gen chem 2 final (chapters 19, 20, 21)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
acid base buffer
a solution that resists changes in pH when a small amount of either strong acid or strong base is added
acid base titration curve
a plot of the pH of a solution of acid (or base) vs. the volume of base (or acid) added to the solution
buffer capacity
a measure of the ability of a buffer to resist a change in pH; related to the total concentrations and relative proportions of buffer components
buffer range
the pH range over which a buffer acts effectively
common ion effect
shift in the position of an ionic equilibrium away from an ion involved in the process that is caused by the addition or presence of that ion
complex ion
an ion consisting of a central metal ion covalently bonded to two or more anions or molecules called ligands
end point
the point in a titration at which the indicator changes color permanently
equivalence point
the point in a titration when the number of moles of the added species is stoichiometrically equivalent to the original number of moles of the other species
formation constant (Kf)
an equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion from the hydrated metal ion and ligands
Henderson[Hasselbalch equation
an equation for calculating the pH of a buffer system
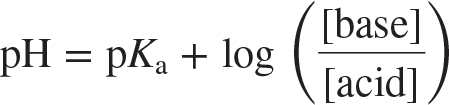
Ligand
a molecule or an anion bonded to a central metal ion in a complex ion
selective precipitation
the process of separating ions through differences in the solubility of their compounds with a given precipitating ion
solubility product constant (Ksp)
an equilibrium constant for a slightly soluble ionic compound dissolving in water
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
a high energy molecule that serves most commonly as a store and source of energy in organisms
coupling of reactions
the pairing of reactions of which one releases enough free energy for the other to occur
entropy (S)
a thermodynamic quantity related to the number of ways the energy of a system can be dispersed through the motions of its particles
free energy (G)
a thermodynamic quantity that is the difference between the system’s enthalpy and the product of the absolute temperature and the system’s entropy: G = H-TS
microstate
an instantaneous, quantized state of a system of particles throughout which the total energy of the system is dispersed
second law of thermodynamics
a law stating that a process occurs spontaneously in the direction that increases the entropy of the universe
spontaneous change
a change that occurs under specified conditions without an ongoing input of external energy
standard entropy of reaction (ΔG°rxn)
the entropy change that occurs when all components are in their standard states
standard free energy change (ΔG°)
the free energy change that occurs when all components of a system are in their standard states
standard free energy of formation (ΔGf°)
the standard free energy change that occurs when 1 mol of a compound is made from its elements with all components in their standard states
standard molar entropy (S°)
the entropy of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state
third law of thermodynamics
a law stating that the entropy of a perfect crystal is zero at 0K
ampere (A)
the SI unit of electric current
1 ampere of current results when 1 coulomb of charge flows through a conductor in 1 second
anode
the electrode at which oxidation occurs in an electrochemical cell
electrons are given up by the reducing agent and leave the cell at the anode
cathode
the electrode at which reduction occurs in an electrochemical cell
electrons enter the cell and are acquired by the oxidizing agent at the cathode
cell potential (Ecell) also electromotive force or cell voltage
the difference in electrical potential between the two electrodes of an electrochemical cell
coulomb (C)
the SI unit of electric charge
one coulomb is the charge of 6.242 × 1018 electrons
one electron possesses a charge of 1.602 × 10−19 C.
electrochemical cell
a system that incorporates a redox reaction to produce or use electrical energy
electrochemistry
the study of the relationship between chemical change and electrical work
electrode
the part of an electrochemical cell that conducts the electricity between the cell and the surroundings
Faraday constant (F)
the physical constant representing the change of 1 mol of electrons
F = 96,485 C/mol e−
half-cell
a portion of an electrochemical cell in which a half-reaction takes place
half-reaction method
a method of balancing redox reactions by treating the oxidation and reduction half-reactions separately
Nernst equation
an equation stating that the voltage of an electrochemical cell under any conditions depends on the standard cell voltage and the concentrations of the cell components
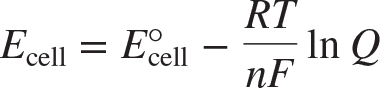
salt bridge
an inverted U tube containing a solution of nonreacting ions that connects the compartments of a voltaic cell and maintains neutrality by allowing ions to flow between compartments
standard cell potential (E°cell)
the potential of a cell measured with all components in their standard states and no current flowing
standard electrode potential (E°half-cell) also standard half-cell potential
the standard potential of a half-cell, with the half-reaction written as a reduction
standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
a specially prepared platinum electrode immerse in 1M H+(aq) through which H2 gas at 1 atm is bubbled
E°half-cell is defined as 0V
volt (V)
the SI unit of electrical potential
1V = 1 J/C
voltaic/galvanic cell
an electrochemical cell that uses a spontaneous redox reaction to generate electrical energy