cram
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
Absolute Pathname
starts with a slash (/), which represents the root directory. The slash is followed by the name of a file located in the root directory. An absolute pathname can continue, tracing a path through all intermediate directories, to the file identified by the pathname. String all the filenames in the path together, following each directory with a slash (/). This string of filenames is called an absolute pathname because it locates a file absolutely by tracing a path from the root directory to the file.
2
New cards
Relative Pathname
traces a path from the working directory to a file. The pathname is relative to the working directory. Any pathname that does not begin with the root directory (represented by /) or a tilde (\~) is a relative pathname
3
New cards
3 ways to return to your home directory
cd \~, cd, cd $HOME
4
New cards
What‘s the arrangement of directories and files in the unix system?
a tree-like structure called the file system, called a directory tree. At the very top of the file system is a directory called “root” which is represented by a “/”. All other files are “descendants” of root.
5
New cards
What directory does it take you to when you first log in?
The home directory.
6
New cards
What’s the command that gives helpful information on a utility?
man (eg: ‘man cat’ will display a manual on the cat utility)
7
New cards
What symbol do hidden files in a directory start with?
dot character (.)
8
New cards
What’s the command that tells you the current name of the shell?
echo $0 (returns -bash)
9
New cards
Set a variable value in a borne shell. How do you display the variable?
echo $variname
10
New cards
What does echo $PATH display?
Which directories your shell is set to check for executable files. $PATH is the list of said directories.
11
New cards
What is the command and option that lets you see all the meta information of a file?
ls -l filename
12
New cards
Inside a borne shell script, what’s the symbol used for the PID?
$$
13
New cards
What’s the command that can be used to change permission information for a file?
chmod
syntax: chmod a+r filename (makes filename readable to all)
syntax: chmod a+r filename (makes filename readable to all)
14
New cards
What’s the command that copies files?
cp
syntax: cp ogfile copyfile
syntax: cp ogfile copyfile
15
New cards
What’s the command that is used to tell the type information of a file?
file
eg: file filename (displays filename: ASCII text)
eg: file filename (displays filename: ASCII text)
16
New cards
What’s the command used on a file to display one page of information of the file contents at a time?
more or less (less allows you to scroll up, more does not)
eg: cat filename | less
eg: cat filename | less
17
New cards
What’s the command to make soft links?
ln -s filename linkname
Allows multiple filenames to be linked to a file
Allows multiple filenames to be linked to a file
18
New cards
What’s the command that outputs the contents of a text file?
cat filename
19
New cards
What’s the command that searches for patterns in a text file?
grep string filename
20
New cards
Basic redirection syntax.
cat > filename
Create a file called filename. Type the desired input and press CTRL+D to finish. The text will be in file filename.
cat < filename
Just cats the content of filename.
Create a file called filename. Type the desired input and press CTRL+D to finish. The text will be in file filename.
cat < filename
Just cats the content of filename.
21
New cards
What is the command that makes a new subdirectory/directory?
Mkdir dirName
22
New cards
What’s the command that removes a file? Moves a file?
rm filename
mv filename newfile
mv filename newfile
23
New cards
What’s the command that displays the information about the users logged into the system?
who
24
New cards
What’s the command that deletes a non-empty directory?
rmdir or rm -d
25
New cards
If I touch a file name, and the file name doesn't already exist, does touch create it?
Yes, touch creates an empty file.
26
New cards
If you set the variable value in the shell and you want a program/script to read and display it, what command do you have to do on the variable to make it available to the script?
export
27
New cards
How do you read in a value in a shell prompt?
read

28
New cards
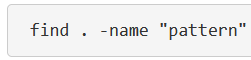
What does the command “find” do? find -name?
used to find files and directories and perform subsequent operations on them. It supports searching by file, folder, name, creation date, modification date, owner and permissions.
\
find -name searches filenames specifically.
\
find -name searches filenames specifically.
29
New cards
What is the command to list all the files in your working directory that start with a dot?
ls -a lists all files including hidden files that start with a dot. do not try ls .\* it broke my thing
30
New cards
Metacharacter for pipe?
|
31
New cards
Which key stroke will enter command mode in VIM?
esc
32
New cards
in VIM, which keystroke will allow you to enter editor mode?
i
33
New cards
What mode is VIM in at first?
command mode
34
New cards
Command to write (save) the contents of the files then quit the editor?
esc :wq!
35
New cards
What symbols do commands start with in VIM?
\:
36
New cards
Can you chmod a file you don’t own?
No
37
New cards
Can you list metadata on files you don’t own?
Yes
38
New cards
What is a root?
A user that can do anything (ex: chmod any file)
39
New cards
What does touching an already existing file do? Does it reset it’s permissions?
if the file existed beforehand, touch will not change its permissions, just update its last edited timestamps
40
New cards
What is a token?
A non blank character/sequences of characters
\
A token is made up of ordinary characters, or of operator characters ()<>&|;, but not both. For example, foo
\
A token is made up of ordinary characters, or of operator characters ()<>&|;, but not both. For example, foo
41
New cards
What symbol do options start with?
\-
42
New cards
Identify commands with 0 arguments.
cd, pwd
43
New cards
What is an example of a built-in command?
echo, cd
44
New cards
How do you do piping?
A pipe is a form of redirection (transfer of standard output to some other destination). Allows you to use 2 commands at once
ex: history | tail
calls history command and tail to display the last 10 executed commands
ex: history | tail
calls history command and tail to display the last 10 executed commands
45
New cards
What’s the comments you need on the first line of the script to ensure it gets executed on the bash shell?
\#!/bin/bash
46
New cards
What are the 2 metasymbols you have to put at the beginning of a script for it to run correctly?
./
47
New cards
What’s the syntax for creating an alias?
alias ‘someAlias=someCommand’
48
New cards
What does grep do? Syntax?
Identifies line with requested string.
grep “l” filename
works on directories to search file names
grep “l” filename
works on directories to search file names
49
New cards
Which file do you save variables, functions, and aliases to so they are available upon log in?
In the \~/.bashrc file
50
New cards
What are the single dot and double dot directory entries?
mkdir automatically adds these 2 entries.
The . is synonymous with the pathname of the-working directory and can be used in its place; the .. is synonymous with the pathname of the parent of the working directory. These entries are hidden because their filenames begin with a period.
The . is synonymous with the pathname of the-working directory and can be used in its place; the .. is synonymous with the pathname of the parent of the working directory. These entries are hidden because their filenames begin with a period.
51
New cards
num=875
number1=”Add $num”
number2=’Add $num’
\
What will echo $number1 and echo $number2 display?
number1=”Add $num”
number2=’Add $num’
\
What will echo $number1 and echo $number2 display?
Add 875
Add $num
Add $num
52
New cards
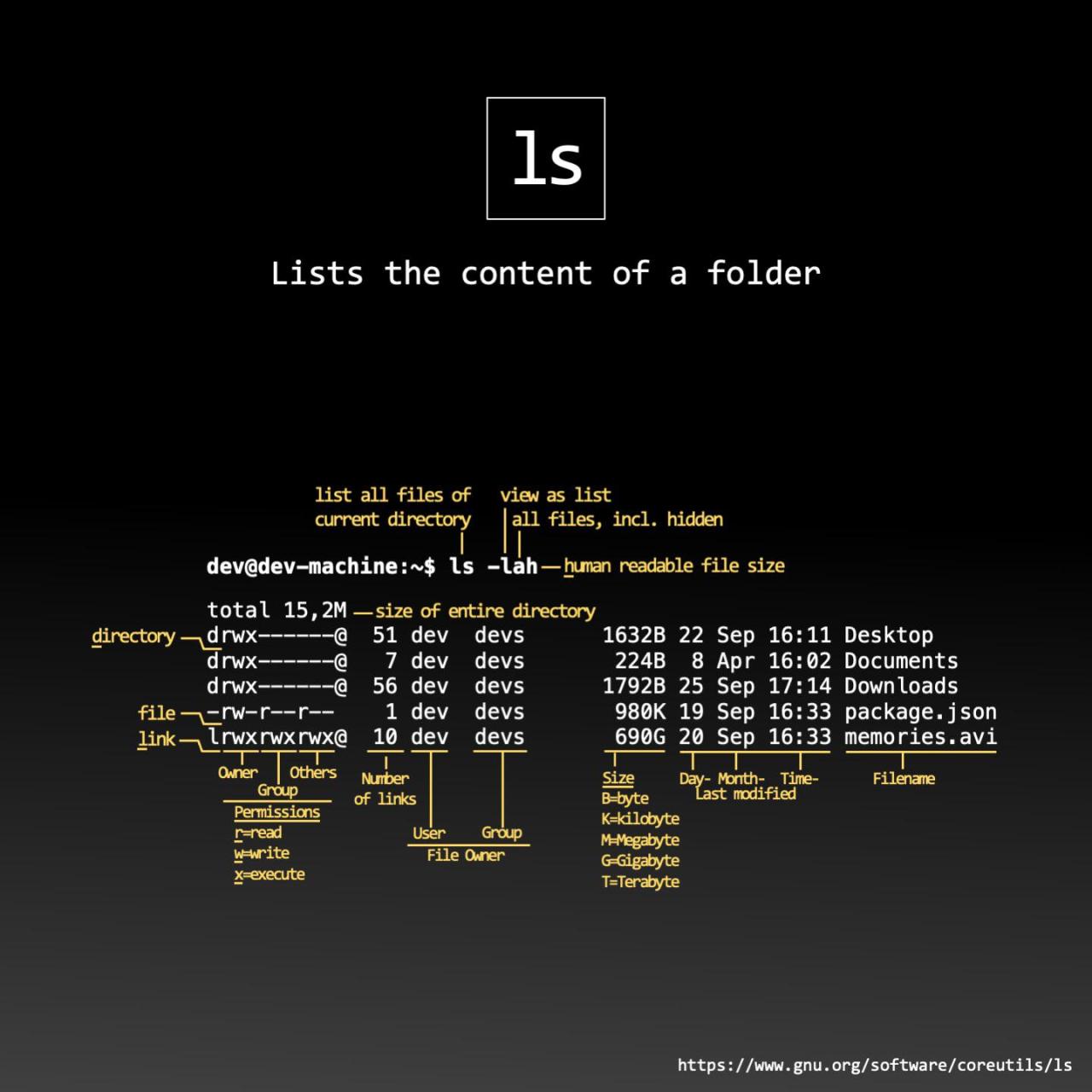
ls -l info idk just memorize this
53
New cards
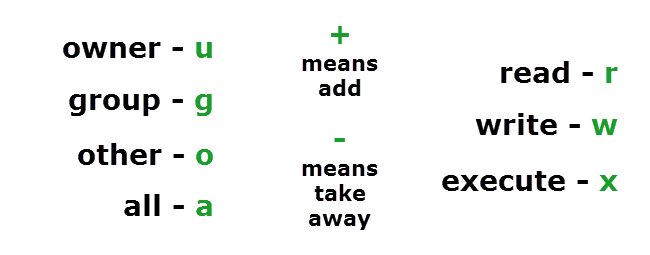
chmod symbols (just memorize this too)
54
New cards
Do I have to put symbols in front of a function name to run it or can I just put the name of the function?
Just name of function.
55
New cards
What is the shell metacharacter that matches 0 or more characters?
\*
56
New cards
What is the shell metacharacter that matches 1 character?
?
57
New cards
Inside a script, what are the symbols that contain the arguments on the command line to the script?
$1, $2, … , $n for each argument n on the command line