Chapter 21: Cranial Nerves
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
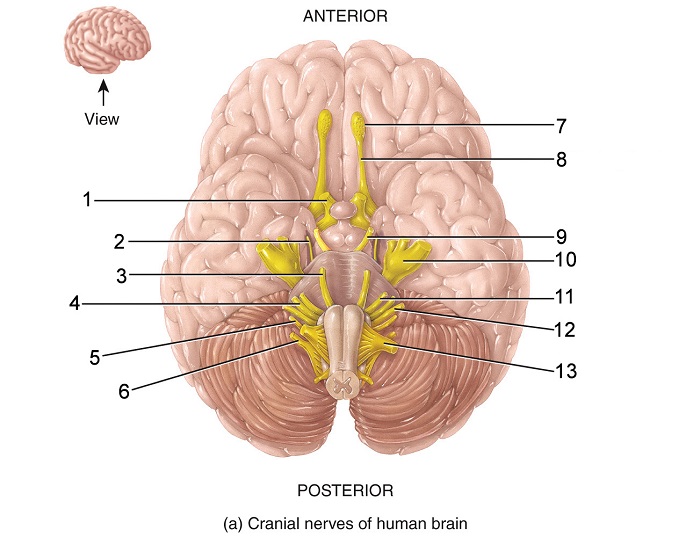
what is 1
optic nerve
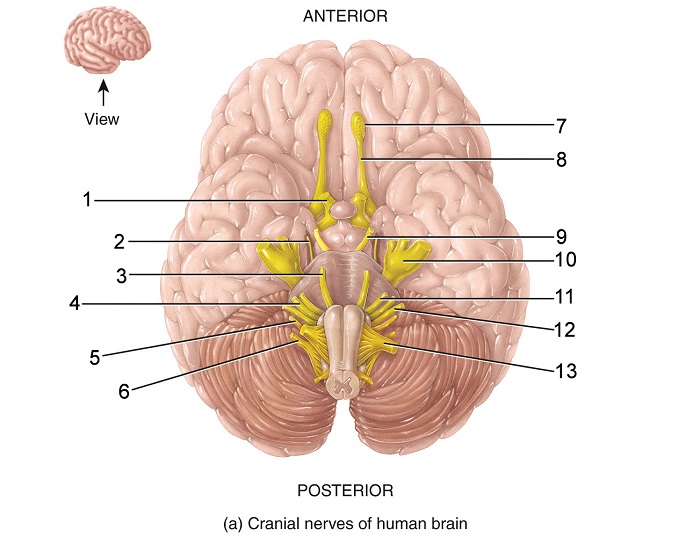
what is 2
trochlear nerve
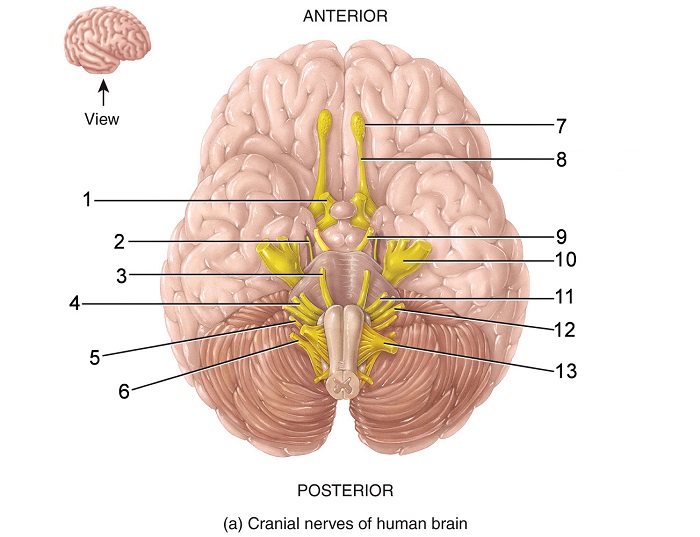
what is 3
abducens nerve
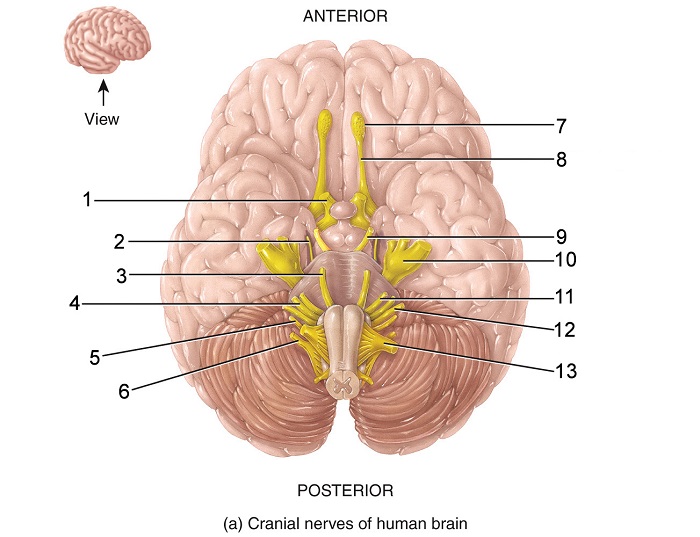
what is 4
vestibulocochlear nerve
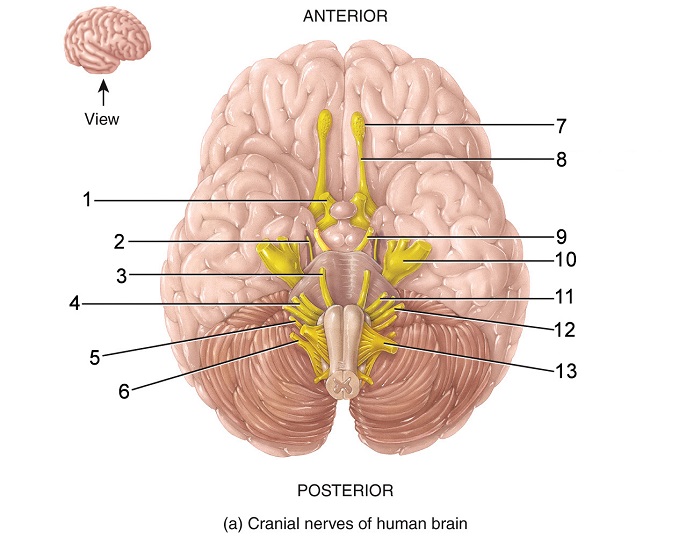
what is 5
vagus nerve
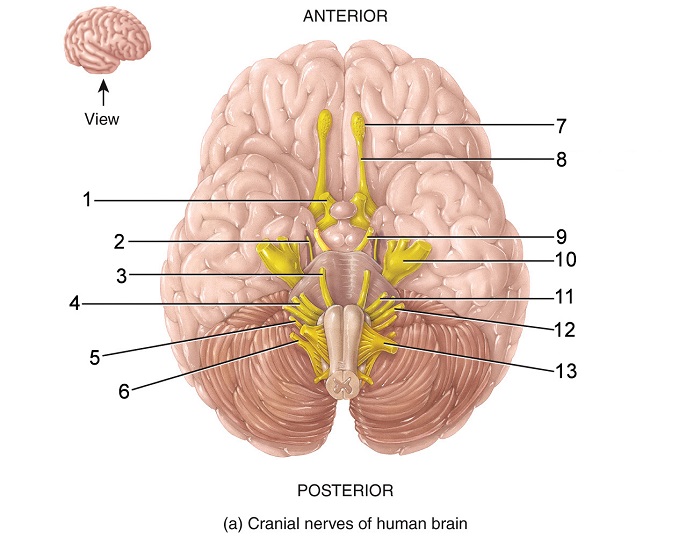
what is 6
accessory nerve
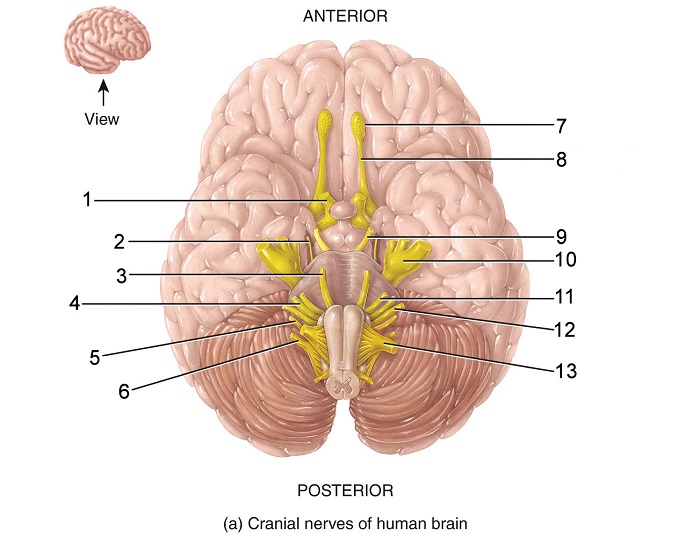
what is 7
olfactory bulb
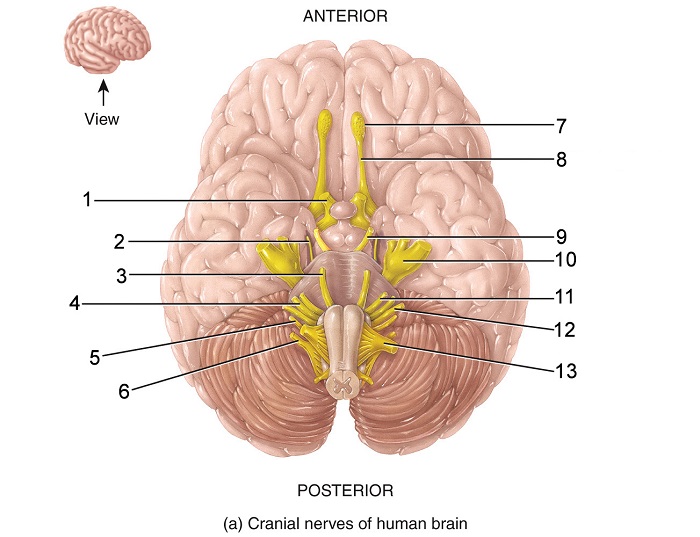
what is 8
olfactory tract
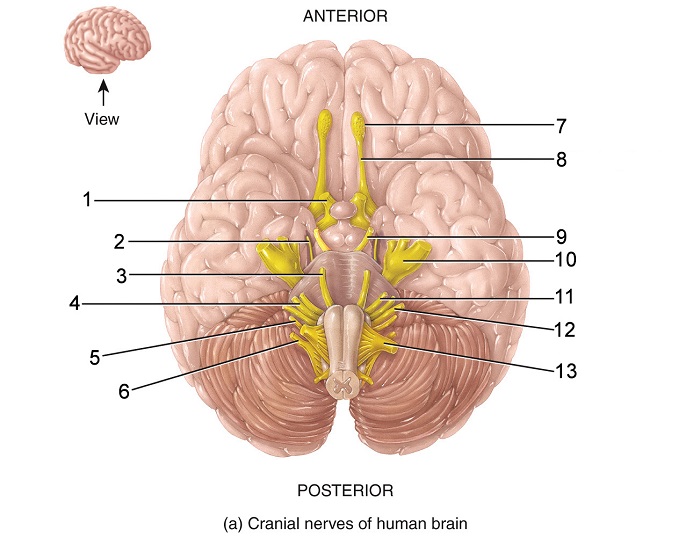
what is 9
oculomotor nerve
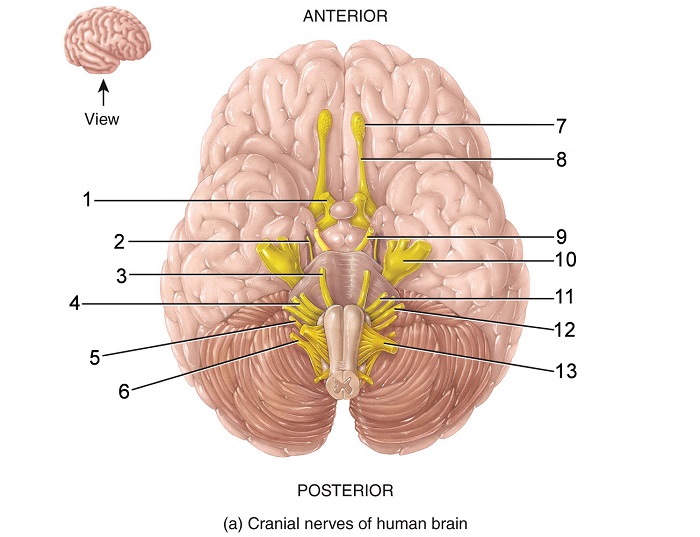
what is 10
trigeminal nerve
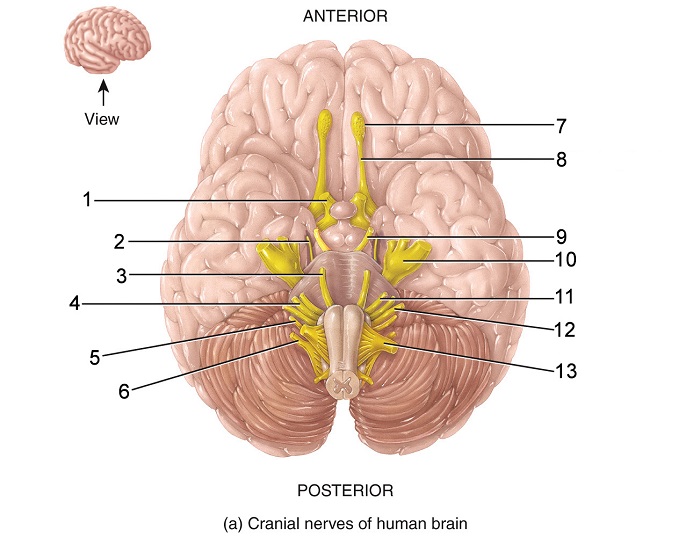
what is 11
facial nerve
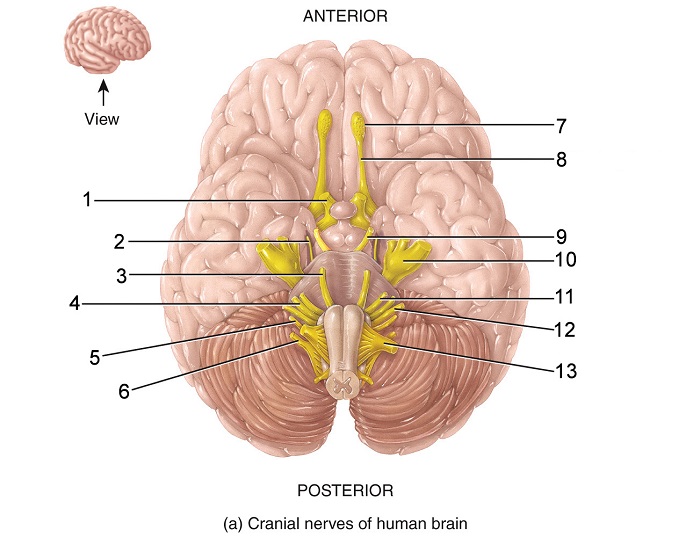
what is 12
glossopharyngeal nerve
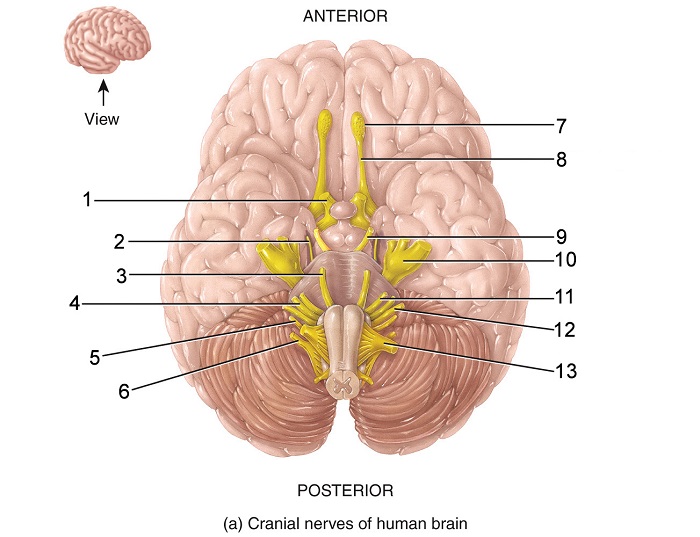
what is 13
hypoglossal nerve
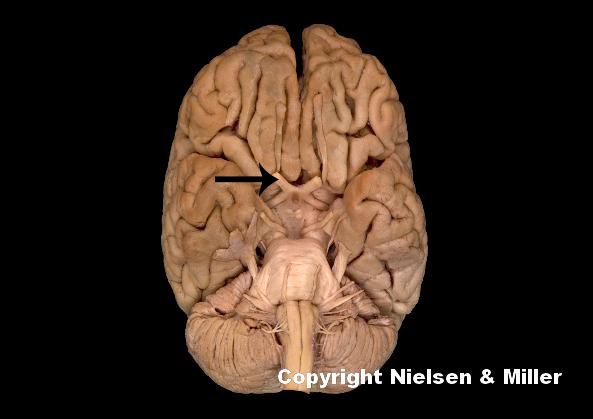
what is indicated nerve
optic nerve
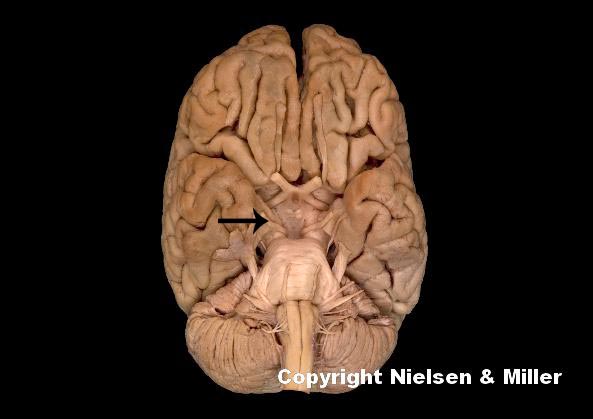
what is indicated nerve
oculomotor
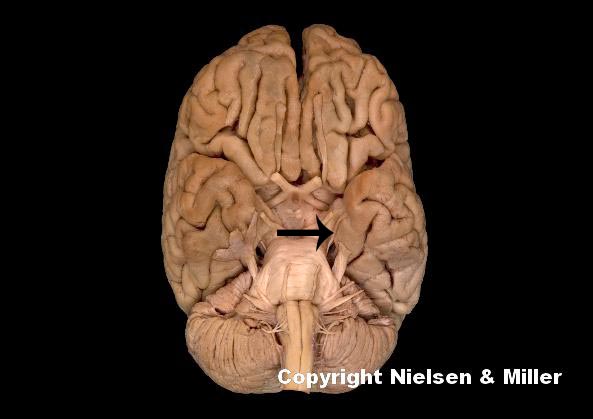
what is indicated nerve
trochlear
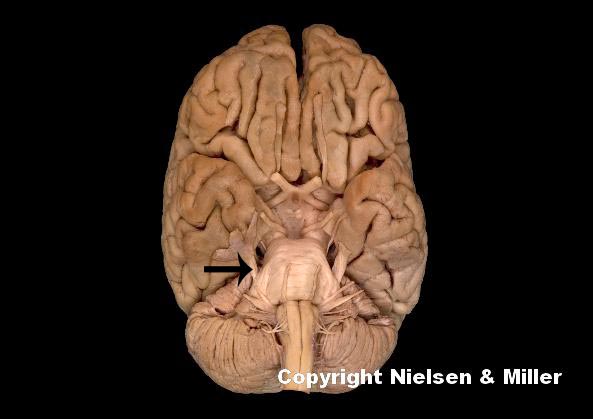
what is indicated nerve
trigeminal
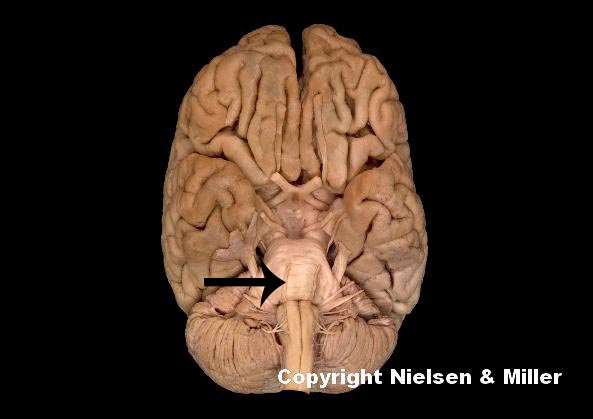
what is indicated nerve
abducens
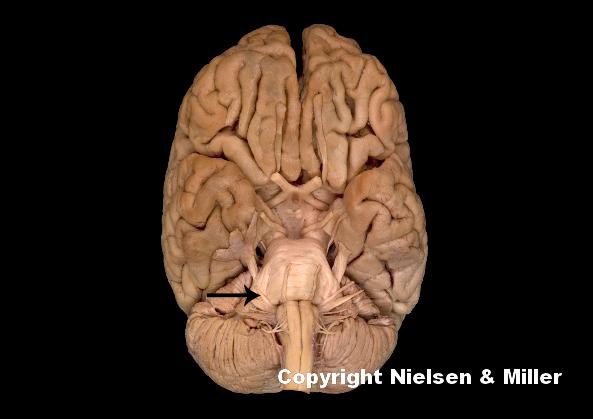
what is indicated nerve
facial
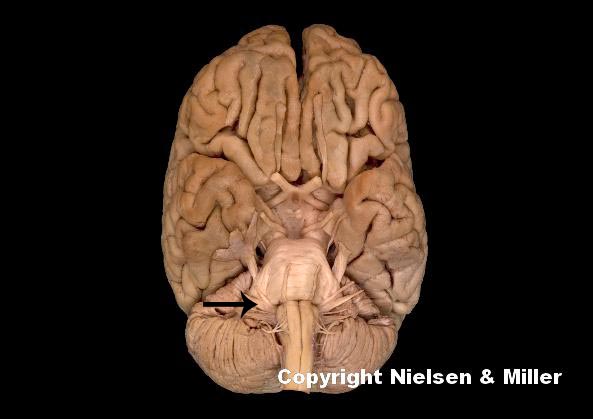
what is this indicated nerve
vestibulocochlear
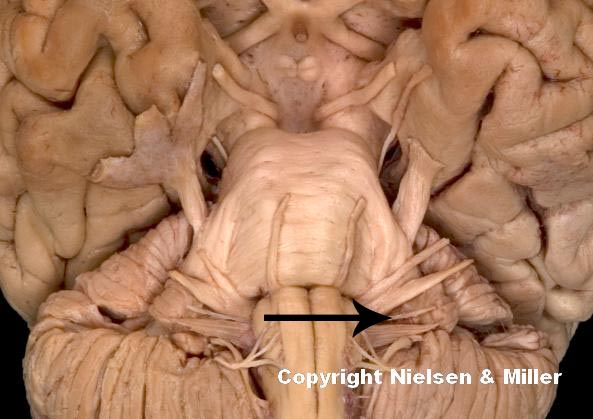
what is indicated nerve
glossopharyngeal
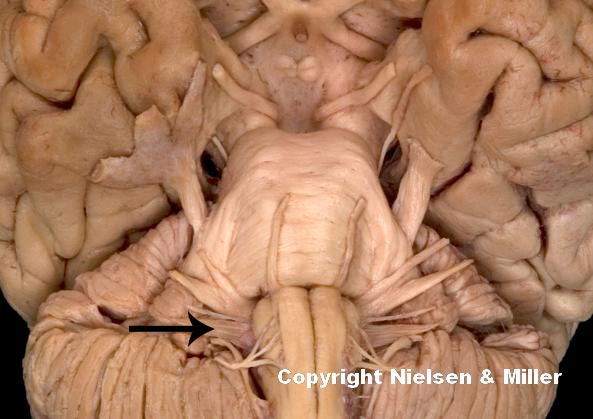
what is indicated nerve
vagus
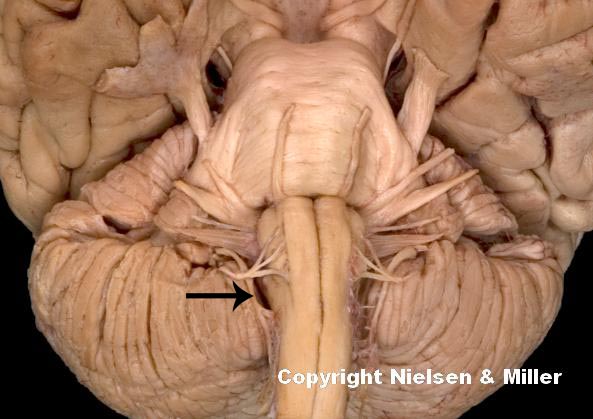
what is indicated nerve
accessory
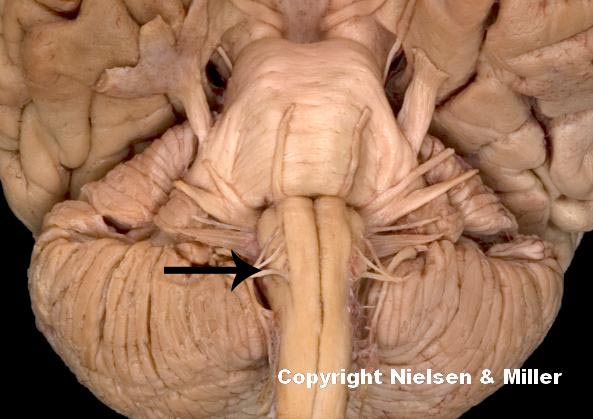
this indicated cranial nerve functions in ____, manipulation of food, swallowing
speech
the trochlear nerve is primarily _____
motor
the trigeminal nerve is _____
sensory and motor
the abducens nerve is primarily ____
motor
the facial nerve is ____
sensory and motor
the vestibulocochlear primary function is ____
sensory
the glossopharyngeal nerve is _____
sensory and motor
the vagus nerve is _____
sensory and motor
the hypoglossal nerve is primarily _____
motor
the accessory nerve is primarily ____
motor
injury to this nerve causes Bell’s palsy - a loss of taste, decreased salivation, and loss of ability to close eyes
facial
injury to this nerve causes loss of taste sensation, decreased salivation, and difficulty swallowing
glossopharyngeal
injury to this nerve causes paralysis of vocal cords, interferes with swallowing, increased heart rate, and interrupts sensation from organs
vagus
what nerve controls smell
olfactory
what nerve controls vision
optic
what nerve controls rectus eye muscle movement
oculomotor
what nerve controls oblique eye muscle movement
trochlear
what nerve controls cutaneuous sensations and chewing
trigeminal
what nerve controls movement of eyeballs
abducens
what nerve controls facial expressions, taste, salivation, and tears
facial
what nerve controls taste, swallowing, coughing, voice production
vagus
what nerve controls equilibrium and hearing
vestibulocochlear
what nerve controls taste, swallowing, speaech
glossopharyngeal
what nerve controls swallowing and movement of head and shoulders
accessory
what nerve controls speech and swallowing
hypoglossal
where does olfactory nerve come from
olafactory foramina
where does optic nerve come from
optic foramen
where does oculomotor and trochlear nerve come from
superior orbital fissure
what nerve is in opthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular foramen
trigeminal nerve
where does abducens nerve come from
superior orbital fissure
where does vestibulocochlear nerve come from
internal auditory meatus
where do glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerve come from
jugular foramen
where does hypoglossal nerve come from
hypoglossal canal