LR II
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What organisms are we most concerned about for HAP/VAP?
MRSA, Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas
What antibiotics do we use to treat HAP/VAP in a patient with no MDRO risk factors?
Pip/tazo
Cefepime
Levofloxacin
Merppenem/Imipenem
All patients get empiric coverage for MSSA, Enterobacterales, and Pseudomonas
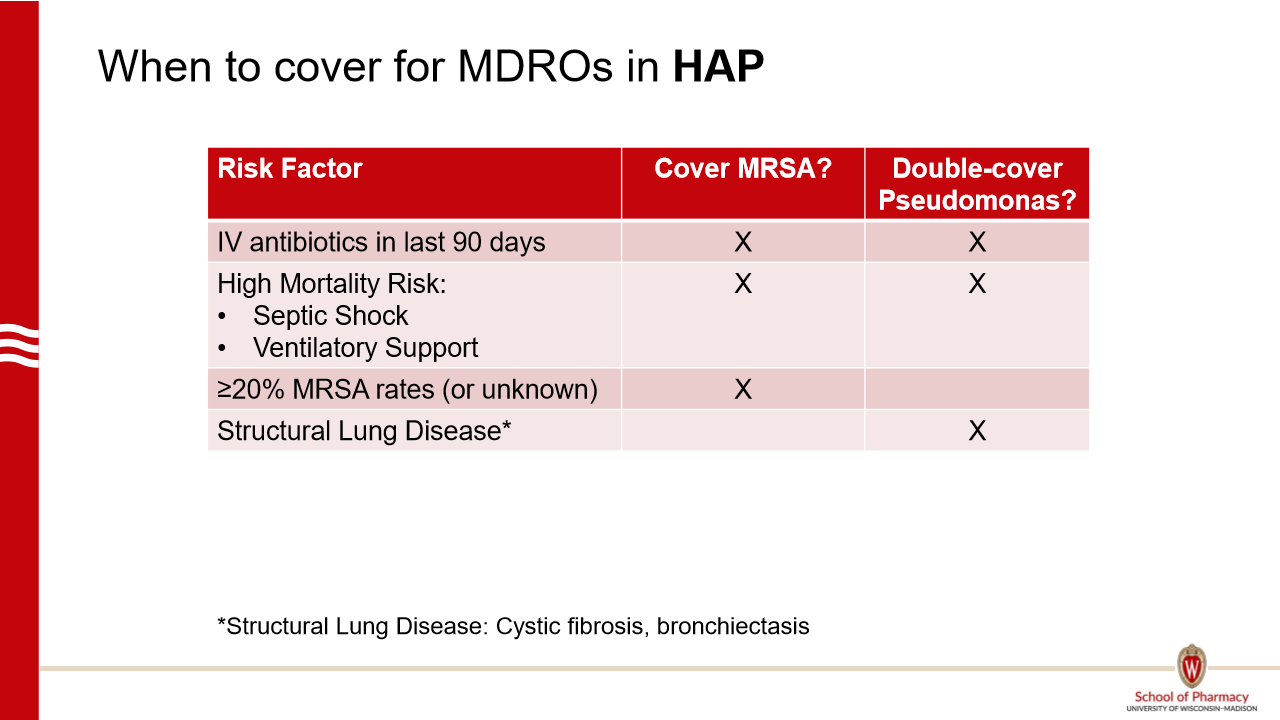
Which HAP require empiric MRSA coverage?
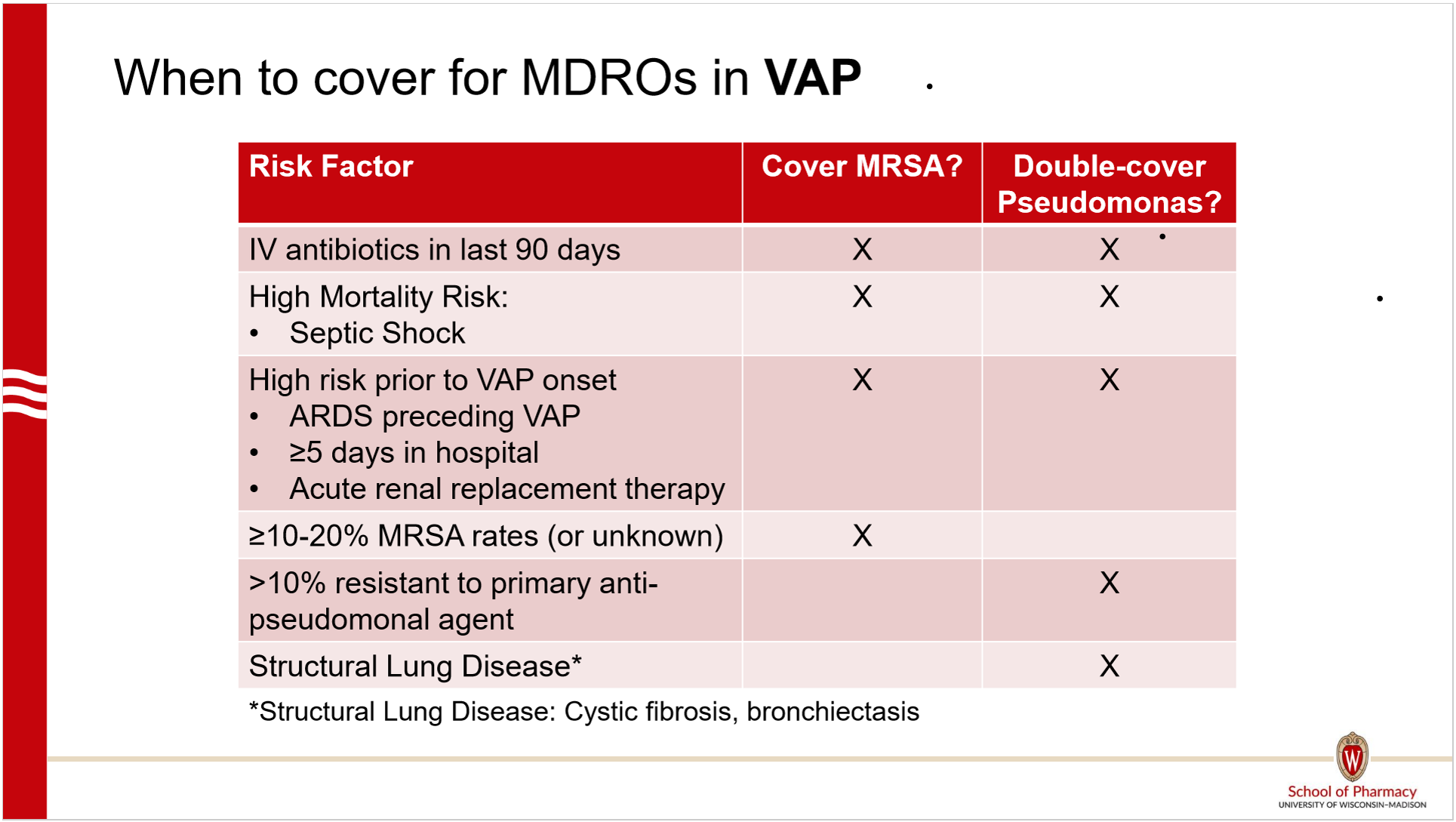
Which VAP require empiric MRSA coverage?
What antibiotics do we use if a patient requires MRSA coverage?
Vanco (or linezolid)
and
Piptazo (or cefepime or levofloxacin or mero/imipenem)
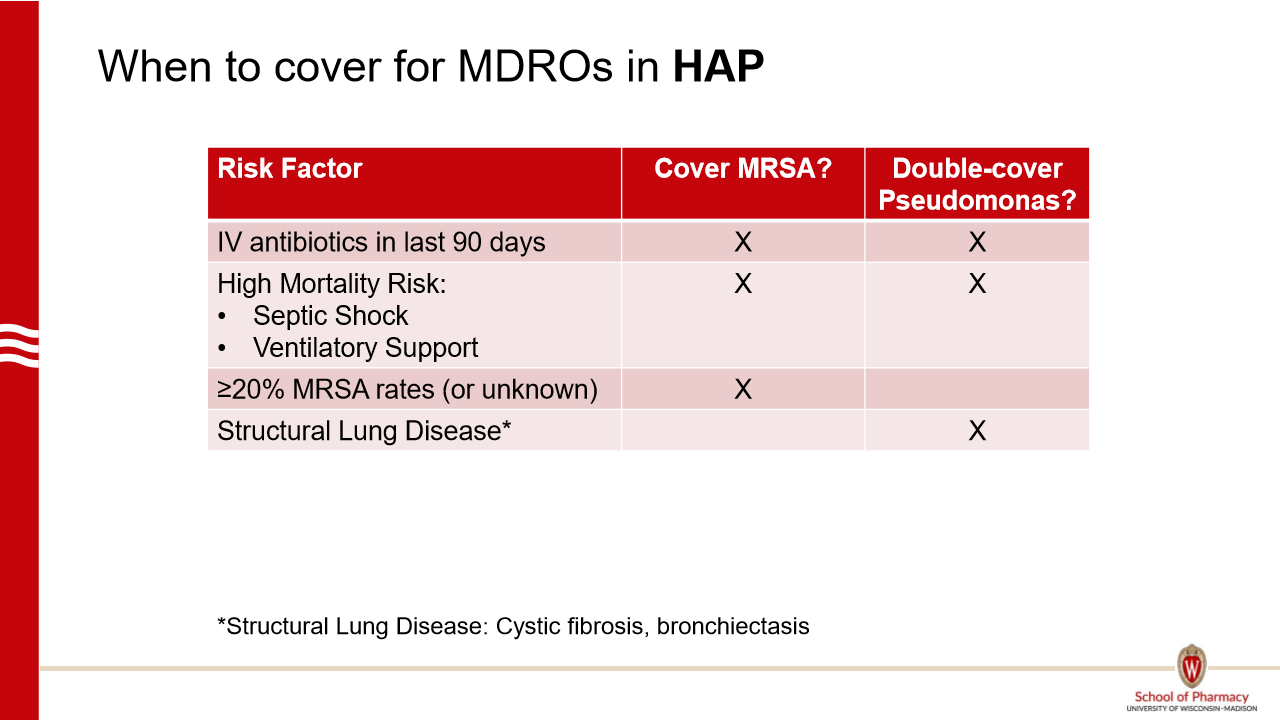
Which HAP patients require double pseudomonas coverage?
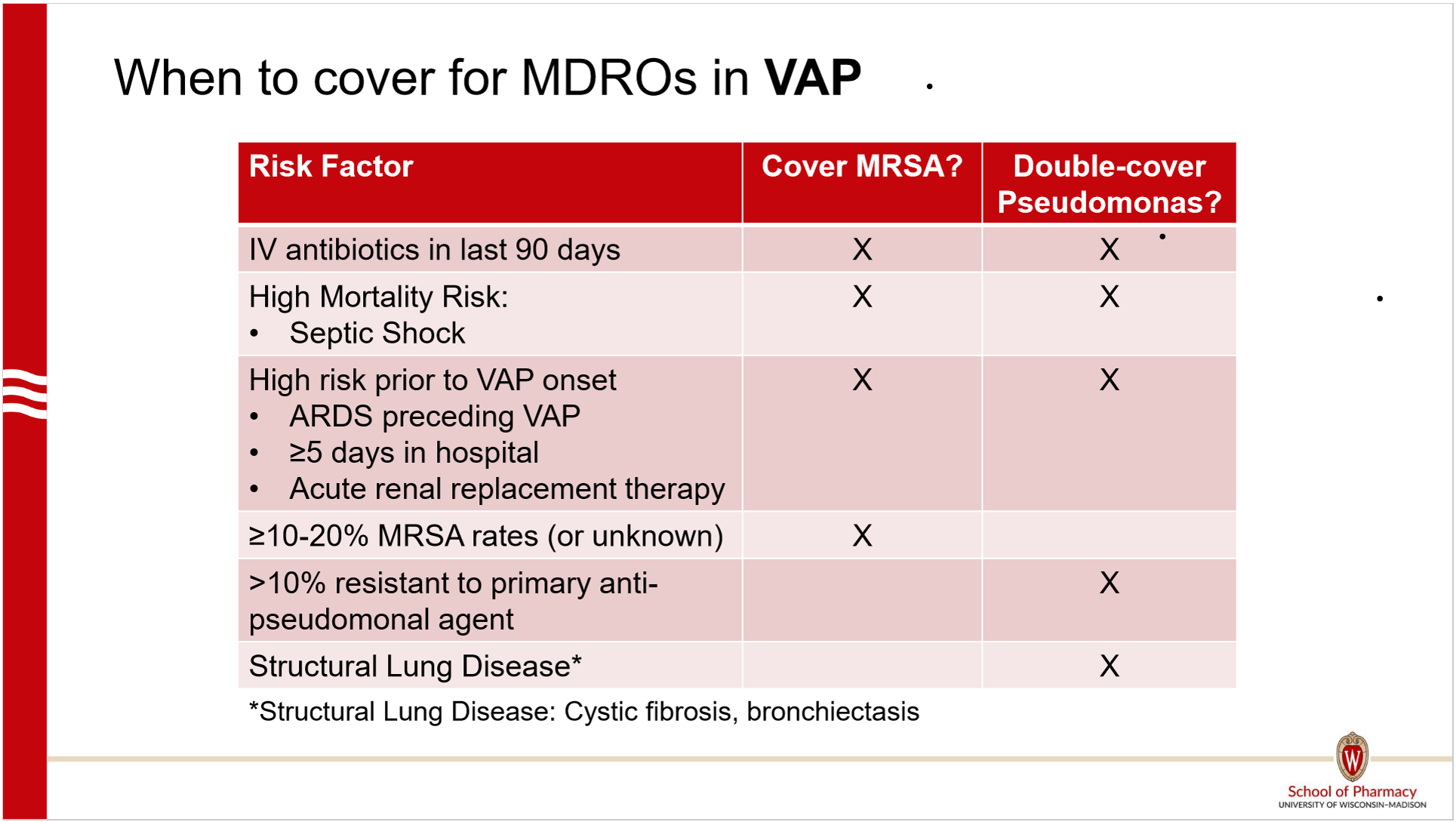
Which VAP patients require double pseudomonas coverage?
What antibiotics do we use if a patient requires double pseudomonas coverage?
Piptazo or cefepime or ceftazidime or Mero/imipenem or Aztreonam
AND
Levo/cipro or aminoglycoside (which one help reem pls) or colisitin (not for staph coverage)
What antibiotics do we use if a patient requires double pseudomonas and MRSA coverage?
Vanco or linezolid
AND
Pip tazo or cefepime or ceftazidime or Mero/imipenem or Aztreonam
AND
Levo/cipro or aminoglycoside (which one help reem pls) or colisitin (not for staph coverage)
How long should patients with HAP/VAP be treated?
7 days
de-escalate when appropriate
What is the primary cause of bronchiolitis? Acute bronchitis?
Both are mostly viral, Broncholitis is mostly RSV
Distinguishing factors between broncholitis and acute bronchitis
Broncholitis is mostly kids <2 whereas acute bronchitis is mostly adults
Fever present with broncholitis
How is bronchiolitis typically managed?
Management | Details |
|---|---|
Outpatient Management | Hydration, Antipyretics |
Inpatient Management | Hydration, Respiratory/Oxygen support, Nasal suctioning |
Antibiotics | Should be discouraged (viral cause) |
Prophylaxis | Nirsevimab (Beyfortus) – Single IM dose before first RSV season, repeat in high-risk babies |
RSV Vaccines – Given during pregnancy or to adults 75+ / high risk |
How is acute bronchitis managed?
Management | Details |
|---|---|
Outpatient Management | Hydration, Antipyretics, Antitussives (guaifenesin, dextromethorphan), Beta-2 agonists (if baseline bronchoconstriction) |
Inpatient Management | Rare |
Antibiotics | Should be discouraged (viral cause) |
Prophylaxis | None available |
How is whooping cough managed?
Azithromycin x 5 days
or
Erythro x 14d
Clarithro x 7d
TMP/SMZ x 14d
What are the common organisms that cause AECB?
Haomophilus influenzae
Strep pneumoniae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Pseudomonas
For ACEB, do not offer abx to
One cardinal symtpom and not requiring hospitalization
Cardinal sx:
Increased dyspnea
Increased sputum volume
Increased sputum purulence
For ACEB, DO offer abx to
3 cardinal sx
Sputum purulence + one other
Mechanical ventilation
Cardinal sx:
Increased dyspnea
Increased sputum volume
Increased sputum purulence
Which patients with AECB should be treated with an anti-pseudomonal agent?
Pseudomonas colonization
Culture for pseudomonas in 12 months
Hospitalization or abx use in 3 months
Concominant bronchiectasis
Which agent(s) do we use for AECB needing pseudomonas coverage?
IV/PO: Levo or Cipro
IV: Pip/tazo, cefepime