A&P1 Finals Review
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Histology
The study of tissues
Cephalic
Pertaining to the head
Gluteal
Pertaining to the buttocks
Patellar
Kneecap
Thoracic
Pertaining to the chest
Brachial
Pertaining to the arm
Thoracic Cavity
Cavity housing lungs and heart
Cranial Cavity
Cavity housing the brain
Abdominal Cavity
Cavity that houses the stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
Vertebral Cavity
Cavity housing the spinal cord
Cation
A positively charged ion
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking
Phagocytosis
Cell eating
Collagen
Tissue fiber that gives connective tissue great tensile strength
Osteoblast
What is the primary blast cell for bone?
Serous
Type of membrane that lines the CLOSED ventral cavities of the body
Serous
The abdominal cavity is lined by _____ membrane
Mucous
Type of membrane that lines the body cavities OPEN to the exterior membrane
Mucous
Type of membrane that also lines the digestive and respiratory tracts
Mucous
The nasal cavity is lined by the ______ membrane
Endothelium
Type of membrane that lines the blood vessels and the heart
Cutaneous
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Jaundice
Skin condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin due to a buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream
Liver
Jaundice is often a sign of _ complications
Cyanosis
Skin condition characterized by the bluish or purplish discoloration of the skin
Oxygen
Cyanosis is often a sign of low ______ levels
Erythema
Skin condition characterized by the redness of the skin
Pallor
Skin condition characterized by the unusual paleness of the skin
Anemia
Pallor is often a sign of
Skin Cancer
Overexposure to UV radiation is the biggest risk factor for
Melanoma
What is the most dangerous skin cancer which is highly metastatic?
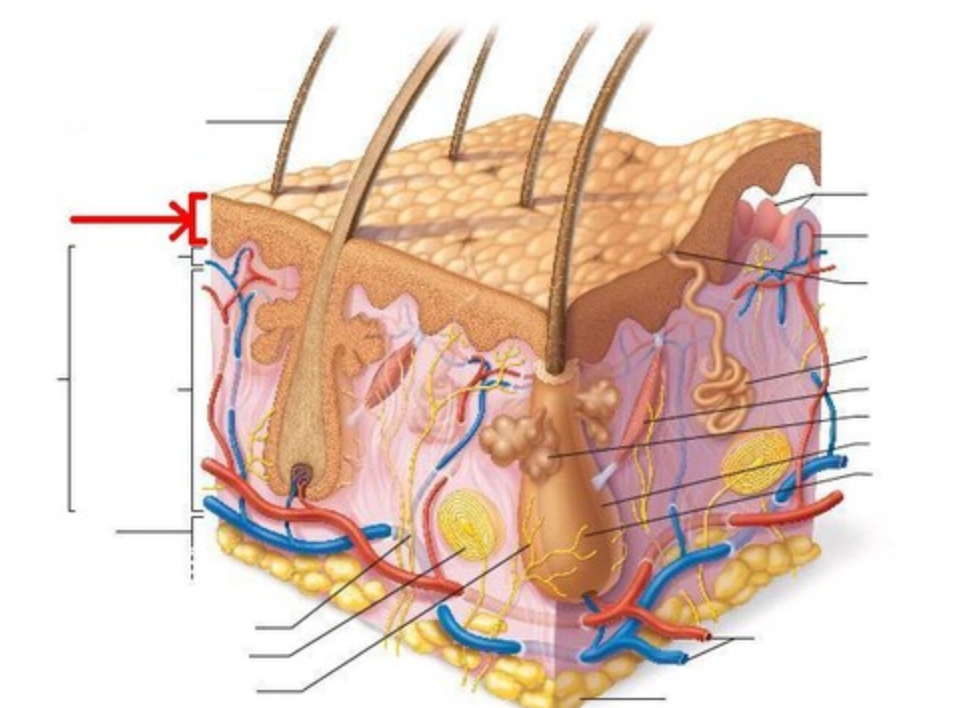
Epidermis
Which layer of the dermis is this?
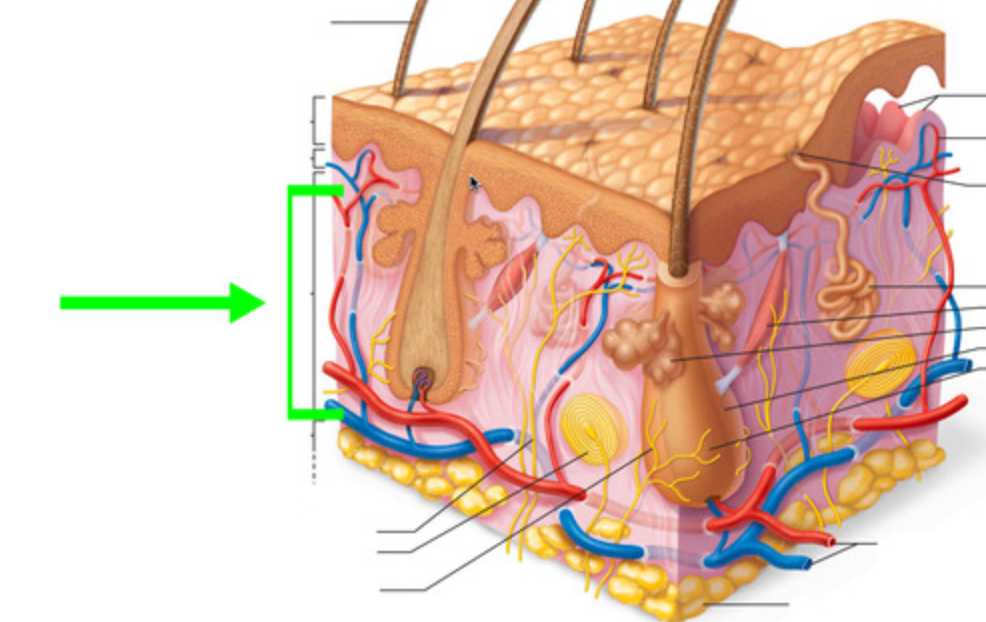
Reticular
Which layer of the dermis is this?
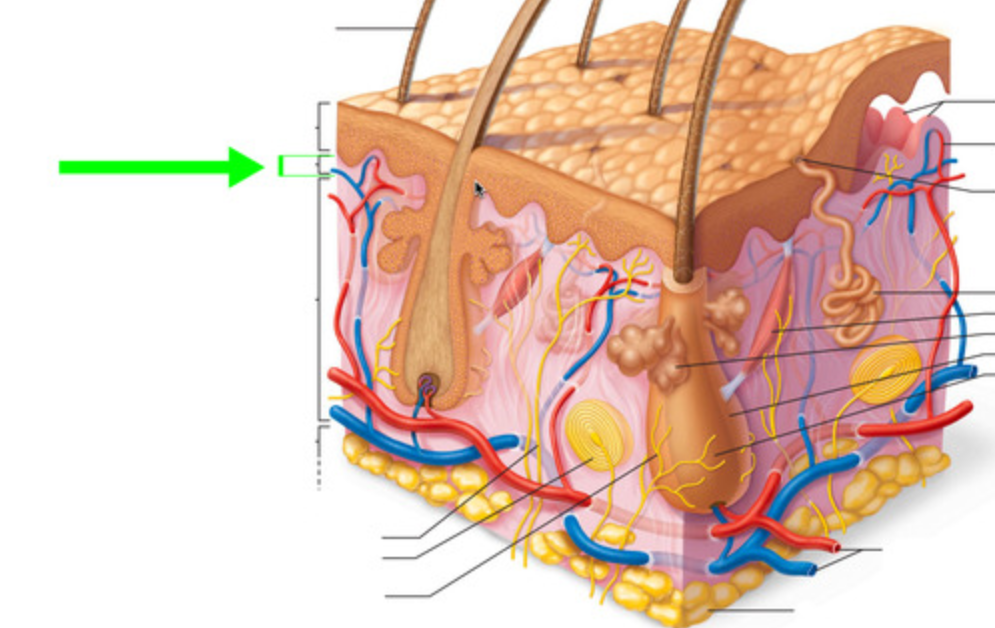
Papillary
Which layer of the dermis is this?
Compact
Type of bone tissue that can support weight and withstand torsion stress
Adipocytes
What does yellow bone marrow contain?
Fat Cells
What are adipocytes?
Foramen
Round or oval opening through a bone
Epiphysis
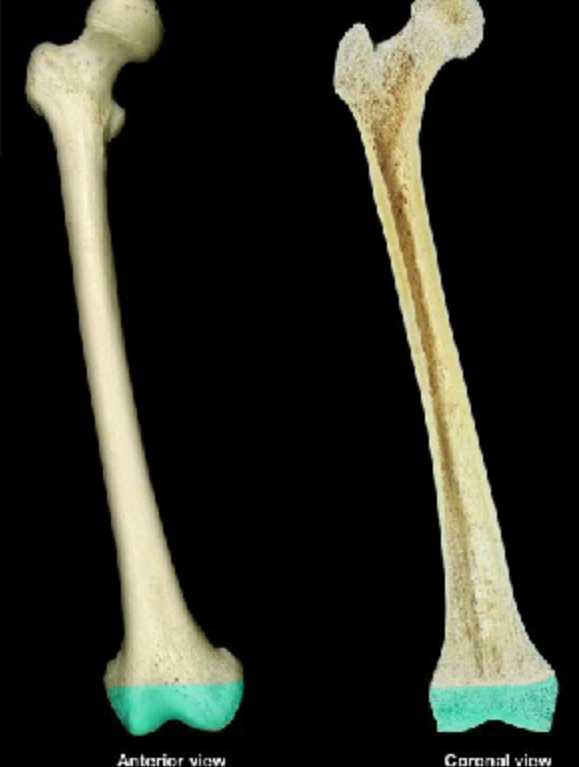
End of a long bone
Epiphysis
What is this bone structure?
Diaphysis
What is this bone structure?
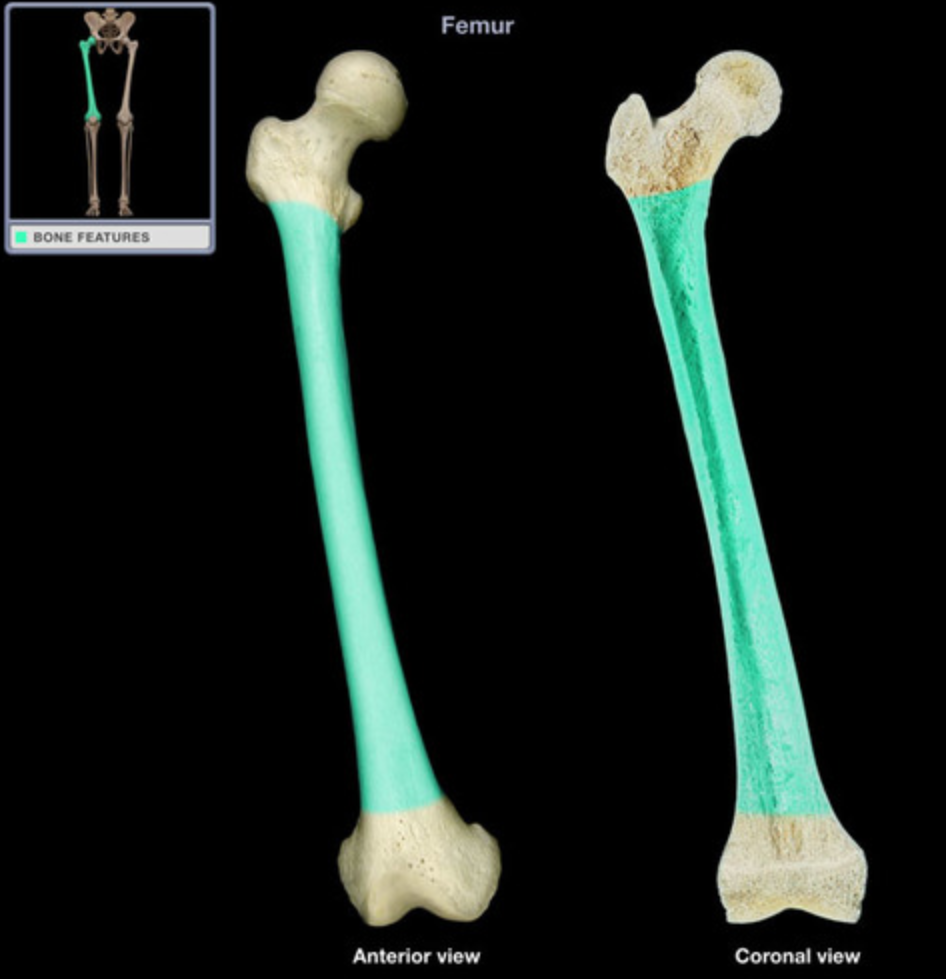
Compact Bone
What is this bone structure?

Compact Bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
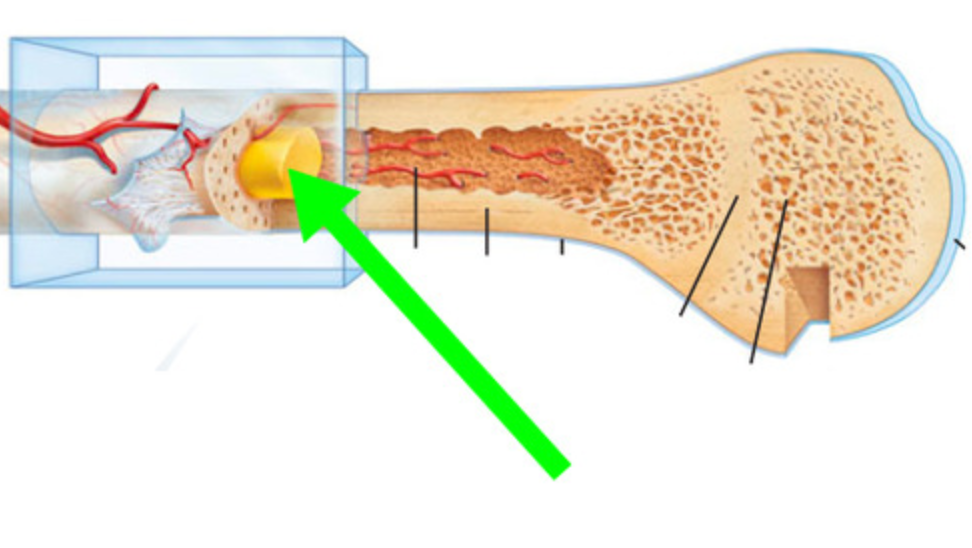
Yellow Bone Marrow
What is this bone structure?
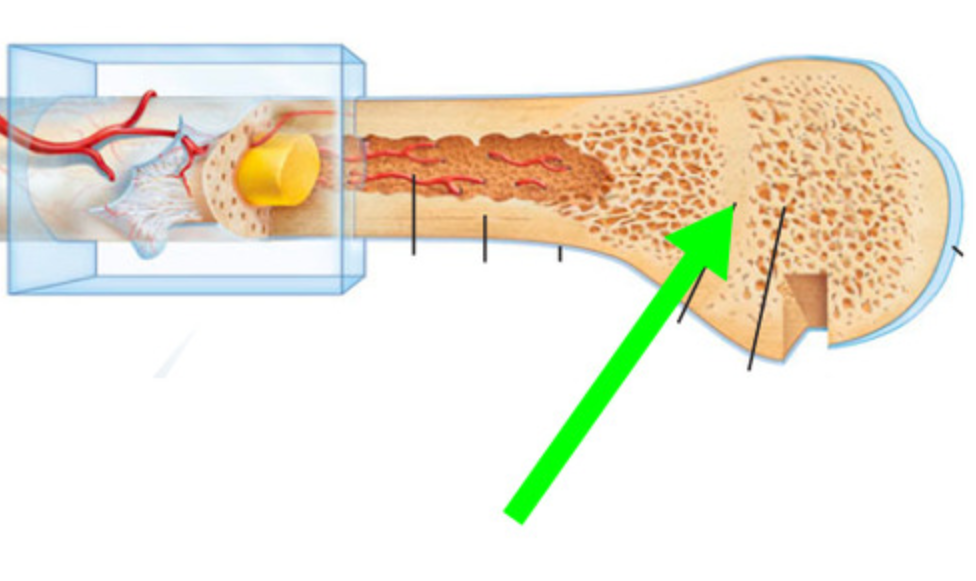
Epiphyseal Line
What is this bone structure?
Compact Bone
Type of bone structure that provide strength and structural support to the body, acting as a rigid foundation for muscles and protecting internal organs
Yellow Bone Marrow
Bone structure that stores fat and stem cells, which can produce fat, cartilage, or bone cells
Epiphyseal Line
Bone structure that facilitates the longitudinal growth of long bones during childhood and adolescence
Epiphyseal Line
Growth plate
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
Flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
Circumduction
Circular movement of a limb at the distal end
Hyperextension
The extreme or overextension of a limb or body part beyond its normal limit
Plantar Flexion
Bends the foot downward at the ankle
Muscle
Most distinguished type of tissue that can transform chemical energy into mechanical energy to move the body
Creatine Phosphate
An energy storage molecule used by muscle tissue. The phosphate from ______ ______ can be removed and attached to an ADP to generate ATP quickly.
Muscle Contraction
What is cross bridging also known as?
Cross Bridges
Myosin ______ ______ and attaches to actin for muscle contraction
Myosin
______ cross bridges and attaches to actin for muscle contraction
Actin
Myosin cross bridges and attaches to ______ for muscle contraction
Muscle Contraction
Myosin cross bridges and attaches to actin
Rigor Mortis
The stiffening of the body after death
Lactic Acid
Chemical produced as a byproduct of cellular metabolism, especially during intense exercise or when there's a low oxygen supply
Lactic Acid
What does pyruvic acid get converted into?
Insertion
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a moveable bone
Origin
The attachment of a muscle to the proximal end of a bone and does not move during contraction
Fascicle
Bundle of muscle fibers
Sarcomere
What is the smallest contractile unit of a muscle fiber?
Epimysium
CT sheath that surrounds the entire muscle
Perimysium
CT sheath that surrounds each fascicle
Endomysium
CT sheath that surrounds each muscle fiber
Corpus Callosum
A broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain.
Broca's Area
Area of the brain responsible for speech
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Central
The ______ nervous system contains the brain and spinal cord
Sympathetic Division
A branch of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to deal with perceived threats.
Parasympathetic Division
A branch of the autonomic nervous system that maintains normal body functions; it calms the body to conserves energy.
Hypothalamus
A neural structure that directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Alkaloids
What molecule is bitter taste elicited by?
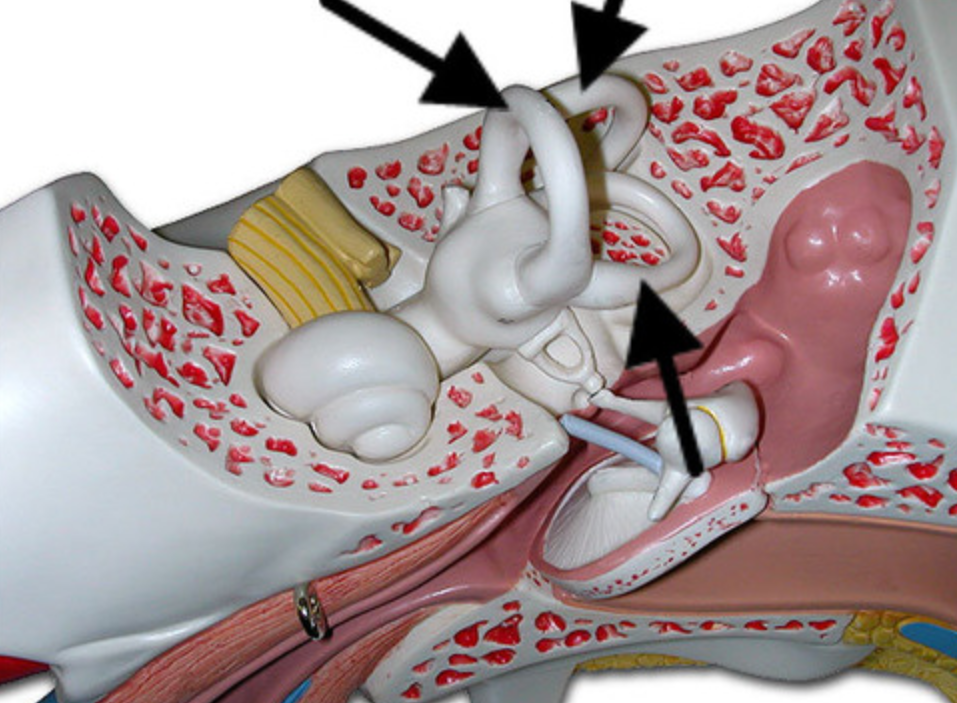
Cochlea
Where are the hearing receptors located in?
Olfactory Receptor Cells
Neurons responsible for smell and are replaced throughout adult life
Auricle
External portion of the ear
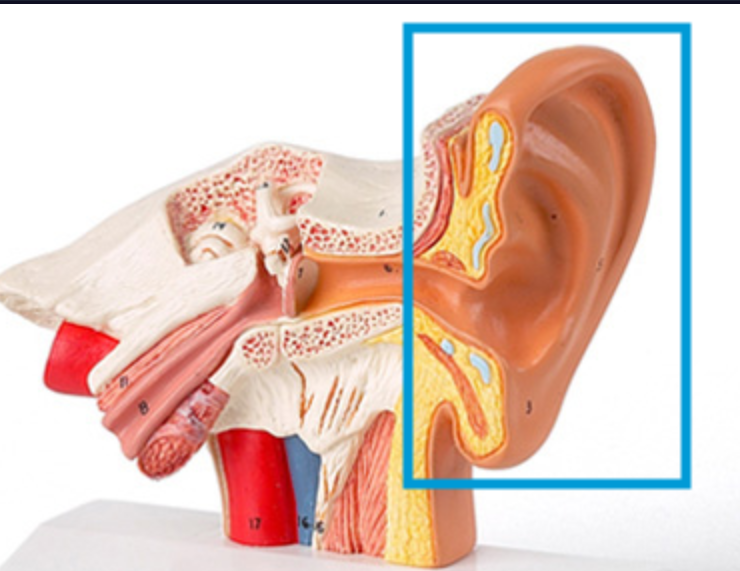
Tympanic Membrane
The eardrum
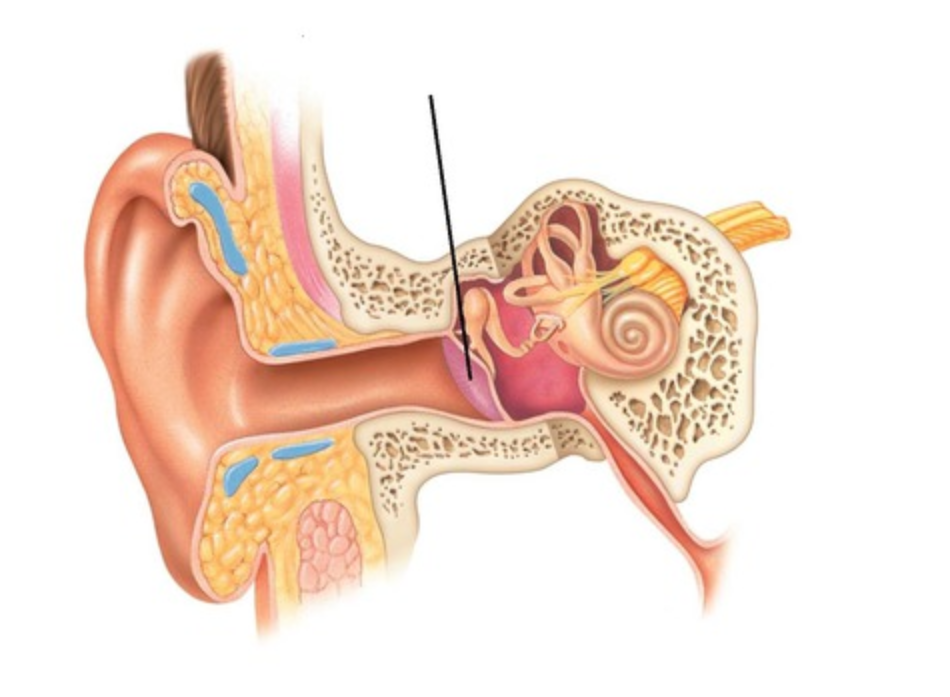
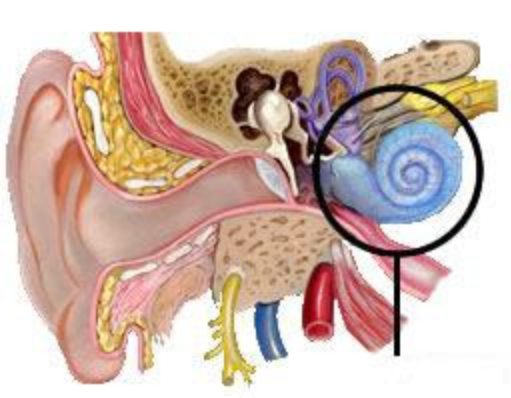
Cochlea
A coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
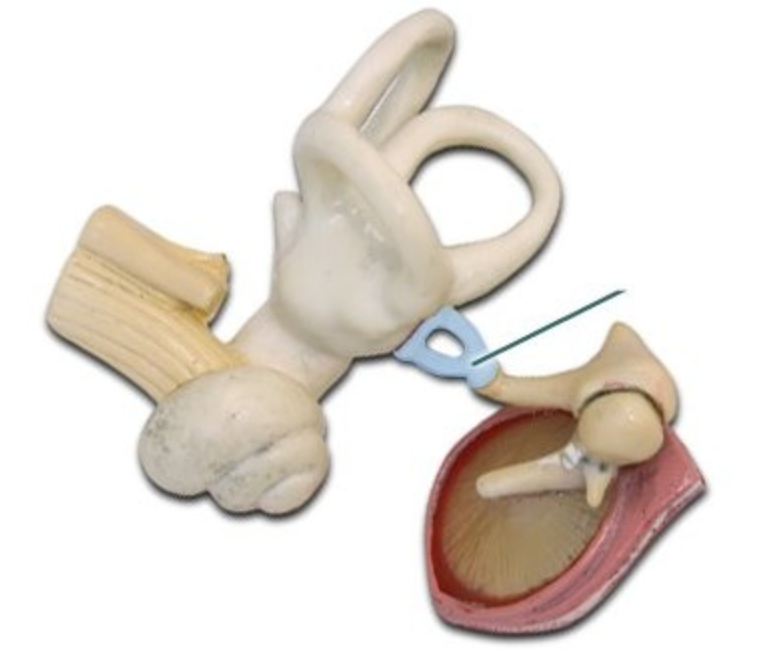
Stapes
Stirrup
Semicircular Canals
Three canals within the inner ear that contain specialized receptor cells that generate nerve impulses with body movement
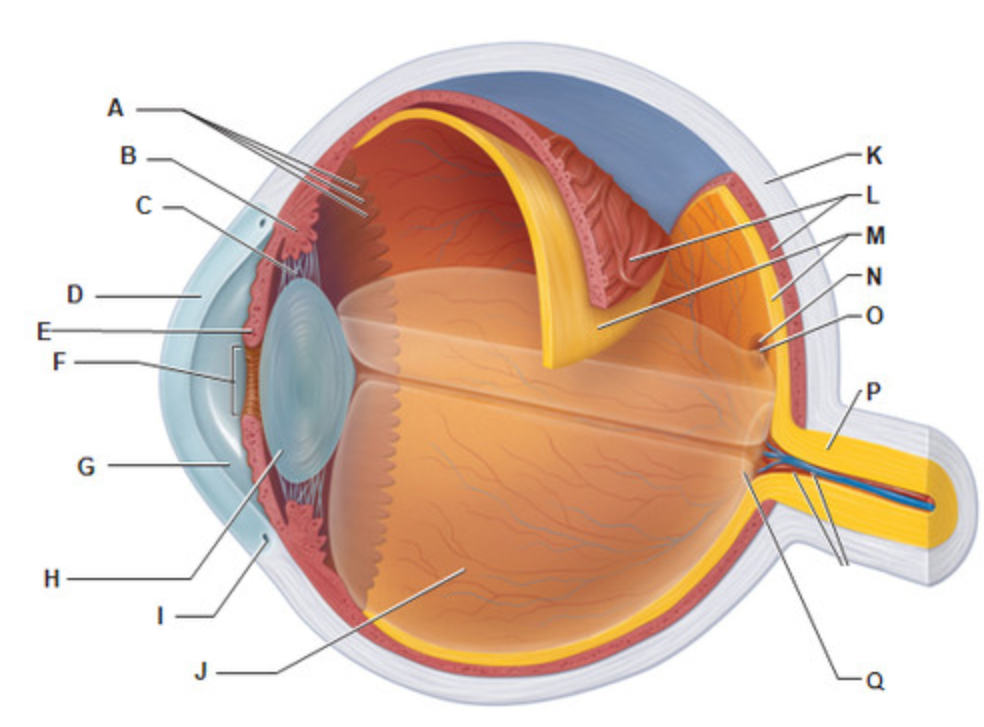
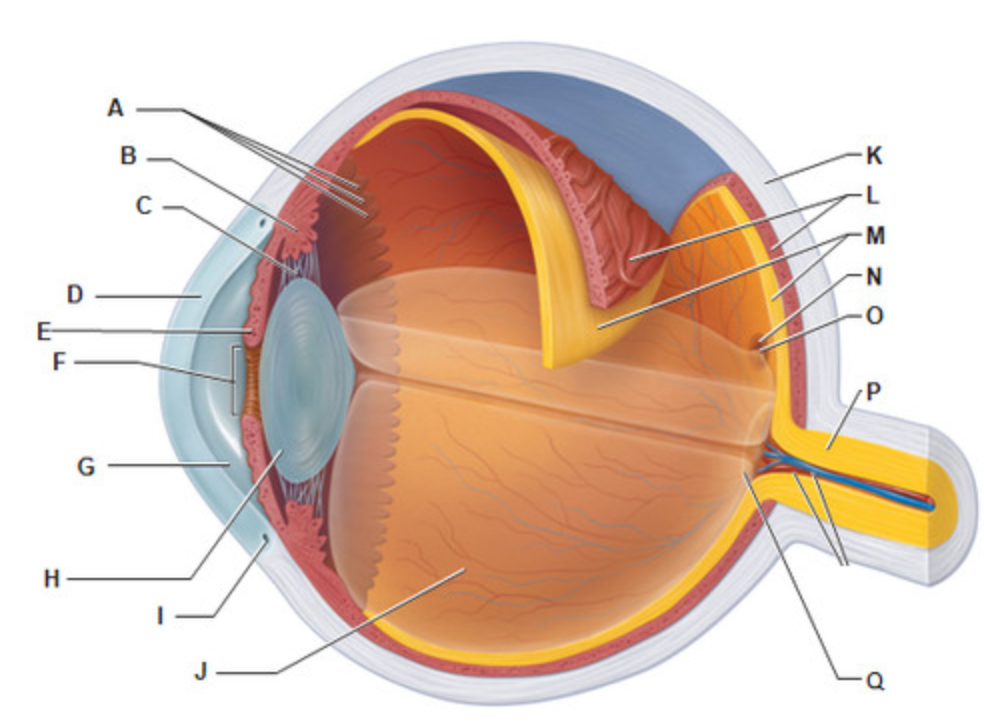
Sclera
What is letter K?
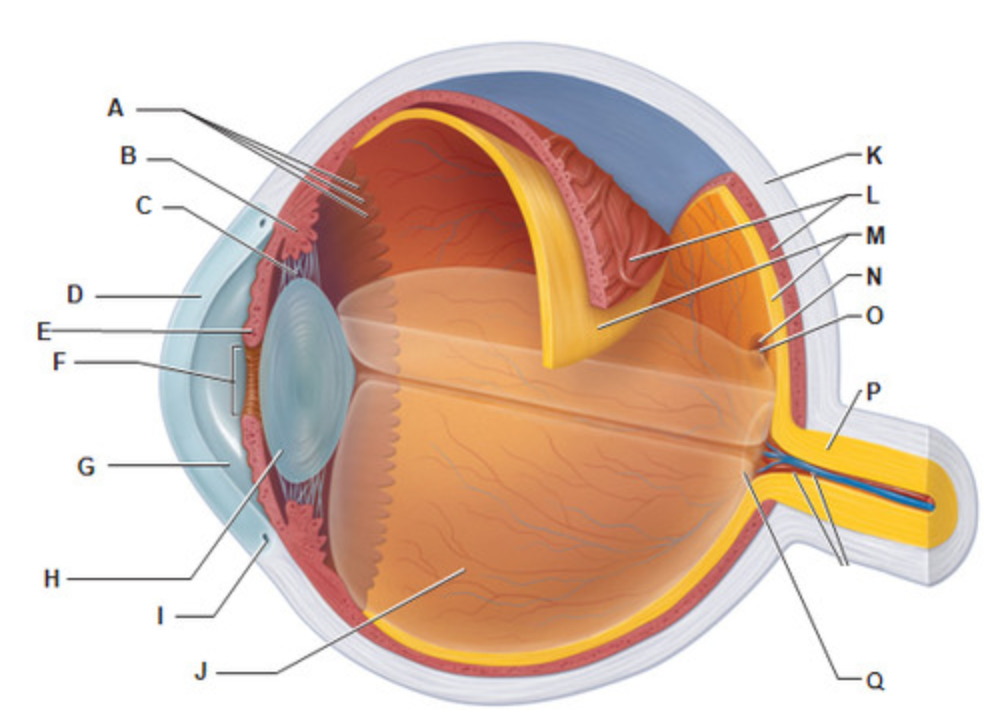
Sclera
Which structure of the eye is considered the "whites" of the eye?
Fovea Centralis
What is letter O?
Fovea Centralis
Which structure of the eye contains only CONES?
Optic Disc
What is letter Q?
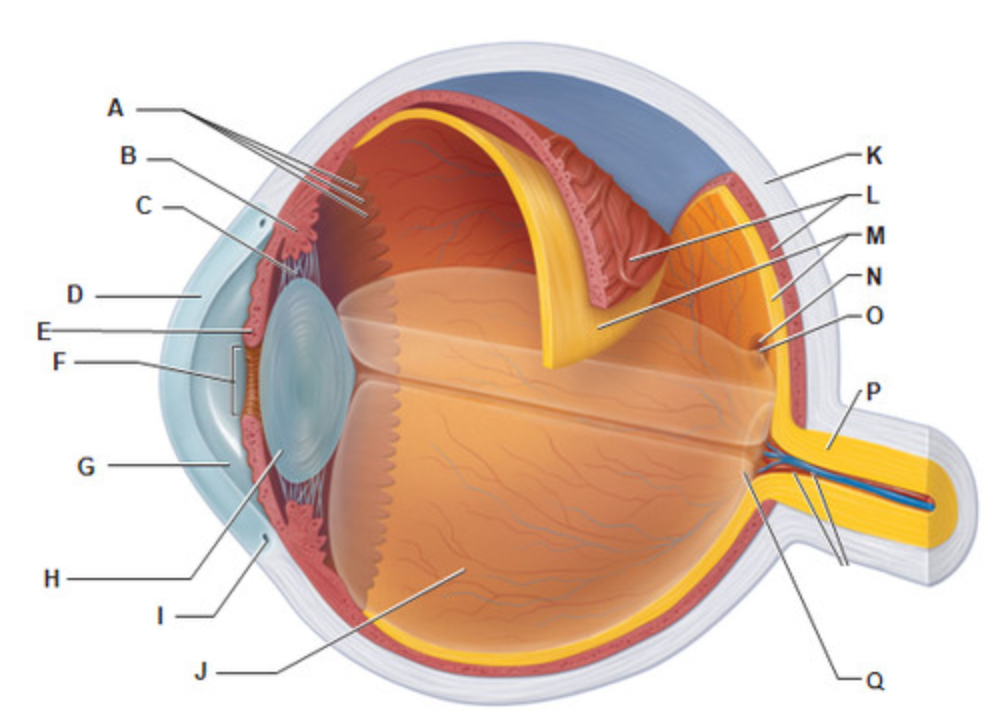
Optic Disc
Which structure of the eye is considered the "blind spot"?
Iris
What is letter E?
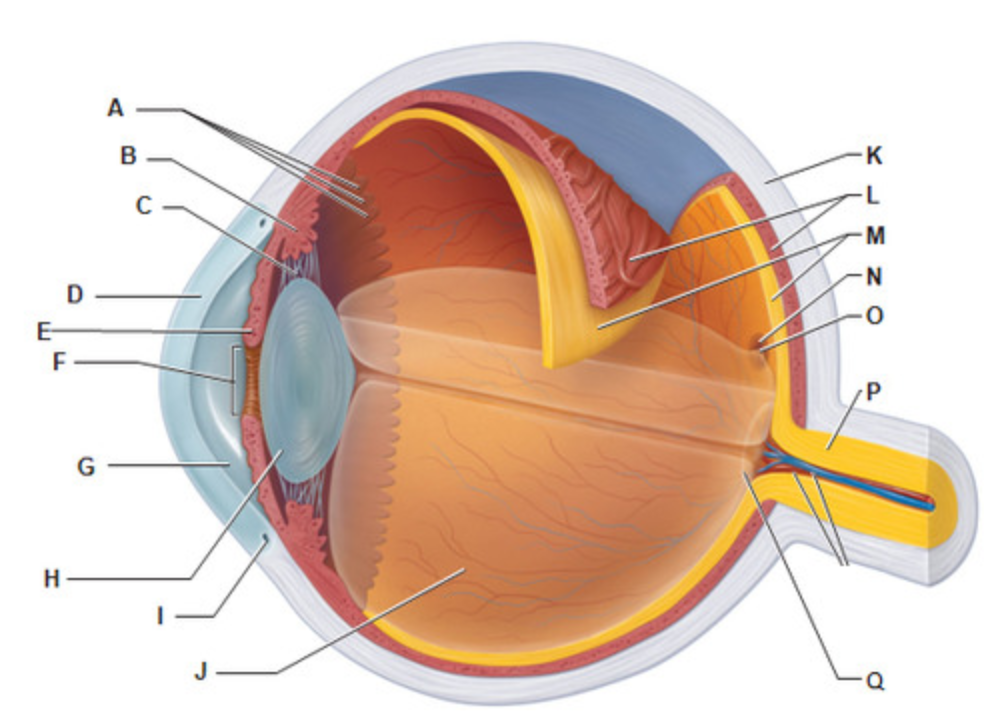
Iris
Which structure of the eye is considered the "colored" parts of the eye?
Cornea
What is letter D?
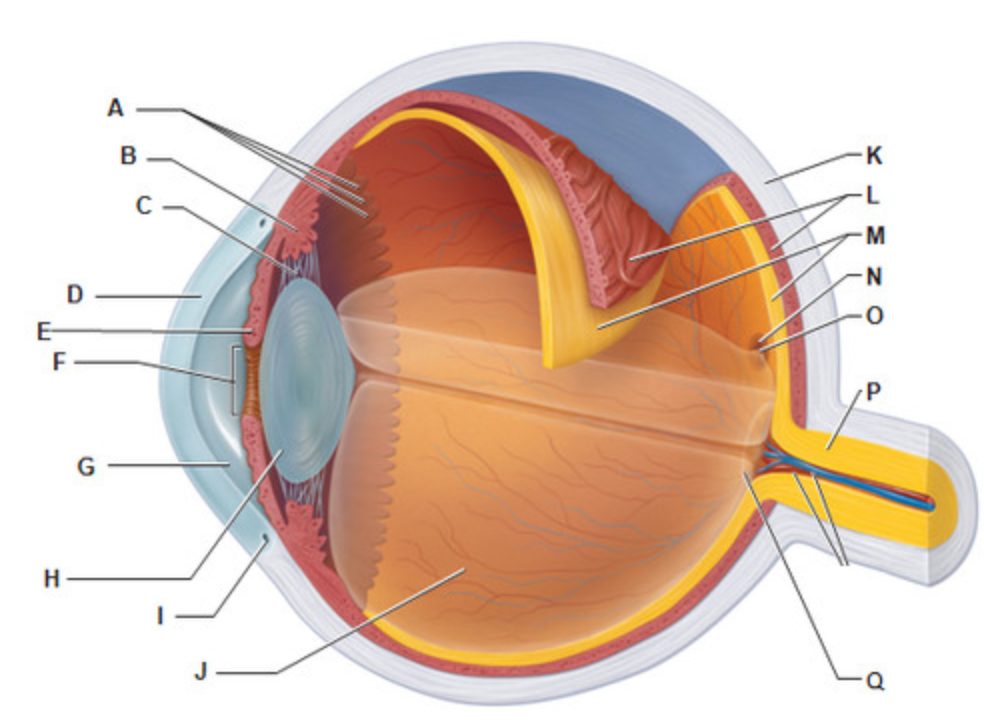
Cornea
What is the only tissue that can be transplanted without rejection?
Ciliary Body
What is letter B?
Ciliary Body
Which structure of the eye controls the lens shape?
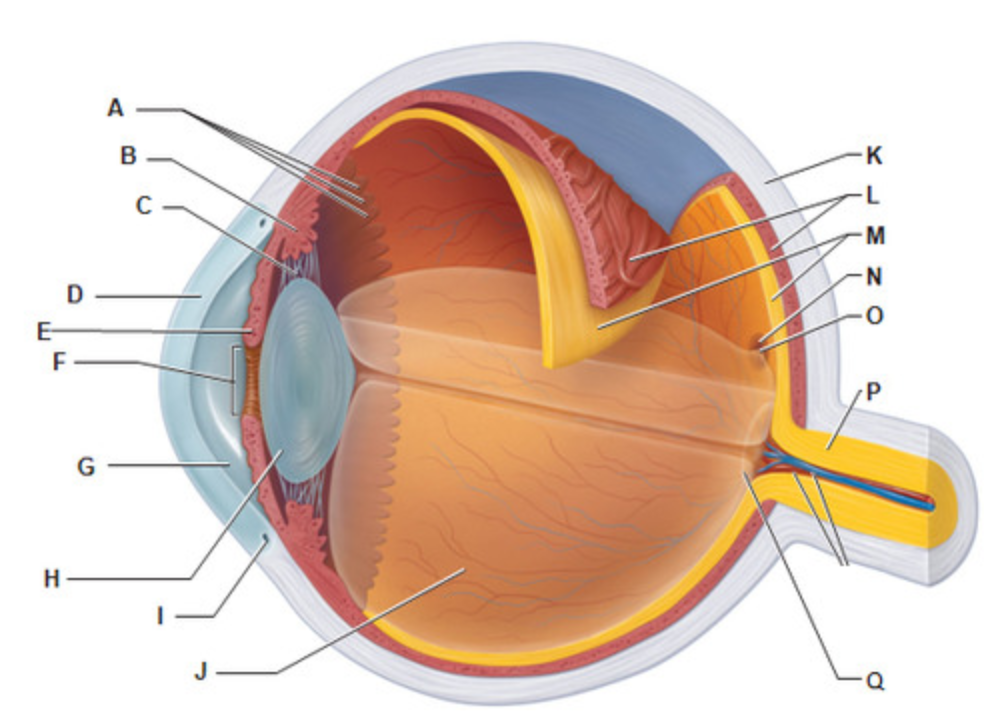
Posterior Segment
What is letter J?