N209 - Abdomen
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
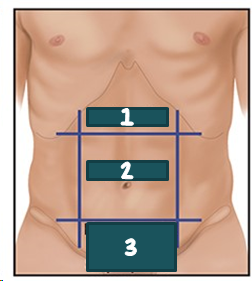
1
RUQ?
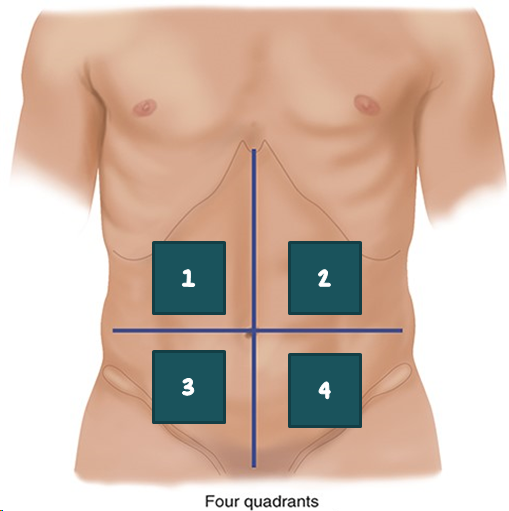
2
LUQ?
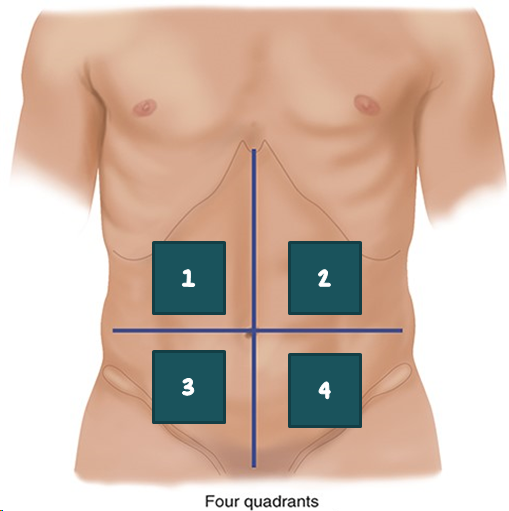
3
RLQ?
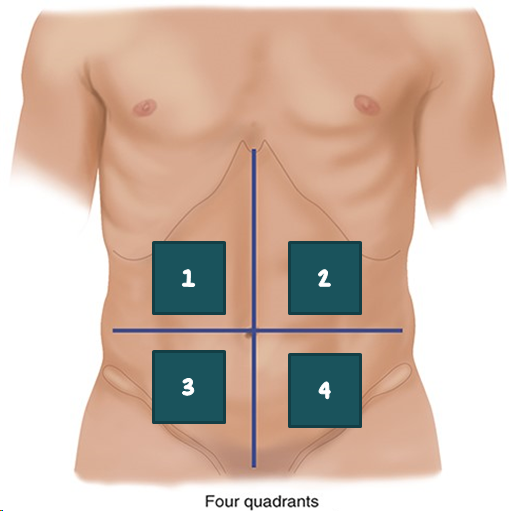
4
LLQ?
1
epigastric?
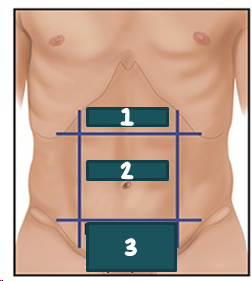
2
Umbilical?
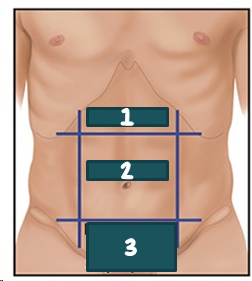
3
Suprapubic?
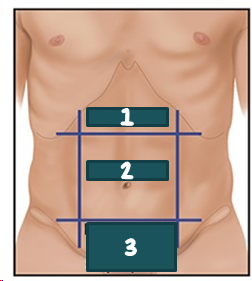
3
Hypogastric?
liver
gallbladder
duodenum
head of pancreas
right kidney & adrenal gland
part of ascending and transverse colon
Which organs are anatomically located in the RUQ?
stomach
spleen
left lobe of liver
body of pancreas
left kidney and adrenal gland
part of transverse and descending colon
Which organs are anatomically located in the LUQ?
part of descending colon
sigmoid colon
L ovary and tube
L ureter
L spermatic cord
Which organs are anatomically located in the LLQ?
cecum
appendix
R ovary and tube
R ureter
R spermatic cord
Which organs are anatomically located in the RLQ?
epigastric
umbilical
hypogastric; suprapubic
Regional names for dividing the abdomen exists, such as __________ for the area b/t the costal margins, ___________ for the area around the umbilicus, and __________ or ___________ for the area above the pubic bone.
Anorexia
What is a loss of appetite from GI disease as a result of medications, pregnancy, & mental health disorders
Pyrosis (heartburn)
= a burning sensation in esophagus & stomach from reflux of gastric acid
Visceral; internal organ
What is dull, general, poorly localized abdominal pain? What is likely the cause?
Parietal; from inflammation of peritoneum
What is sharp, precisely localized, aggravated by movement abdominal pain? What is likely the cause?
appendicitis
cholecystitis
bowel obstruction
diverticulitis
vascular occlusion
perforated organ
What are conditions with acute pain that require urgent diagnoses & referral?
Hematemesis
= occurs w stomach or duodenal ulcers (looks like “coffee grounds”)
Melena
= black or tarry stools from Occult blood from upper GI bleed or nontarry from iron medications
lower GI bleed
anal bleeding (e.g., hemorrhoids)
What does bright red blood in the stool suggest?
hepatitis
What does grey stool suggest?
peptic ulcers
_______ ______ frequently occur w use of NSAIDs, alcohol, smoking, and helicobacter pylori
Adequate lighting
Expose abdomen (drape genitalia & female breasts)
Position for comfort to enhance abdominal wall relaxation
What is important when preparing to assess the abdomen?
Empty bladder b4 examination (save specimen if needed)
Warm stethoscope & fingers
examine areas identified as painful last to prevent guarding
position pt. supine w pillow below head & knees bent
What should you do to enhance abdominal wall relaxation?
Inspect, AUSCULTATE, Percuss, Palpate
Place the following in the correct order for assessment of the abdomen?
Percuss
Inspect
Palpate
Auscultate
percussion and palpation can increase peristalsis, which would give a false interpretation of bowel sounds
Why shouldn’t you palpate or percuss b4 auscultating?
stand on the persons right side & look down on the abdomen, then stoop/sit to gaze across (eye level)
How would you inspect the abdomen for contour?
contour
What describes nutritional state and ranges normally from flat to rounded?
Distension
= unusual stretching & enlargement of abdomen
implies disease
can be symmetric or asymmetric
Fluid (ascites, hemorrhage)
Flatulence (gas)
Feces (constipation)
Fetus (pregnancy)
Fibroid/fatal (tumor; CA)
Fat (obesity; adipose)
What are the causes of abdominal distension?
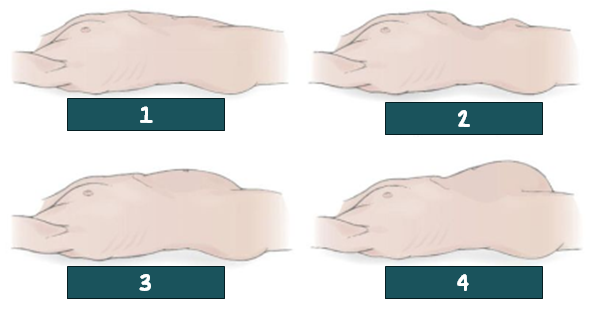
flat; normal
1? Is the normal or abnormal?
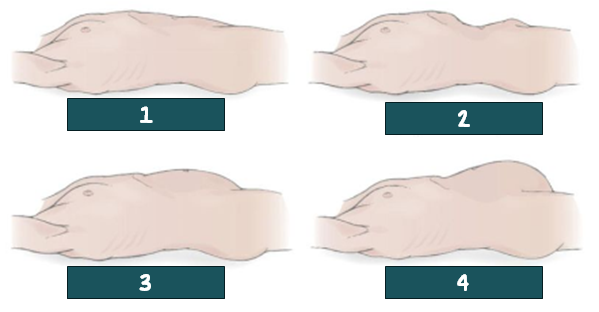
Scaphoid; abnormal
2? Is the normal or abnormal?
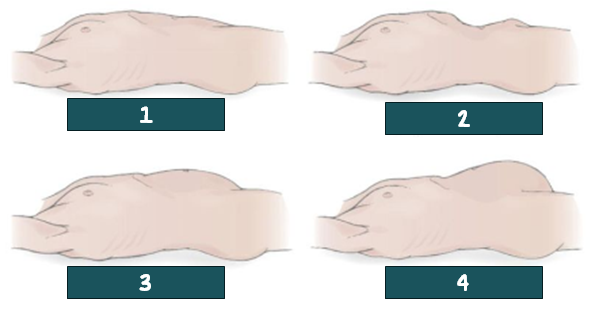
rounded; normal
3? Is the normal or abnormal?
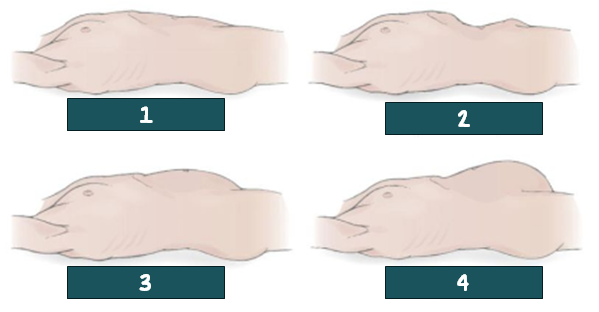
protuberated; abnormal
4? Is the normal or abnormal?
Shine a light across the abdomen
Have the pt. take a deep breath or perform a sit up (should stay smooth and symmetric)
Abdomen should be symmetric bilaterally
How would you inspect the abdomen for symmetry? What should you find?
hernia
= protrusion of abdominal viscera through abnormal opening in muscle wall
Sister Mary Joseph nodule
= a hard nodule in umbilicus that occurs w metastatic CA of stomach, large intestines, ovary, or pancreas
Normally it is midline (unless previous abdominal surgery) and inverted, with no sign of discoloration, inflammation, or hernia
What should you find when inspecting the umbilicus?
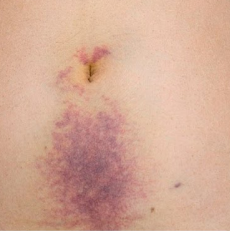
= bluish periumbilical color
occurs with intraperitoneal bleeding
What is Cullen’s sign? What does it occur with?
smooth and even w homogenous color
good turgor
healed scars (not size, shape, location & character)
What are normal findings when inspecting the skin of the abdomen?
ascites
What does a tense or glistening abdomen indicate?
Striae (linae albicantes) & pigmented nevi (moles)
What are common pigment changes that may be inspected on the abdomen?
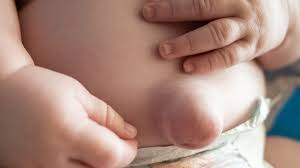
umbilical hernia
= soft, skin covered mass. protrusion of the omentum or intestine through a weakness or incomplete closer in the umbilical ring
common in premature infants
resolves in 1 year
diastasis recti
= midline longitudinal ridge that is a separation of the abdominal rectus muscles (occurs congenitally and as a result of pregnancy and marked obesity)
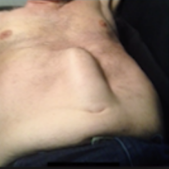
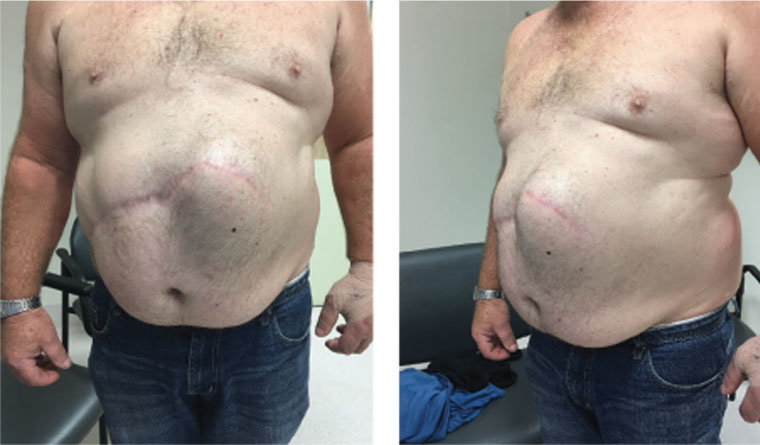
incisional hernia
= bulge near an old operative scar that may not show when a person is supine but is apparent when intra-abdominal pressure is increased
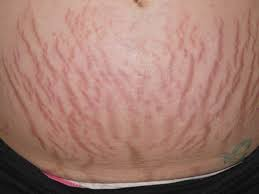
Striae
= silvery, white, linear jagged marks 1-6 cm long caused by rapid or prolonged stretching, obesity, ascites, and hormones
pink/blue
What color would you expect recent striae to be?
white/silvery
What color would you expects older striae to be?
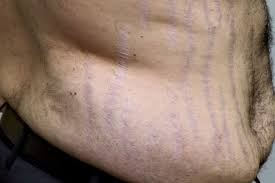
purple/blue from diseases such as cushings
What color is abnormal striae? What could this indicate?
should not be visible
How should the venous pattern appear on the abdomen?
caput medusae
= prominent, dilated epigastric veins that occur with portal HTN, cirrhosis, ascites, or venal cava obstruction
ABNORMAL
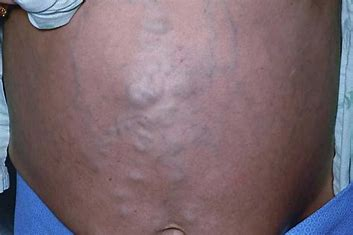
thinned adipose tissue
no
Why is the venous pattern more visible with malnutrition? Is this a normal finding?
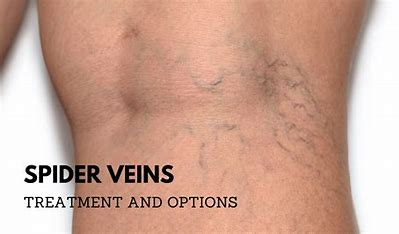
spider veins
What venous pattern occurs with portal HTN & liver damge?
pulsations from the aorta in the epigastric area
What movement is normally seen in thin people with good muscle wall relaxation?
abdominal aortic aneurysm
no
What might a bounding, diffuce, and wide pulsation mean? Is this a normal finding?
respiratory movement
peritonitis or other abdominal problems
What movement is normal in men? What does it mean if this movement is absent?
peristalsis
Involuntary, progressive wavelike movement that is visible in very thin people.
intestinal obstruction
marked peristalsis + abdominal distension =
right; left
Peristalsis moves __________ to _________ and slightly ripples.
pyloric stenosis
With what condition (in infants), do you see reverse peristalsis?
diamond shaped
What is the male pubic hair growth factors?
upside down triangle
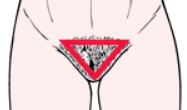
What is the female pubic hair growth pattern?
endocrine or hormone abnormalities, or chronic liver disease
What might alter the male and female pubic hair growth pattern?
relaxed quietly on examining table & has a benign facial expression & slow, even respirations
What demeanor would you expect from a comfortable person?
pain/discomfort
What does restlessness and constantly turning indicate?
bowel sounds are relatively high-pitched
Why should you use the diaphragm to listen to bowel sounds?
RLQ @ ileocecal valve area
Where are bowel sounds normally always present? (also where you should start listening)
high-pitched, gurgling, clicks
very irregular
occur 5-30 times/min
What are normal bowel sounds?
Absent Bowel Sounds
= no sounds in any quadrant after 5 minutes (EXTREMELY UNCOMMON)
Hypoactive
= Less than 5 times/min from decreased motility
hyperactive
= loud, high-pitched, rushing, tickling sounds that are more than 30 times/min from increases motility
Borborygmi
= loud, gurgling, spashing “stomach growling” sound that is common
type of hyperactive bowel sound
4-20%
What percentage of healthy people have a bruit heard over the abdomin?
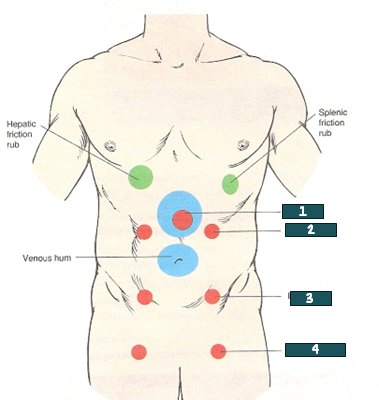
aorta
What artery is auscultated @ #1?
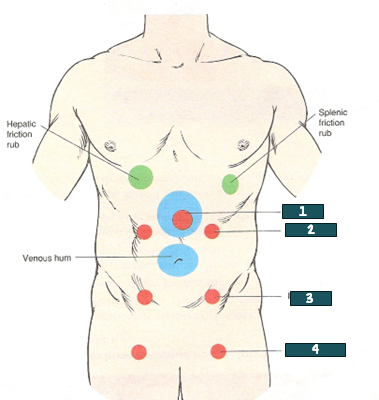
renal artery
What artery is auscultated @ #2?
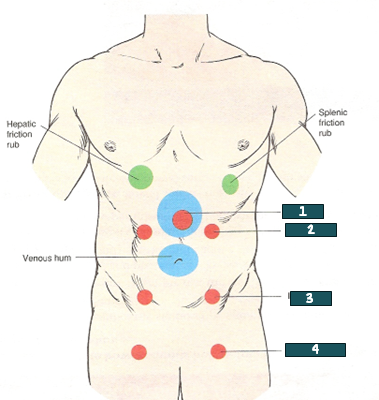
iliac artery
What artery is auscultated @ #3?
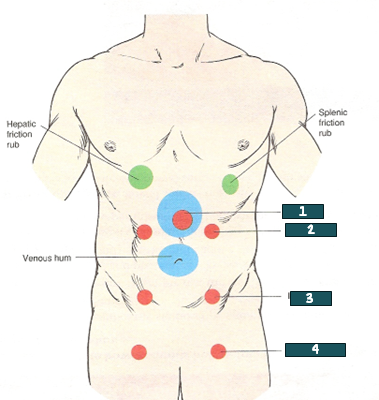
femoral artery
What artery is auscultated @ #4?
no
imaging and assessment of external tube length and pH of stomach aspirate
Can auscultation be used to place NG tubes? If not, what should be used instead?
bruit
= pulsatile blowing sound that occurs w stenosis, partial occlusion, or aneurysm
Peritoneal friction rub
= Grating, leather rubbing together, soft sound that indicates peritoneal inflammation
Associated with each breath
Could be from enlarged liver (lower R rib cage) or spleen (lower L rib cage) rubbing on organs or peritoneum
Could also be from other organs, an abscess, or tumor
Venous Hum
= low pitch, soft, continuous sound
Abnormal over liver or umbilicus (from portal hypertension, splenic artery obstructions)
May be normal in children due to inc. blood velocity, or can be the hum of muscles
assess relative density of abdominal contents
locates organs
screen for abnormal fluid or masses
What is the purpose of percussing the abdomen?
in all 4 quadrants in a clockwise manner
How should the abdomen be percussed?
tympany
What sound is predominantly heard upon percussion (bc air rises when the person is supine)?
Dullness
What sound is heard upon percussion over a distended bladder, adipose tissue, fluid or masses?
hyperressonance
What sound is heard upon percussion over gaseous distention?
place one hand over 12th rib @ costovertebral angle on back. Thump that hand with ulnar edge of your other fist.
assesses kidney
How should you percuss costovertebral angle tenderness? What organ is being assessed?
normally feels thud but no pain
What should a person feel when costovertebral angle tenderness is percussed?
during thoracic assessment
When is costovertebral angle tenderness assessed during the complete examination?
to judge size, location, and consistency of certain organs
screen for an abnormal mass or tenderness
What is the purpose of palpating the abdomen?
Bend the person’s knees, keep palpating hand low & parallel to the abdomen
Have the person breathe slowly
Keep examiner’s voice low & soothing
Use “emotive imagery” (“imagine you are dosing on the beach”)
Determine if individual is ticklish
Alternatively perform palpation just after auscultation
Begin with light palpation then proceed to deep palpation
What are additional measures to enhance complete muscle relaxation?
light palpation
= gentle exploration by rolling 4 fingers and pressing in about 1 cm
voluntary
What type of guarding can occur if a person is cold, tense or ticklish?
involuntary
What type of guarding is constant board-like hardness of the muscles?
deep palpation
= exploration by rolling 4 fingers and pressing in about 5-8 cm
if the abdomen is resistant or the person is obese
When should you use the bimanual technique?
if the pt. reports pain or when tenderness is elicited during palpation
When would you assess rebound tenderness?
Hold your hand @ 90 degrees to abdomen on a site remote from the pain/tenderness
Push down slowly & deeply, then lift quickly
How would you assess rebound tenderness?
peritoneal inflammation
While assessing rebound tenderness, there is pain on release. What might this indicate?