chapter 46 role of ultrasound in INFERTILITY
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Purpose of Evaluation:
To assess whether the cervix provides a sperm-friendly environment and to rule out structural issues that could impact fertility.
Key Things Being Evaluated:
Cervical stenosis (narrowing <1 mm) — may hinder sperm passage
Detected via HSG (hysterosalpingography), not well assessed with ultrasound
Nabothian cysts — usually benign, not typically related to infertility
Cervical length — mainly evaluated in pregnancy for competence, limited utility in nongravid patients
Cervix
Purpose of Evaluation:
To check for structural anomalies or masses that might impair implantation or gestation.
Key Things Being Evaluated:
Structural anomalies:
Congenital uterine anomalies:
Septate uterus (associated with high infertility risk due to poor blood supply to septum)
Bicornuate uterus
Uterus didelphys
T-shaped uterus (related to DES exposure; no treatment available)
These are often visualized with 2D/3D ultrasound, HSG, or MRI
Masses or irregularities:
Submucosal fibroids — can distort cavity, affect implantation
Uterus
Purpose of Evaluation:
To assess lining thickness and appearance, which reflects hormonal response and implantation potential.
Key Things Being Evaluated:
Endometrial thickness:
>6mm is associated with better implantation potential
Measured in sagittal plane
Endometrial appearance:
Triple-line sign (proliferative phase, pre-ovulation)
Homogeneous, echogenic lining (secretory phase, post-ovulation)
Abnormalities:
Polyps — hyperechoic, narrow base, vascular stalk (seen on SIS)
Fibroids — isoechoic with broad base, circumferential flow
Synechiae — adhesions from trauma/infection; appear as linear bands
Endometrium
Purpose of Evaluation:
To determine whether the tubes are open (patent) and free of damage.
Key Things Being Evaluated:
Hydrosalpinx — fluid-filled tube (50% lower pregnancy rate, higher miscarriage risk)
Patency testing:
Saline infusion with air bubbles or contrast to check for spillage into the cul-de-sac
No spillage = possible obstruction
Tools used: SIS, HSG, or laparoscopy with chromopertubation
Pre-assessment with transvaginal ultrasound:
Evaluate anatomy, ovarian-tubal relation, mobility
Fallopian Tubes
Purpose of Evaluation:
To evaluate ovulatory function and detect PCOS or other ovulatory disorders.
Key Things Being Evaluated:
Follicular development:
Antral follicles <5 mm
Dominant follicle ~22 mm = ready for ovulation
Ovulation signs:
Follicular rupture
Corpus luteum cyst
Free fluid in cul-de-sac
Serum progesterone >3 ng/mL confirms ovulation
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
Diagnostic triad:
Oligo- or anovulation
Hyperandrogenism
Polycystic ovaries
Sonographic sign: “String of pearls” — ≥25 small peripheral follicles (2–9 mm)
Thickened endometrium may also be present
Ovaries
Purpose of Evaluation:
To identify external uterine or ovarian conditions (like adhesions or endometriosis) that impact fertility.
Key Things Being Evaluated:
Endometriosis:
Especially when involving ovaries → forms endometriomas
Typical sonographic appearance: “ground glass” echoes, homogenous low-level echoes
Adhesions:
May block tubes or restrict mobility
Difficult to assess via ultrasound alone; best seen with laparoscopy
Peritoneal inclusion cysts:
Fluid trapped by adhesions
Peritoneal Factors
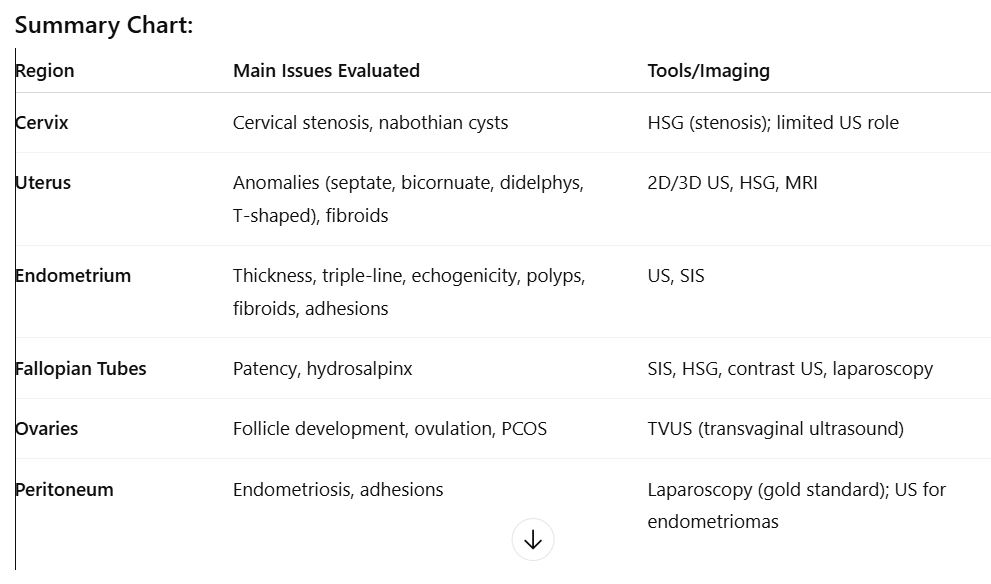
Summary Chart
Purpose:
Stimulate the ovaries to produce one or more follicles to increase the chance of ovulation and pregnancy.
Steps & Evaluation:
Baseline Transvaginal Ultrasound (early cycle):
Rule out ovarian cysts (>15mm could interfere with meds)
Check for dominant follicle or intracavitary masses
Medications Used:
Oral: Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) or Letrozole
Injectable: Human menopausal gonadotropins
Monitoring:
Ultrasound on days 10–14 of cycle to:
Count and measure all follicles >1cm
Assess for mature follicles (target: ~20mm)
Estradiol levels may be checked for correlation
Trigger Ovulation:
When follicles mature, hCG injection is given to mimic LH surge
Additional Evaluation:
Antral Follicle Count (AFC):
Evaluates ovarian reserve by counting 2–6mm follicles in both ovaries
Low AFC (<5) = poor prognosis
High AFC = better response to stimulation
2. Monitoring the Endometrium
Purpose:
To confirm the endometrial lining is receptive for implantation.
What is Evaluated:
Thickness:
Should increase from 2–3 mm to 12–14 mm
Measured in sagittal plane from anterior to posterior interface
Echogenicity/Pattern:
Trilaminar (triple-line) pattern is ideal
<6mm thickness or abnormal pattern = lower chance of implantation
Ovulation Induction Therapy (OIT)
Purpose:
Fertilize eggs outside the body and transfer embryos into the uterus.
Process:
Ovarian Monitoring (similar to OIT, but more aggressive):
Goal: Produce multiple mature follicles
Oocyte Retrieval:
Done via transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration
Needle inserted through vaginal wall into follicles
Fertilization & Incubation:
Oocytes are mixed with sperm in lab
Embryo Transfer:
Done under transabdominal ultrasound guidance with a full bladder
Embryo placed within 2 cm of fundus
Air bubble may be seen after release
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Purpose:
Deliver sperm directly into the uterine fundus to bypass cervical or mild male factor issues.
Procedure:
Catheter delivers washed sperm into the uterus
Donor sperm may be used (donor insemination)
Ultrasound not typically used during the insemination itself
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
complication
Cause:
Excessive response to ovulation induction drugs
Sonographic Findings:
Enlarged ovaries (5–10 cm)
Multiple cysts
Ascites, possibly pleural effusion
Seen more in young patients or those with PCOS
Symptoms:
Abdominal pain, bloating, back pain
Severe cases: hypotension, leg edema, hemoconcentration
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
complication
Cause:
Transfer of multiple embryos (IVF) or overstimulation of ovaries (OIT)
Stats:
~30% of IVF pregnancies result in twins or higher
Risks:
Higher chance of:
Preterm birth
Neonatal complications
Miscarriage
Triplets or more may require fetal reduction
Done under ultrasound guidance by injecting potassium chloride into fetal heart
Multiple Gestations
complication
Cause:
Higher risk in ART patients due to manipulation of embryo transfer or tubal pathology
Location:
Usually in the fallopian tube
Ectopic Pregnancy
complication
Definition:
Coexistence of an intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy
Incidence:
Natural: ~1 in 4,000
ART Patients: ~1 in 100
Key Point:
Even if an intrauterine pregnancy is seen, always check the adnexa for possible ectopic pregnancy
Heterotopic Pregnancy
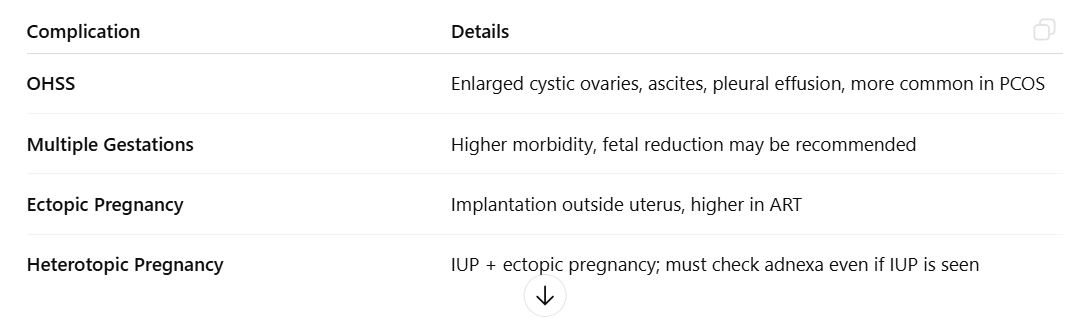
complication summary chart
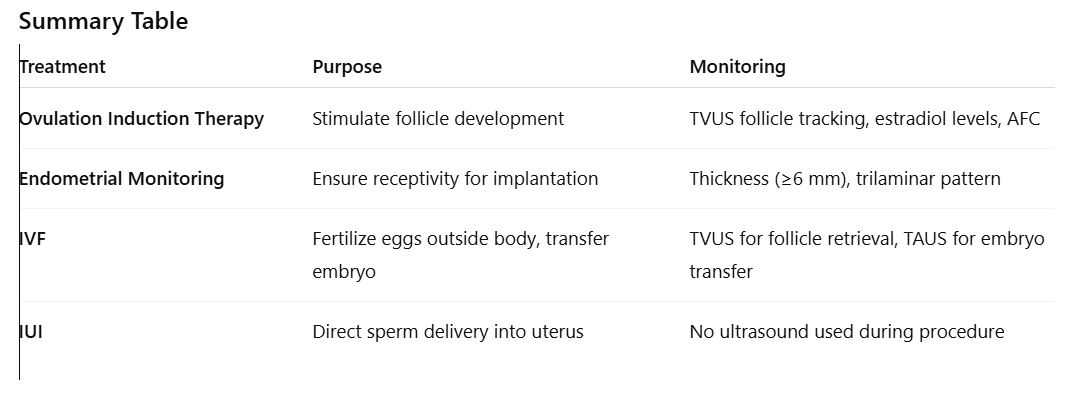
treatment summary chart
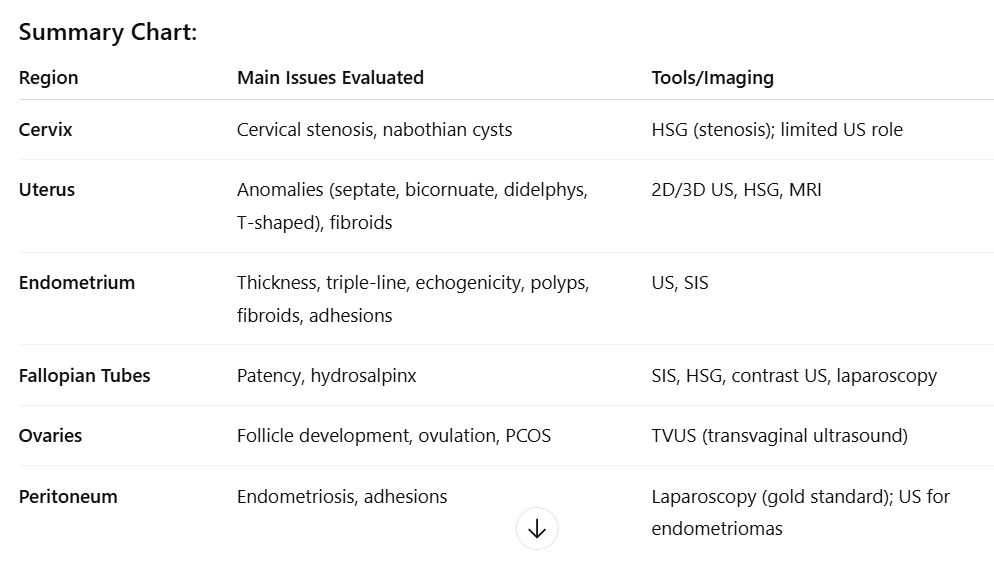
main organs evaluation chart