Microanatomy Muscle Fiber Model- lab practical 2 study
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Myofibrils
Microscopic protein filaments that make up muscle cells.
(number 1 in the image)
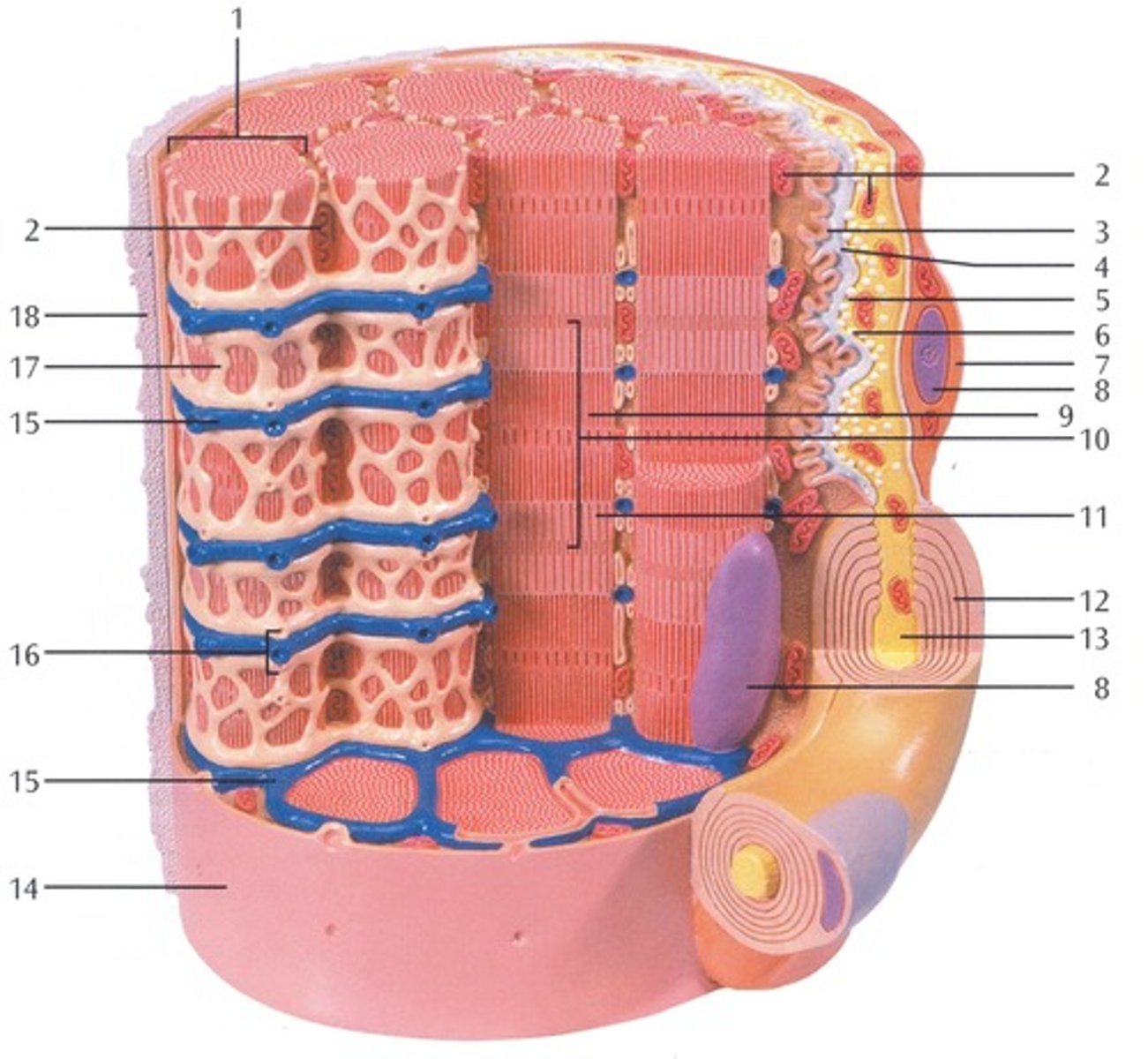
Mitochondrium
organelle where cellular respiration occurs and most ATP is generated
(number 2 in the image)
Postsynaptic Membrane
the cell membrane opposite the terminal button in a synapse; the membrane of the cell that receives the message
(number 3 in the image)
Synaptic Gap with Basal Lamina
(number 4 in the image)
presynaptic membrane
the membrane of a terminal button that lies adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane and through which the neurotransmitter is released
(number 5 in the image)
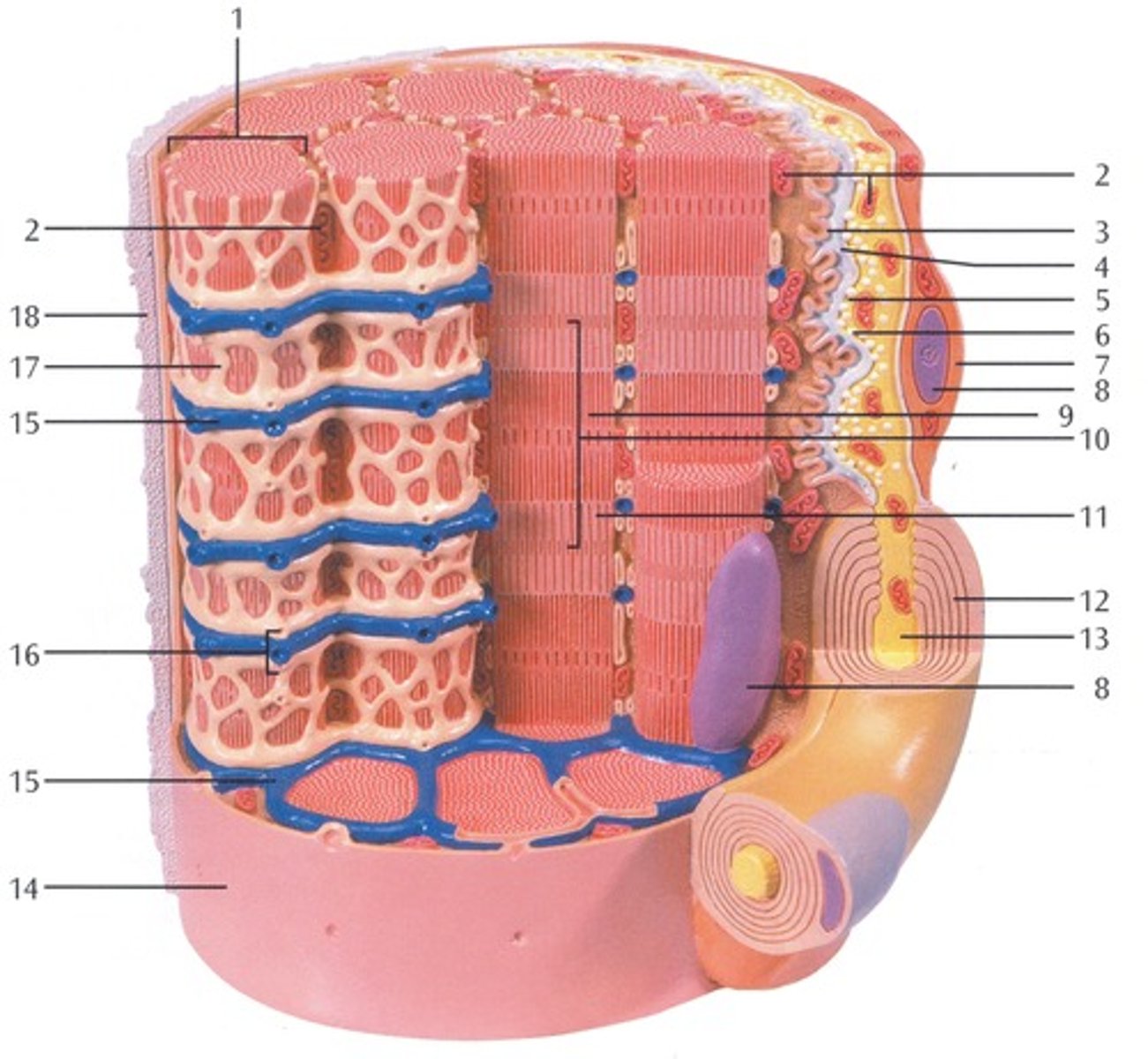
Presynaptic Vesicle
(number 6 in the image)
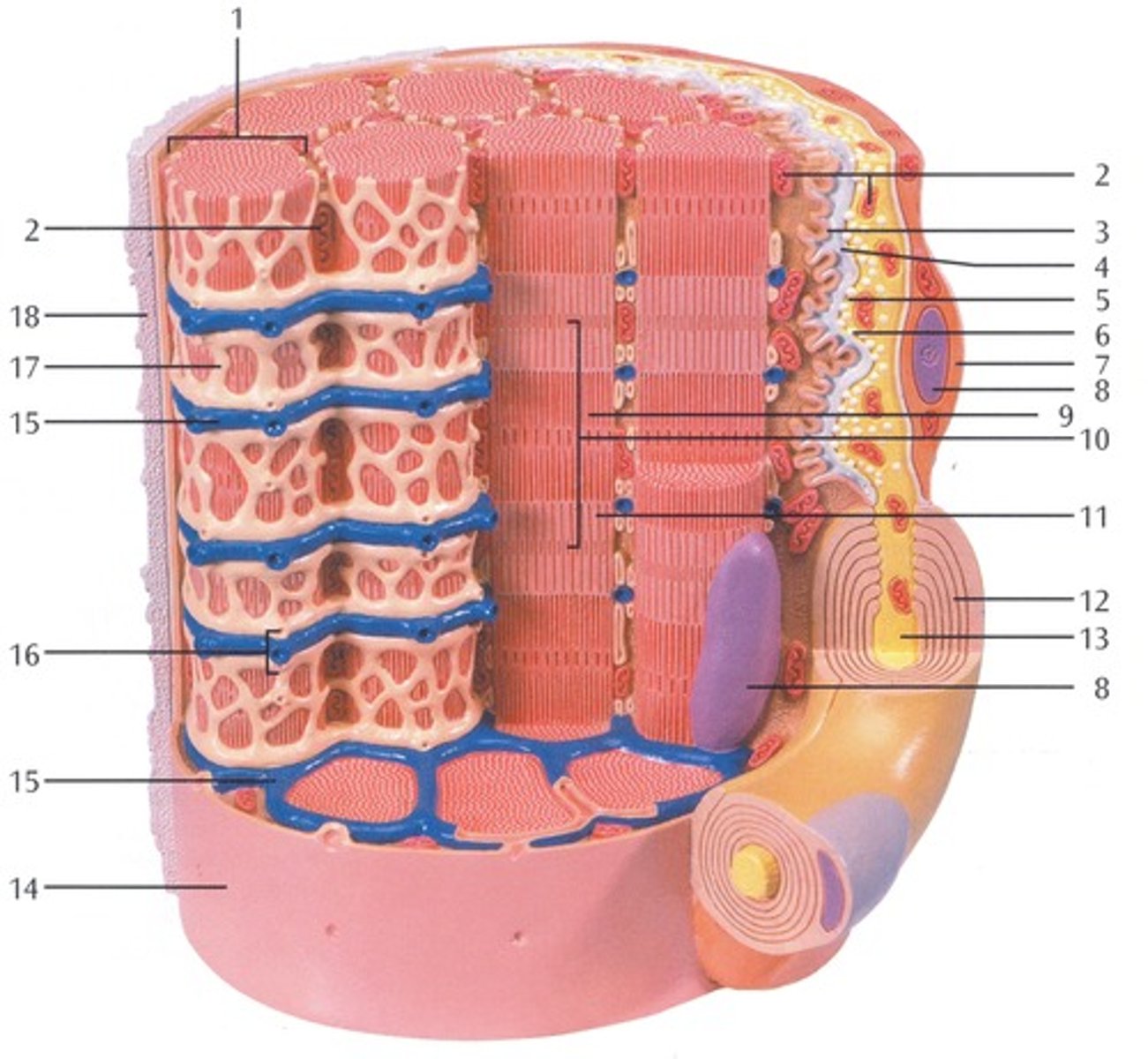
Schwann Cell
Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin.
(number 7 in the image)
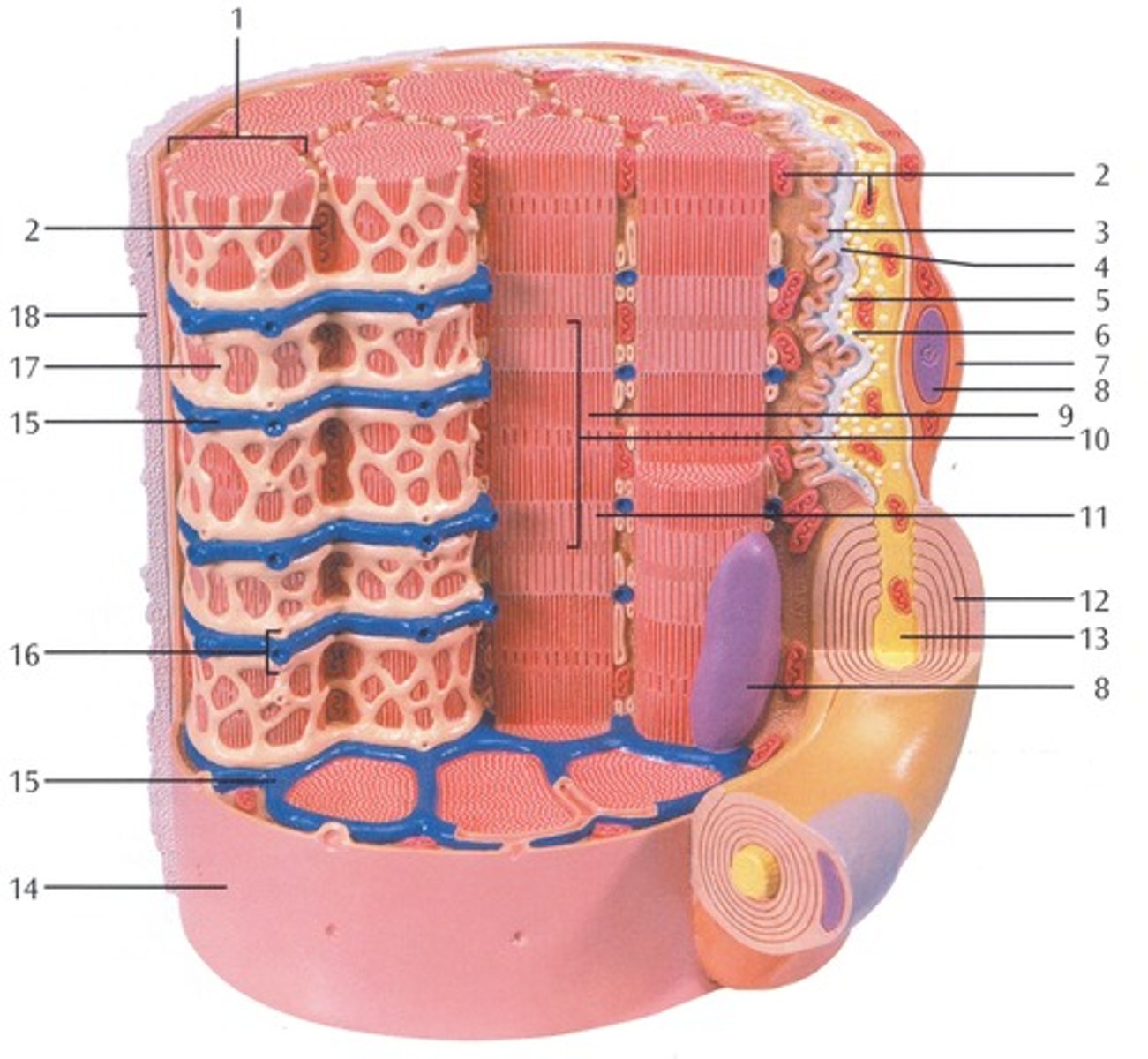
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
(number 8 in the image)
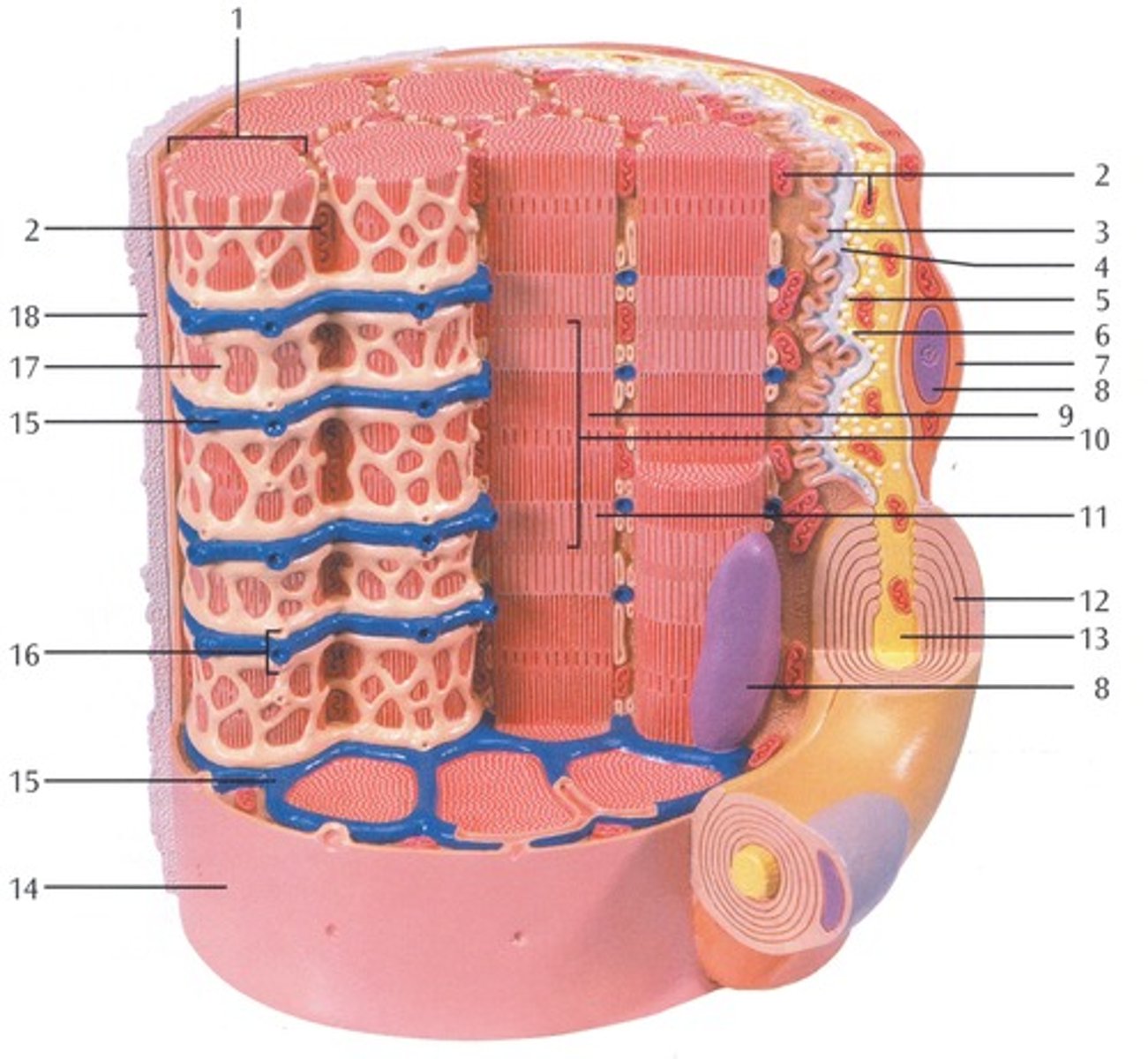
Myosin and actin filament
(number 9 in the image)
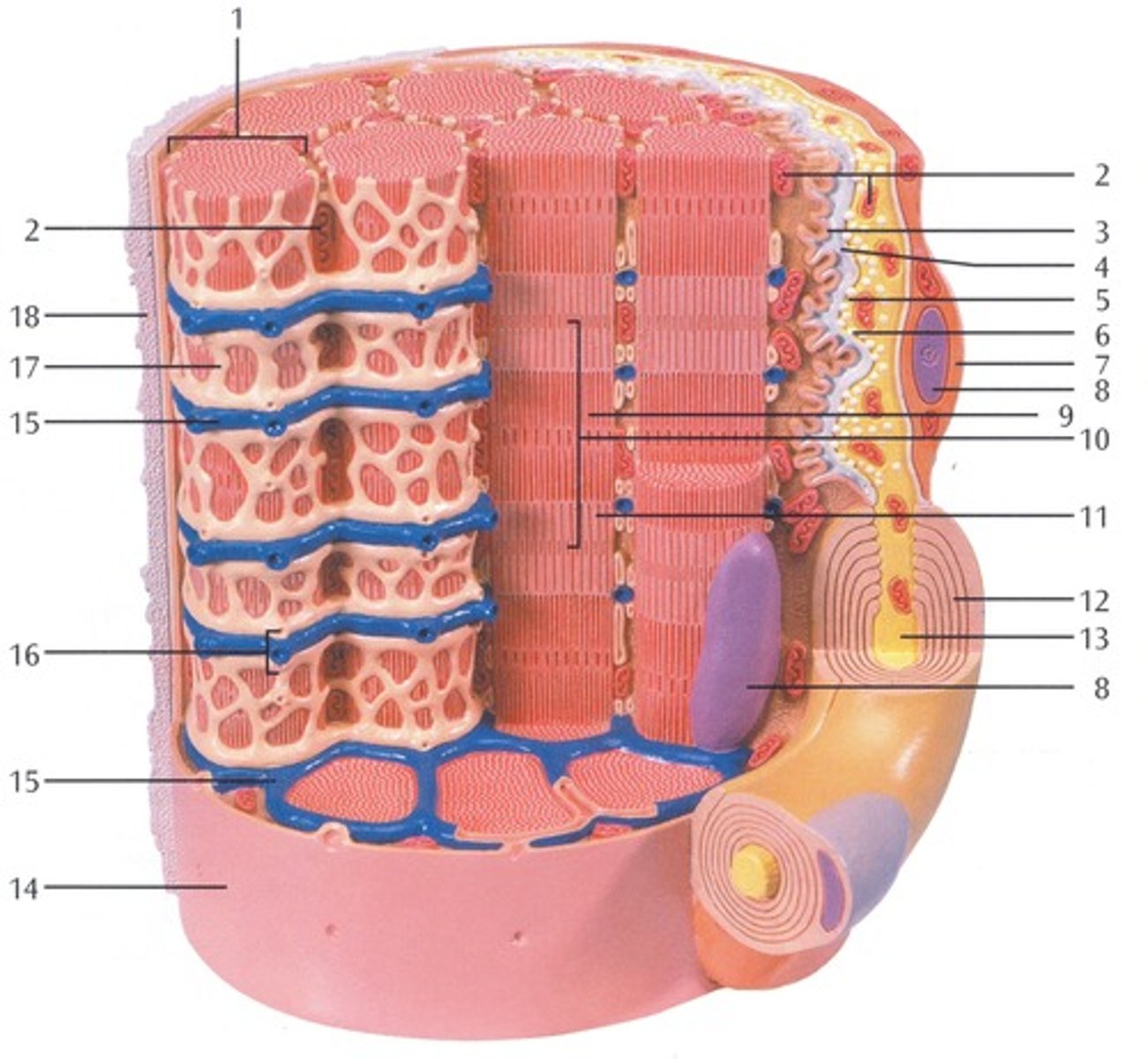
Sacromere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
(number 10 in the image)
Actin Filament
twisted protein fibers that are responsible for cell movement
(number 11 in the image)
Myelin Sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
(number 12 in the image)
Neurofibers
structures in the neuron that carry information inside the neuron from the dendrites to the terminal branches
(number 13 in the image)
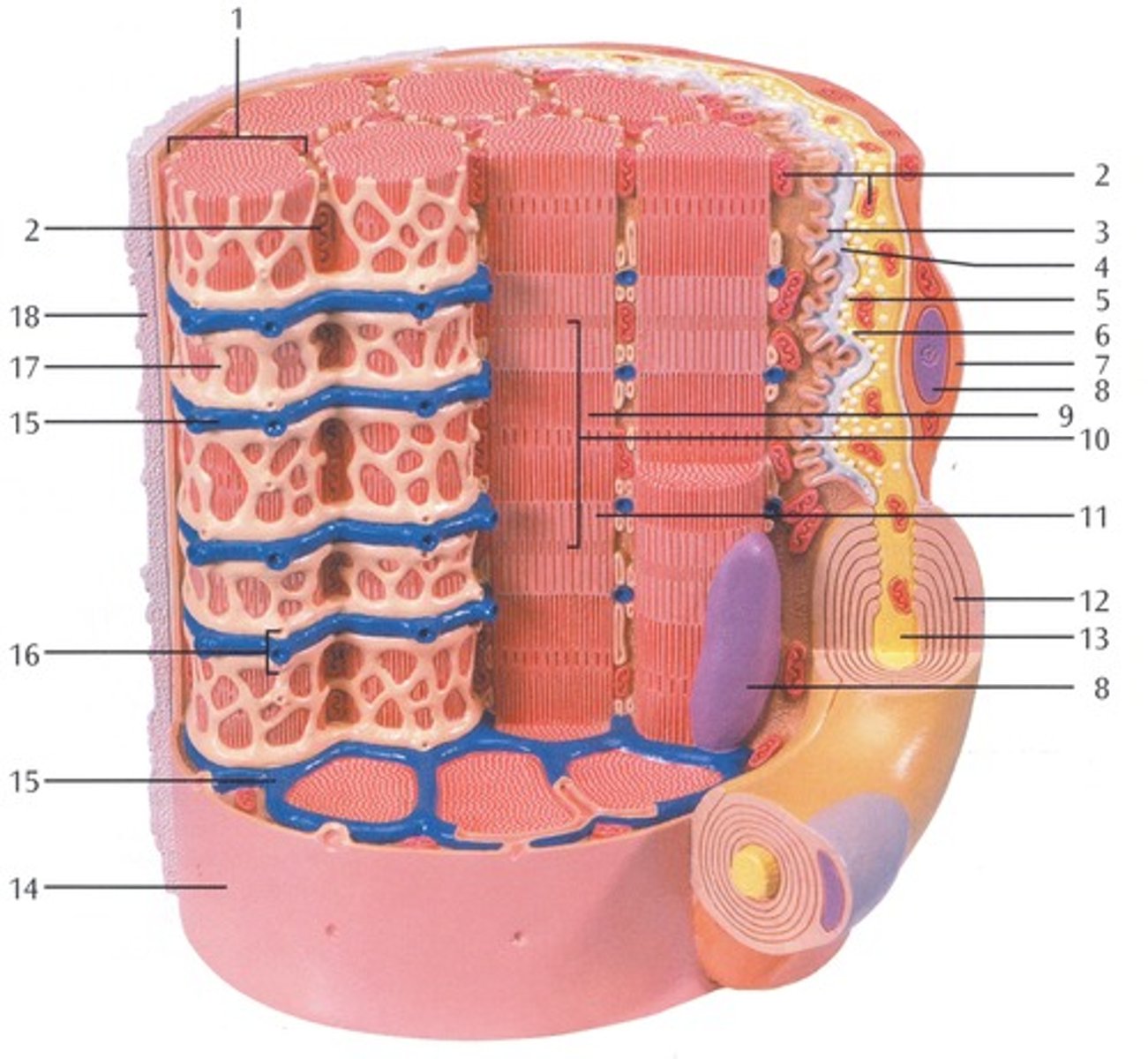
Cell membrane (sarcolemma)
semipermeable membrane that separates the cell from the extracellular environment
(number 14 in the image)
Transverse Membrane Tube
(number 15 in the image)
Triad
(number 16 in the image)
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium.
(number 17 in the image)
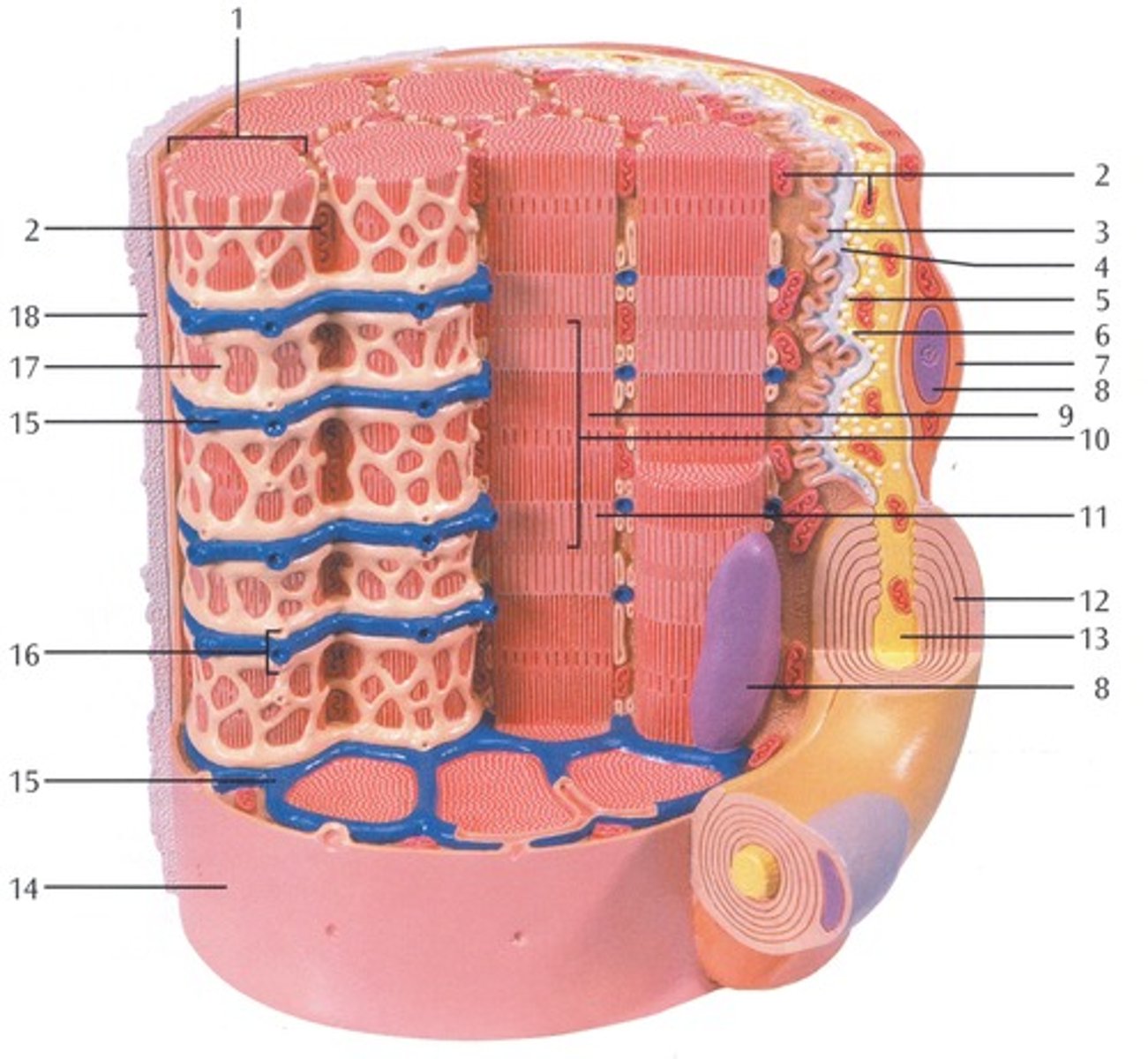
Basal Lamina
thin extracellular layer that lies underneath epithelial cells and separates them from other tissues
(number 18 in the image and on the back side of the model covered by reticular fibers)
Reticular fibers
Fibers made of collagen fibers that are very thin and branched. Forma tightly woven fabric that joins connective tissue to adjacent tissues.
(the fibers covering the basal lamina on the back side of the model)