ADH1 FINAL (Neuro, Acid/Base, PVD)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Risk factors Alzhemier’s (8)
Fam hx of AD/ Down syndrome
Genes (apolipoprotein—obese)
Old age
Head injury
PTSD
Female
Ethnicity (AA or Hispanic)
Environment/ Chemical
Assessment tool for Alzheimer’s Dementia (5)
Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE)
Clock Drawing
Set test—Fruits, Animals, Colors, Towns (FACT)
Montral Cognitive Assessment (MoCA)
3 unrelated words
Brief Interview
Nursing care Alzheimer’s: (4)
Assess cognitive status, memory, judgement and personality
Bowel& Bladder schedules
Self-care if possible
No Overstimulation
Promote safety for Alzheimer’s pt: (7)
Walk often to reduce wandering
Remove clutter, throw rugs
Install handrails
Sleeping schedule
skin checks
Visual checks (q1-2h)
Snacks and small frequent meals
How to communicate for Alzheimer’s pt: (5)
Communication board
Therapeutic comm
calm voice
Reorientation
Short, simple sentences/ choices
Give time to response
Delirium is a clinical syndrome that causes what state?
acute confusional
Who at risk for developing delirium? (7)
Critical care settings—ICU
Infections
Alcohol toxicity
Head trauma
Insomnia—disturbed circadian rhythm
Sudden change in living environment
Sensory deprivation/ overload
3 hallmark signs delirium?
Inattentiveness
Confusion/ Disorganized thoughts
Altered LOC
3 Types of Delirium:
Hyperactive
Hypoactive
Mixed
Hyperactive delirium presentation: (4)
Agitated
Hallucinations
Restless
Aggressive
Hypoactive delirium presentation: (5)
Withdrawn/ drowsy
Lethargic
More common
Harder to detect
Higher risk of mortality
Main feature differentiating delirium from depression and dementia:
acute—fluctuating nature of symptoms
Mixed delirium manifestation:
periods of withdrawn and drowsy to agitated and restlessness
PREVENTION strategies for delirium: (8)
glasses/ hearing aids
day/night orientation (circadian rhythm)
method of comm. if barrier
no close ended
comm board w/ place and date
clock in view
noise control
promote sleep
cluster care activities
Delirium screening tools: (4)
Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS)
0 & -1 = alert/calm; awakens to voice
+4= combative
-4= unarousable
Confusion Assessment Method (CAM)
ICU CAM
Delirium Rating Scale
Tx and management delirium—in general: (3)
ID contributing factors
No overstimulation
Interdisciplinary team
Nursing INTERVENTIONS delirium: (4)
NO overstimulate
Anticipate & Prevent/ Manage complications
Urinary incontinence
Immobility/ Falls
Pressure ulcers
Sleep disturbances
Feeding disorders
Remove contributing factors causing confusion
Reorient frequently
What are complications OF delirium? (5)
Sleep disturbances
Immobility/ Falls
Pressure Ulcers
Urinary Incontinence
Feeding disorders
Parkinson’s is progressive degenerative disorder that affects what kind of function and loss of what activity?
affects motor function
loss of extrapyramidal activity
Neurotransmitter lost in PD?
dopamine!!
Risk factors associated w/ PD? (3)
genetically male
environmental toxins/ chemicals
CO
Carbon disulfide
pesticides
chronic antipsychotic med use
4 cardinal symptoms PD:
Tremors at rest (pill-rolling)
Rigidity of muscles
Akinesia: loss of mvmt/ bradykinesia
Postural instability
Whats the goal of anti-cholinergic med in tx of Parkinson’s?
Reduce tremors, drooling, rigidity!!
What should nurse monitor for if pt is taking a dopamine agonist in PD??
(3)
Ortho Hypotension
Dyskinesia
Hallucinations
What is Deep Brain Stimulation?? (2)
Stimulator electrode implanted in upper chest in Parkinson’s pt
Targeted area receives mild electrical stimulation to reduce tremors and rigidity
What should nurse monitor post-op in Deep Brain Stimulation?? (3)
s/s infection
drainage
vs: increased HR, RR, temp
Hemorrhage
decreased BP, LOC
increase HR, RR, ICP
Stroke-like symptoms
FAST
Face, Arms, Speech, Time
Normal pH, PaCO2, and HCO3 ranges:
pH: (a) 7.35-7.45 (b)
PaCO2: (b) 35-45 (a)
HCO3: (a) 22-26 (b)
pH: 7.36
PaCO2: 48
HCO3: 24
pH: N (A)
PaCO2: A
HCO3: N
Fully compensated Respiratory Acidosis
pH: 7.26
PaCO2: 35
HCO3: 16
pH: A
PaCO2: N
HCO3: A
Uncompensated Metabolic Acidosis
pH: 7.30
PaCO2: 58
HCO3: 30
pH: A
PaCO2: A
HCO3: B
Partially compensated Respiratory Acidosis
pH: 7.52
PaCO2: 26
HCO3: 22
pH: B
PaCO2: B
HCO3: N
Uncompensated Respiratory Alkalosis
PAD affects vessels carrying blood?
AWAY from heart!!
Risk factors PAD: (10)
HTN
HLD
DM
Obese (BMI >30)
Old age >50 +
Female
Smoking
Sedentary life
Elevated CRP
Hyperhomocysteinemia
Expected clinical findings for PAD? (7)
Intermittent claudication
burning, cramping pain in legs when exercising
Numbness/ Burning pain in feet in bed
bc no blood flow
Pain relieved w/ legs at rest in dependent position
dangling = easier blood flow (rubor)
Bruit over abdominal aorta/ femoral arteries
Pallor/Cold/Cyanotic
No pulse
Shiny legs/ Ulcer toes
Positioning for pt w/ PAD would elevate legs BUT:
NOT above heart
bc PAD makes it hard already for blood to flow away from heart
no pillow
What is Medical emergency for a pt w/ PAD??
Compartment Syndrome!!
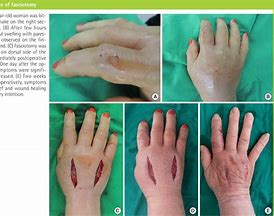
6 P’s associated w/ Compartment syndrome (PAD)
Pallor
Paresthesia
Pulselessness
Pain
Paralysis
Poikilothermia
How does Raynaud’s occur?
Vasospasm causing narrowing of arteries

Cause of primary Raynauds disease and what 3 things triggers it:
Idiopathic (arises spontaneously)
Exposure to cold temps
Stress
Blood vessel vasospasms
Cause of secondary Raynauds and examples of it: (5)
from comorbidities
Scleroderma (tightening of skin)
Lupus
RA
Arterial disease
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
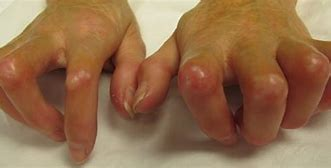
Pt education for Raynaud’s: (5)
Smoking cessation
Exercise
Stress reduction
Limit caffeine
Avoid cold temps
Peripheral Venous Disease affects vessels carrying blood:
TOWARDS heart
Expected findings of DVT/VTE: (4)
Calf/ groin pain, tenderness, sudden onset of edema in extremity
Warmth, edema, induration & hardness over involved blood vessel
Changes in size (circumference) to affected leg
Pt could be asymptomatic
How would you know if a embolus moved to lungs in PVD?
embolus moves from legs causing SOB and CP!!! (PE)
emergency!!
Labs/ Diagnostics to draw for a DVT: (3)
D-Dimer (blood specimen)
measures fibrin degradation present in blood produced from fibrinolysis
Venous Duplex USN (DVT & Thrombophlebitits)
Doppler flow

Whats a complication of PVD?
Pulmonary Embolism!!
How does PE form? and what are results of it (2)
Thrombus breaks off —> embolus —> travels to pulmonary vessel and blocks flow
decreases systemic O2
Hypoxia
Clinical manifestations of PE: (4)
Dyspnea/ SOB
CP
Hemoptysis (cough blood)*
feeling of “impending doom”*
Nursing Intervention for Pulmonary Embolism: (5)
Assist to comfy position
O2
ABGs
Admin anticoagulant (heparin/warfarin)
Notify HCP!!
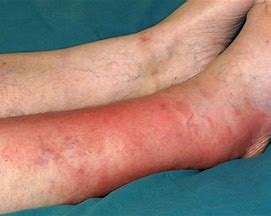
Describe what cellulitis is:
local bacterial infx in subQ tissue
Risk factors of cellulitis: (5)
older pt
weak immune system
break in skin (1st defense)
IV drug use
DM
Manifestations Cellulitis: (5)
Tenderness/ Inflammation
Skin sore or rash spreading quickly
Tight, glossy skin
Abscess/pus formation
Fever, elevated WBCs (infx)
Cellulitis medication management: (2)
IV abx
Analgesics
acetaminophen
ibuprofen for pain