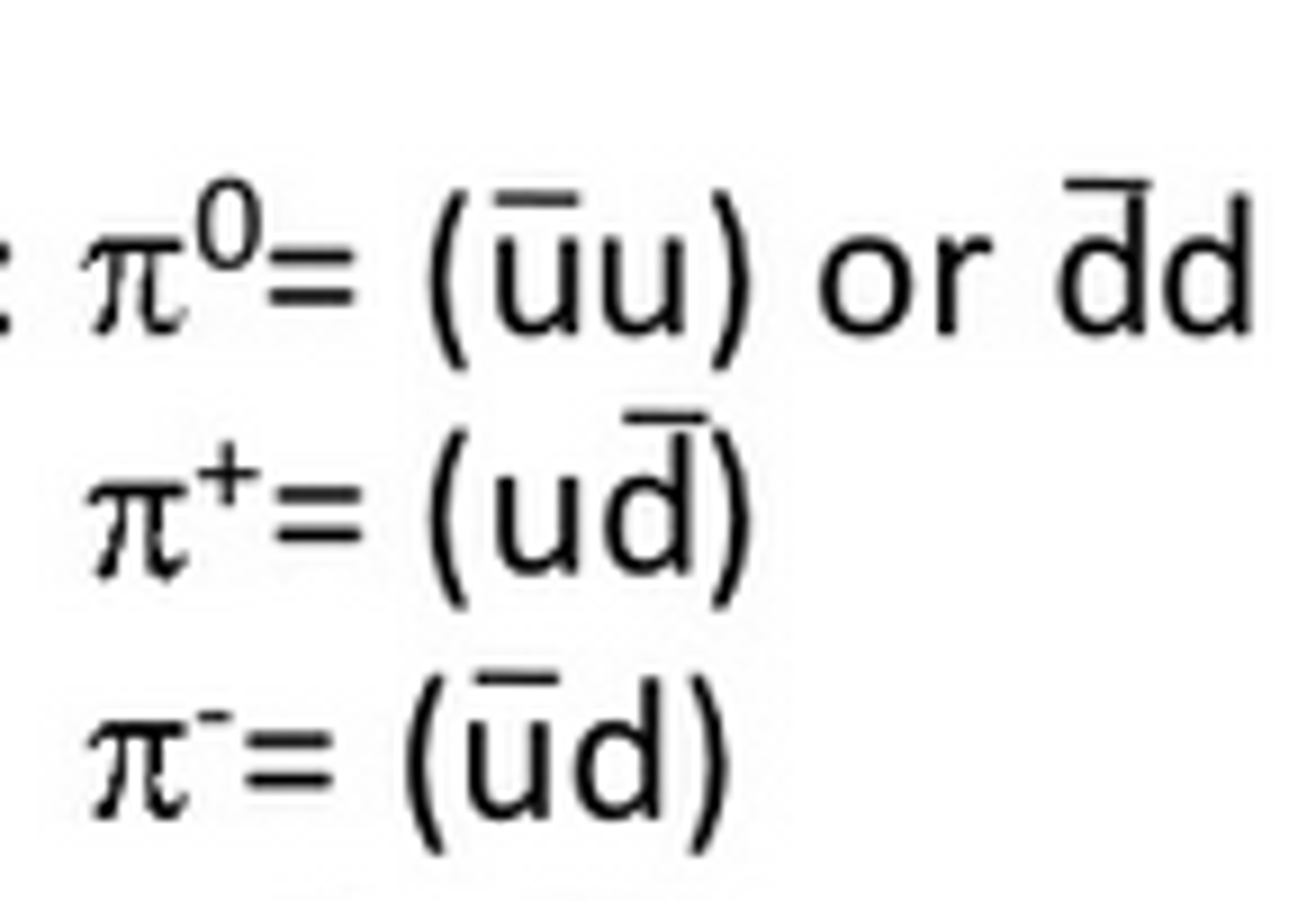
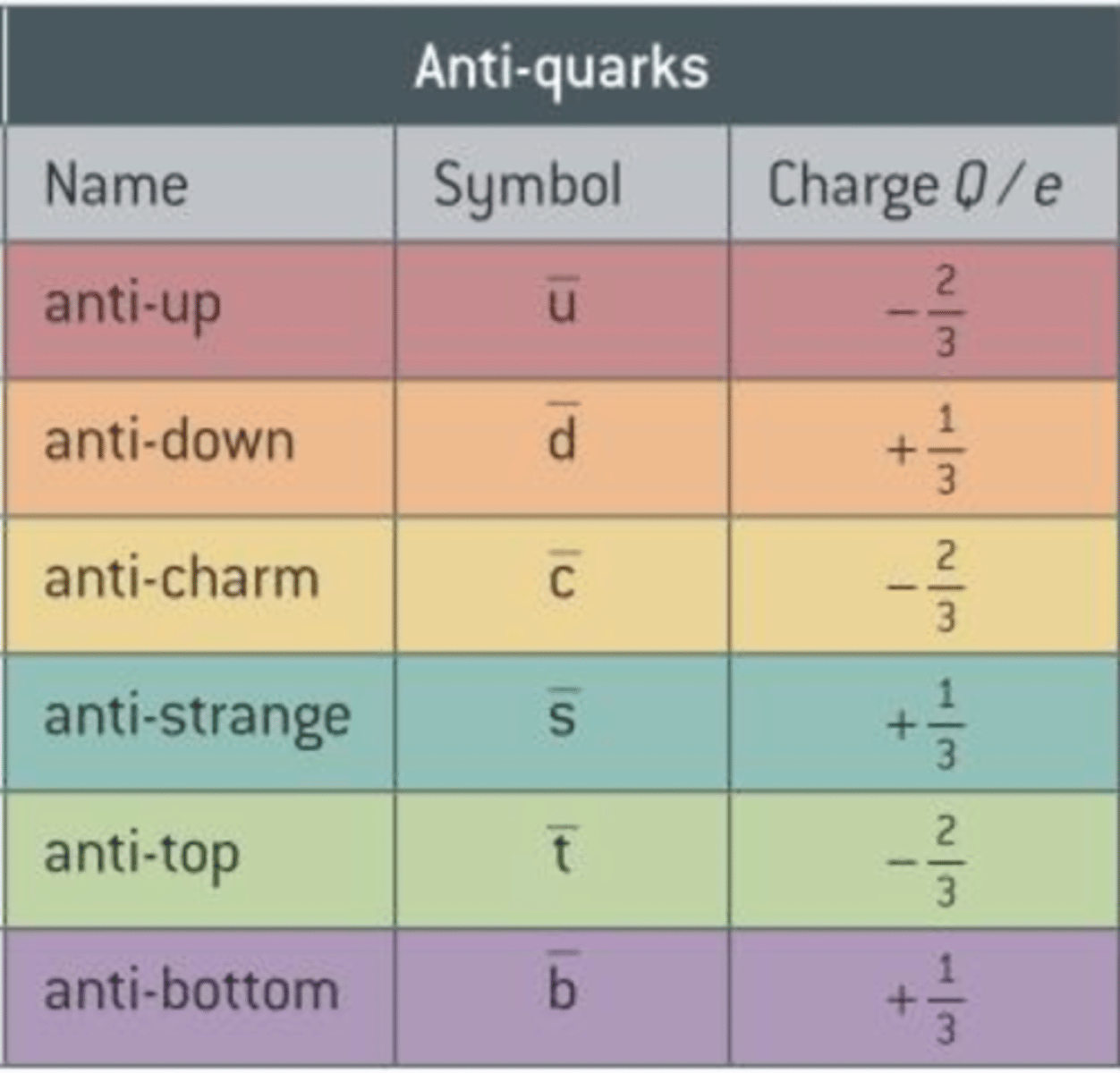
Anti-Quarks
1 electronvolt (1 eV)
The energy transferred when an electron travels through a potential difference of 1 volt.

Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
Weak nuclear force
Responsible for beta decay.
Strong nuclear force
the attractive force that binds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus.
unified atomic mass unit (u)
a unit of mass that is exactly 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
