Biology Study Set: Key Terms & Definitions for Final Exam
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from
an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Which is an example of an organ?
Heart
When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same, the molecules will
Move across the membrane in both directions
The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of?
Proteins
Compare and contrast passive and active transport across cell membranes
Passive - Particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, does not use cellular energy,
Active - Includes endo and exocytosis, requires cellular energy, particles more from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration
Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into the compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use?
Mitochondrion
The model shows a substance crossing a cell membrane. Which of the following describes the process?
The model shows the process of diffusion because the solute particles are moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
The illustration shows a model of the transport of solute particles from outside the cell to inside the cell. Wha type of cell transport is shown in the model?
The model shows active transport because energy is required for solute particles to cross the cell membrane.
A cell is placed in an isotonic solution. How does the cell maintain homeostasis in this environment?
Water will move across the cell membrane in both directions because the concentration of solute particles is the same inside and outside.
Which of the following statements is part of the cell theory?
All cells are produced from existing cells
Which scientist was the first to use a light microscope to observe cells in a slice of cork?
Robert Hooke
The cells of all organisms contain DNA. In cells of which of the following groups is the cellular DNA enclosed in a nucleus?
Eukaryotes
The cell theory applies to
all living things
Which of the following structures serves as the cells boundary from its enviroment?
Cell membrane
Which of the following is a function of a cell membrane?
Regulates which materials enter and leave the cell
Lysosomes are an organelle that contain enzymes. Which of the following is a function of lysosomes?
Break down lipids, carbohydrates and proteins
Which of the following structures are typically present in both plant and animal cells?
Mitochondria
Which organelles allow plants to support heavy structures such as leaves and flowers?
The vacuoles because they are filled with fluid which provide rigidity
All cells contain cell membranes. Which of the following describes the composition of cell membranes?
Cell membranes are composed of lipid molecules which provide a flexible structure
Which sequence correctly traces the path of a protein in the cell?
rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, released from the cell
Based on the structures of erythrocytes, how do red blood cells help maintain homeostasis in mammalian organisms?
Oxygen diffuses into and out of red blood cells. The biconcave shape of erythrocytes provides an increased surface area on the cells for diffusion to occur.
Which structures carry out cell movement?
Microtubules and Microfilaments
Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell?
Active transport
Which organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can use?
Lysosome
Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton?
Helps the cell keep its shape
Which of the following is an organ in the digestive system?
Stomach
Which of the following is a function of the nucleus?
Coordinating cell activity, growth, metabolism and reproduction.
Eukaryotes usually contain
Nucleus, membrane bound organelles, and genetic material stored in chromosomes.
Which of the following structures is found in the cytoplasm
Ribosome
The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by saying that
All plants and animals are made of cells
The main function of the cell wall is to
support and protect the cell
A group of similar cell that preform a particular function is called a(an)
Tissue
Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory?
Very few cells reproduce
Chlamydomonas is a genus of single-celled photosynthetic algae. Which of the following is NOT a way that chlamydomonas maintains homeostasis?
The reproductive system of chlamydomonas contains specialized cells that enable the organism to reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Multicellular organisms contain organ systems. Which of the following BEST describes the organs in an organ system?
The organs in an organ system work together to preform a specific funtction
Looking at a cell under a microscope, you note that it is a prokaryote. How do you know?
The cell lacks a nucleus
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called
Osmosis
Which of the following organisms are prokaryotes?
Bacteria
An animal cell that is surrounded by fresh water will burst because the osmotic pressure causes
Water to move into the cell
Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells?
Chloroplast
Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is
usually made of tough fibers
Which organelle helps provide cells with energy?
mitochondria and chloroplasts
You will NOT find a cell wall in which of these kinds of organisms?
Animal
Why is the nucleus important to cells?
The nucleus contains coded instructions for making proteins
Which structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus?
Ribosomes
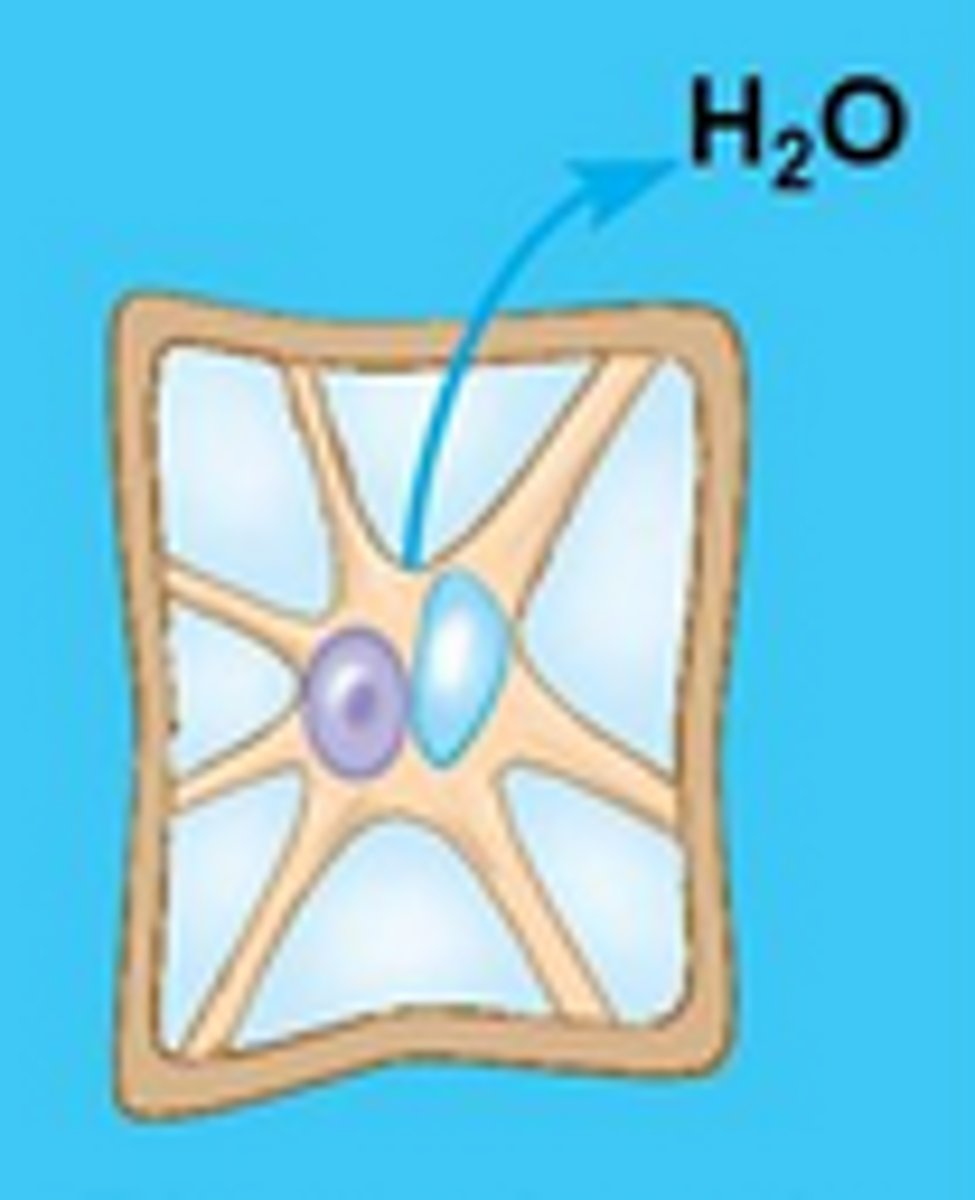
What type of solution is surrounding the plant cell below and what is the proper terminology for this environment for plants?
Hypertonic; Plasmolyzed
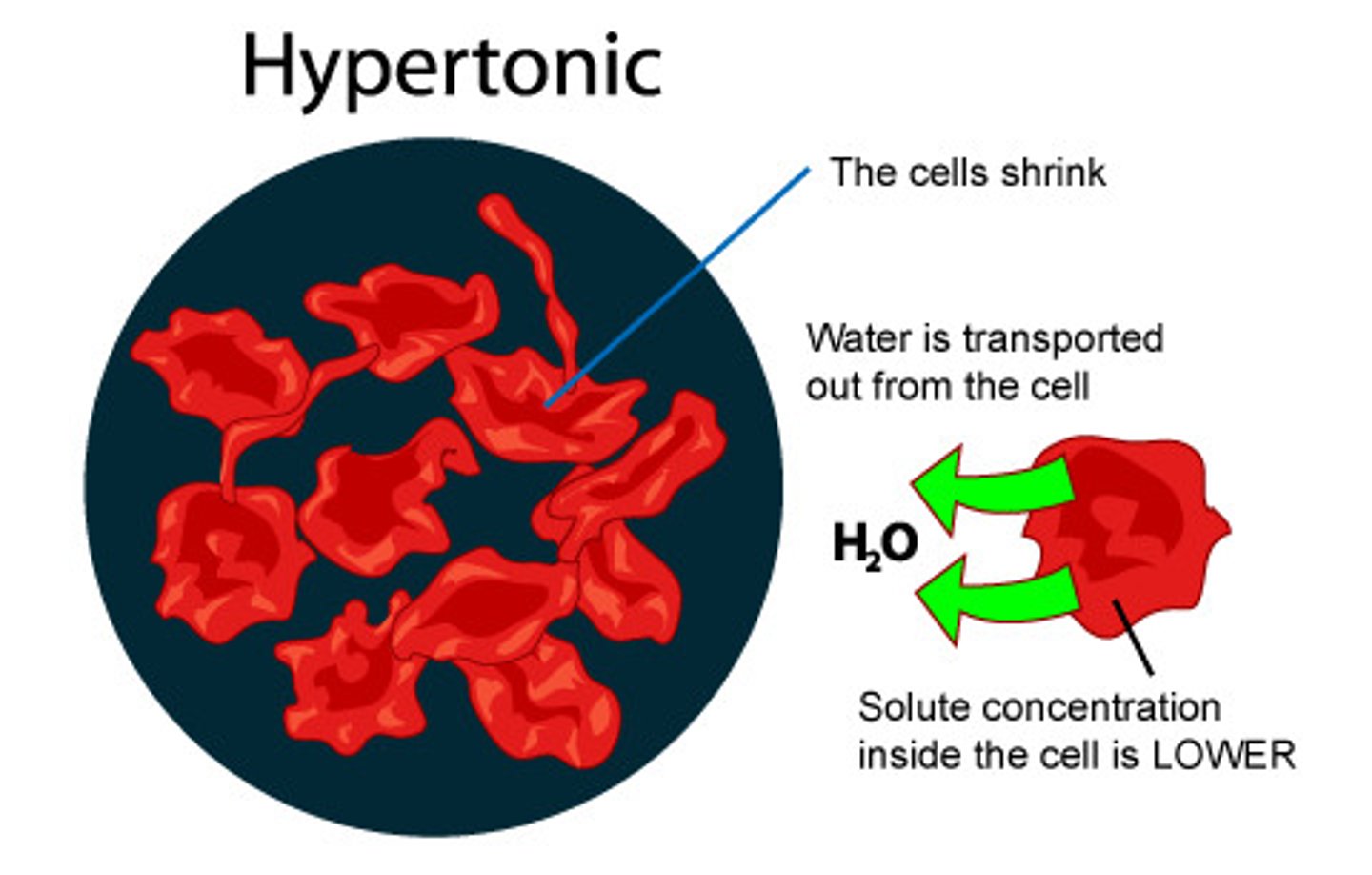
What type of solution are the red blood cells surrounded by and what scientific term applies to the scenario?
Hypertonic; Crenated
What are products of the light dependent reactions?
All of the above
Which of the following acts as an electron carrier in cellular respiration?
NAD+
Which of the following affects the rate of photosynthesis?
All of the above
The starting molecule for the Krebs cycle is
pyruvic acid
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into
oxygen and high energy sugars and starches
Which pathway represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
H20--->NADPH---->Clavin Cycle
Why does the inside of the thylakoid membrane become positively charged during the light dependent reactions?
H+ ions are released as water splits
One cause of soreness is
Lactic acid fermentation
Photosynthesis is to chloroplasts as cellular respiration is to
Mitochondria
Where do the light-dependent reactions take place?
within the thylakoid membranes
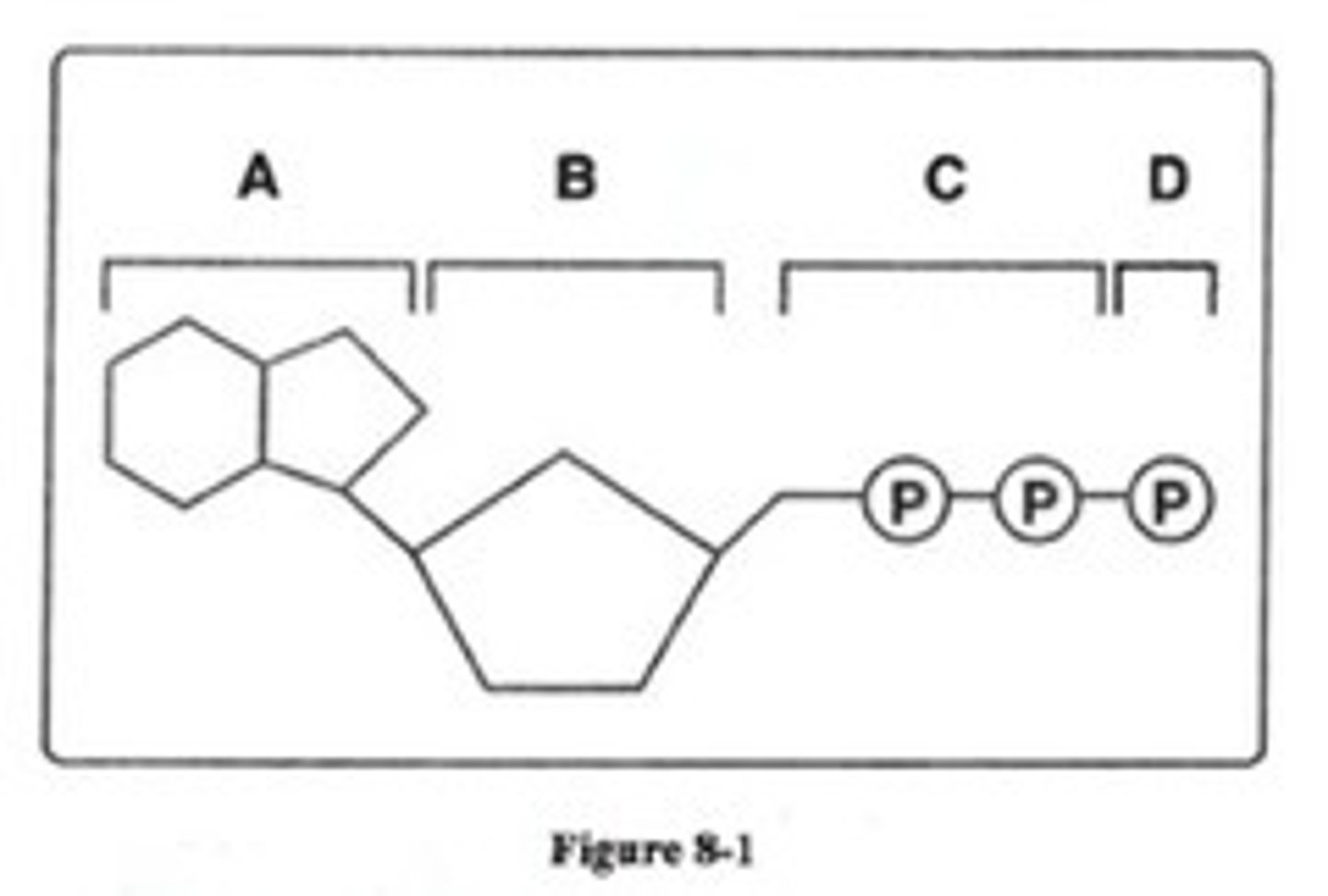
In Figure 8-1, between which parts of the molecule must the bonds be broken to form an ADP molecule?
C and D
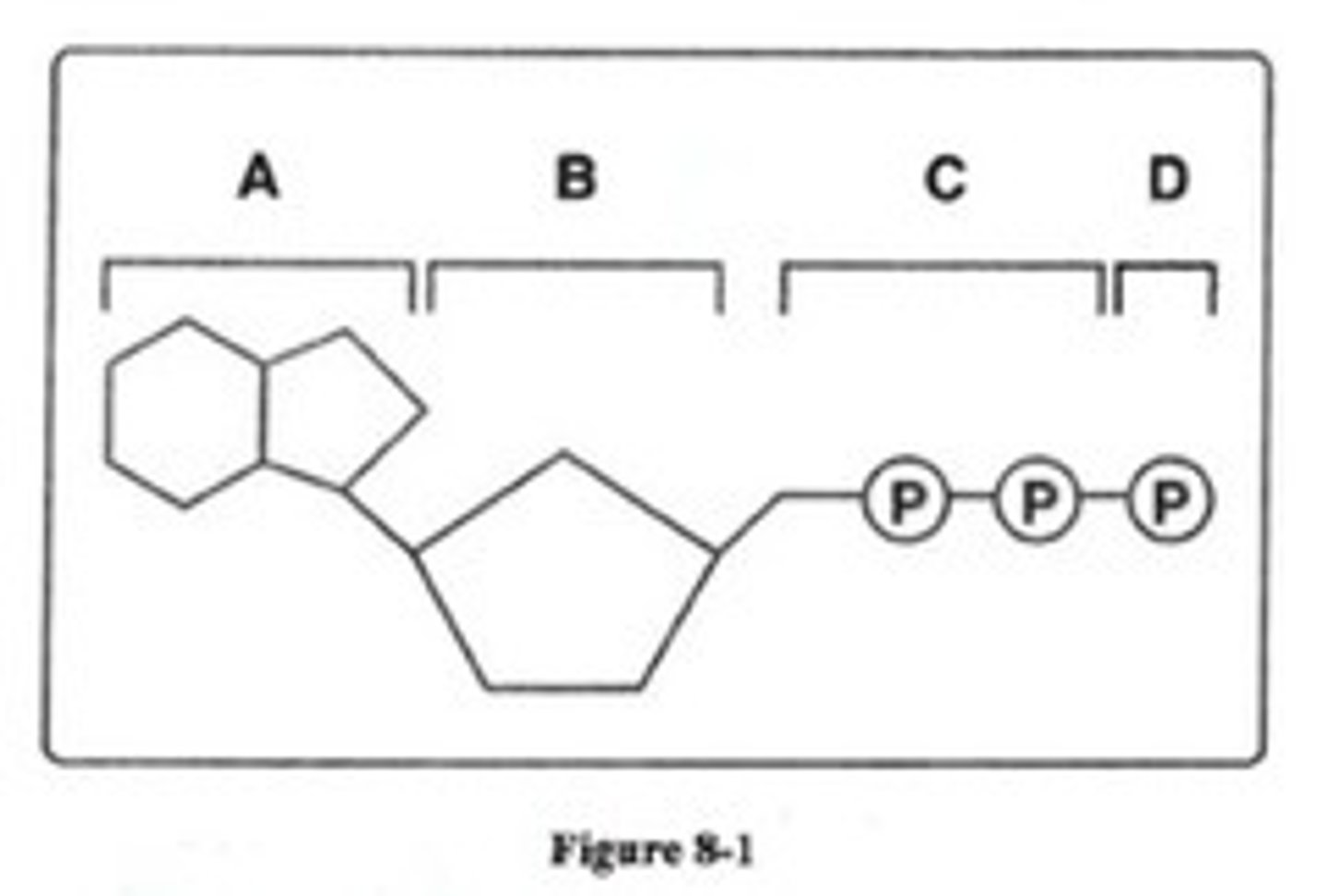
Which structures shown in figure 8-1 make up an ATP molecule?
A,B,C, and D
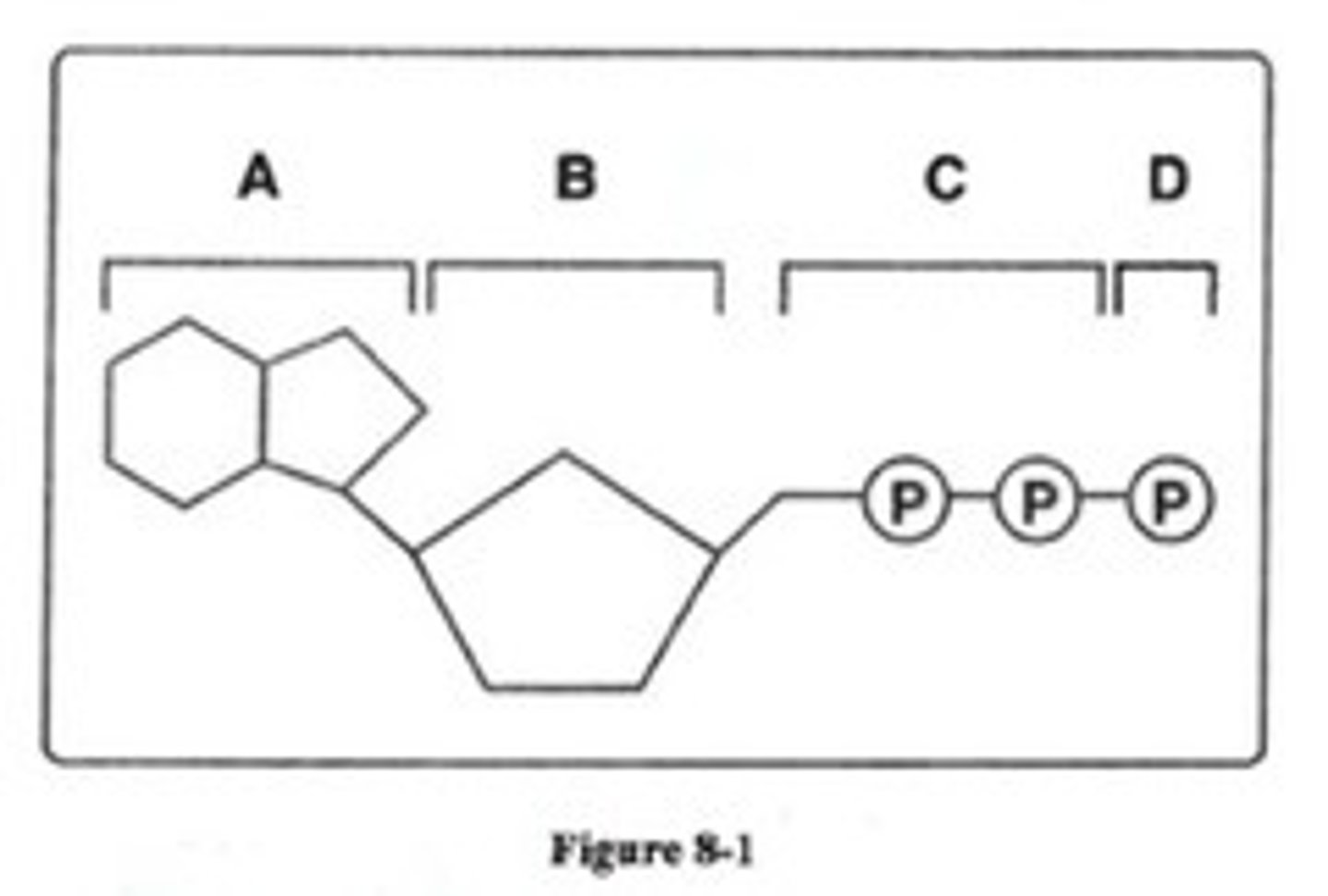
Look at Figure 8-1. All of the following are parts of an ADP molecule EXCEPT
Structure D
What is a product of the Calvin cycle?
high-energy sugars
What are the three parts of an ATP molecule?
adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups
Most plants appear green because chlorophyll
does not absorb green light
Unlike photosynthesis, cellular respiration occurs in
All eukaryotic cells
Which of there is a product of cellular respiration?
Water
The stroma is the region outside the
Thylakoids
Which of the following is not an example of a heterotroph?
Grass
The Krebs Cycle produces
Electron Carriers
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in cellular respiration?
glycolysis--->krebs cycle--->electron transport
What are the reactants in the equation for cellular respiration?
Glucose and Oxygen
Which of the following is released during cellular respiration?
Energy
If the scientist's predictions are shown to be accurate, then which conclusion about photosynthesis do they support? (HINT: Apply scientific principles such as the Law of Conservation of Mass.)
Some but not all of the matter in carbon dioxide is converted to sugars
Where are photosystems I and II found?
thylakoid membrane
What is the correct equation for cellular respiration?
6O2+C6H12O6---->6CO2+6H2O+Energy
The Calvin cycle is another name for
light independent reactions
The air bubbles and spongy texture of bread are due to which process?
Alcoholic fermentation
In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is followed by
The Krebs cycle
Plants gather the sun's energy with light-absorbing molecules called
Pigments
Cellular respiration is called an aerobic process because it requires
Oxygen
Organisms, such as plants, that make their own food are called
Autotrophs
Milk is converted to yogurt under certain conditions when the microorganisms in the milk produce acid. Which process would be key in the production of yogurt?
Lactic acid fermentation
Breathing heavily after a race is your body's way of
Repaying an oxygen debt
Which of the following is an autotroph?
tree
Which of the following is not a stage of cellular respiration?
fermentation
Cellular respiration uses one molecule of glucose to produce
36 ATP molecules
A granum is
stack of thylakoids
The two main types of fermentation are called
alcoholic and lactic acid
The energy of the electrons passing along the electron transport chain is used to make
ATP
A student is collecting gas off of a plant in bright sunlight at a temperature of 27°C. The gas being collected is probably
Oxygen
In eukaryotes, the electron transport chain occurs in the
Mitochondria
Glycolysis requires
an energy input
The starting molecule for glycolysis is
glucose
Which of the following is not a step in the light dependent reactions
ATP and NADPH are used to produce high energy sugars
Which of these processes takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell?
Glycolysis
Organisms that cannot make their own food and must obtain energy from the foods they eat are called
heterotrophs
Which of the following passes high energy electrons into the electron transport chain?
NADH and FADH2
Which organism is NOT likely to carry out cellular respiration?
anaerobic bacterium
Which step is the beginning of photosynthesis?
Pigments in photosystem II absorb light
The electron transport chain can be found in
All of the above
The calvin cycle takes place in the
stroma