chapter questions exam 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/147
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:36 PM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
1
New cards
Cellular respiration does NOT include which of the following events?
A. glycolysis
B. citric acid cycle
C. light reactions
D. electron transport chain
E. preparatory reaction (prep)
A. glycolysis
B. citric acid cycle
C. light reactions
D. electron transport chain
E. preparatory reaction (prep)
C. light reactions
2
New cards
Which molecules are the reactants or substrates for aerobic respiration?
A. glucose and carbon dioxide
B. carbon dioxide and water
C. oxygen and glucose
D. glucose and water
A. glucose and carbon dioxide
B. carbon dioxide and water
C. oxygen and glucose
D. glucose and water
C. oxygen and glucose
3
New cards
Which molecules are the products of aerobic respiration?
A. glucose and water
B. glucose and oxygen
C. lactate and carbon dioxide
D. carbon dioxide and water
A. glucose and water
B. glucose and oxygen
C. lactate and carbon dioxide
D. carbon dioxide and water
D. carbon dioxide and water
4
New cards
Which of the following is a substrate of cellular respiration?
A. carbon dioxide
B. water
C. glucose
D. energy
A. carbon dioxide
B. water
C. glucose
D. energy
C. glucose
5
New cards
Which of the following does not describe the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
A. It accepts two electrons.
B. It is a coenzyme.
C. It is necessary for glycolysis.
D. It is broken down to CO2 and water.
A. It accepts two electrons.
B. It is a coenzyme.
C. It is necessary for glycolysis.
D. It is broken down to CO2 and water.
D. It is broken down to CO2 and water.
6
New cards
What role does NAD+ play in cellular respiration?
A. It is a coenzyme.
B. It is an enzyme.
C. It provides the oxygen.
D. It provides the energy.
A. It is a coenzyme.
B. It is an enzyme.
C. It provides the oxygen.
D. It provides the energy.
A. It is a coenzyme.
7
New cards
What are the input requirements of glycolysis?
A. NAD+, FAD, acetylCoA, and ADP,
B. ATP, NAD+, glucose, and ADP
C. pyruvates, NADH, and ADP
D. glucose and oxygen
A. NAD+, FAD, acetylCoA, and ADP,
B. ATP, NAD+, glucose, and ADP
C. pyruvates, NADH, and ADP
D. glucose and oxygen
B. ATP, NAD+, glucose, and ADP
8
New cards
The final products of glycolysis are
A. pyruvate, ATP, and NADH + H+.
B. pyruvate and ATP.
C. pyruvate and NADH + H+.
D. ATP and NADH + H+.
E. pyruvate
A. pyruvate, ATP, and NADH + H+.
B. pyruvate and ATP.
C. pyruvate and NADH + H+.
D. ATP and NADH + H+.
E. pyruvate
A. pyruvate, ATP, and NADH + H+.
9
New cards
Where does glycolysis take place within the cell?
A. endoplasmic reticulum
B. mitochondrial matrix
C. mitochondrial membrane
D. cytoplasm
A. endoplasmic reticulum
B. mitochondrial matrix
C. mitochondrial membrane
D. cytoplasm
D. cytoplasm
10
New cards
Choose the one correct statement?
A. Glycolysis results in the release of carbon dioxide.
B. Glycolysis is a cyclical reaction.
C. Glycolysis is a reduction reaction where only glucose is reduced.
D. Glycolysis occurs twice per glucose molecule.
E. Glycolysis breaks glucose down to two pyruvate molecules
A. Glycolysis results in the release of carbon dioxide.
B. Glycolysis is a cyclical reaction.
C. Glycolysis is a reduction reaction where only glucose is reduced.
D. Glycolysis occurs twice per glucose molecule.
E. Glycolysis breaks glucose down to two pyruvate molecules
E. Glycolysis breaks glucose down to two pyruvate molecules
11
New cards
Muscles undergo fermentation when
A. no oxygen is available.
B. no carbon dioxide is available.
C. no ATP is available.
D. no pyruvate is available
A. no oxygen is available.
B. no carbon dioxide is available.
C. no ATP is available.
D. no pyruvate is available
A. no oxygen is available.
12
New cards
Pyruvate can be converted to lactate instead of going to the preparatory reaction. Why does this occur?
A. The cells need lactate to produce ATP.
B. The cells doing the reaction are prokaryotes.
C. Oxygen is not available.
D. There is a shortage of glucose.
A. The cells need lactate to produce ATP.
B. The cells doing the reaction are prokaryotes.
C. Oxygen is not available.
D. There is a shortage of glucose.
C. Oxygen is not available.
13
New cards
Why do organisms without oxygen need to convert pyruvate to lactate?
A. in order to regenerate NAD+
B. because lactate is needed to produce ATP
C. because pyruvate is toxic to the cells
D. in order to use lactate in the citric acid cycle
A. in order to regenerate NAD+
B. because lactate is needed to produce ATP
C. because pyruvate is toxic to the cells
D. in order to use lactate in the citric acid cycle
A. in order to regenerate NAD+
14
New cards
What phase(s) of cellular respiration produce(s) NADH?
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. glycolysis and preparatory reaction
E. glycolysis, preparatory reaction, and citric acid cycle
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. glycolysis and preparatory reaction
E. glycolysis, preparatory reaction, and citric acid cycle
E. glycolysis, preparatory reaction, and citric acid cycle
15
New cards
Which stage(s) will produce carbon dioxide in cellular respiration?
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. both glycolysis and the electron transport chain
E. both the preparatory reaction and the citric acid cycle
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. both glycolysis and the electron transport chain
E. both the preparatory reaction and the citric acid cycle
E. both the preparatory reaction and the citric acid cycle
16
New cards
The largest number of ATP molecules is produced in which phase of cellular respiration?
A. glycolysis
B. preparation reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain
A. glycolysis
B. preparation reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain
D. electron transport chain
17
New cards
Pyruvate is converted to a two-carbon acetyl group attached to coenzyme A (CoA), and CO2 is given off. This phase is called
A. substrate-level ATP synthesis.
B. the preparatory reaction.
C. the citric acid cycle.
D. fermentation.
A. substrate-level ATP synthesis.
B. the preparatory reaction.
C. the citric acid cycle.
D. fermentation.
B. the preparatory reaction.
18
New cards
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A. The end product of glycolysis is pyruvate.
B. The citric acid cycle begins and ends with pyruvate.
C. NADH2 will eventually produce three ATP molecules.
D. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
A. The end product of glycolysis is pyruvate.
B. The citric acid cycle begins and ends with pyruvate.
C. NADH2 will eventually produce three ATP molecules.
D. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
B. The citric acid cycle begins and ends with pyruvate.
19
New cards
Which pathway in cellular respiration will produce ATP, NADH, and carbon dioxide?
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain
C. citric acid cycle
20
New cards
The production of ATP as a result of an electrochemical gradient is called
A. substrate-level phosphorylation.
B. chemiosmosis.
C. deamination.
D. substrate level phosphorylation.
A. substrate-level phosphorylation.
B. chemiosmosis.
C. deamination.
D. substrate level phosphorylation.
B. chemiosmosis.
21
New cards
Why does chemiosmosis require a membrane?
A. to anchor proteins within the mitochondria
B. because the phospholipids are involved in the electron transport chain
C. to separate two compartments of the cell to allow for gradient formation
D. to generate H+ from water
A. to anchor proteins within the mitochondria
B. because the phospholipids are involved in the electron transport chain
C. to separate two compartments of the cell to allow for gradient formation
D. to generate H+ from water
C. to separate two compartments of the cell to allow for gradient formation
22
New cards
What is the final electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain in respiration?
A. Oxygen
B. Water
C. NADH
D. ADP
A. Oxygen
B. Water
C. NADH
D. ADP
A. Oxygen
23
New cards
Which molecules donate electrons to the electron transport chain of respiration?
A. NADH and FAD
B. ATP and ADP
C. Water and Oxygen
D. Carbon Dioxide and Water
A. NADH and FAD
B. ATP and ADP
C. Water and Oxygen
D. Carbon Dioxide and Water
A. NADH and FAD
24
New cards
Where is NAD+ converted to NADH?
A. Cytoplasm and Matrix of the Mitochondrion
B. Cytoplasm Only
C. Matrix of the Mitochondrion Only
D. Intermembrane Space of the Mitochondrion Only
A. Cytoplasm and Matrix of the Mitochondrion
B. Cytoplasm Only
C. Matrix of the Mitochondrion Only
D. Intermembrane Space of the Mitochondrion Only
A. Cytoplasm and Matrix of the Mitochondrion
25
New cards
ATP and ADP have a strong negative charge. How could that get into and out of the mitochondrion?
A. Through a membrane transport protein.
B. By diffusion throught the phospholipid bilayer.
C. Diffusion through the mitochondrial membranes since those membranes are not made of phospholipids.
D. By endocytosis and exocyctosis of the mitochondrial membranes.
A. Through a membrane transport protein.
B. By diffusion throught the phospholipid bilayer.
C. Diffusion through the mitochondrial membranes since those membranes are not made of phospholipids.
D. By endocytosis and exocyctosis of the mitochondrial membranes.
A. Through a membrane transport protein.
26
New cards
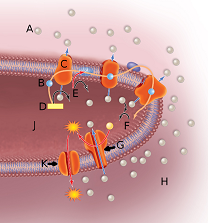
In the above image, the sphere next to the letter A represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. an electron.
C. the matrix.
D. oxygen.
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. an electron.
C. the matrix.
D. oxygen.
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
27
New cards
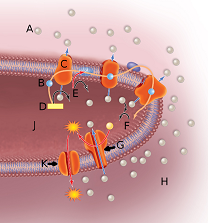
In the above image, the sphere next to the letter B represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. an electron.
C. the matrix.
D. oxygen.
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. an electron.
C. the matrix.
D. oxygen.
B. an electron.
28
New cards
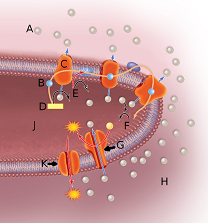
In the above image, the orange globule embedded in the membrane labeled by the letter C represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. a proton pump.
C. the ATP synthase complex.
D. NADH
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. a proton pump.
C. the ATP synthase complex.
D. NADH
B. a proton pump.
29
New cards
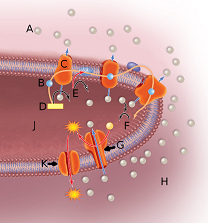
In the above image, the orange globule embedded in the membrane labeled by the letter G represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. a proton pump.
C. the ATP synthase complex.
D. NADH
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. a proton pump.
C. the ATP synthase complex.
D. NADH
C. the ATP synthase complex.
30
New cards
CHAPTER 8
CHAPTER 8
31
New cards
What are the products of photosynthesis?
A. water and carbon dioxide
B. carbohydrate and water
C. oxygen and carbohydrate
D. carbon dioxide and carbohydrate
A. water and carbon dioxide
B. carbohydrate and water
C. oxygen and carbohydrate
D. carbon dioxide and carbohydrate
C. oxygen and carbohydrate
32
New cards
The raw materials or reactants of the photosynthetic process include
A. glucose and oxygen.
B. carbon dioxide and glucose.
C. carbon dioxide and water.
D. glucose and water
A. glucose and oxygen.
B. carbon dioxide and glucose.
C. carbon dioxide and water.
D. glucose and water
C. carbon dioxide and water.
33
New cards
At the cellular level, photosynthesis occurs within
A. the chloroplast.
B. the cristae of the mitochondria.
C. both chloroplasts and mitochondria.
D. all plant cell organelles.
A. the chloroplast.
B. the cristae of the mitochondria.
C. both chloroplasts and mitochondria.
D. all plant cell organelles.
A. the chloroplast.
34
New cards
Solar energy is captured by
A. pigments.
B. nucleus.
C. glucose.
D. NAD+.
A. pigments.
B. nucleus.
C. glucose.
D. NAD+.
A. pigments.
35
New cards
Which of the following statements is TRUE concerning sunlight radiation used for photosynthesis?
A. All of the sunlight that hits the atmosphere is used for photosynthesis.
B. Only the highest energy wavelengths are used for photosynthesis.
C. Only the red, blue, and violet wavelengths of visible light are used for photosynthesis.
D. Only the green visible light is used for photosynthesis.
A. All of the sunlight that hits the atmosphere is used for photosynthesis.
B. Only the highest energy wavelengths are used for photosynthesis.
C. Only the red, blue, and violet wavelengths of visible light are used for photosynthesis.
D. Only the green visible light is used for photosynthesis.
C. Only the red, blue, and violet wavelengths of visible light are used for photosynthesis.
36
New cards
Why are plant leaves green?
A. They absorb only green wavelengths of light.
B. They absorb only yellow and blue wavelengths of light.
C. They reflect green wavelengths of light.
D. They reflect yellow and blue wavelengths of light.
A. They absorb only green wavelengths of light.
B. They absorb only yellow and blue wavelengths of light.
C. They reflect green wavelengths of light.
D. They reflect yellow and blue wavelengths of light.
C. They reflect green wavelengths of light.
37
New cards
The metabolic events that move electrons from water to NADP+ are referred to as what?
A. noncyclic electron pathway
B. CO2 fixation stage of Calvin cycle reactions
C. citric acid cycle
D. CO2 reduction phase of Calvin cycle reactions
A. noncyclic electron pathway
B. CO2 fixation stage of Calvin cycle reactions
C. citric acid cycle
D. CO2 reduction phase of Calvin cycle reactions
A. noncyclic electron pathway
38
New cards
Water is split and oxygen is released in
A. the citric acid cycle.
B. the Calvin cycle reactions.
C. the noncyclic electron pathway.
D. photosystem I.
A. the citric acid cycle.
B. the Calvin cycle reactions.
C. the noncyclic electron pathway.
D. photosystem I.
C. the noncyclic electron pathway.
39
New cards
What are the stages of the Calvin cycle?
A. carbon dioxide fixation and regeneration of RuBP
B. the noncyclic electron pathway and the cyclic electron pathway
C. the light reactions, regeneration of RuBP, and cyclic electron pathway
D. carbon dioxide fixation, carbon dioxide reduction, and regeneration of RuBP
A. carbon dioxide fixation and regeneration of RuBP
B. the noncyclic electron pathway and the cyclic electron pathway
C. the light reactions, regeneration of RuBP, and cyclic electron pathway
D. carbon dioxide fixation, carbon dioxide reduction, and regeneration of RuBP
D. carbon dioxide fixation, carbon dioxide reduction, and regeneration of RuBP
40
New cards
One of the products of the Calvin cycle is
A. RuBP carboxylase.
B. 3PG.
C. G3P.
D. RuBP.
A. RuBP carboxylase.
B. 3PG.
C. G3P.
D. RuBP.
C. G3P.
41
New cards
The Calvin cycle reactions are dependent upon a supply of
A. water and carbon dioxide.
B. carbon dioxide and NADPH.
C. carbon dioxide, NADPH, and ATP.
D. glucose and carbon dioxide.
A. water and carbon dioxide.
B. carbon dioxide and NADPH.
C. carbon dioxide, NADPH, and ATP.
D. glucose and carbon dioxide.
C. carbon dioxide, NADPH, and ATP.
42
New cards
NADPH and ATP are used in the
A. noncyclic electron pathway.
B. Calvin cycle reactions.
C. citric acid cycle.
D. light reactions.
A. noncyclic electron pathway.
B. Calvin cycle reactions.
C. citric acid cycle.
D. light reactions.
B. Calvin cycle reactions.
43
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic shared by cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
A. Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur in plant cells.
B. Both processes produce ATP by chemiosmosis.
C. Both processes produce oxygen.
D. Both processes use an electron transport chain located in membranes of organelles.
A. Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur in plant cells.
B. Both processes produce ATP by chemiosmosis.
C. Both processes produce oxygen.
D. Both processes use an electron transport chain located in membranes of organelles.
C. Both processes produce oxygen.
44
New cards
Which statement about photosynthesis and cellular respiration is TRUE?
A. Photosynthesis produces oxygen, while cellular respiration uses oxygen.
B. Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria, while cellular respiration occurs in chloroplasts.
C. Photosynthesis breaks down carbohydrates, while cellular respiration produces carbohydrates.
D. Photosynthesis requires oxygen, while cellular respiration requires sunlight
A. Photosynthesis produces oxygen, while cellular respiration uses oxygen.
B. Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria, while cellular respiration occurs in chloroplasts.
C. Photosynthesis breaks down carbohydrates, while cellular respiration produces carbohydrates.
D. Photosynthesis requires oxygen, while cellular respiration requires sunlight
A. Photosynthesis produces oxygen, while cellular respiration uses oxygen.
45
New cards
Which of the following statements is false?
A. During cellular respiration, carbohydrate energy is converted into ATP.
B. During cellular respiration, mitochondria release carbon dioxide.
C. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is used.
D. During photosynthesis, oxygen is used.
A. During cellular respiration, carbohydrate energy is converted into ATP.
B. During cellular respiration, mitochondria release carbon dioxide.
C. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is used.
D. During photosynthesis, oxygen is used.
D. During photosynthesis, oxygen is used.
46
New cards
What are the two sets of reactions for photosynthesis?
A. light reactions, Calvin cycle reactions
B. light reactions, glycolysis
C. Calvin cycle reactions, citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain, light reactions
A. light reactions, Calvin cycle reactions
B. light reactions, glycolysis
C. Calvin cycle reactions, citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain, light reactions
A. light reactions, Calvin cycle reactions
47
New cards
The substance that initially traps solar energy in photosynthesis is
A. chlorophyll.
B. RuBP.
C. water.
D. glucose.
E. pyruvate.
A. chlorophyll.
B. RuBP.
C. water.
D. glucose.
E. pyruvate.
A. chlorophyll.
48
New cards
In order to tell the source of particular atoms that take part in a metabolic pathway, sometimes radiolabeled molecules are used. These are molecules in which one atom or element has been replaced with its radioactive isotope. Which molecule would you need to radioactively label in order to produce radioactive oxygen during photosynthesis?
A. carbon dioxide
B. water
C. glucose
D. G3P
A. carbon dioxide
B. water
C. glucose
D. G3P
B. water
49
New cards
The light reactions could be viewed as analogous to a hydro-electric dam. In that case, the wall of the dam that holds back the water would be analogous to…
A. the thylakoid membrane.
B. hydrogen ions (protons).
C. the thylakoid space.
D. sunlight.
E. ATP synthase.
A. the thylakoid membrane.
B. hydrogen ions (protons).
C. the thylakoid space.
D. sunlight.
E. ATP synthase.
A. the thylakoid membrane.
50
New cards
The light reactions could be viewed as analogous to a hydro-electric dam. In that case, the water stored in the reservoir above the dam would be analogous to…
A. the thylakoid membrane.
B. hydrogen ions (protons).
C. the thylakoid space.
D. sunlight.
E. ATP synthase.
A. the thylakoid membrane.
B. hydrogen ions (protons).
C. the thylakoid space.
D. sunlight.
E. ATP synthase.
B. hydrogen ions (protons).
51
New cards
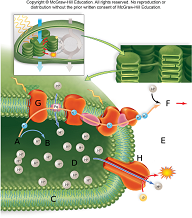
The image above is a representation of
A. the light reactions.
B. the calvin cycle.
C. electron transport in respiration.
D. the breakdown of ATP to ADP + P.
A. the light reactions.
B. the calvin cycle.
C. electron transport in respiration.
D. the breakdown of ATP to ADP + P.
A. the light reactions.
52
New cards
Imagine starting in the innermost space of the chloroplast and moving outward until leaving the chloroplast and entering the cytoplasm. What is the starting points an proper order of things you would move through?
A. thylakoid space - thylakoid membrane - stroma - inner membrane - outer membrane
B. stroma - inner membrane - thylakoid space - thylakoid membrane - outer membrane
C. stroma - inner membrane - thylakoid membrane - thylakoid space - outer membrane
D. matrix - inner membrane - intermemebrane space - outer membrane
A. thylakoid space - thylakoid membrane - stroma - inner membrane - outer membrane
B. stroma - inner membrane - thylakoid space - thylakoid membrane - outer membrane
C. stroma - inner membrane - thylakoid membrane - thylakoid space - outer membrane
D. matrix - inner membrane - intermemebrane space - outer membrane
A. thylakoid space - thylakoid membrane - stroma - inner membrane - outer membrane
53
New cards
The innermost membrane of the chloroplast is referred to as the
A. thylakoid membrane.
B. inner membrane.
C. cristae.
D. stroma.
A. thylakoid membrane.
B. inner membrane.
C. cristae.
D. stroma.
A. thylakoid membrane.
54
New cards
What is the name of the enzyme that fixes carbon dioxide during photosynthesis?
A. RuBP Carboxylase
B. Photosystem II
C. NADPH
D. ATP Synthase
A. RuBP Carboxylase
B. Photosystem II
C. NADPH
D. ATP Synthase
A. RuBP Carboxylase
55
New cards
Chlororplasts are green because chlorophyll absorbs green light.
A. True
B. False
A. True
B. False
B. False
56
New cards
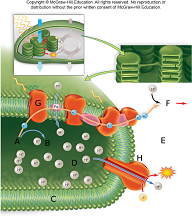
In the image above water is being broken into hydrogen and oxygen at the point represented by letter
A. A.
B. F.
C. H.
D. C.
A. A.
B. F.
C. H.
D. C.
A. A.
57
New cards
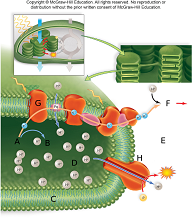
In the image above the stroma is represented by the letter
A. E.
B. D.
C. H.
D. G.
A. E.
B. D.
C. H.
D. G.
A. E.
58
New cards
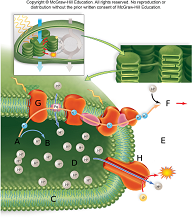
In the image above the thylakoid space is represented by the letter
A. E.
B. D.
C. H.
D. G.
A. E.
B. D.
C. H.
D. G.
B. D.
59
New cards
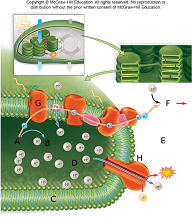
In the image above photosystem 2 is represented by the letter
A. E.
B. D.
C. H.
D. G.
A. E.
B. D.
C. H.
D. G.
D. G.
60
New cards
CHAPTER 23
CHAPTER 23
61
New cards
Alternative forms of a gene that influence the same trait and are found at the same location in homologous chromosomes are called
A. alleles.
B. phenotypes.
C. genotypes.
D. incomplete dominance.
A. alleles.
B. phenotypes.
C. genotypes.
D. incomplete dominance.
A. alleles.
62
New cards
Which of the following represents the physical characteristics of the individual?
A. phenotype
B. genotype
C. alleles
D. dominance
A. phenotype
B. genotype
C. alleles
D. dominance
A. phenotype
63
New cards
What are alleles?
A. genes for different traits, such as hair color and eye color
B. alternative forms of a gene for a single trait, such as blue eyes or brown eyes
C. the locations of genes on a chromosome
D. recessive forms of a kind of characteristic carried by genes
A. genes for different traits, such as hair color and eye color
B. alternative forms of a gene for a single trait, such as blue eyes or brown eyes
C. the locations of genes on a chromosome
D. recessive forms of a kind of characteristic carried by genes
B. alternative forms of a gene for a single trait, such as blue eyes or brown eyes
64
New cards
The _____ indicates the gene combination of an individual.
A. phenotype
B. loci
C. genotype
D. homozygous
A. phenotype
B. loci
C. genotype
D. homozygous
C. genotype
65
New cards
Which of the following is NOT correct concerning the law of independent assortment?
A. It is based upon the process of meiosis.
B. Each pair of factors separates independently.
C. All possible combinations of factors can occur in the gametes.
D. It follows the observation that all maternal chromosomes end up in the egg.
A. It is based upon the process of meiosis.
B. Each pair of factors separates independently.
C. All possible combinations of factors can occur in the gametes.
D. It follows the observation that all maternal chromosomes end up in the egg.
D. It follows the observation that all maternal chromosomes end up in the egg.
66
New cards
Which is NOT true according to Mendel's law of segregation?
A. Each individual contains two alleles for each trait.
B. An individual can have either both dominant alleles, both recessive alleles, or a dominant and recessive allele.
C. Alleles separate from each other during gamete formation.
D. Each gamete contains one copy of each allele.
E. Fertilization restores the presence of two alleles.
A. Each individual contains two alleles for each trait.
B. An individual can have either both dominant alleles, both recessive alleles, or a dominant and recessive allele.
C. Alleles separate from each other during gamete formation.
D. Each gamete contains one copy of each allele.
E. Fertilization restores the presence of two alleles.
B. An individual can have either both dominant alleles, both recessive alleles, or a dominant and recessive allele.
67
New cards
Mendel's law of segregation implies that the two members of an allele pair
A. are distributed to separate gametes.
B. are distributed to the same gamete.
C. are assorted dependently.
D. are segregated pairwise.
A. are distributed to separate gametes.
B. are distributed to the same gamete.
C. are assorted dependently.
D. are segregated pairwise.
A. are distributed to separate gametes.
68
New cards
In a Mendelian monohybrid cross involving two homozygous genotypes, the ____ generation is always completely heterozygous.
A. F1
B. F2
C. P
D. P2
A. F1
B. F2
C. P
D. P2
A. F1
69
New cards
What will the genotypic ratio be of a monohybrid cross of two individuals who are both heterozygous for a trait? Use the link in the instructions to an online Punnet square frame.
A. 100% homozygous dominant
B. 50% homozygous dominant, 50% homozygous recessive
C. 25% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous, 25% homozygous recessive
D. 50% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous
A. 100% homozygous dominant
B. 50% homozygous dominant, 50% homozygous recessive
C. 25% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous, 25% homozygous recessive
D. 50% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous
C. 25% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous, 25% homozygous recessive
70
New cards
A pheasant breeder starts with two birds in the P generation, one of which is AA and the other is aa. If he takes two of the birds from the F1 generation and breeds them together, what can he expect in his F2 offspring?
A. AA and Aa.
B. Aa and aa.
C. AA, Aa, and aa.
D. Aa only.
A. AA and Aa.
B. Aa and aa.
C. AA, Aa, and aa.
D. Aa only.
C. AA, Aa, and aa.
71
New cards
A woman who can roll her tongue (presumably dominant) is married to a man who cannot. Two of their four children can roll their tongues and two cannot. If A = roll tongue and a = cannot roll tongue, then what is the genotype of the parents?
A. woman Aa; man Aa
B. woman AA; man aa
C. woman Aa; man AA
D. woman Aa; man aa
A. woman Aa; man Aa
B. woman AA; man aa
C. woman Aa; man AA
D. woman Aa; man aa
D. woman Aa; man aa
72
New cards
Some plants fail to produce chlorophyll, due to a recessive trait. If we locate a pea plant that is heterozygous for this trait, self-pollinate it, and harvest the seeds, what are the likely phenotypes of the resulting offspring?
A. All will be green with chlorophyll since that is the dominant trait.
B. About one-half will be green and one-half white since that is the distribution of the genes in the parents.
C. About one-fourth will be white and three-fourths green since it is similar to a monohybrid cross.
D. About one-fourth will be green and three-fourths white since it is similar to a monohybrid cross.
A. All will be green with chlorophyll since that is the dominant trait.
B. About one-half will be green and one-half white since that is the distribution of the genes in the parents.
C. About one-fourth will be white and three-fourths green since it is similar to a monohybrid cross.
D. About one-fourth will be green and three-fourths white since it is similar to a monohybrid cross.
C. About one-fourth will be white and three-fourths green since it is similar to a monohybrid cross.
73
New cards
. A cross is made between two parents with genotypes AaBB and aabb. If there are 32 offspring, how many of them would be expected to exhibit both dominant characteristics?
A. 32
B. 24
C. 16
D. 8
E. 0
A. 32
B. 24
C. 16
D. 8
E. 0
C. 16
74
New cards
. In guinea pigs, B = black, b = brown, S = short hair, s = long hair. A heterozygous black, short-haired animal reproduces with a brown, long-haired animal. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of the offspring?
A. 1 black short hair, 1 black long hair, 1 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair
B. 9 black short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 brown short hair
C. 9 black short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair
D. 9 black short hair, 6 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 brown short hair
A. 1 black short hair, 1 black long hair, 1 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair
B. 9 black short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 brown short hair
C. 9 black short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair
D. 9 black short hair, 6 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 brown short hair
A. 1 black short hair, 1 black long hair, 1 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair
75
New cards
. In humans, aniridia, a type of blindness, is due to a dominant allele A. Migraine headaches are due to another dominant allele M. If a man who suffers from both conditions (AaMm) marries a woman who suffers from both (AaMm), what are the chances of an offspring expressing both traits.
A. 9/16
B. 3/16
C. 1/2
D. 1/16
A. 9/16
B. 3/16
C. 1/2
D. 1/16
A. 9/16
76
New cards
In which kind of cross could you expect to find ratios of 1:1:1:1 among the offspring?
A. monohybrid cross
B. dihybrid cross
C. one-trait test cross
D. two-trait test cross
A. monohybrid cross
B. dihybrid cross
C. one-trait test cross
D. two-trait test cross
D. two-trait test cross
77
New cards
In guinea pigs, B = black, b = brown, S = short hair, s = long hair. Two heterozygous individuals reproduce. The expected results are
A. 9 black long hair, 3 black short hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 brown short hair.
B. 9 black short hair, 6 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 black short hair.
C. 9 black short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair.
D. 9 brown short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 black short hair.
A. 9 black long hair, 3 black short hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 brown short hair.
B. 9 black short hair, 6 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 black short hair.
C. 9 black short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair.
D. 9 brown short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown long hair, 1 black short hair.
C. 9 black short hair, 3 black long hair, 3 brown short hair, 1 brown long hair.
78
New cards
What genetic disorder is associated with the lack of an enzyme necessary for the normal metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine?
A. phenylketonuria (PKU)
B. Huntington disease
C. sickle cell disease
D. cystic fibrosis (CF)
A. phenylketonuria (PKU)
B. Huntington disease
C. sickle cell disease
D. cystic fibrosis (CF)
A. phenylketonuria (PKU)
79
New cards
. Which genetic disorder is associated with an irregular shape of the red blood cells?
A. sickle cell disease
B. Marfan syndrome
C. Huntington disease
D. cystic fibrosis (CF)
A. sickle cell disease
B. Marfan syndrome
C. Huntington disease
D. cystic fibrosis (CF)
A. sickle cell disease
80
New cards
What are the chances that two individuals with wavy hair (an incomplete trait) will have a curly-haired child? Curly hair and straight hair exhibit incomplete dominance.
A. none
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
A. none
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
B. 25%
81
New cards
. The four o'clock flower is an example of incomplete dominance: R = red, r = white, and Rr = pink. If two hybrids are crossed, what are the chances that an offspring will have pink flowers?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
E. 100%
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
E. 100%
C. 50%
82
New cards
Traits that are controlled by several sets or pairs of alleles, such as skin color and height in humans, are the result of what form of inheritance?
A. polygenic
B. incomplete dominance
C. simple Mendelian inheritance
D. codominance
A. polygenic
B. incomplete dominance
C. simple Mendelian inheritance
D. codominance
A. polygenic
83
New cards
Which of the following is an example of the blending of phenotypes?
A. codominance
B. polygenic inheritance
C. simple Mendelian inheritance
D. incomplete dominance
A. codominance
B. polygenic inheritance
C. simple Mendelian inheritance
D. incomplete dominance
D. incomplete dominance
84
New cards
You have two true-breeding rose bushes, one with red flowers and one with white flowers. A cross between these two roses yields a bush with pink flowers. What condition does this demonstrate?
A. codominance
B. incomplete dominance
C. environmental effects
D. polygenetic inheritance
A. codominance
B. incomplete dominance
C. environmental effects
D. polygenetic inheritance
B. incomplete dominance
85
New cards
When two or more genes with multiple alleles affect the same trait in an additive fashion, it is termed
A. a double-trait cross.
B. codominant.
C. incomplete dominance.
D. polygenic inheritance.
A. a double-trait cross.
B. codominant.
C. incomplete dominance.
D. polygenic inheritance.
D. polygenic inheritance.
86
New cards
. You have two true-breeding rose bushes, one with red flowers and one with white flowers. A cross between these two roses yields a bush with white flowers that have red splotches. What condition does this demonstrate?
A. codominance
B. incomplete dominance
C. environmental effects
D. polygenetic inheritance
E. monohybrid inheritance
A. codominance
B. incomplete dominance
C. environmental effects
D. polygenetic inheritance
E. monohybrid inheritance
A. codominance
87
New cards
Cold weather can change the ______ of a Himalayan rabbit.
A. genotype
B. phenotype
C. alleles
D. sex
A. genotype
B. phenotype
C. alleles
D. sex
B. phenotype
88
New cards
Hydrangeas are a flowering plant with large showy blooms. When a plant is grown in aluminum-rich soil it has blue flowers. If the same plant is transplanted into soil that is lacking aluminum, the flowers produced will be pink. This is an example of
A. codominance.
B. incomplete dominance.
C. environmental effects.
D. polygenetic inheritance.
A. codominance.
B. incomplete dominance.
C. environmental effects.
D. polygenetic inheritance.
C. environmental effects.
89
New cards
In peas, yellow is dominant over green in seeds. With which of these is it best to cross a yellow-seeded pea plant to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous?
A. a green-seeded plant
B. a heterozygous yellow-seeded plant
C. a pure yellow-seeded plant
D. a heterozygous yellow-seeded plant or a pure yellow-seeded plant
A. a green-seeded plant
B. a heterozygous yellow-seeded plant
C. a pure yellow-seeded plant
D. a heterozygous yellow-seeded plant or a pure yellow-seeded plant
A. a green-seeded plant
90
New cards
CHAPTER 24
CHAPTER 24
91
New cards
Principles of Biology Chapter 24 Questions
1. The location of a gene on a chromosome is called
A. a locus.
B. a linkage map.
C. a linkage group.
D. an allele.
1. The location of a gene on a chromosome is called
A. a locus.
B. a linkage map.
C. a linkage group.
D. an allele.
A. a locus.
92
New cards
Considering that males can have Klinefelter (XXY) syndrome, XYY, and normal XY chromosomal combinations, and females can have Turner (XO) syndrome, poly-X (XXX, XXXX), and normal XX combinations, it is obvious that
A. maleness results from the presence of only one X chromosome.
B. maleness results from the absence of two or more X chromosomes.
C. maleness results from the minimal presence of one Y chromosome.
D. femaleness results from the presence of two or more X chromosomes.
A. maleness results from the presence of only one X chromosome.
B. maleness results from the absence of two or more X chromosomes.
C. maleness results from the minimal presence of one Y chromosome.
D. femaleness results from the presence of two or more X chromosomes.
C. maleness results from the minimal presence of one Y chromosome.
93
New cards
Genes on the ___ chromosome determine if the sex of a child will be male or female.
A. X
B. Y
C. 21st
D. 5th
A. X
B. Y
C. 21st
D. 5th
B. Y
94
New cards
A normal male marries a color-blind woman. What percent of their female children will be color-blind?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
E. 100%
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
E. 100%
A. 0%
95
New cards
Color-blindness is inherited as an X-linked recessive trait. A male who is color-blind marries a heterozygous woman. What percent of their total children will be color-blind?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
E. 100%
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
E. 100%
C. 50%
96
New cards
A color-blind (recessive trait) woman will pass the allele to
A. her sons only.
B. all her children.
C. her daughters only.
D. none of her children.
E. her husband.
A. her sons only.
B. all her children.
C. her daughters only.
D. none of her children.
E. her husband.
B. all her children.
97
New cards
If a woman is a carrier for the color-blind recessive allele and her husband has normal vision, what are their chances that a son will be color-blind?
A. None, because the father is normal.
B. 50%, since the mother is only a carrier.
C. 100% because the mother has the gene.
D. 25% because the mother is a hybrid.
E. None since the son will also be just a carrier.
A. None, because the father is normal.
B. 50%, since the mother is only a carrier.
C. 100% because the mother has the gene.
D. 25% because the mother is a hybrid.
E. None since the son will also be just a carrier.
B. 50%, since the mother is only a carrier.
98
New cards
Which of the following sex-linked diseases is characterized by the absence of a clotting factor?
A. hemophilia
B. color-blindness
C. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
D. None of the answer choices is true.
A. hemophilia
B. color-blindness
C. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
D. None of the answer choices is true.
A. hemophilia
99
New cards
Which refers to the loss of a complete chromosome?
A. inversion
B. translocation
C. deletion
D. monosomy
A. inversion
B. translocation
C. deletion
D. monosomy
D. monosomy
100
New cards
A person who has an extra copy of a chromosome is said to have
A. monosomy.
B. trisomy.
C. nondisjunction.
D. duplication.
A. monosomy.
B. trisomy.
C. nondisjunction.
D. duplication.
B. trisomy.