Physics Unit 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:39 AM on 6/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1
New cards
Work
done to an object when a force displaces the object in the direction of the force or a component of the force; can only be determined if a constant amount of force is applied
Units: J
Units: J
2
New cards
2 cases when no work is done
if the force is perpendicular to the displacement and if force is applied but no displacement occurs
3
New cards
positive work
when the force is in the same direction as the displacement
4
New cards
negative work
when the displacement and force are in opposite directions
5
New cards
area underneath a force-position graph represents…
work
6
New cards
energy
capacity to do work
7
New cards
kinetic energy
the energy of a moving object
8
New cards
Potential energy
energy stored in a non moving object
9
New cards
gravitational potential energy
energy stored by an object due to its position relative to the surface of the earth
10
New cards
work-energy principle
the change in Ek = Work, so if there is a change in energy, there must be work being done
11
New cards
mechanical energy remains constant in…
a system with no external forces
12
New cards
Hooke’s Law
The amount of force exerted by the spring is proportional to the displacement of the spring. applies to anything that can be stretched or compressed
13
New cards
Restorative Force
the force a spring exerts which is opposite to the direction of the applied force
14
New cards
Ideal Spring
any spring that obeys Hookes law (has no external or internal force)
15
New cards
spring force is proportional to
displacement
16
New cards
Elastic Potential Energy
energy stored in objects that are compressed or stretched
determined by calculating the change in kinetic energy (work)
determined by calculating the change in kinetic energy (work)
17
New cards
Linear Momentum
a vector quantity that describes the motion of an object travelling in a straight line as the product of its mass and velocity
kg\*m/s
kg\*m/s
18
New cards
momentum is proportional to…
mass and velocity
19
New cards
Impulse
the product of force and time that acts on an object to produce a change in momentum
N\*s
N\*s
20
New cards
a small force for a long time yields _____________ impulse as a large force for a short time
the same
21
New cards
total energy in an isolated system must…
stay constant
22
New cards
Mechanical energy
the sum of all the energies in a system
23
New cards
____________ and ____________ are always conserved in a collision
total energy and total momentum
24
New cards
Inelastic Collisions
momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not
25
New cards
Perfectly Inelastic Collision
an ideal collision where 2 objects stick together perfectly so that they move with the same final velocity
26
New cards
Elastic Collisions
both kinetic energy and momentum are consderved
27
New cards
Perfectly Elastic Collision
an ideal situation where friction and other forces are negligible
28
New cards
Efficiency
the ratio of the amount of useful energy produced to the amount of energy used, expressed as a percent
29
New cards
Power
The rate at which energy is transformed, or the rate at which work is done
* speed of energy transformation
J/s = W
* speed of energy transformation
J/s = W
30
New cards
1 kWh =
3\.6 x 10^6 J
31
New cards
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Based on the premise that matter is made up of small particles, known as atoms and molecules, that attract each other, and that all possess kinetic energy.
An increase in the motion of the particles of a substance makes the substance feel warmer; a decrease in motion makes the substance feel colder.
An increase in the motion of the particles of a substance makes the substance feel warmer; a decrease in motion makes the substance feel colder.
32
New cards
the greater the space between molecules the greater the ________
energy
33
New cards
Thermal Energy
the total amount of kinetic (motion of particles) and potential (attraction between particles) energy possessed by the particles of a substance
34
New cards
Temperature
measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance
SI Units: Celsius
SI Units: Celsius
35
New cards
Heat
describes the transfer of thermal energy from a substance with higher temperature to a substance with lower temperature
36
New cards
same temperature does not mean same _____________
thermal energy
37
New cards
Celsius is based off…?
the temperature at which water freezes and boils
38
New cards
State changes
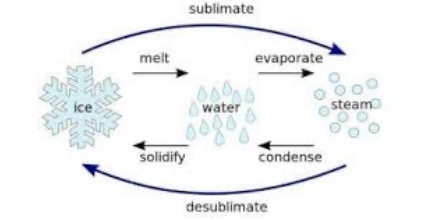
39
New cards
Methods of transferring thermal energy
1. conduction
2. convection
1. radiation
40
New cards
Thermal Conduction
the transfer of thermal energy that occurs when warmer objects are in physical contact with colder objects
41
New cards
Convection
When colder, denser fluids fall and push up warmer, less dense fluids
Applies to liquids and gases
Applies to liquids and gases
42
New cards
Radiation
transfer of thermal energy through electromagnetic waves
43
New cards
Thermal Conductors
materials that allow thermal energy to pass through them relatively easily and quickly. Materials with low heat capacities
44
New cards
Specific Heat Capacity
the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 °C
J/kg°C
J/kg°C
45
New cards
Quantity of Heat
total amount of thermal energy transferred from a warmer substance to a colder substance.
J
J
46
New cards
Principle of Thermal Energy Exchange
when a warmer object comes in contact with a colder object, the thermal energy is transferred from the warmer object to the colder object until all of the thermal energy is evenly distributed in both objects.
Qreleased = -Qabsorbed (same absolute values)
Qreleased = -Qabsorbed (same absolute values)
47
New cards
Thermal Expansion
The increase in the volume of an object due to an increase in its temperature.
48
New cards
Thermal Contraction
the decrease in the volume of an object when thermal energy is released
49
New cards
Fusion
absorption of thermal energy when an object changes from a solid to a liquid
50
New cards
when does temperature change
when 1 state is present
51
New cards
why is temperature constant when states are changed
thermal energy is used to change potential energy (bonds), not kinetic energy
52
New cards
Latent Heat
Total Thermal energy absorbed or released when a substance changes state (J)
53
New cards
Specific Latent Heat
the amount of thermal energy needed for 1 kg of a substance to change from one state to another
54
New cards
Latent Heat of Fusion
the amount of thermal energy released when a substance freezes or absorbs when it melts
55
New cards
Latent Heat of Vapourization
The amount of thermal energy absorbed when a substance evaporates or released when it condenses
56
New cards
Why is solid water more dense than liquid
hydrogen bonding causes oxygen molecules to be more organized when frozen so they take up more space
57
New cards
Why is latent heat “hidden“?
thermal energy change remains hidden until the opposite state change occurs.