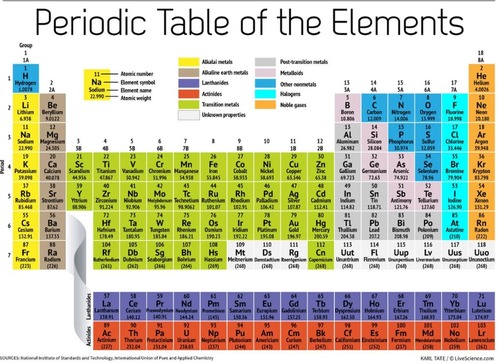
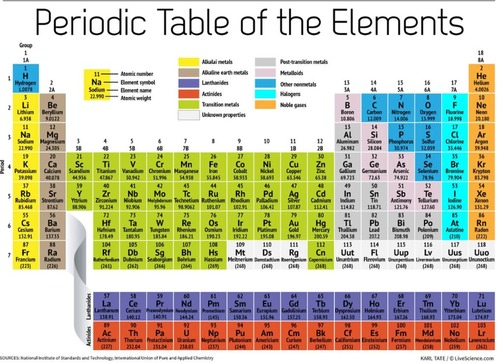
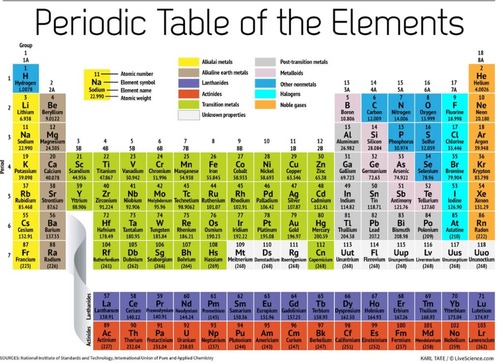
Periodic Table (The Periodic Table)
4.4(7)
4.4(7)
Card Sorting
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1
New cards
Group 1
Alkali metals.
2
New cards
Group 2
Alkaline earth metals
3
New cards
Groups 3-12
transition metals
4
New cards
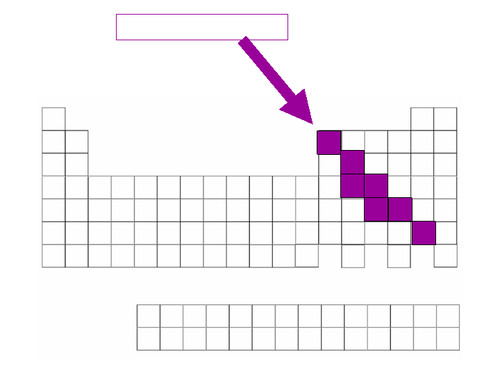
metalloids
Found along the 'staircase'. Have properties of both metals and nonmetals
5
New cards
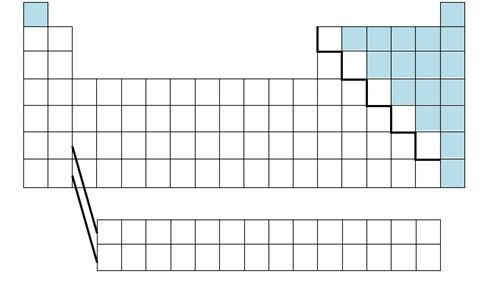
nonmetals
brittle , dull, poor conductors of heat and electricity
6
New cards
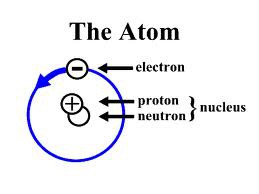
Proton
Positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom

7
New cards
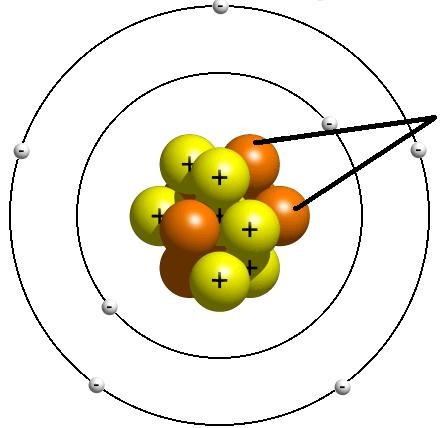
Neutron
A neutral subatomic particle that is neutral and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
8
New cards
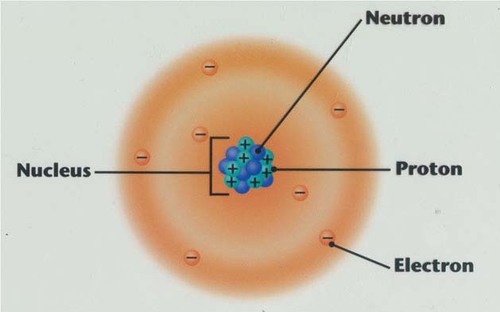
Electron
A tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom.
9
New cards
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element

10
New cards
Mass Number
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus
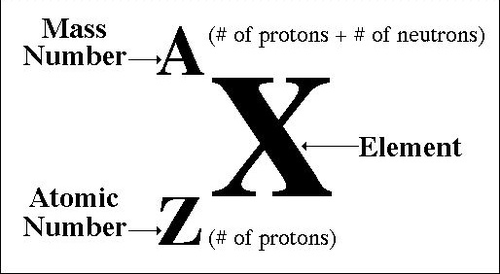
11
New cards
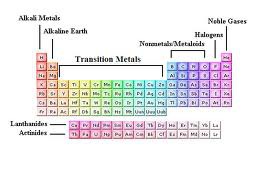
Periodic table
A chart of all chemical elements currently known, organized by atomic number.
12
New cards
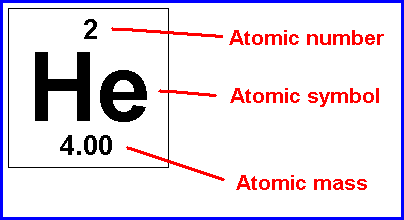
Element
pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom
13
New cards
atom
the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element
14
New cards
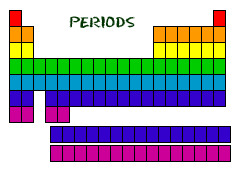
periods
horizontal rows on the periodic table
15
New cards
Chemical groups (families)
vertical columns on the periodic table
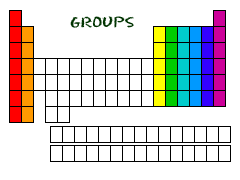
16
New cards
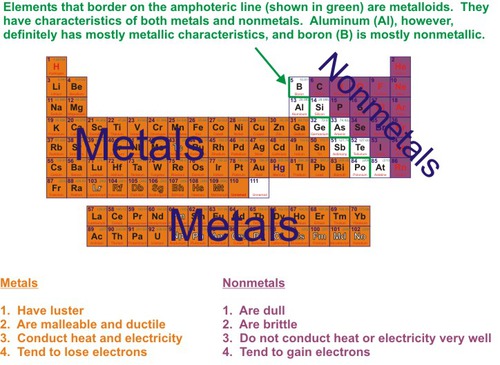
metal
Good conductor of heat and electricity. Has luster and high density.
17
New cards
luster, metallic luster
reflecting light;metallic luster, shiny

18
New cards
malleable
physical property of metals; able to be hammered into thin sheets

19
New cards
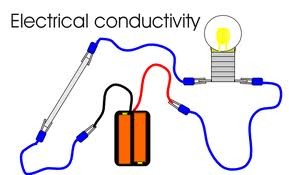
conductivity
the ability of an object to transfer heat or electricity to another object
20
New cards
reactivity
the ease and speed with which an element combines or reacts with other elements and compounds
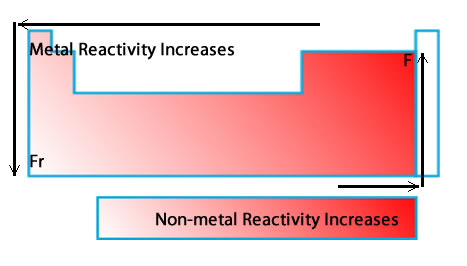
21
New cards
alkali metals
very reactive, not found alone in nature, potassium and sodium are examples, Group 1 elements
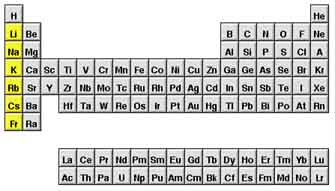
22
New cards
alkaline earth metals
hard, grey-white, good conductors of electricity, calcium and magnesium are examples, Group 2 elements
23
New cards
Transition metals
most are hard and shiny, less reactive, examples are iron, copper, nickel and gold
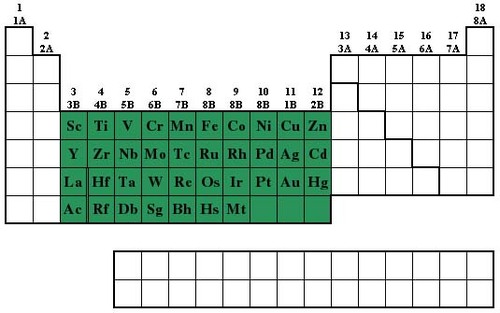
24
New cards
synthetic elements
not found naturally on earth, all elements higher than 92

25
New cards
nucleus of an atom
Positively charged, dense center of an atom that contains protons and neutrons
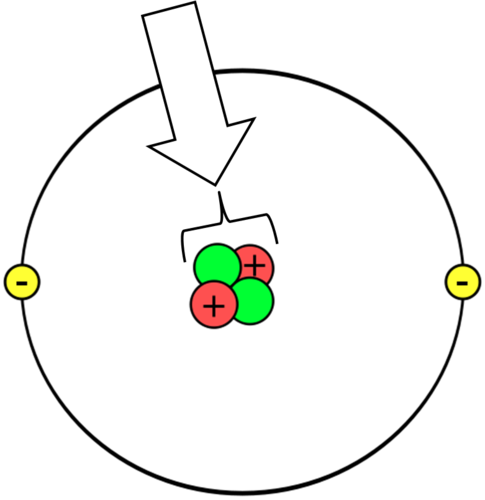
26
New cards
hydrocarbon
Organic compound composed of only carbon and hydrogen
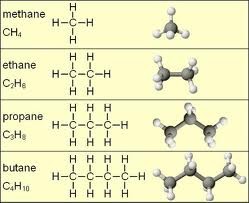
27
New cards
average atomic mass
The average mass of the isotopes of an element, including their percent abundance.

28
New cards
covalent
Type of bond in which atoms share electrons
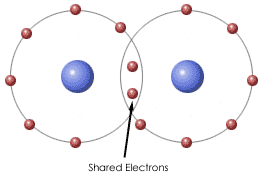
29
New cards
valence
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
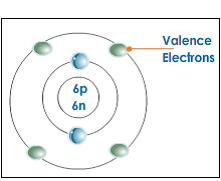
30
New cards
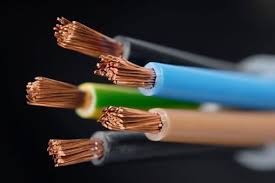
ductile
can be made into a wire
31
New cards
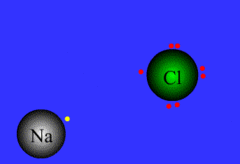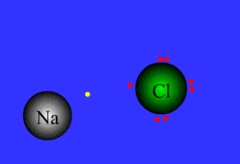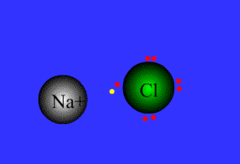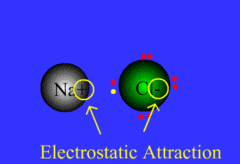
Bonding
Process of atoms joining to form molecules or formula units. Electrons are transferred or shared in this process.
32
New cards
alcohol
a type of liquid that is flammable and floats on water
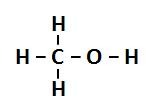
33
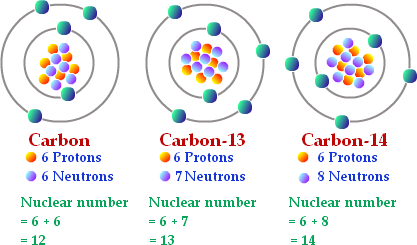
New cards
isotope
An atom with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
34
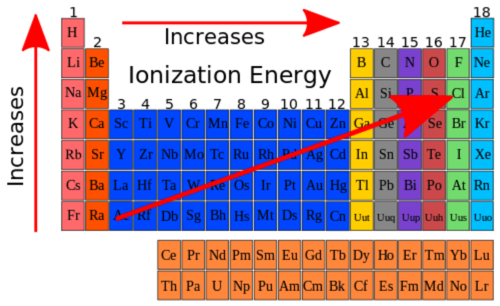
New cards
Ionization energy
The energy needed to remove the outermost electron from a gaseous atom.
35
New cards
atom
smallest part of a substance that cannot be divided by chemical means.
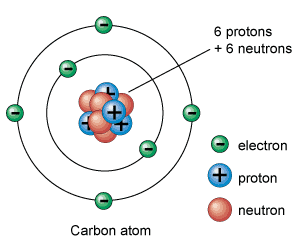
36
New cards
mass
The measure of matter in a substance. Units grams, kilograms

37
New cards
nonmetal
Brittle, poor conductors, no luster; can be a solid (s), liquid (l) or gas.(g)
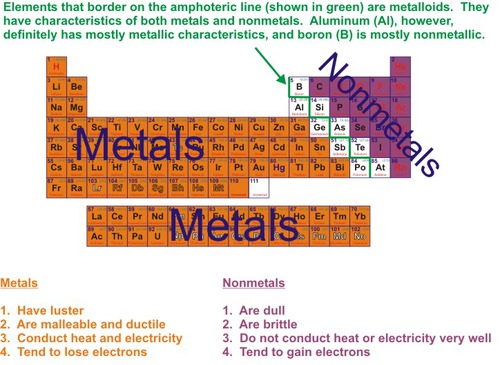
38
New cards
ionic bond
Type of bonding where an atom gains or loses electrons to form an ion.(+/-)
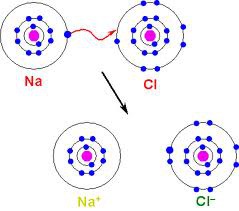
39
New cards
metallic bond
type of bonding where electrons are shared around positive metal ions in a "sea of electrons"
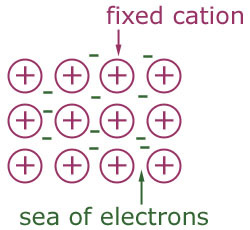
40
New cards
atomic radius
The radius of an atom
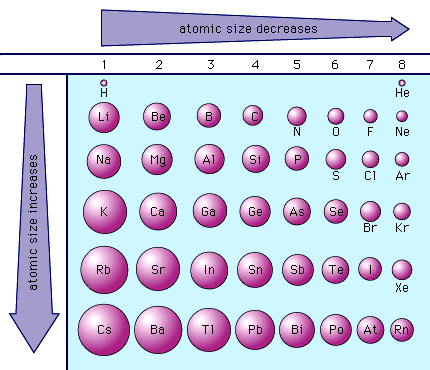
41
New cards
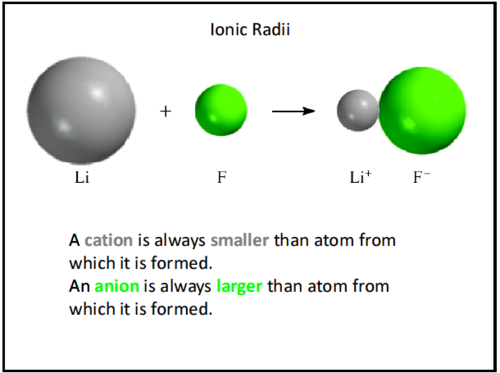
ionic radius
The radius of an atom. Cations are smaller, anions are larger than their atom
42
New cards
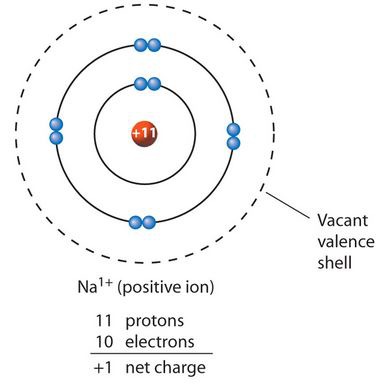
Cation
A positively charged ion, formed by a lost of electrons
43
New cards
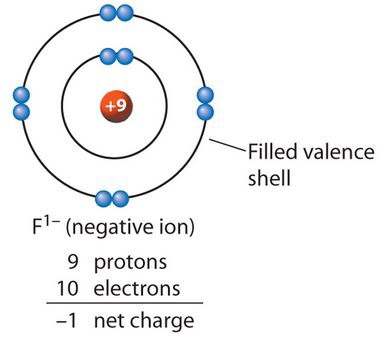
Anion
A negativity charged ion, formed by a gain of electrons
44
New cards
Ionic compound
A compound containing cations and anions.
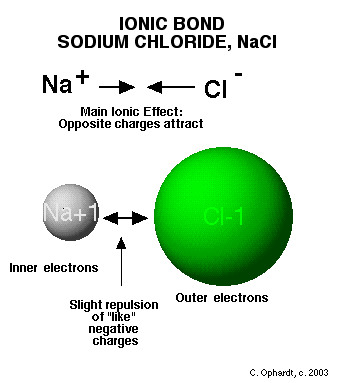
45
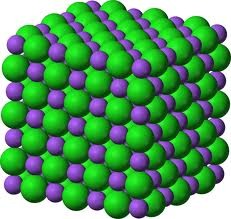
New cards
Crystal lattice
A 3-dimensional geometric arrangement of the atoms or molecules or ions composing a crystal
46
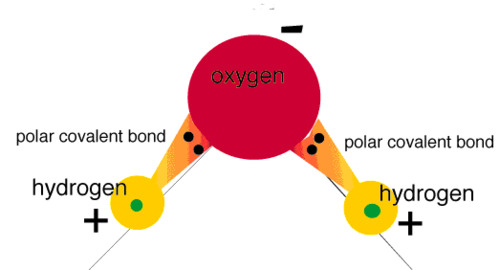
New cards
Covalent molecule
Two or more nonmetallic atoms joined together by covalent bonds.
47
New cards
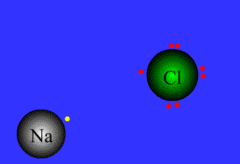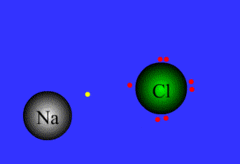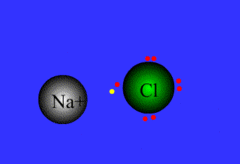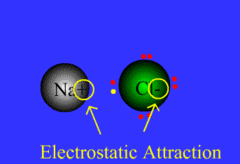
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
48
New cards
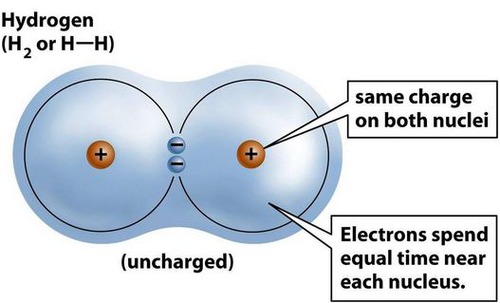
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms and can be polar or non-polar.
49
New cards
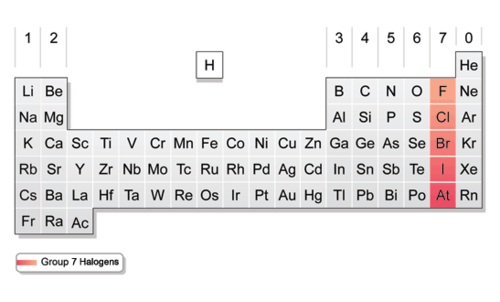
Halogens Group 17
A group of reactive nonmetals. Group 17
50
New cards
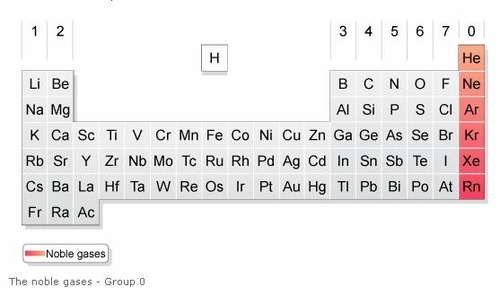
Nobel gases Group 18
Unreactive nonmetals. Atoms of this group have a full set of electrons in their outer level.
51
New cards
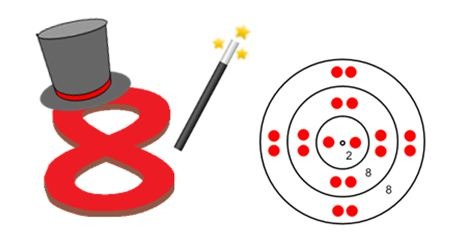
Octet rule (rule of 8)
States that atoms lose, gain or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons
52
New cards
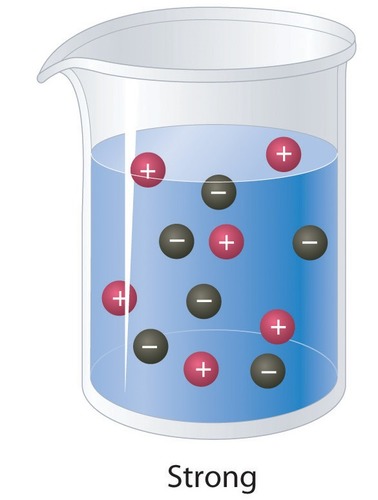
Electrolyte
A substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electric current
53
New cards
melting point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid

54
New cards
boiling point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas

55
New cards
chemical change/ reaction
the process by which one or more substances change to produce one or more different substances
56
New cards
physical change
a change of matter from one form to another without a change in chemical properties
57
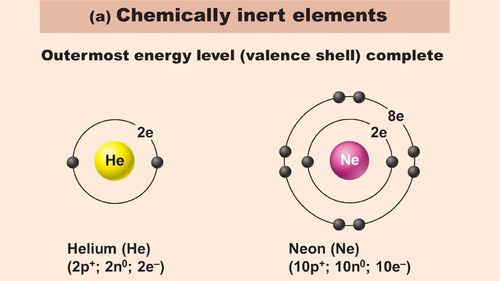
New cards
inert
Unreactive, like noble gases
58
New cards
covalent network solids
solids in which the units that make up the three-dimensional network are joined by covalent bonds