American Pageant Chapter 7
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
republicanism
A philosophy of limited government with elected representatives serving at the will of the people. The government is based on consent of the governed.
radical Whigs
A group of British political commentators. They were very nervous about the power of Parliament and the arbitrary powers of the monarch. They warned the colonists to be always on the lookout for a violation of their rights.

mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought

Sugar Act
(1764) British deeply in debt partly due to French & Indian War. English Parliament placed a tariff on sugar, coffee, wines, and molasses. colonists avoided the tax by smuggling and by bribing tax collectors.

Quartering Act
March 24, 1765 - Required the colonials to provide food, lodging, and supplies for the British troops in the colonies.

stamp tax
Passed by Parliament in 1765, it required colonists to purchase a small stamp to be affixed to legal and other documents

admiralty courts
British courts originally established to try cases involving smuggling or violations of the Navigation Acts which the British government sometimes used to try American criminals in the colonies. Trials in Admiralty Courts were heard by judges without a jury.

Stamp Act Congress
A meeting of delegations from many of the colonies, the congress was formed to protest the newly passed Stamp Act It adopted a declaration of rights as well as sent letters of complaints to the king and parliament, and it showed signs of colonial unity and organized resistance.

nonimportation agreements
Agreements not to import goods from Great Britain. They were designed to put pressure on the British economy and force the repeal of unpopular parliamentary acts.

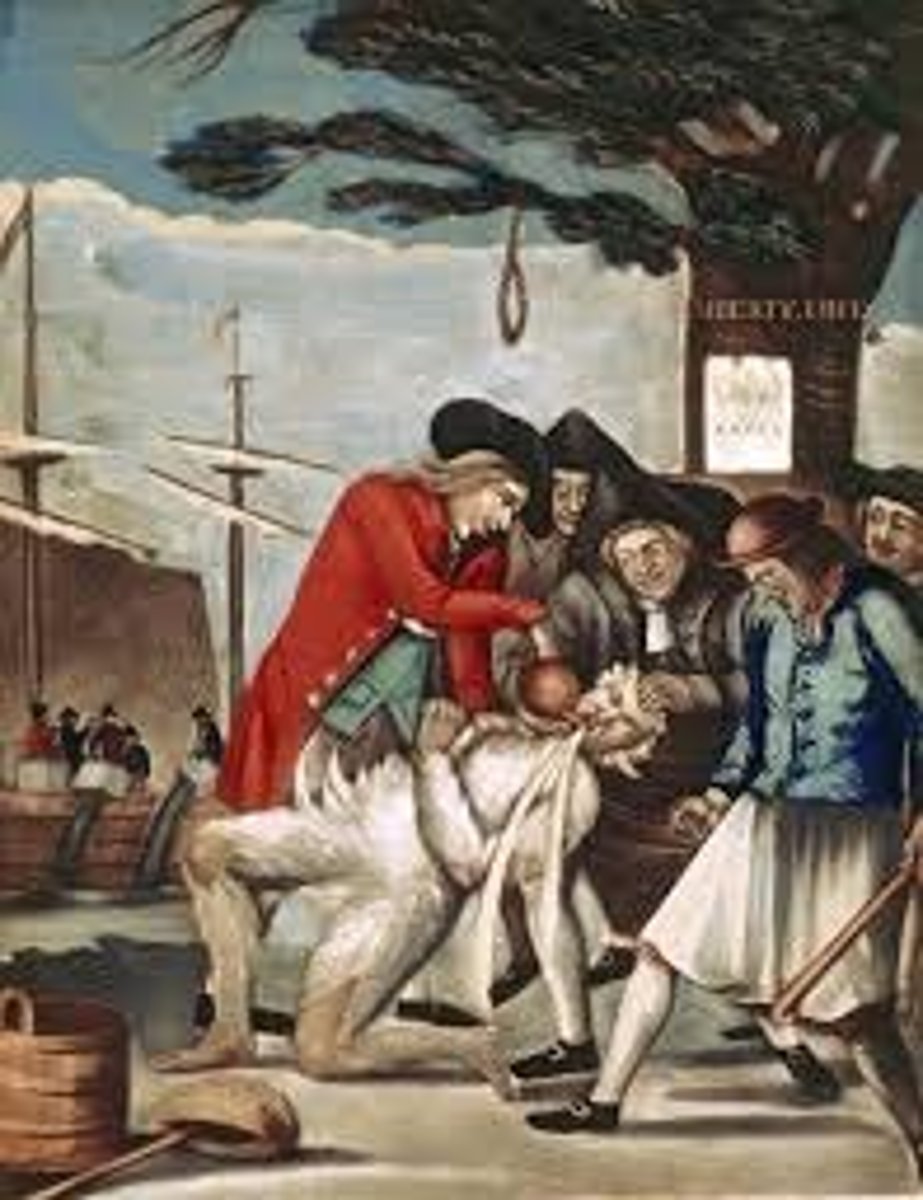
Sons of Liberty
A radical political organization for colonial independence which formed in 1765 after the passage of the Stamp Act. They incited riots and burned the customs houses where the stamped British paper was kept. After the repeal of the Stamp Act, many of the local chapters formed the Committees of Correspondence which continued to promote opposition to British policies towards the colonies. The Sons leaders included Samuel Adams and Paul Revere.

Daughters of Liberty
This orginization supported the boycott of British goods. They urged Americans to wear homemade fabrics and produce other goods that were previously available only from Britain. They believed that way, the American colonies would become economically independent.

Declaratory Act
Passed in 1766 just after the repeal of the Stamp Act, the Declaratory Act stated that Parliament could legislate for the colonies in all cases. Most colonists interpreted the act as a face-saving mechanism and nothing more. Parliament, however, continually interpreted the act in its broadest sense in order to legislate in and control the colonies.

Townshend Acts
Laws passed in 1767 that taxed goods such as glass, paper, paint, lead, and tea

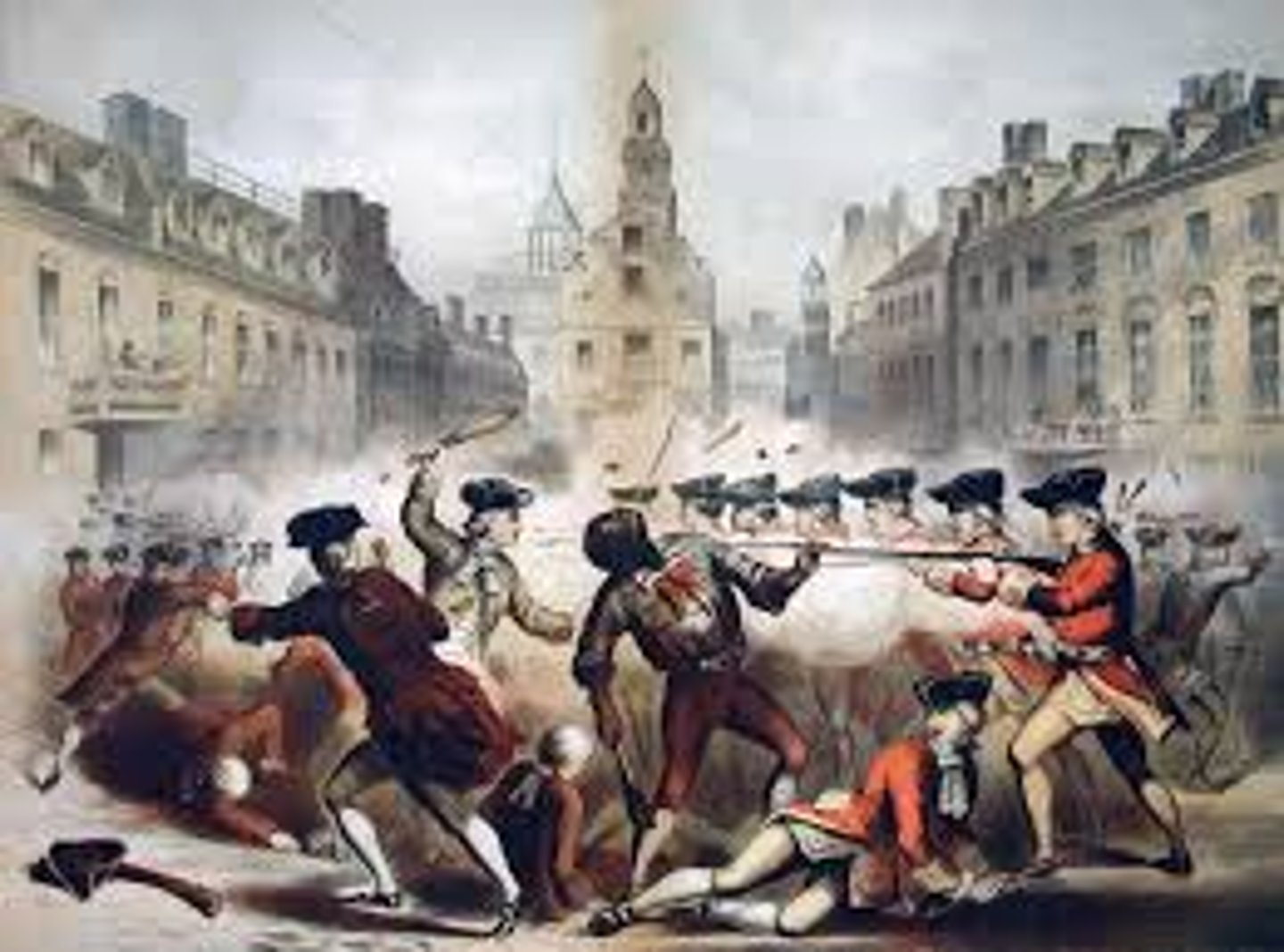
Boston Massacre
British soldiers fired into a crowd of colonists who were teasing and taunting them. Five colonists were killed. The colonists blamed the British and the Sons of Liberty used this incident as an excuse to promote the Revolution.

committees of correspondence
Committees of Correspondence, organized by patriot leader Samuel Adams, was a system of communication between patriot leaders in New England and throughout the colonies. They provided the organization necessary to unite the colonies in opposition to Parliament. The committees sent delegates to the First Continental Congress.

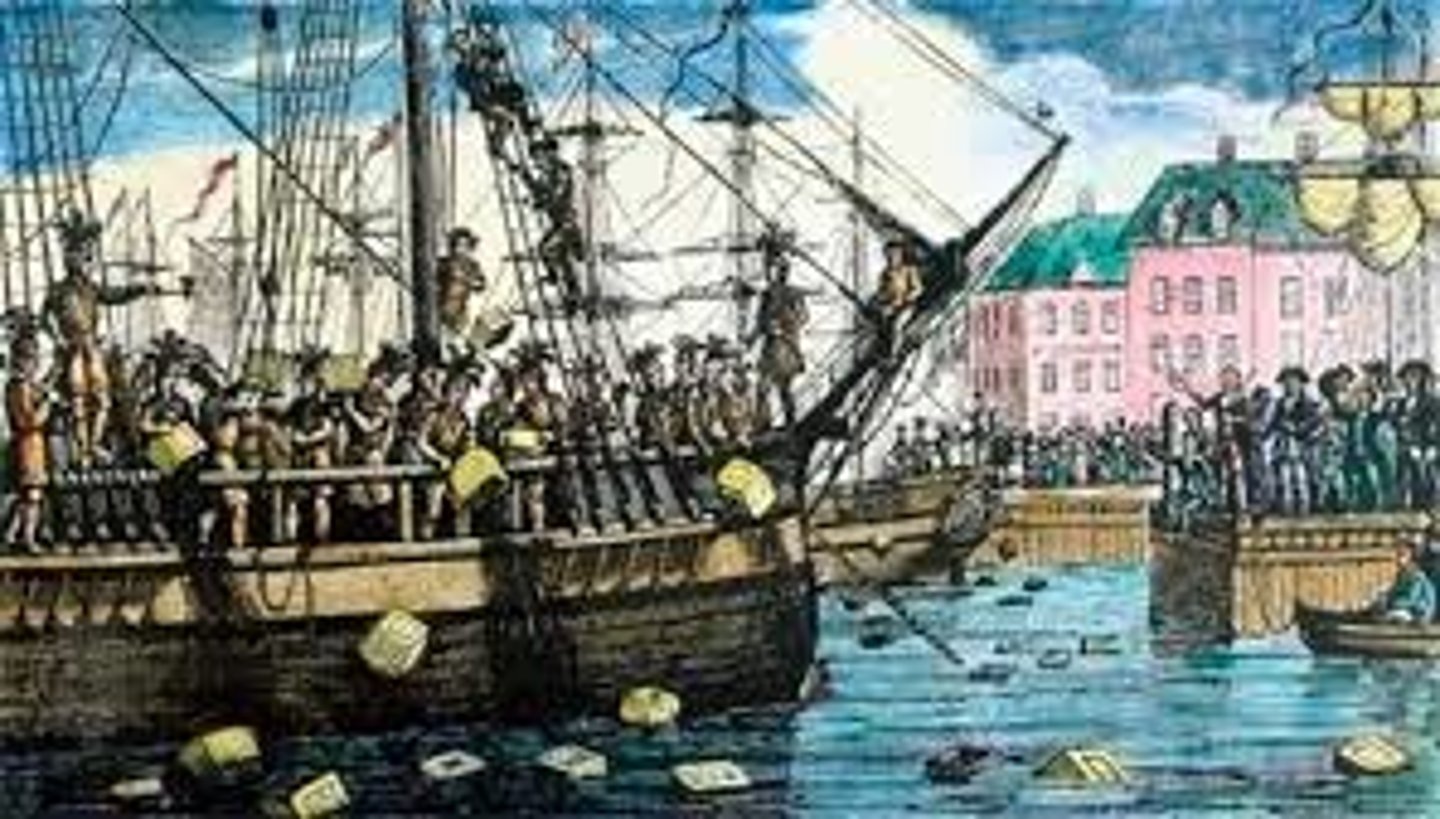
Boston Tea Party
demonstration (1773) by citizens of Boston who (disguised as Indians) raided three British ships in Boston harbor and dumped hundreds of chests of tea into the harbor

"Intolerable Acts"
in response to Boston Tea Party, 4 acts passed in 1774, Port of Boston closed, reduced power of assemblies in colonies, permitted royal officers to be tried elsewhere, provided for quartering of troop's in barns and empty houses

First Continental Congress
Delagates from all colonies except Georgia met to discuss problems with britain and to promote independence

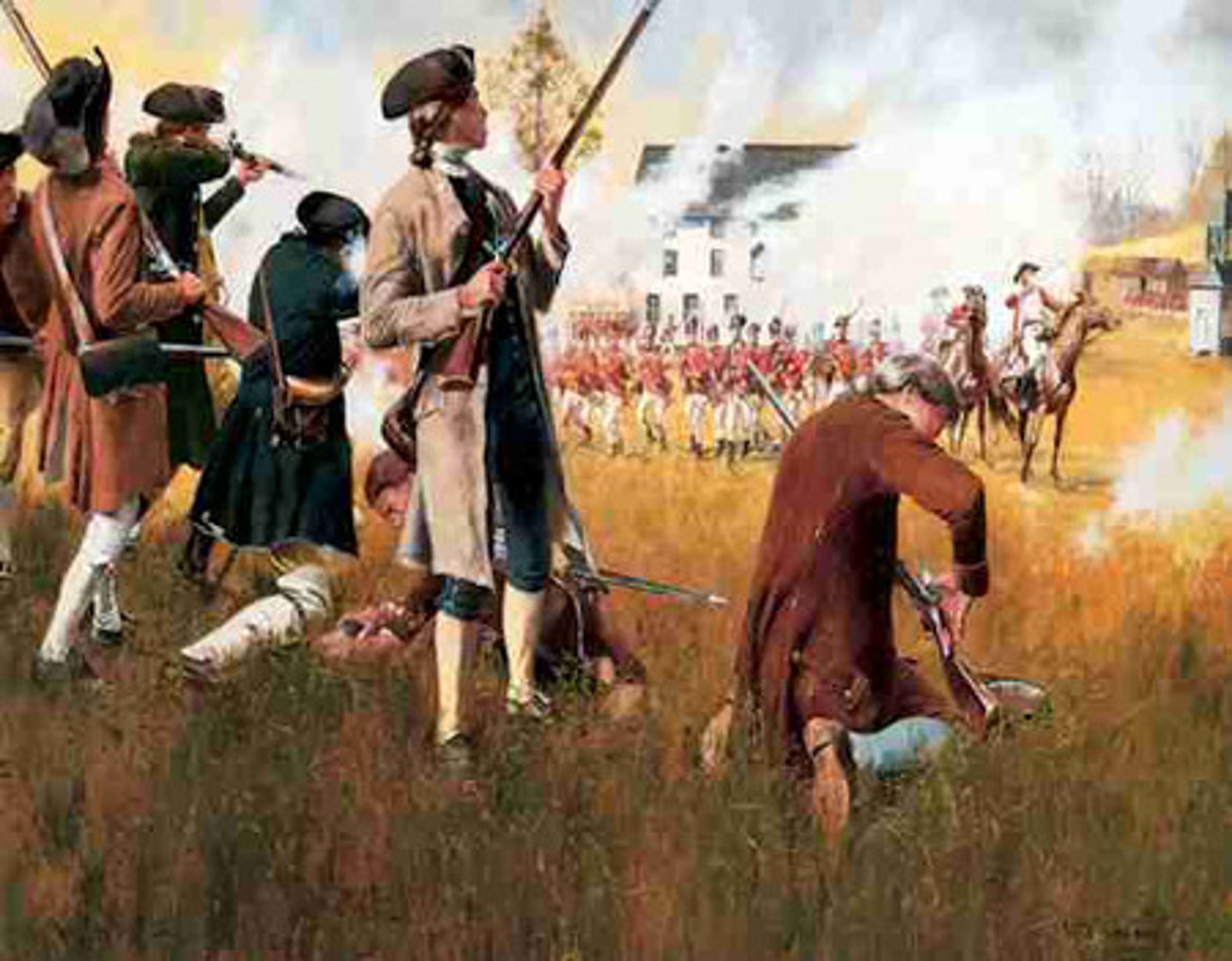
Battles of Lexington and Concord
The battles of Lexington and Concord initiated the Revolutionary War between the American colonists and the British. British governor Thomas Gage sent troops to Concord to stop the colonists who were loading arms. The next day, on April 19, 1775, the first shots were fired in Lexington, starting the war. The battles resulted in a British retreat to Boston

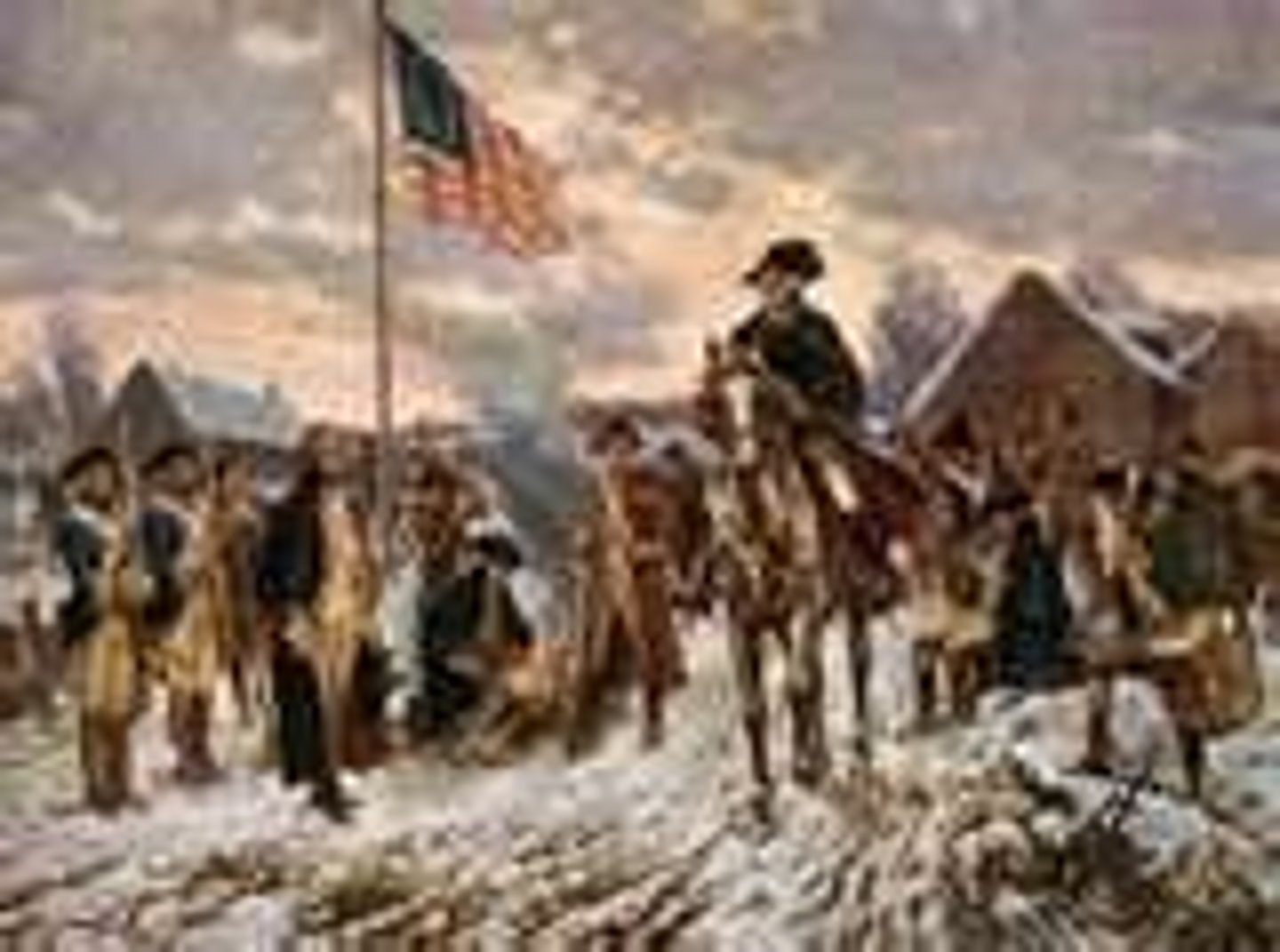
Valley Forge
Place where Washington's army spent the winter of 1777-1778, a 4th of troops died here from disease and malnutriton, Steuben comes and trains troops

John Hancock
American revolutionary patriot who was president of the Continental Congress

George Grenville
Became prime minister of Britain in 1763 he persuaded the Parliament to pass a law allowing smugglers to be sent to vice-admiralty courts which were run by British officers and had no jury. He did this to end smuggling.

Charles Townshend
government official, close to the king, likeable, sponsored taxes, "Champagne Charlie", sponsored taxes for: lead, glass, paper, paint & tea,

Crispus Attucks
Killed in Boston Massacre, black laborer, only African-American person killed in Boston Massacre. Because a martyr for African-Americans.

George III
King of Great Britain and Ireland from 1760 to 1820

Lord North
Prime Minister of England from 1770 to 1782. Although he repealed the Townshend Acts, he generally went along with King George III's repressive policies towards the colonies even though he personally considered them wrong. He hoped for an early peace during the Revolutionary War and resigned after Cornwallis' surrender in 1781.

Samuel Adams
Founder of the Sons of Liberty and one of the most vocal patriots for independence; signed the Declaration of Independence

Marquis de Lafayette
He was very rich and noble when he arrived in America at the age of 19 years old. He believed in the liberty that the Americans were fighting for and asked to help. He became a general on Washington's staff and fought hard. He was known as "the soldier's friend," and is buried in france but his grave is covered with earth from Bunker Hill.

Baron von Steuben
volunteer, general in Prussia, offered help to Patriots after Washington won the battles at Trenton & Princeton, arrived at Valley Forge in the spring of 1778

Lord Dunmore
Royal governor of Virginia who issued a proclamation promising freedom for any enslaved black in Virginia who joined the British army
