kinesiology exam 1
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
bone function:
support, protection, movement, mineral storage, blood cell formation
axial skeleton:
center point of body
skull, ribs, spine, pelvis
appendicular skeleton
anything attached i.e. appendages
more bones than axial
epiphyseal plate
point of bone growth (growth plate)
closes when bone reaches full maturity
articular cartilage
outer covering of epiphyses of bone
provides smooth joint movement
wolffs law
bone will respond to a direction and magnitude of a habitually applied force
how bones come to look the way they do
ex: cross country vs swimmer
osteokinematic motion
the motion of bones relative to 3 cardinal planes (occurs due to movement between articular surfaces of joint)
what you can SEE
flexion, extension, movement of bone
arthrokinematic motion
motion between articular surfaces (3 accessory motions, gliding, spinning, rolling)
accessory motions allowing big motion to happen
each joint has its own set of arthrokinematic motions
ligament
cord, band, or sheet of strong, fibrous connective tissue that unites the articular ends of bones to tie them together and facilitate movement between them
sole function is not support or stability
diarthrodial joint
round, movement is taking place
distinguished by separation of the bones and presence of joint cavity
synarthrodial joint
fused and less mobile joint
(teeth gomphosis, skull suture, public symphysis, synchondrosis, syndenmosis)
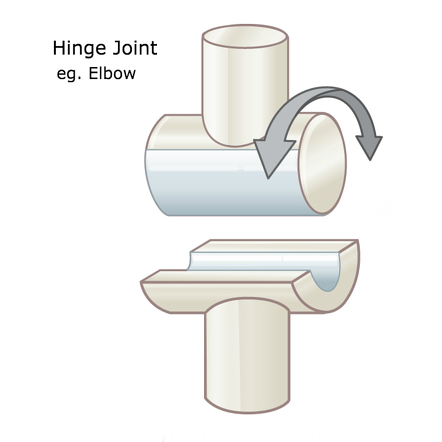
hinge joint
ginglymus
one concave surface, other surface spool-like
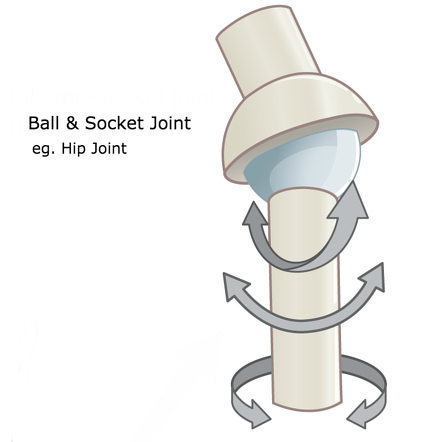
ball and socket joint
enarthrodial
rounded head of one bone fitting into the cuplike cavity of another bone
hip, shoulder
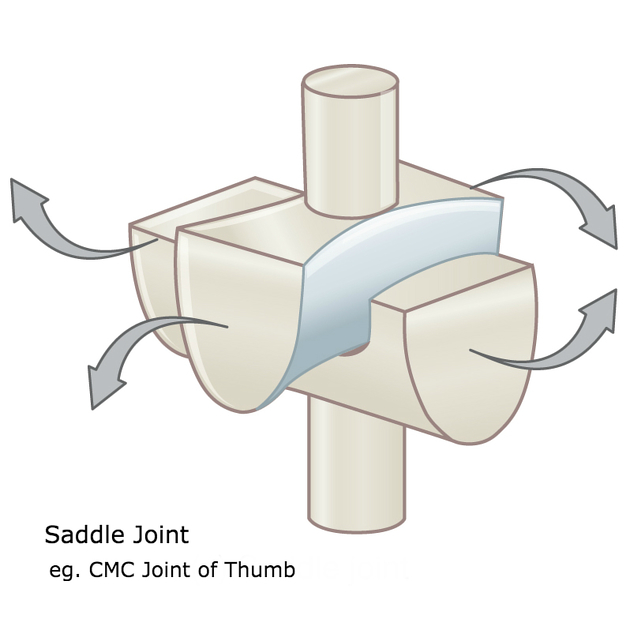
saddle joint
sellar joint
both bones have a surface that is convex in one direction and concave in the opposite direction
wrist, thumb
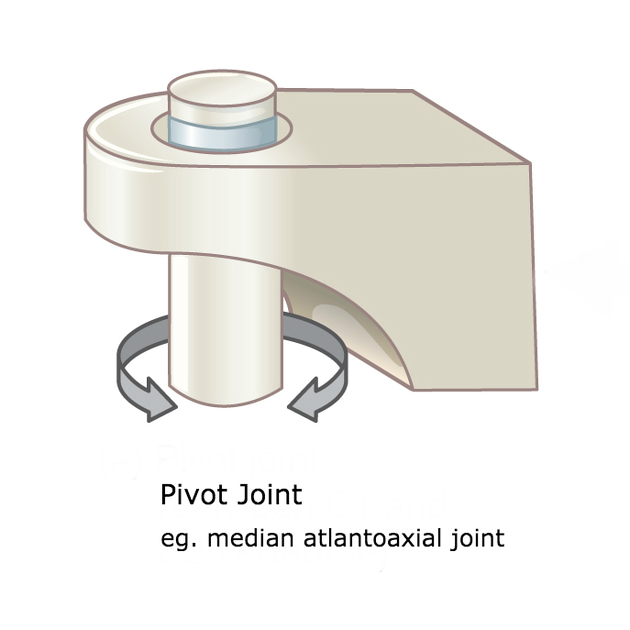
pivot joint
trochoidal
one bone rotates around another bone
radius joint
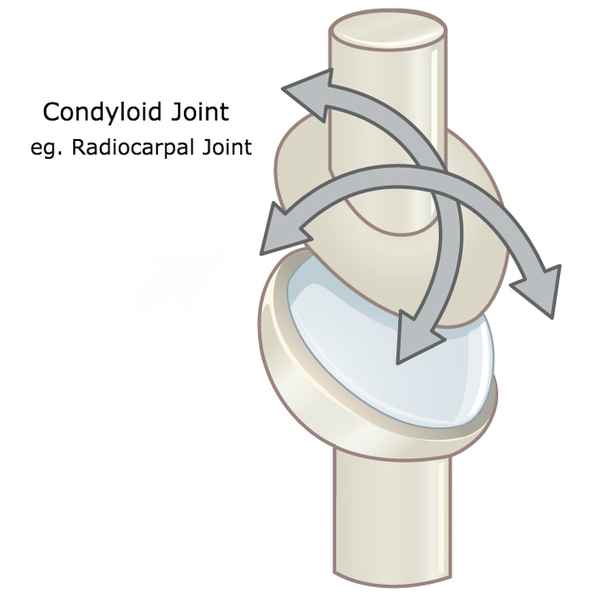
condyloid joint
ellipsoidal
one convex surface fitting into a concave surface
different than ball and socket as condyloid is capable of movement in only two planes
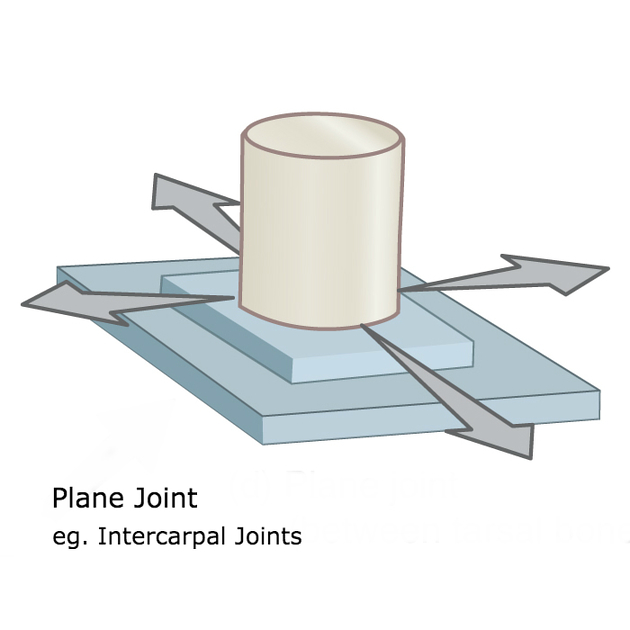
arthrodial joint
gliding joint
irregularly shaped surfaces that are typically flat or slightly rounded, only allows for gliding movement
carpals
nonaxial joint
allows only gliding movement
uniaxial joint
permit one movement in only one plane about one axis
biaxial joint
permits movement in two planes, about two axes
triaxial joint
allows movement in three planes, three axes
suture joint
no detectable movement, appears to be sewn together
bones of skull
cartilagenous joint
allows some movement, no other than the joints in spinal column
shock absorber
pubic symphysis
ligamentous joint
ties together bones that have very limited or no movement
joint between acromion and coracoid process
joint strength is determined by
the physical structure of the bones
the strength, number, and anatomical position of the ligaments
other structures (blood vessels, nerves, skin, fascia)
degree of movement in joints determined by
bones involved
thickness and laxity
amount of fat and muscular tissue
strength and flexibility of muscle tissue crossing joint
resistance of other structures
origin of muscle
proximal bone of joint
less movement
insertion of muscle
attached to distal bone of joint
more movement
properties of muscle
extensibility
elasticity
contractility
excitability
extensibility
ability to passively stretch
elasticity
ability to return to resting length
contractility
ability to develop tension
excitability
sensitive to a stimulus
a greater cross section in muscle
means greater force exertion (more muscle fibers = more work ability)
length of muscle
can determine force
longer muscles = more force generated = greater range of motion
the agonist muscle
the main muscle moving to produce a movement
ex: biceps brachii in elbow flexion
the synergist muscle
the muscle aiding in the agonist to accomplish a movement
ex: triceps brachii in elbow flexion
the antagonist muscle
the muscle opposing movement of the agonist
muscle do not pull
they push
concentric contraction
develops tension while shortening
no tension to tension
isotonic / dynamic
eccentric contraction
maintains tension while lengthening
tension to tension
isotonic / dynamic
isometric contraction
there is no movement, but tension is generation
tension to tension
isometric / static
myosin
thick band
contains cross bridges
cross bridges will attach to actin receptor sits when brain reveals them
myosin itself does not move
similar to row boating
this action is REQUIRED to generate muscle tension
actin
thin band
contains receptor sites for myosin attachment
will be pulled forward
fast twitch muscle
strength functions
use of sugar storage that will run out quickly, but is efficient for short term use
ex: breast of chicken
slow twitch muscles
endurance activities
uses myoglobin (takes time to produce ATP, but consistent)
ex: thigh of chicken
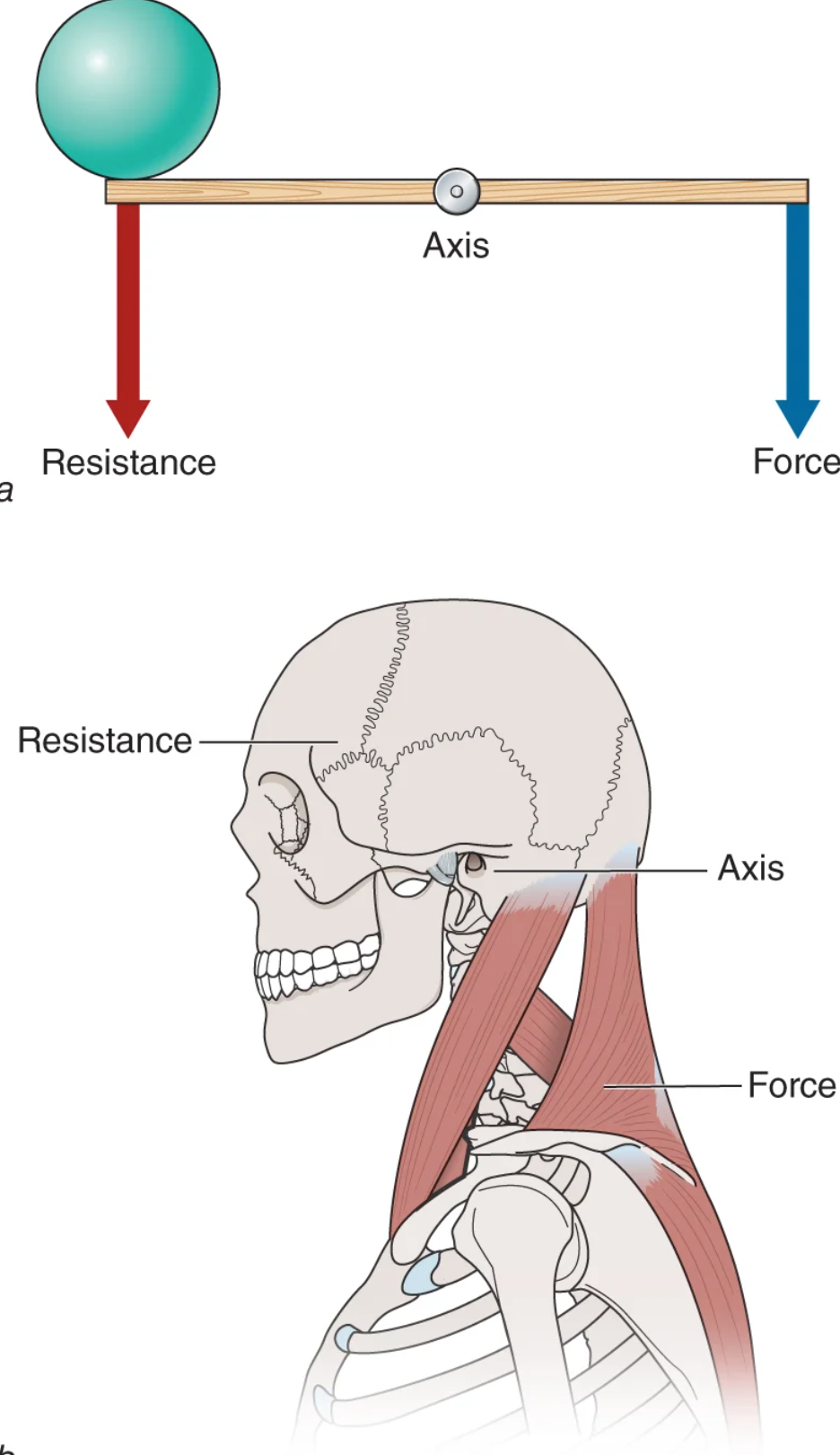
class one lever
resistance in opposition to force
axis in middle
see saw, neck muscles supporting head
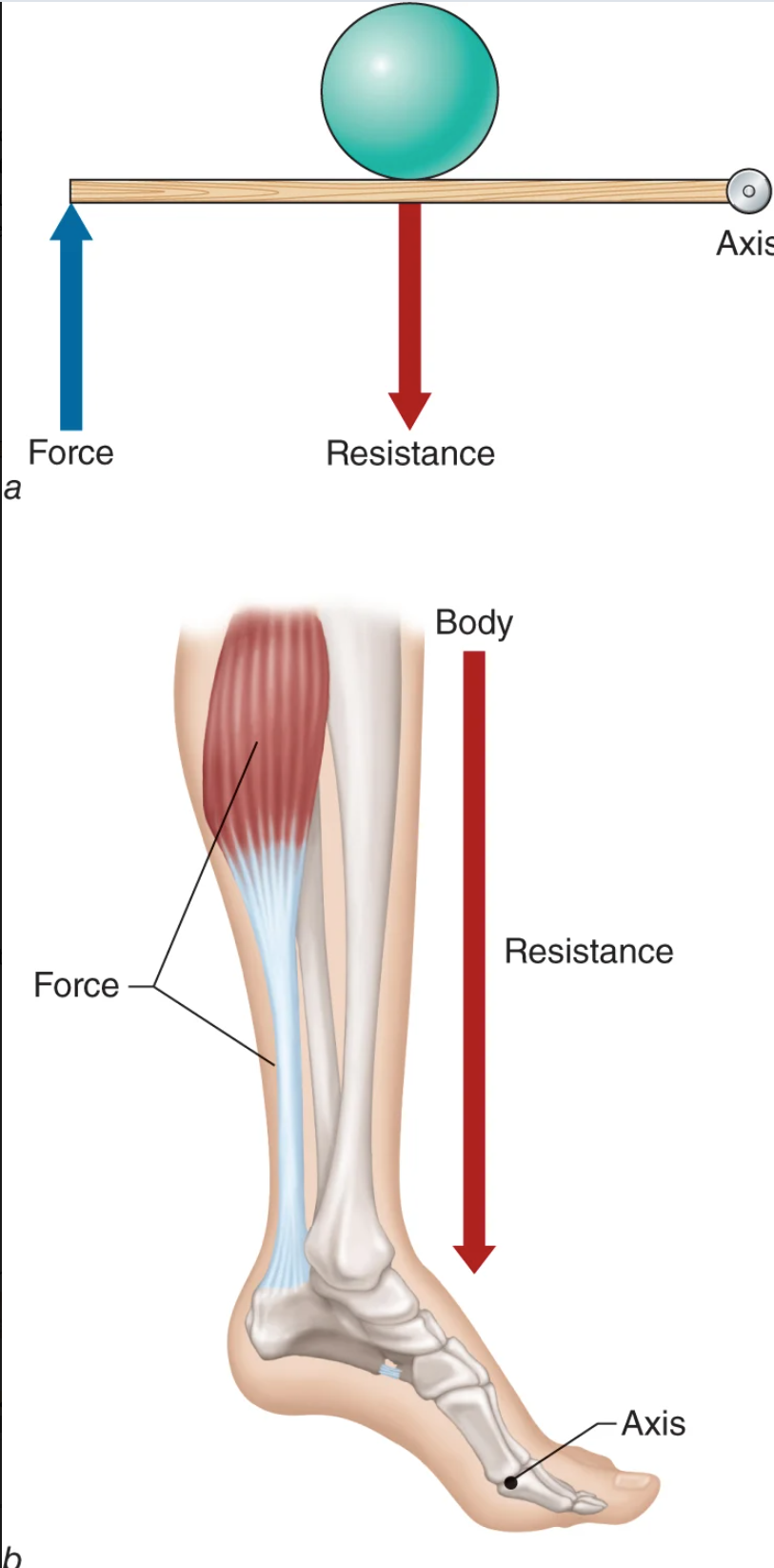
class two lever
axis in opposition to force
resistance in the middle
wheel barrow
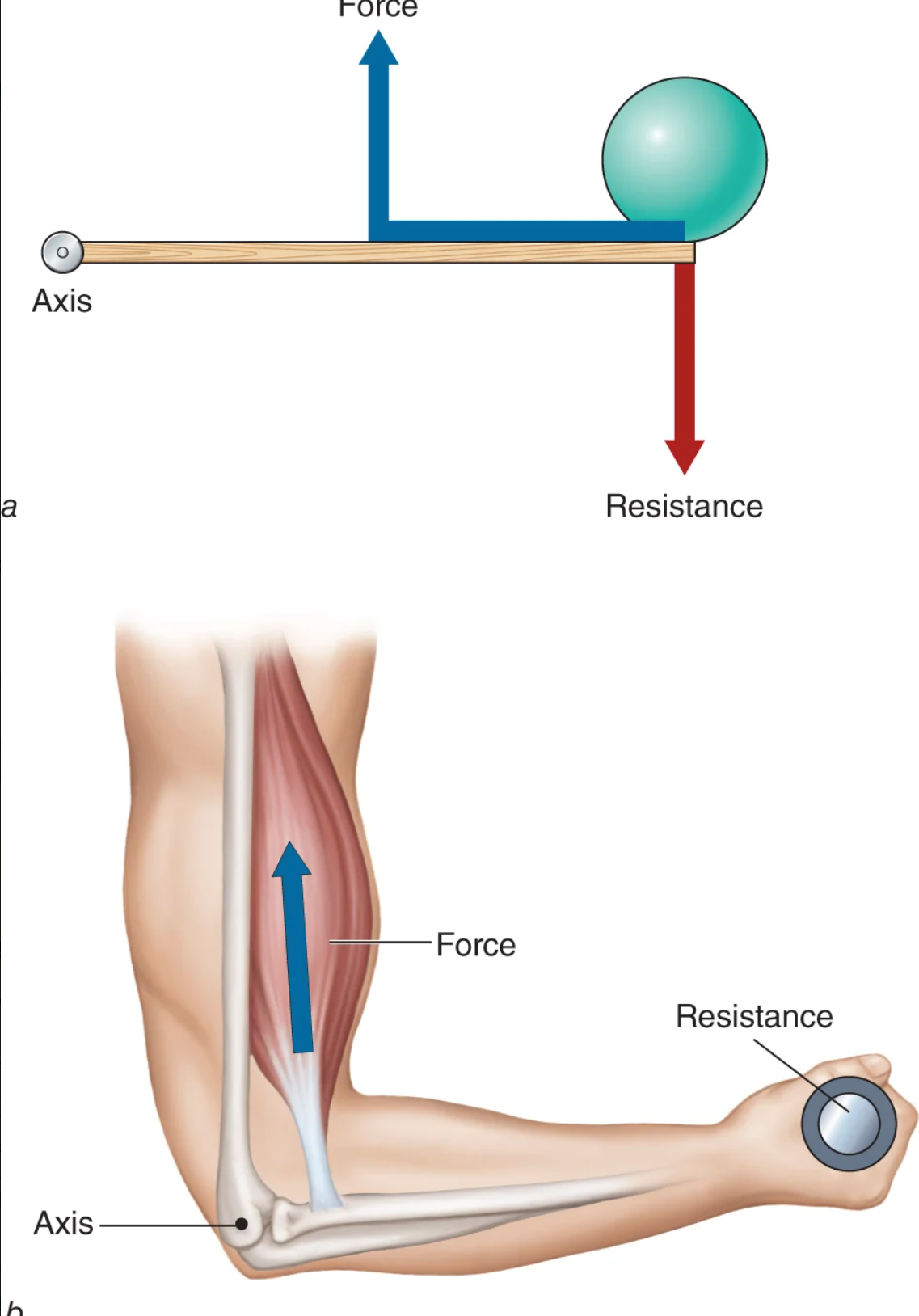
class three lever
resistance in opposition to axis
force in the middle
hand holding resistance, axis in elbow, force is biceps brachii)
goal of lever
use of a tool to overcome a resistance
helps to use less force in overcoming big resistance
muscle spindle function
is sensitive to how much muscle is being pulled/ how fast it is
will send a signal to the brain to tell the muscle how to react
ex: dog pulling hand and not letting go
SAME DAVE
sensory afferent motor efferent
dorsal afferent ventral efferent
proprioception
subconscious mechanism by which body regulates posture and movement
kinesthesis
conscious awareness of the position and movement of body and space
the all or none principal
the more motor units you have per muscle, the more control you have
the neuron either tells something to happen or doesnt
threshold
the motor units will have set thresholds (levels of stimulus from nerve depends on how many motor units will react)
makes to where control is allowed in muscles
pulleys
simple pulleys change direction of pull on an applied force