AS101 exam 4
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
What is a nutrient?
feed constituent that is vital and functions in the support of life
what are the 2 methods of estrus synchronization?
administer prostaglandin
"give and take" progesterone
how long after birth do sheep go into estrus?
next season
how long after birth do swine go into estrus?
3-5 day AFTER WEANING
what kind of donors are used for ET
superovulated females
how long after birth do horses go into estrus?
5-10 days
how long after birth do cattle go into estrus
60 days
True or False
the older a crop gets the thinner the cell wall gets
False, the cell wall gets thicker the older the crop gets
True or False
NPN is utilized in older animals
True
LH causes the formation of ___________
the corpus luteum
what hormone causes the corpus luteum to regress?
prostaglandin
what hormone is meant to maintain pregnancy?
progesterone
What hormone induces growth and development?
estrogen
As NDF increases intake _________
decreases
What are the 6 classes of nutrients?
carbohydrates
fats
proteins
vitamins
minerals
water
What is the function(s) of water as a nutrient?
transport of nutrients
temp regulation
lubrication
metabolism
What is the most important nutrients?
water
What is the "Rule of Thumb" calculation water consumption in unstressed animals?
1 gallon per 100 lbs live weight
What is the primary function(s) of Carbohydrates?
supply energy - to body cells
Type of carbohydrates
Simple Sugars (glucose)
Starch
Cellulose
Who primarily uses Cellulose?
the Ruminant
What nutrient is required but can be toxic in large amounts?
a. Minerals
b. Vitamins
c. Fats and Lipids
d. Carbohydrates
a. Minerals
What is the function(s) of Fats and Lipids?
dietary energy supply
insulation
protection
carrier of fat-soluble vitamins
source of essential fatty acids
How much more energy does fat have than carbohydrates?
2.25 x more energy
What percent Nitrogen = 100% protein?
~16%
How to calculate crude proteins?
% N x 6.25 = %CP
What are proteins made of?
amino acids
What is the difference between essential and non-essential amino acids?
essential AA: cannot be synthesized must be supplied in diet
non-essential AA: can be synthesized
What is the function(s) of proteins?
growth of muscle/connective tissue
Metabolism
Energy source (last resort)
Protein requirements ________ as age _________
Decreases, Increases
What are the 2 classes of vitamins?
fat soluble and water soluble
All vitamins should be supplied in the diet of __________
non-ruminants
What is the function(s) of vitamins?
regulate metabolism
Minerals are what type of compounds?
inorganic
List the macro-minerals
Ca, P, Mg, Na, Cl, K, S
List the micro-minerals
Fe, Cu, Se, Zn
Marco minerals are needed in _________ amounts
large
Micro minerals are needed in _______ amounts
trace or small
What is the function(s) of minerals?
-Skeletal function
-Maintenance
-Oxygen transport
-Regulation of Acid/Base balance and enzyme system
What is digestion?
preparation of food for absorption
mechanically
chemically
enzymatically
microbially
What is absorption?
Taking digested food into the blood stream
What is metabolism?
sum of all physical and chemical proccesses in the body
What is a simple stomach?
Monogastric
Who are simple stomachs?
humans,
swine,
poultry,
dogs,
cats
Who are monogastric with a functional cecum?
horses
elephants
rabbits
What kind of stomachs do ruminants have?
Polygastric
how many compartments in the stomach do ruminants have?
4
Who are polygastric/ruminants?
cattle
sheep
goats
deer
What are the basic components of the digestive system? (5)
mouth
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
Funtion of Esophagus
movement of food
Function of stomach
1. storage
2. physical breakdown of food
3. chemical digestion
Function of small intestine
digestion and absorption
Function of large intestine
1. water resorption
2. storage
3. microbial fermentation
What are the 4 chambers of a polygastric stomach?
Rumen
Abomasum
Omasum
Reticulum
What's the gizzard for?
grinds feed
What is the cecum?
site of microbial fermentation in horse
produces VFAs and microbial protein
synthesis of B vitamins by the microbes
What does VFA stand for?
volatile fatty acids
How large is the rumens capacity in cattle?
~50 gallons
What does the rumen chamber of the stomach do?
1. storage
2. physical mixing
3. fermentation chamber
what does the reticulum do?
traps foreign objects
regurgitation (cud chewing)
What does the omasum do?
water absorption
What does the abomasum do?
true stomach
chemical digestion
what is the very first step in any feed analysis?
Representative sample needed
What does DM stand for and what does it measure?
Dry Matter;
measures the water content in a feedstuff
What does TDN stand for and what does it measure?
Total Digestible Nutrients;
measures energy
What does CF stand for and what does it measure?
Crude Fiber;
measures lowly digestible nutrients
What does NDF stand for in regards to cattle feeding protocols?
Neutral-Detergents Fibers
What does ADF stand for and what does it measure?
Acid Detergent Fibers;
measure of insoluble residue
What is ADF used for?
used as an indicator of forage digestibility
Whats it mean if you have a THIN cell wall in terms of ADF and NDF?
Low NDF (=high intake)
Low ADF (=high energy)
Whats it mean if you have a THICK cell wall in terms of ADF and NDF?
High NDF (=low intake)
High ADF (=low energy)
what has a thicker cell wall?
early harvested forage or late harvested forage?
late harvested forage
What does CP stand for and what does it measure?
Crude Protein;
measures amino acids / nitrogenous compounds
how to measure CP?
CP = % nitrogen x 6.25
What does NPN stand for?
Non-Protein Nitrogen
define Relative Feed Values
A prediction of feeding value that combines estimated intake (NDF) and estimated digestibility (ADF) into a single index.
-RFV is used to evaluate legume hay.
-RFV is often used as a benchmark of quality when buying or selling alfalfa hay.
-RFV is not used for ration formulation.
When converting DM to as-fed what does it mean in terms of weight and nutrient concentration
nutrient concentration will decrease
weight will increase
When converting as-fed to DM what does it mean in terms of weight and nutrient concentration
nutrient concentration will increase
weight will decrease
what is the As-Fed to DM math
multiply by DM% --> smaller number
what is the DM to As-Fed math
divide by DM% --> larger number
describe dry forages and roughages
low energy
>18% CF
>25% DM
describe fresh forages
high moisture
high CF
describe silage
whole plants
30-60% DM
describe feed concentrates
energy feed
< 18% CF
< 20% CP
describe protein supplements
> 20% CP
plant or animal sources
ex: urea (281% CP)
Feed value increases as crude fiber ___ and crude protein ___.
decrease
increases
what do you need to consider when feeding livestock?
-species
-weight
-stage of production (lactation, prego, growing)
-expected performance level
-availability of feed stuff
-cost
define diet and ration
Diet = feed, including water, consumed
Ration = amt of feed consumed in 24 hrs
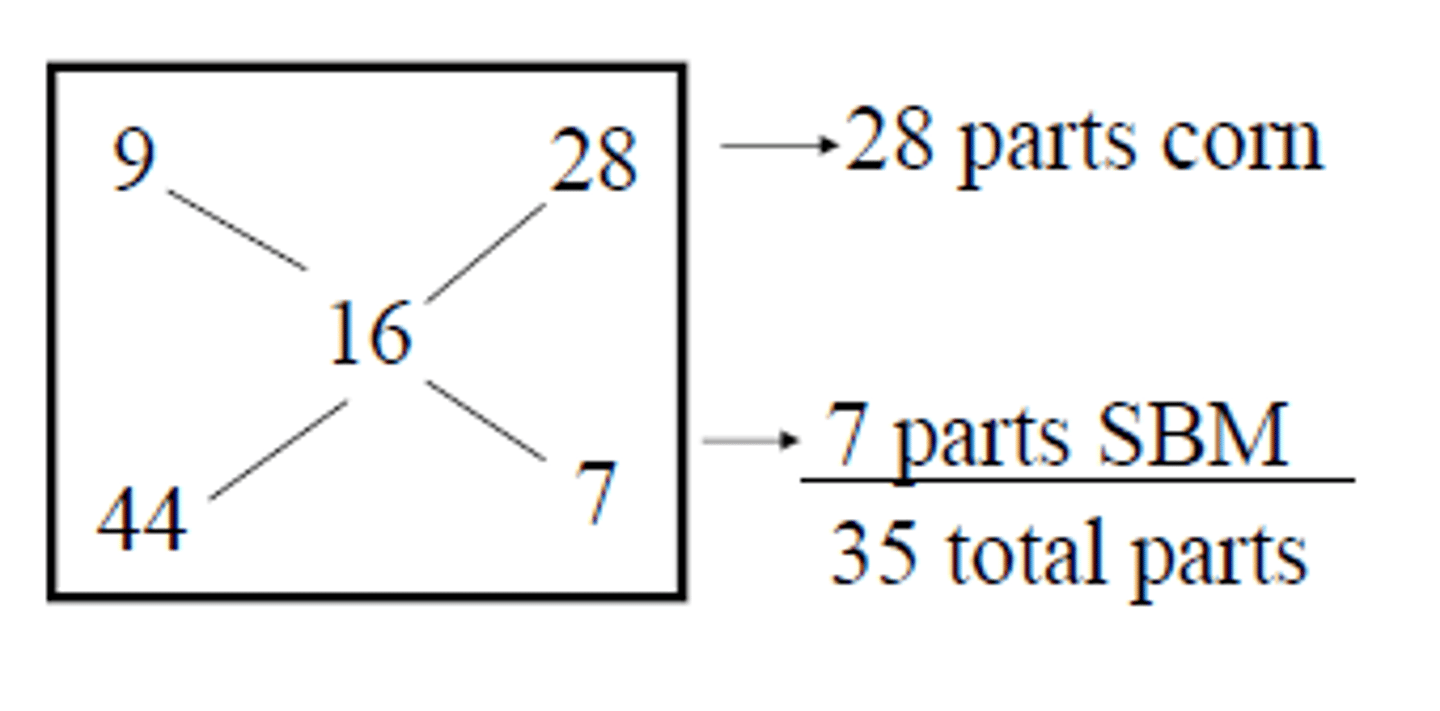
study pearsons square
what's the body condition scale for cattle
1-9
1=malnutritioned
5=moderate
9=obese
What is the male's 3 main roles in reproduction?
1. produce ample quantities of semen
2. find the receptive female
3. ability to mount and serve
in general as semen volume ____ the sperm concentration ____
increases
decreases
What does the epididymis do?
storage and maturation of sperm
What does the scrotum do?
provides support for the testicles
temperature regulation for sperm viability
What do the vas deferens do?
transports sperm to urethra
What does the urethra do?
transports urine out of body
What do the accessory glands do?
adds fluid and nutrients to sperm
who has the greatest volume of sperm
a. Bull
b. Ram
c. Stallion
d. Boar
d. Boar
what are the roles of a female in reproduction? (6)
develop and release the egg
mate (estrus/ standing heat)
conceive, develop, carry, and nurture baby
give birth
produce milk for baby
rebreed
What do the ovaries do?
produce eggs (ova)