Biology HL Unit 1 (Water, Carbohydrates, Lipids: A1.1, B1.1)
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Definition of Life
Ability to reproduce (sexual/asexual)
Must be made of cell(s)
Must have a way to get rid of waste products (sweat, respiration, digestion)
Must have a life cycle (stages of growth/development)
Ability to do cellular respiration
Gas exchange (aerobic/anaerobic respiration)
Maintaining homeostasis/ responding to stimuli
Able to take in (photosynthesis/cellular respiration)/ utilize energy (metabolism)
Living
Currently alive
Once living
Was alive, but is not at present time
Nonliving
Never living
Covalent bond
A bond between atoms in which pairs of electrons are shared (within a molecule)
Hydrogen bond
A weak attractive intermolecular (between two molecules) force.
A H atom in a molecule is attracted to an electronegative atom (oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine) in a different molecule.
Accounts for unique properties of water.
Polar molecule
A molecule with an unequal distribution of electric charge. The ends are slightly positive or negative. (Ex. water)
Cohesion
The force by which individual molecules of the SAME type attract and associate (stick together)
Adhesion
The force by which individual molecules stick to surrounding materials and surfaces.
Surface tension
The property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force, due to the cohesion between water molecules (hydrogen bonding).
Viscosity
A fluid’s resistance to flow, affected by temperature
Hydrophilic
Materials and substances with an affinity for water
Hydrophobic
Materials and substances that are repelled by water. Insoluble in water. Non-polar substances. Ex. all lipids
Capillary tubes
Channels with a very small internal diameter. Soil has many vertical, thin channels in which plant tubes are located.
Capillary action (aka capillarity)
The tendency of a liquid to move up against gravity when confined within a narrow tube (capillary)
Solute
Dissolved molecule or ion in a solution
Solvent
A liquid in which another substance (solute) can be dissolved
Buoyancy
The ability of any fluid to provide a vertical upwards force on an object placed in or on it.
Thermal conductivity (k)
The measure of how easily heat flows through a specific type of material.
Specific heat capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 degree C.
Goldilocks zone (aka the ‘habitable zone’)
The area around a star where the temperature isn’t too hot or cold for liquid water to exist on the surface of surrounding planets.
Enzymes
Biological molecules that increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed.
Carbonaceous chondrites
Meteors with water incorporated into their mineral structure. Hydrogen isotope ratio similar to Earth’s seawater.
Carbon
All lifeforms are carbon-based
Have 4 valence electrons in outer shell, allowing for formation of strong covalent bonds
Create large, stable structures that can only be broken through h
Structures of carbon
Chain, branched-chain, ring
Carbohydrates
C, H, O, N
Sugars, starches, and cellulose
Lipids
C, H, O
Insoluble in water
Waxes, steroids, fatty acids, triglycerides
Proteins
C, H, O, N, S
Enzymes, muscles/skin
One or more polypeptide chains of amino acids that folds into a 3D structure to become a protein
Nucleic acids
C, H, O, N, P
DNA/RNA
Chains of nucleotides
Sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous base
Anabolic reaction
Putting things together (adding)
Net energy loss
Energy + small molecules = larger molecule
Protein synthesis: ribosomes creating proteins by assembling amino acids
Storage of excess glucose: starch for plants, glycogen for animals
Dehydration synthesis: condensation reactions
Catabolic reaction
Breaking down molecules (cats break things)
Net energy gain
Large molecule = smaller molecules + energy
Digestion of proteins, carbs, lipids in the digestive system
Seed germination: starch breakdown for anaerobic respiration
Glycogen breakdown in liver for energy
Hydrolysis reactions (Ex. photosynthesis)
Monosaccharide
Single sugar units
Form ring structures in cells
Hexoses: glucose, fructose, galactose
Pentose: ribose
Polysaccharide
Many monosaccharides linked together
Starch, glycogen, cellulose
Disaccharide: maltose, sucrose, lactose
Condensation reaction (aka dehydration synthesis)
An anabolic chemical reaction - net energy loss
Loss of an —OH group from one molecule and a —H from another
Monosaccharides combine to form a polysaccharide and water molecules
Hydrolysis
Water helping to break two monomers apart
Restores the —OH and —H that were lost in the condensation reaction
Catabolic reaction - net energy gain
Lactose intolerance
Low levels of enzyme lactase in the digestive system means that the hydrolysis of lactose doesn’t occur. Lactose enters the large intestine, where bacteria convert it into gas.
Amylose
A straight chain of starch that will coil up into a helix
About 20-25% of a plant’s starch
Long-term and more efficient energy storage
C1, C4 bonds; chains of alpha-glucose
Amylopectin
Branched structure of starch
Short-term energy storage
C1, C6 bonds; glycosidic bonds
75-80% of the starch in a plant
Starch
Amylose & Amylopectin
Stores carbohydrates for plants in seeds, bulbs, and tubers
Long-term storage
Chains of alpha-glucose molecules
Glycogen
Temporary storage of excess glucose for animals
In liver or muscles
Cellulose
Structural support for plant cell walls
Beta-glucose molecules bond upside down
Hydrogen bonds
Lipid function
Energy source & long-term storage → release 2x more energy per gram than carbs when metabolized
Insulation (lipids have a low thermal conductivity)
Components of cell membranes (phospholipid bilayer)
Triglyceride
Condensation reaction
3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol → 1 triglyceride + 3 H2O
Simple lipid
Fat vs oil
Fat: solid at room temperature
Oil: liquid at room temp
Saturated fatty acid
Long hydrocarbon chain capped by a carboxyl group (-COOH)
Have a hydrogen at every possible position (straight)
Usually in meats → unhealthy as they stack easier & can clog arteries
Unsaturated fatty acid
Long hydrocarbon chain capped by a carboxyl group (-COOH)
Double carbon bond means not complete saturation with hydrogen (bent)
In seeds & plant products → healthier, less likely to stick in veins
Monounsaturated: one double bond; Polyunsaturated: more than one
Cis: same side H on the carbon that’s double bonding, healthiest
Trans: H are on different sides
Polypeptide
Chain of amino acids
Amino acids are combined by condensation reactions into a polypeptide chain, linked with peptide bonds
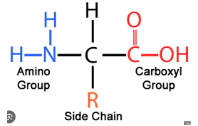
Parts of an amino acid
Double bond C=O
Central carbon (alpha-carbon) C-H
Carboxyl group (aka carboxylic acid) -COOH
Amine group -NH2
R group (varies)
Functions of protein
Transport (e.g. hemoglobin)
Storage
Building & repairing tissues
Catalyzing metabolic reactions (enzymes)
Strength & structure (muscle contraction & movement)
Protection (immune functions & antibodies)
Cellular communication & coordination (hormones)
Essential vs non-essential amino acids
Essential: 9/20 amino acids, can’t be made by the human body so have to be gotten from diet
Non-essential: can be made by the human body, but made from essential amino acids
Combinations of amino acids
20 amino acids
Almost infinite combinations (order, length of chain, etc)
Primary structure of protein
Linear chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
Aka simple protein or polypeptide chain
Secondary structure of protein
Folding/coiling of the primary chain due to hydrogen bonds (carboxyl—amine) between polypeptide backbones
Alpha-helix: a delicate coil (hair, wool, feathers)
Beta-pleated sheet: 2 parts lie parallel, relatively insoluble in water (tend to be fibrous with structural function - muscle fibers)
A and B can be found in the same chain
Tertiary structure of protein
Folding of the chain caused by interactions between R groups
Hydrophobic groups cluster together on the inside, hydrophilic groups on the outside (amphipathic)
Hydrogen bonds: between polar R groups
Ionic bonds: interactions between ions in R groups
Disulfide bridges: 2 cysteine amino acids w/ sulfur in R groups will form H bonds
Quaternary structure of protein
Multiple chains of amino acids linked together
Held together by hydrogen & ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, and hydrophobic structures
Not all proteins have a quaternary structure
Non-conjugated: no prosthetic group
Conjugated: incorporates other non-protein parts/prosthetic group (e.g. hemoglobin)
Hemoglobin
Quaternary, globular, conjugated protein
4 chains - 2 alpha, 2 beta
Each chain has a globular shape that is folded around the haem (prosthetic), which contains an iron atom that helps transport oxygen (a non-polar molecule)
Globular protein
Round/spherical shape with irregular amino acid sequences
Tend to be more specialized
Generally soluble in water & sensitive to pH and temperature changes
Ex. hemoglobin, enzymes, immunoglobulin, insulin
Fibrous protein
Long and narrow, typically composed of repeating, regular structures
Insoluble in water & stable in a large range of conditions
Have a structural role - strength and support
Ex. keratin, myosin, acting, fibrin, elastin, collagen
Insulin
A small, globular, non-conjugated protein
Shape allows it to bind to insulin receptors on the surface of liver, muscle, and fat cells, initiating a cellular response
Secreted by beta cells in the pancreas
A hormone - acts as a signal to cells in the body to absorb glucose and help reduce blood glucose concentration
Collagen
Fibrous, non-conjugated quaternary protein
3 chains forming a triple helix, each strand composed of 3 repeating amino acids, 1200 amino acids in each chain
Regular and geometric fibrous shape that allows it to form rope-like fibers with high tensile strength
Makes up ~25% of all protein in the human body, structural support
Helps prevent cracks in teeth and bones
Forms a mesh of fibers in skin and blood vessels that resists tearing, also forms connective tissue
Amphipathic substances
Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts
Ex. soap - can wash away both polar and non-polar substances
Phospholipid bilayer: hydrophilic heads & hydrophobic tails
Glucose
The most important monosaccharide
Used in photosynthesis & cellular respiration to store & release energy
Polar molecule - soluble in water, can be transported in blood to all cells
Ring form & 4 covalent bonds for each carbon make it a stable molecule
Enzyme
Denaturation
The process in which a protein unravels to its primary structure, becoming inactive
Renaturation can occur in some cases
Enzymes are especially sensitive to denaturation
Human enzymes work best at 37 C (optimum temperature)
The optimum pH for human enzymes changes based on location (e.g. stomach vs intestines)
Reaction rate of enzymes
Temp increase = kinetic energy increase; more chance of enzyme/substrate collision
Substrate concentration increases, reaction rate increases
The reaction rate levels off if:
The enzyme is saturated
All enzymes have their active site engaged
There are limiting factors
Metabolism
Anabolism & catabolism
A complex network of interacting and interdependent chemical reactions
Nearly all metabolic reactions are enzyme-catalyzed in multi-step pathways and cycles
Ex. blood clotting, cellular respiration, photosynthesis, digestion
Reactions/energy can be controlled & regulated by enzymes
Linear pathway
A series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions which run in one direction from reactant'/substrate → product
Ex. glycolysis in cellular respiration & light independent reactions of photosynthesis
Cyclical pathway
Circular series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions where there is no end, as the initial substance is eventually reformed
Ex. citric acid cycle aka Krebs cycle aka tricarboxylic acid cycle
Inhibition
Controls enzymes to ensure that metabolism is regulated
Negative feedback cycle, important for maintaining homeostasis
Competitive & noncompetitive inhibitors, end-product & mechanism-based inhibition
Competitive inhibitors
Molecules that bind to the active site of an enzyme
Complete with the substrate - will still allow enzyme-substrate complexes to form, and if more substrate is added, it will be out-competed
Ex. Statin: a medicine used to treat high blood cholesterol by competitively inhibiting the enzyme that forms cholesterol
Noncompetitive inhibitors
Binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme
Causes the enzyme to change shape, making the active site less effective
Not affected by the amount of substrate, but can be overcome by the addition of more enzymes
Ex. ACE inhibitor: medicine used to treat hypertension by preventing molecules from signaling constriction of the blood vessels
End-product inhibition
The end of a metabolic pathway shuts down that pathway
Prevents a cell from wasting chemical resources by synthesizing more product than is needed
The end product can become a noncompetitive inhibitor and bind to the enzyme
Mechanism-based inhibition
Aka suicide inhibitors
Ex. heavy metals (mercury, lead): bind non-specifically and irreversibly to a wide range of enzymes through covalent bonding of the SH group in the active site
Penicillin
A group of antibiotic chemicals obtained from molds
Have a similar shape to the terminal ends of peptide chains, allowing them to bind in the active site
As peptidoglycan synthesis is halted, its cell wall is compromised, leading to cell lysis & death as the cell is unable to maintain osmotic pressure