Physiology Unit 1: Anatomy, Directional & Body Planes Terms, Levels of Organization, Homeostasis
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
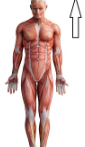
Superior
Upper part of body structure
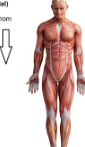
Inferior
Below
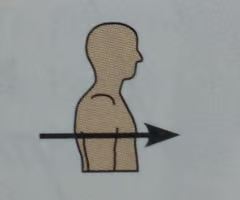
Anterior
Toward or at the front of the body
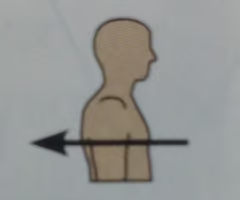
Posterior
Toward or at the backside
Medial
Toward or at the midline of the body
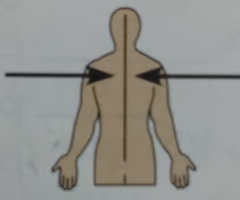
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side
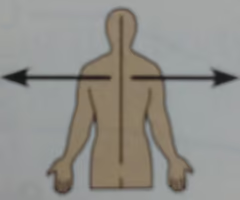
Proximal
Close to the origin of body part or the point of attachment of limb
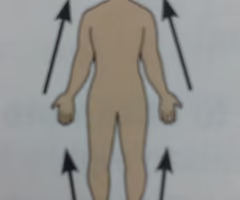
Distal
Farther from origin of attachment
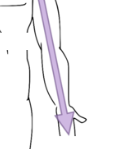
Superficial
External
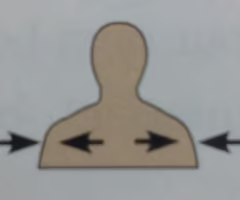
Deep
More internal

Dorsal
Spine side, "back"
Ventral
Belly side (front side)
Anatomical position
Standing up, feet together, arms at side, palms forward
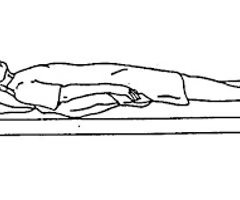
Supine
Laying down, FACE UP
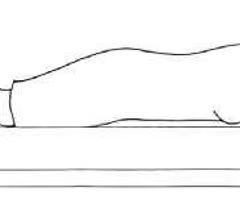
Prone
Laying down, FACE DOWN
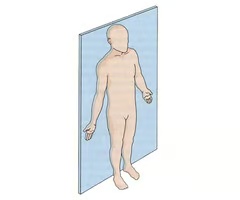
Body Planes
Flat surface that passes through the body to create TWO regions.
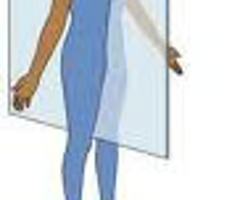
Frontal
Divides the body: into ANTERIOR & POSTERIOR sections
Transverse
Divides the body into SUPERIOR and INFERIOR sections.
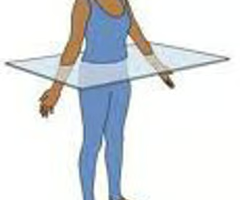
Sagittal
Divides the body into UNEQUAL lateral parts
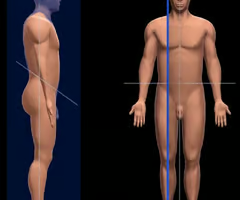
Midsagittal
Divides the body EXACTLY at midline (equal)
Organelle
Specialized subunit with a cell with a specialized function-WHAT MAKES UP A CELL
Cell
Made up of ORGANELLES
Tissue
Made up of CELLS
Organ
Made up of TISSUES
Organ system
Made up of ORGANS ex: digestive system
Body Cavities
Fluid filled space in body that holds and protects organs
Dorsal Cavity has ______ Cavity & _____ Canal
Cranial Cavity & Vertebral Canal
Ventral Cavity has ______ Cavity, _______, ____________ Cavity, _________ Cavity and ________ Cavity
Thorasic cavity, Diaphragm, Abdominopelvic Cavity, Abdominal Cavity and Pelvic Cavity.
Cell Specialiation: Each cell is uniquely suited to _________________________ in an organism.
Perform a PARTICULAR function.
Cells have an _______________ that will allow them to function properly
Identifiable structure
Sperm Cell Location
Male reproductive cells produced in testes.
Sperm Cell Function
Helps produce offspring
Sperm Cell Features (2)
Half chromosomes set for future offspring
Flagellum-tail to move cell
Red Blood Cell Location
Produced in red bone marrow.
Red Blood Cell Function
Carries oxygen.
Red Blood Cell Features (2)
Biconcave shape makes it flexible to fit in vessels.
2.NO ORGANELLES to maximize molecule transport
Adipocyte Location
Under the skin, surrounding the internal organs.
Adipocyte Function
Energy reserve
Adipocyte Features (2)
Flexible, can increase to maximize storage.
Large vacuole with oil
Cyte
Means cell
Simple Columnar Cell Location
Lines INTESTINAL tract
Simple Columnar Cell Function
Absorbs nutrients and secretes mucus
Simple Columnar Cell Features (2)
Goblet cells secrete mucus.
Microvilli to increase surface area for absorption
Pseudostratified Columnar Cell Location
Lines RESPIRATORY tract.
Pseudostratified Columnar Cell Function
Propels air molecules, mucus traps pathogens.
Pseudostratified Columnar Cell Features (2)
Cillia sway back/forth to move air molecules.
Goblet cells secrete mucus.
Skeletal Muscle Cell Location
ATTACHED to BONES
Skeletal Muscle Cell Function
Aids in moving skeleton
Skeletal Muscle Cell Feature (1)
Multiple mitochondria for more energy.
Neuron Location
Brain, Spinal Cord, 5 senses
Neuron Function
Sends and receives messages.
Neuron Feature (1)
Myelin sheath speeds up signal
Placement of Dendrite on Neuron
On the branches, at the top.
Histology
Study of TISSUES at the microscopic level
Histology examines ______ within _____. It also determines ____________ based on _______.
Cell structures. Tissues. Tissue Function. Structure.
Muscle Tissue is found ______, ______, ______
Connected to bone, surrounding the heart, lining digestive/respiratory/circulatory systems.
Muscle Tissue Functions
Aids in movement within the body and body as a whole.
Cardiac muscle : ______, Skeletal muscle: _______, Smooth muscle: ______.
Branches out, straight and striped lines, no stripes.
Nervous Tissue Location
Found WITHIN Brain, Spinal Cord, between 5 senses.
Nervous Tissue Function
Communication between internal and external environments.
Epithelial Tissue Location
Lines the body
Epithelial Tissue Functions (4)
Protect,
Secrete,
Propel/Move,
Diffuse/Absorb
Epithelial Shapes (3)
Cuboidal: Square,
Columnar: Tall, Rectangle,
Squamous: Flat, Rectangle
Epithelial Layers (2)
Simple: One layer, Stratified: Many/multiple layers
Epithelial Structure: Apical Layer (2)
Top layer
Determines tissue shape.
Epithelial Structure: Basal Layer
Bottom layer
Epithelial Structure: Basement Membrane (2)
Found below basal layer.
Anchors epithelial tissue.
Epithelial Structure: Connective Tissue (2)
Another type of tissue.
Found below basement membrane.
Epithelial Features: Avascular
All tissue contains NO BLOOD SUPPLY.
Epithelial Features: Cilinted
SOME tissue contains mobile hair-like structures.
Epithelial Features: Microvilli
SOME tissue contains statoinary cell membrane extensions.
Connective Tissue is ONLY
Internal
Connective Tissue Functions (5)
Support and Protect ex: bone, cartilage
AIDS in MOVEMENT of body internally & externally
TRANSPORTATION ex: blood
Storage of energy reserve ex: adipose (fat)
Defense of the body ex: lymph
Specialized Cells: Fibroblast
Makes FIBER & ground substance (extracellular matrix)
Specialized Cells: Chondrocytes
CARTILAGE cell
Specialized Cells: Osteocytes
BONE cell
Specialized Cells: Adipocytes
FAT cell, STORES energy, (Can change size)
Specialized Cells: White Blood Cells (WBC)
IMMUNE, fights infection
Specialized Cells: Red Blood Cells (RBC)
Carries Oxygen
Extracellular
Out of cell (think extraterrestrial)
Fibers: Collagen Fibers & What it Provides
Long, straight, unbranched. MOST common type of fiber. Strong, flexible.
PROVIDES TOUGHNESS
Fibers: Elastic Fibers & What it Provides
Branched & Wavy. Very stretchable, can return to original shape.
PROVIDES RESILIENCE.
Ground Substance (3) & What Part it is of
Substance around cells: can be liquidy, syrupy or rigid. (Part of extracellular matrix)
Physiology
Study of body systems and their functions
Skeletal System Function (4)
protection,
support & movement,
stores calcium,
produces blood cells
Ligaments
Bone to bone
Tendons
Muscle to bone
Muscular System Function
Movement
Circulatory/Cardiovascular System Function
Transport nutrients (O2) to tissues & remove waste (CO2) from tissues.
Respiratory System Function
Exchanges O2 & CO2 between lungs & environment, transport O2/CO2 to and from lungs & blood.
Nervous System Functions (3)
Detect stimuli,
send & receive messages,
control activities.
Endrocrine System Function
Slower acting communication within body that uses hormones produced by glands.
Integumentary System Function (2)
Barrier from external environment-protection,
helps regulate body temp
Lympathic/Immune System Functions (2)
Defense,
Protect against pathogens, infections & disease.
Digestive System Functions (3)
Break down food,
absorbs nutrients,
exterminates sold waste.
Urinary System Function (2)
Filters blood,
removes liquid waste from body.
Reproductive Systems (2)
Produces gametes (sperm & egg),
passes genetic info to offspring.
2 Characteristics/features in naming epithelial tissue are __________ & _________
how many layers & what shape.
3 Characteristics specific to connective tissue are _____________, ____________ & ______________.
Specialized cells, Fibers & Ground Substance.
Two types of tissues that serve as protection
Epithelial & Connective.