ALL of bacteria: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, labelling
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
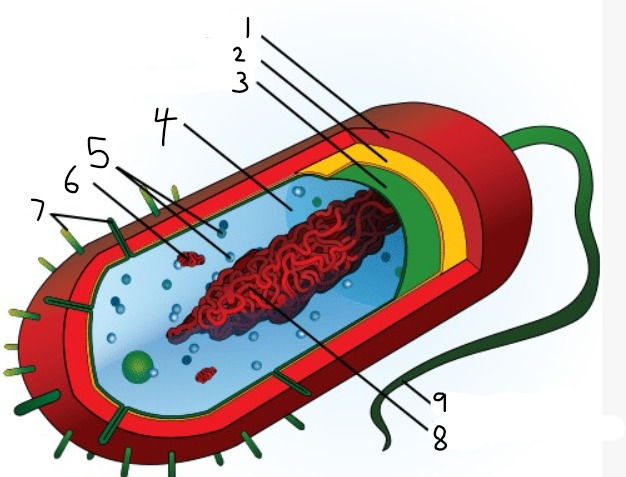
1
capsule
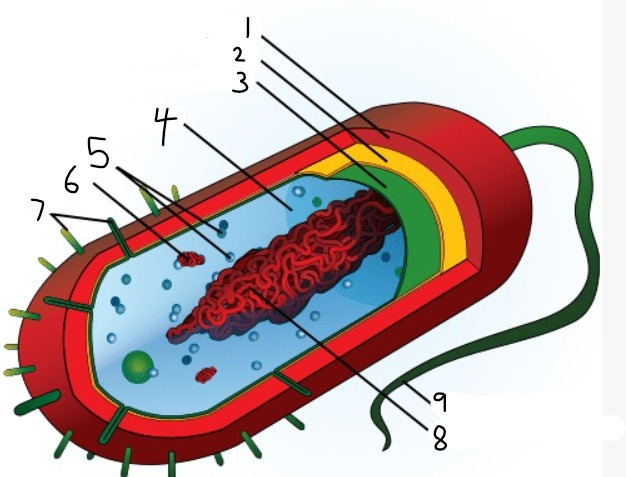
2
cell wall
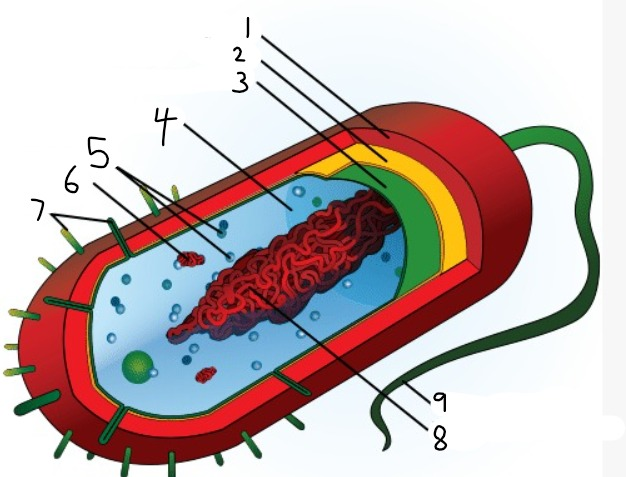
3
plasma membrane
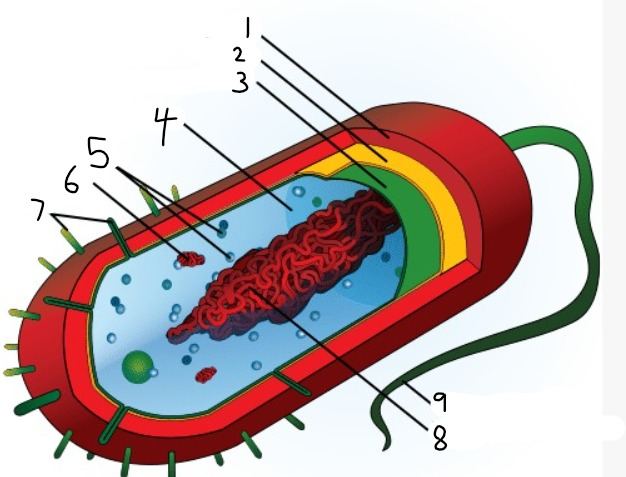
4
cytoplasm
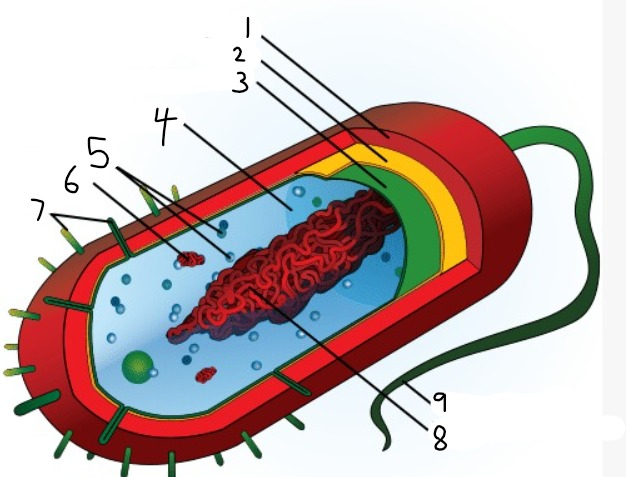
5
ribosomes
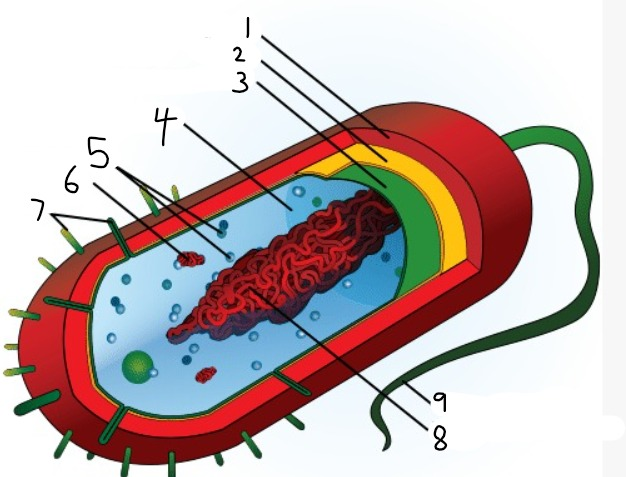
6
plasmid
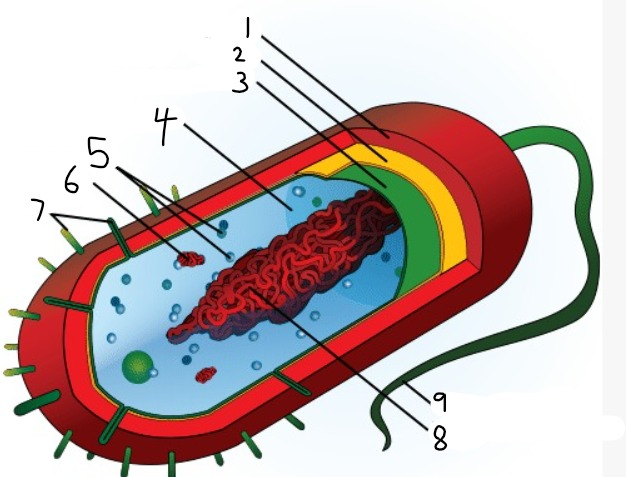
7
pili
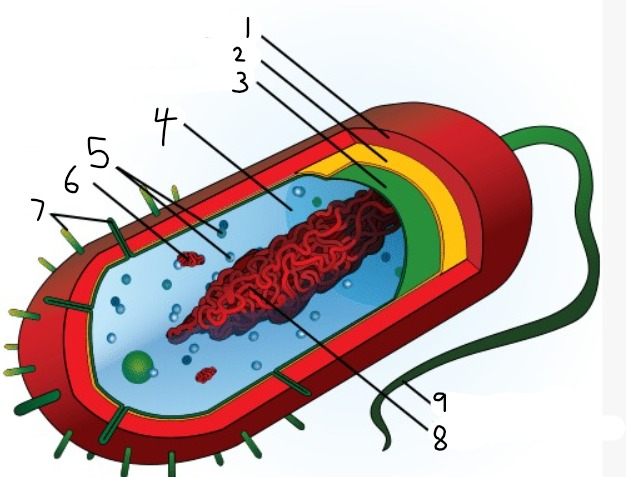
9
flagellum
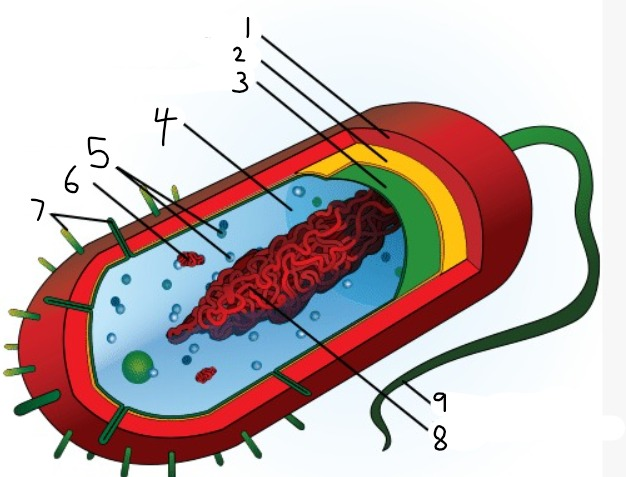
8
nucleoid
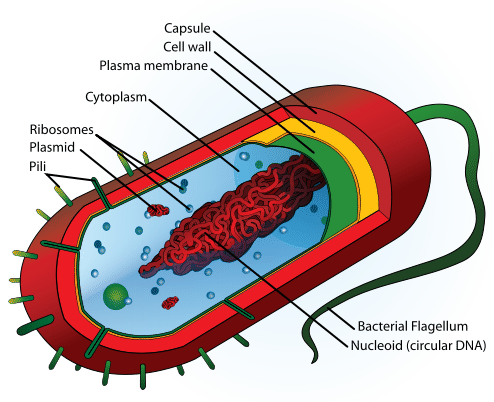
general characteristics of bacteria
single celled
single chromosome
prokaryotes: no nucleus, much smaller
organelles are NOT surrounded by membrane
archaea
oldest group of organisms (evolution)
found in extreme environments
classified by the type of environment they inhabit
methanogens: methane producing, poisoned by oxygen
halophiles: live in high saline, salt loving
thermacidophiles: live in extreme temperatures and pH, heat and acid loving

Eubacteria
unicellular prokaryotes
most bacteria are eubacteria
have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan
how are bacteria classified?
cell shape
gram stain
nutrition
respiration
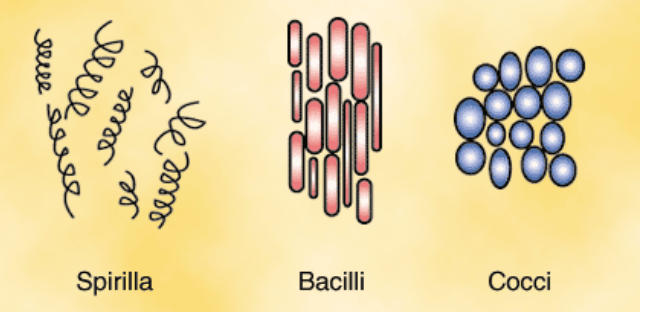
classification of bacteria: cell shape
spirilla: spirals
bacilli: rounded rectangles
cocci/coccus: circles
may also be asymmetrical
classification of bacteria: gram stain
the reaction between bacteria and a crystal violet iodine dye
gram-positive: cell appear purple
gram-negative: cell appears light pink → pathogens

classification of bacteria: nutrition
heterotroph: use organic molecules from their environment to produce their energy (cannot make own food)
autoroph: produces their own organic molecules molecules from their environment (can make own food)
classification of bacteria: respiration
aerobes: use oxygen to produce energy from their food
anaearobes: produce energy from food in the absence of oxygen
pathogens
any organism that causes disease: viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites
reproduction of bacteria
binary fission (asexual)
conjugation (sexual)
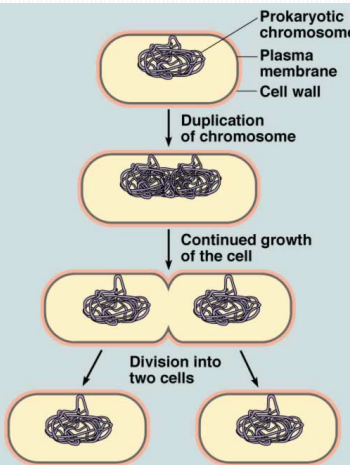
binary fission
asexual reproduction for bacteria
exact copy; no diversity
cell elongates, then forms a septum (pinching part), forms distinct walls, then seperates
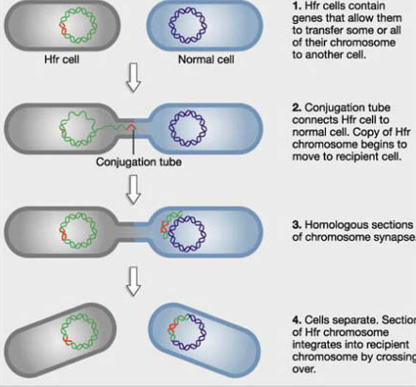
conjugation
sexual reproduction in bacteria
genetically different
two cells form a tube, part of the DNA moves over, results in two genetics diverse cells
how can bacteria be helpful?
most bacteria are helpful
natural recycling through nitrogen cycle, converts nitrogen gas intro useable nitrogen for plants and provides oxygen
health and medicine: foods (yogurt, cheese, pickles), help digestion, release vitamins
clean-up (bioremediation): clean up oil spills and gasoline leaks
pathogenic bacteria release
endotoxins or exotoxins
endotoxins
pathogenic bacteria
release gram-negative bacteria split
cause fever, vomiting, diarrhea
i.e. salmonella
exotoxins
pathogenic bacteria
mostly gram positive
released around bacteria
toxic and fatal