Final exam 1 Biology CH 1,2,3, and 5
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
what is science?
a process of gaining knowledge through evidence and logic
which of the following is an example of a scientific law?
Medel’s law of inheritance
scientific theory
a broad explanation supported by extensive evidence
first step in the scientific method
making an observation
in an experiment, the variable that is measured is called the
dependent variable
a control group is an experiment is important because it
used for comparison to the experimental group
which of the following is a limitation of science?
it cannot answer questions about supernatural events
replication is science refers to
repeating an investigation to verify results
which of the following is NOT a characteristic of all living things?
ability to photosynthesize
homeostasis refers to
maintaining a stable internal environment
the basic unit of life is the
cell
which level of biological organization includes all living and non-living components in an area?
ecosystem
binomial nomenclature gives each species
a unique two word Latin name
the most inclusive taxonomic rank is
domain
which domain contains organisms with a nucleus?
Eukarya
humans are classified in the kingdom
animalia
the four most common elements in the human body are
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
an atom that has gained or lost electrons is called
an ion
a covalent bond involves
sharing of electrons
water is a polar molecule because
oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen
which property of water allows it to resist temp changes?
high heat capacity
a pH of 4 is considered
acidic
buffers are important because they
prevent changes is pH
the monomer of a carbohydrate is
monosaccharide
cellulose is a polysaccharide that
provides structural support in plants
a saturated fatty acid
has no double bonds
phospholipids are important because they
form cell membranes
the primary structure of a protein refers to
the sequence of amino acids
denaturation of protein results from
extreme heat or pH
which nucleic acid is single stranded
RNA
ATP stores energy in
the bonds between phosphates
enzymes function by
lowering activation energy
the cell theory states that
all living things are made if cells
cell remain small because
their surface area to volume ratio limits size
which organelle is the site of protein synthesis?
ribosome
The plasma membrane is composed mainly of:
phospholipids and proteins
facilitated diffusion
uses protein channels
in a hypertension solution, a red blood cell will
shrink
active transport requires
ATP
which organelle is responsible for cellular respiration?
mitochondrion
the endomembrane system includes all EXCEPT
mitochondria
cilia and flagella are composed of
Microtubules
tight junctions function to
create a barrier between cells
glycolysis occurs in the
cytoplasm
the electron transport chain is located in the
inner mitochondrial membrane
fermentation occurs when
oxygen is absent
The ATP-ADP cycle involves
adding/removing phosphate groups
phagocytosis is a type of
endocytosis
which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton?
maintaining cell shape
ribosomes can be found
attached to the ER or free in cytoplasm
in a double blind experiment
neither subjects nor researchers know who is in the treatment group
qualitative data refers to
descriptive observations
metabolism includes
both building up and breaking down molecules
which taxonomic rank is more specific than class but more general than family?
order
a dehydration synthesis reaction
joins monomers into polymers by removing water
a nucleotide consists of
sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base
the fluid mosaic model describes
the dynamic nature of the plasma membrane
which organelle modifies and packages proteins for secretion?
Golgi apparatus
explain the role of hydrogen bonds in the properties of water
hydrogen bonds give water its unique properties: cohesion, high heat capacity, and solvent ability.
water molecules are polar (oxygen is slightly negative, hydrogen slightly positive)
hydrogen bonds form between the positive H of one molecule and the negative O of another
Leads: cohesion, high heat capacity, solvent ability, ice floats
describe the processes by which the organic molecules are assembled and disassembled
assembled via dehydration synthesis; disassembled via hydrolysis
dehydration synthesis: removes a water molecule (OH from one monomer, H from another)
hydrolysis: adds a water molecule (breaks bonds) splits polymers into monomers
summarize the basic chemical properties of a carbohydrate
carbohydrates are made of C,H,O in a 1:2:1 ratio, polar and hydrophilic
functions primarily as energy sources and structural components
state the roles of carbohydrates in human physiology
energy source, energy storage, and structural roles
explanation: immediate energy, short-term storage, structural, and dietary fiber
compare the structures of simple and complex carbohydrates
simple= 1-2 sugar units; complex= long Chinas of sugars
simple carbs
monosaccharides (glucose, fructose) and disaccharides (sucrose lactose)
quick energy, easily digested
complex carbs
polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
long chains of glucose; slower to digest, provide sustained energy/structure
state the function of each class of lipids
fats/oils: long term energy storage, insulation, cushioning
phospholipids: form cell membranes (create bilayer barrier)
steroids: act as hormones (testosterones, estrogen) and stabilize membranes
waxes: protections and waterproofing
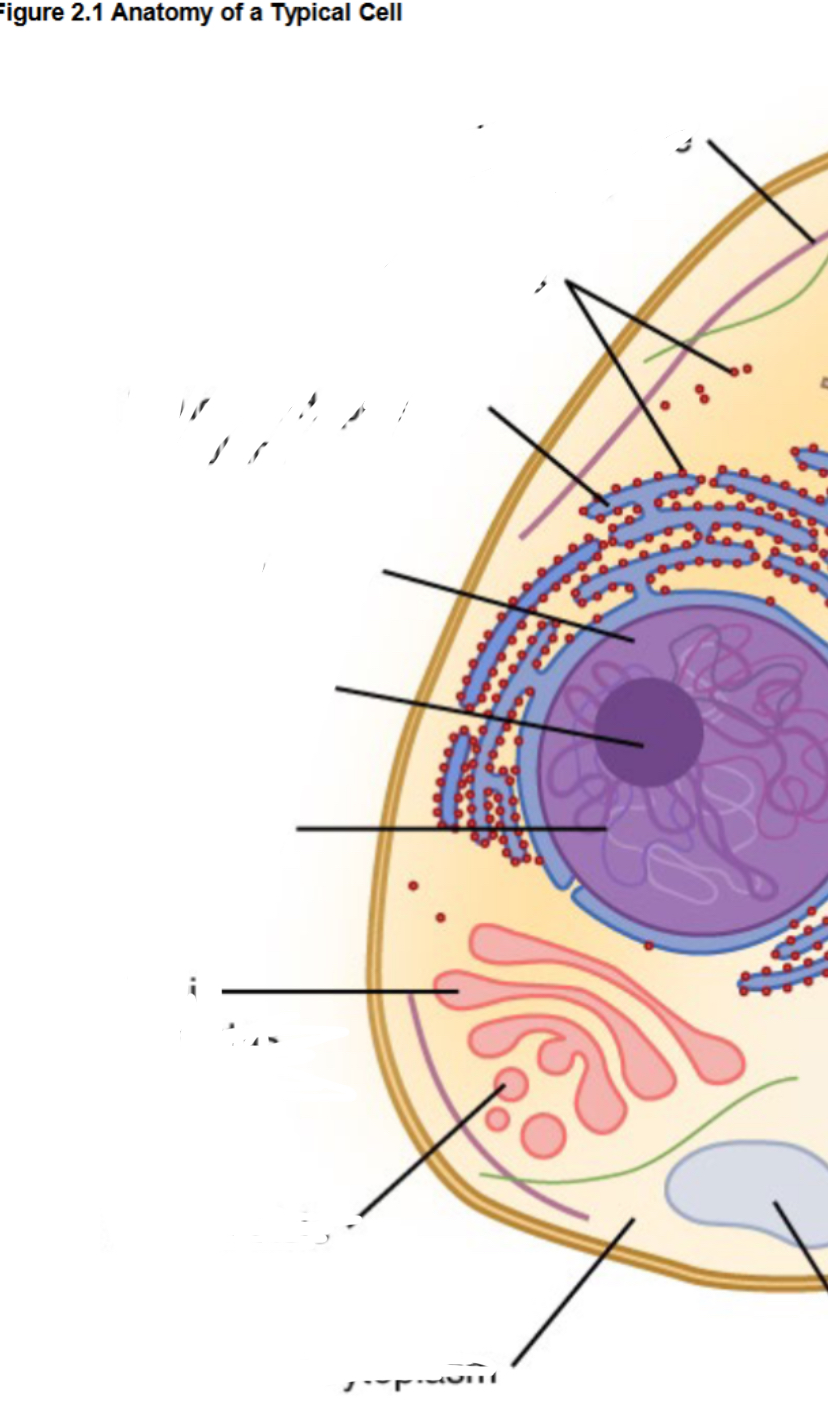
Intermediate filament
Ribosome
Rough endoplamic reticulum
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Golgi apparatus
Golgi vesicles
Cytoplasm
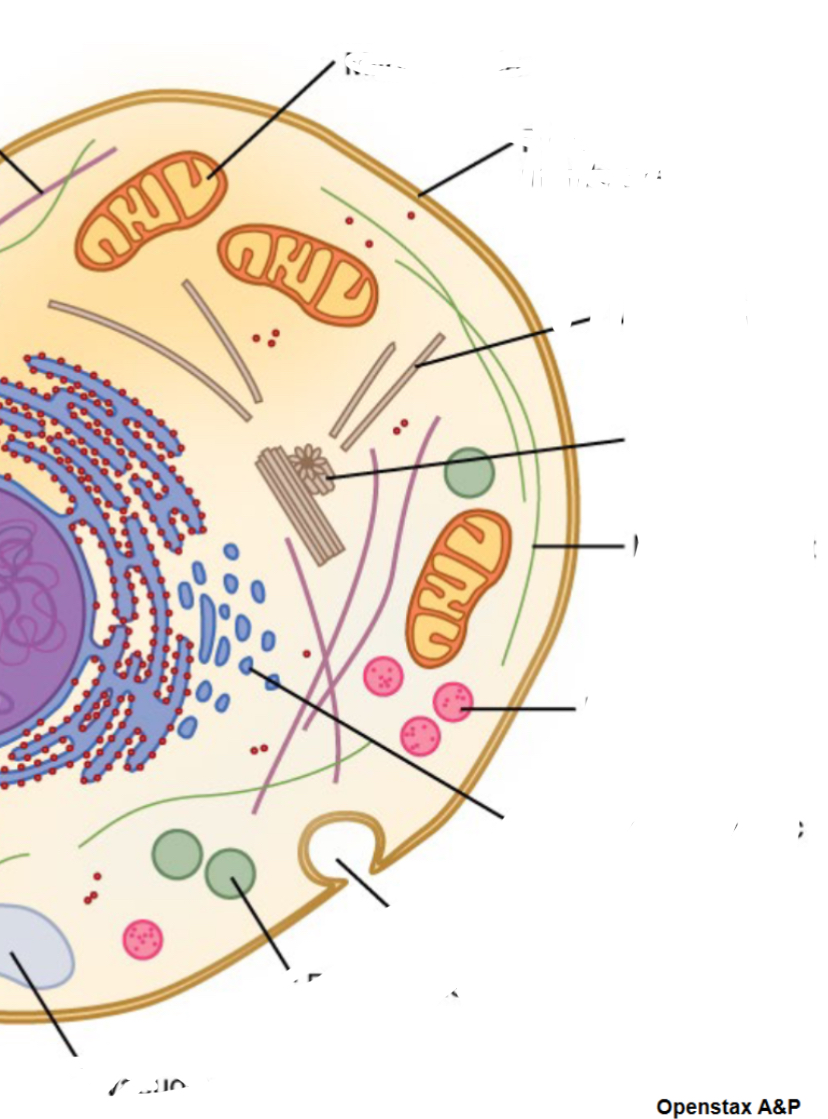
Mitochondria
Plasma membrane
Microtuble
Centrosome
Micro filament
Lysome
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Secretory vesicle
Preoxisome
Vacole
describe the structure of an amino acid
central carbon bonded to: amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and R-group
Anabolism
Building up something
Catabolism
Breaking down something
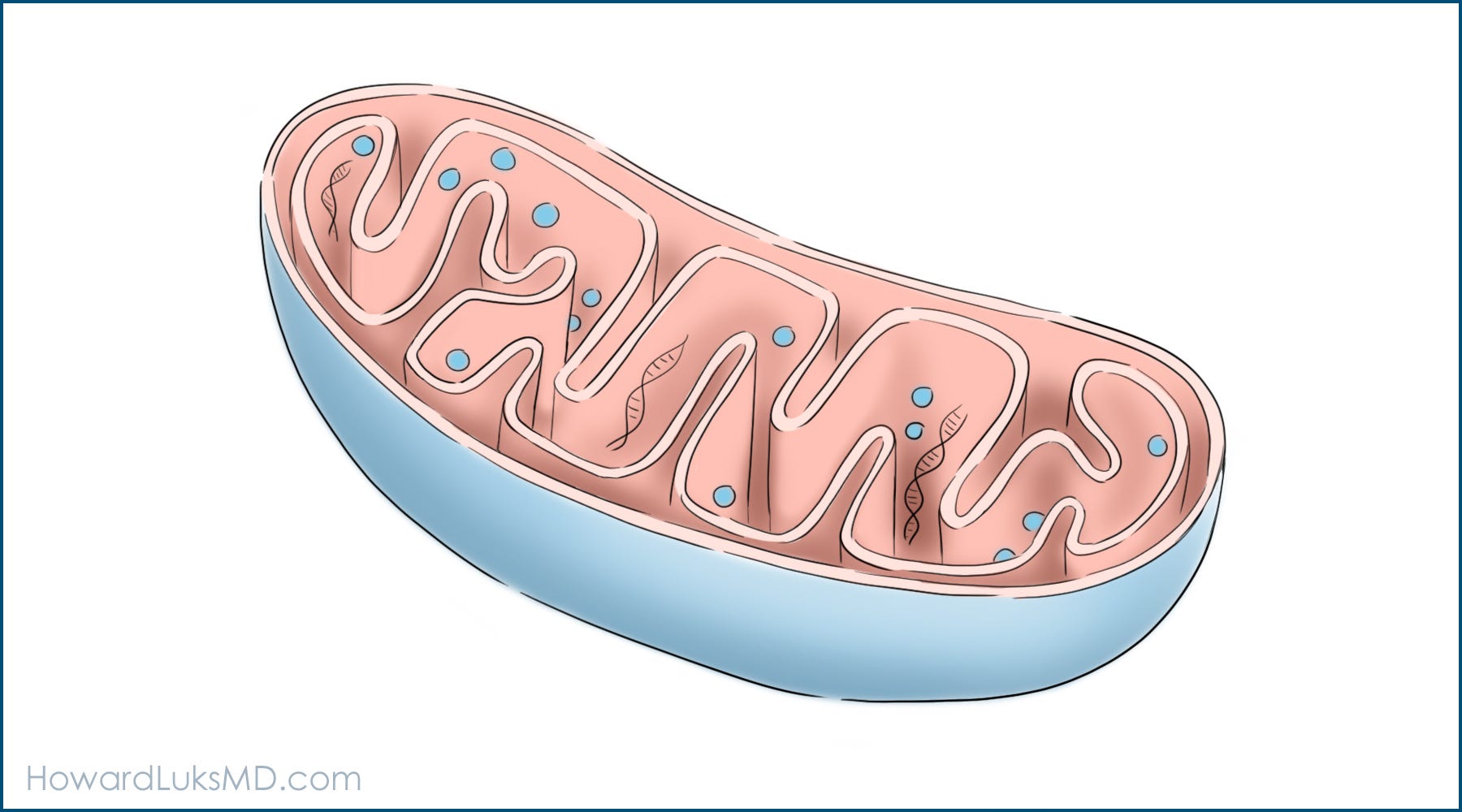
Mitochondria
performs cellular respiration
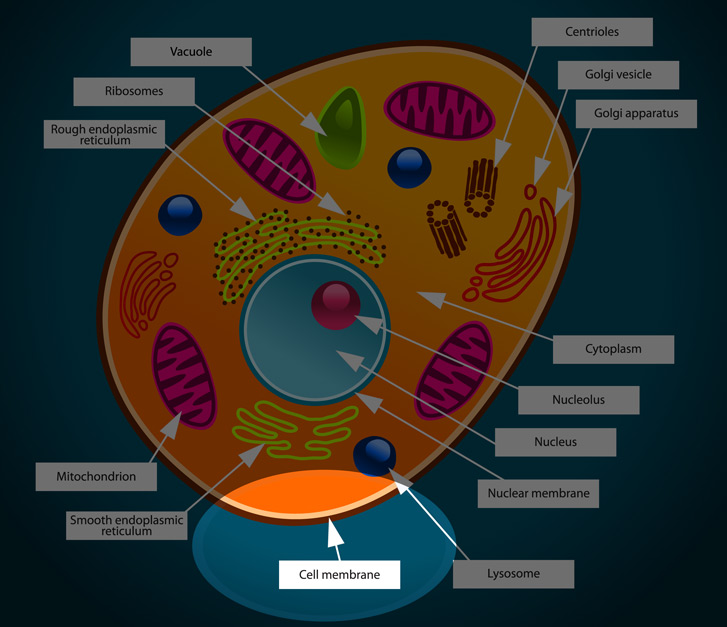
plasma membrane
made of phospholipids that surrounds the cell and it’s help form the shape of the cell
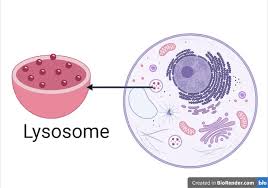
lysosome
contains enzymes to break down molecules
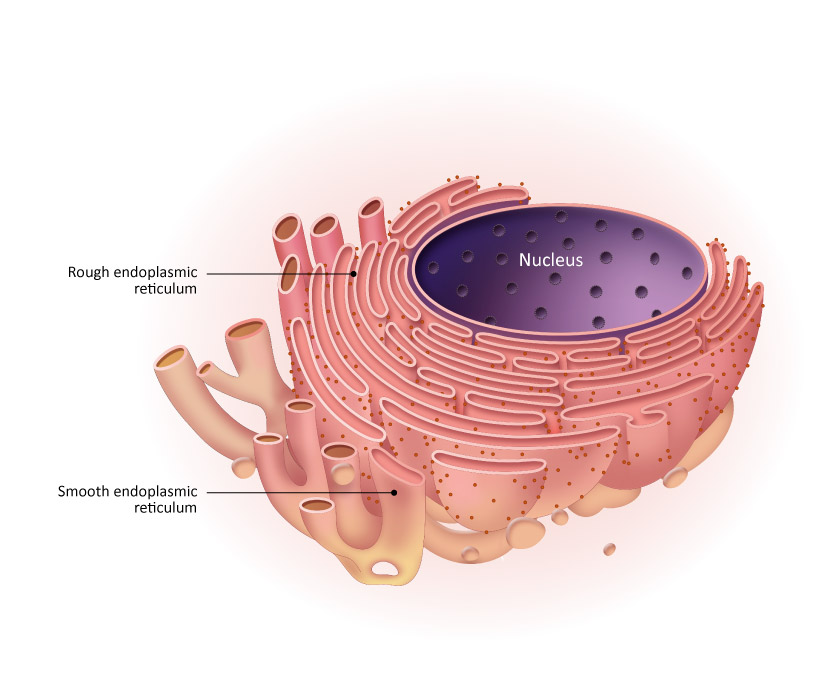
smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth: lacks ribosomes synthesize lipids
rough: contains ribosomes (that’s why its rough) helps process and transport proteins
cytoplasm
watery substance called cytosol and contains other cell structures like ribosomes
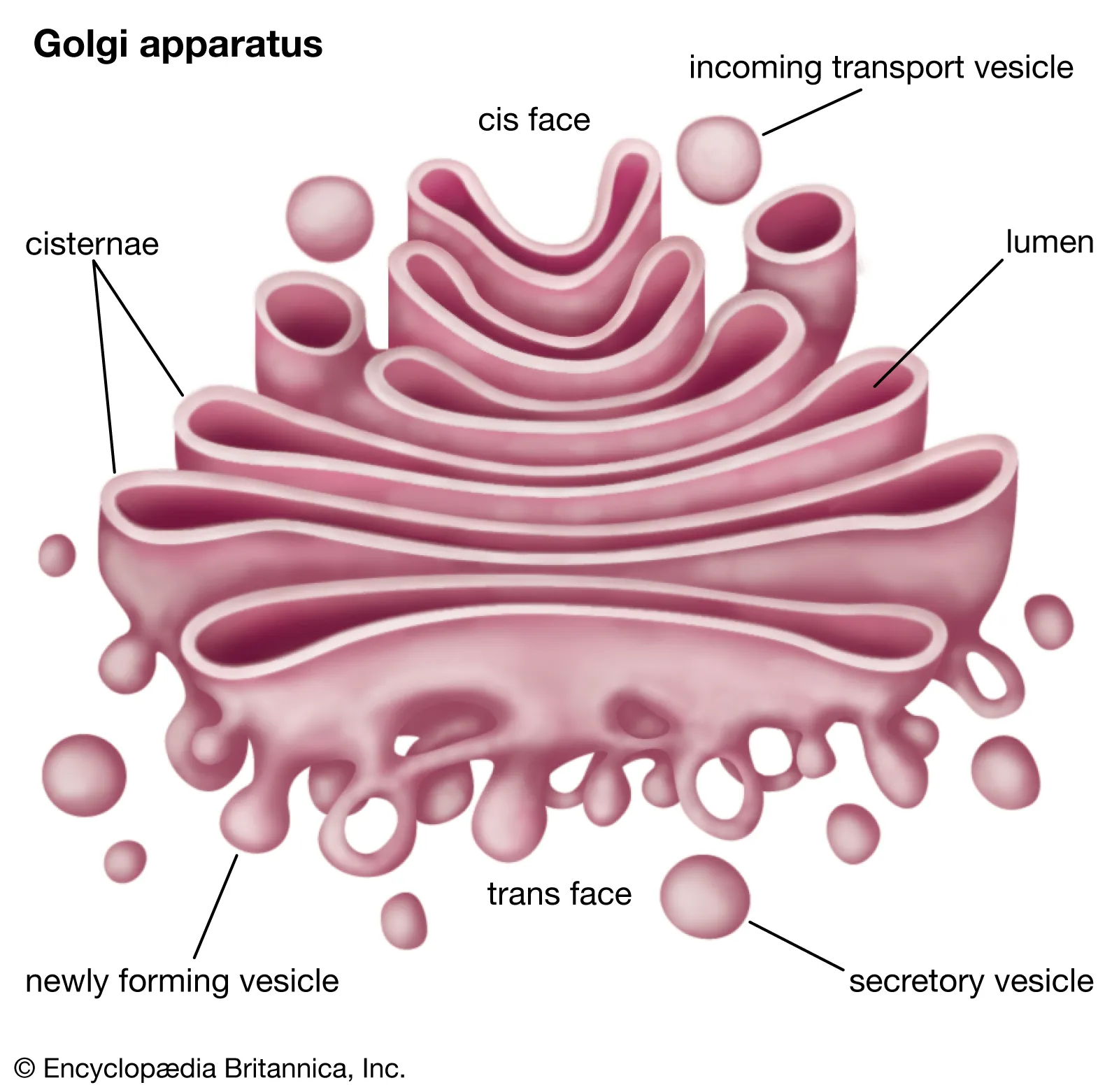
Golgi apparatus
modify proteins and lipids (helps process and package)
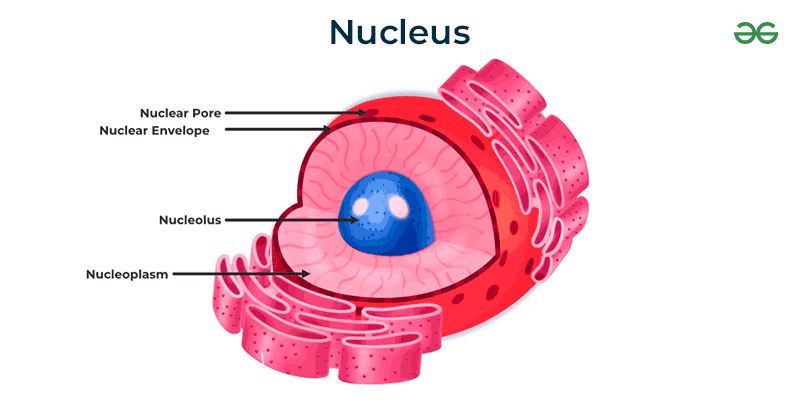
nucleolus and nucleus
nucleolus: contains the DNA
nucleus: contains DNA and directs protein synthesis
ribosomes
makes the protein
describe the structure of an atom
it has a nucleus with proteins and neutrons with electrons orbiting on the valence shell(outer shell).
atomic number= number of protons
mass number= protons + neutrons
difference between ionic and covalent bonds
ionic: donate and take electrons. and it forms between metal and nonmetal (positive attracts negative)
covalent: sharing electrons. forms between nonmetal
polar covalent: unequal sharing
non-polar: equal sharing
explain the role of hydrogen bonds in the properties of water
gives water "high heat capacity= resists temp changes
gives water high heat of vaporization= cooling through sweat
cause cohesion(water sticking to it’s self)
adhesion (water sticking to other surfaces)
summarize the pH and the importance of buffers to biological systems
pH measures H+ concentration
0= acidic
7=neutral
16=basic
buffers= resists pH changes by absorbing excess H+ or OH-
what are the 4 class of organic molecules found in cells
carbohydrates(quick energy), lipids(fats/oils), proteins(enzymes, structure), and nucleic acids(ATP is the energy coin)
describe the process by which the organic molecules are assembled and disassembled
assembled: from monomers through dehydration synthesis, removing a water molecule to form a bond
disassembled: back into monomers through hydrolysis, reaction adds water molecule to break a bond
summarize the basic chemical properties of a carbohydrate
basic units are monosaccharides (sugar rings) they are polar due to hydroxyl (-OH) can polymerize by dehydration reactions to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
state the role of carbohydrates in human physiology
two roles
immediate energy source and primarily forms glucose
short term energy source in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles
compare structures of fats, phospholipids, and steroids
fats: triglycerides one glycerol and three fatty acids
phospholipids: two part structure polar phosphate head and two fatty acid tails
steroids: different structure four fused carbon rings and lack fatty acids
function of each class of lipids
fats/oils: function energy storage, insulation, cushioning
phospholipids: components of cellular membranes
steroids: messengers and membrane stuff
structure of an amino acid
its a monomer of protein. each has a central carbon atom bonded to it
explain how amino acids are combines to form proteins
are combined to form proteins through dehydration synthesis which forms bonds between amino acids
state the basic principles of the cell theory
cell is the basic unit of life
all living things are made up of cells
new cells arise from pre-existing cells
explain the surface area of volume ratio limits cell size
are small because its volume increases
small= harder for nutrients to enter and waste to exit
distinguish between the structure of a prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell
prokaryotic: lack a nucleus, lacks membrane organelles
eukaryotic: has a nucleus, membrane bound organelles, DNA in the nucleus
how eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells
prokaryotic cells was engulfed by a bigger cell and established symbiotic relationship. the mitochondria has their own DNA and was able to reproduce independently
describe the structure of the plasma membrane and list the type of molecules found in the membrane.
structure= fluid mosaic(phospholipid bilayer) where proteins move freely and hydrophobic tails face inward
molecules found: phospholipids, proteins, cholesterols, glycoproteins and glycolipids