Muscles and Tendons of the Distal Limb (Week 2, Mod 7)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
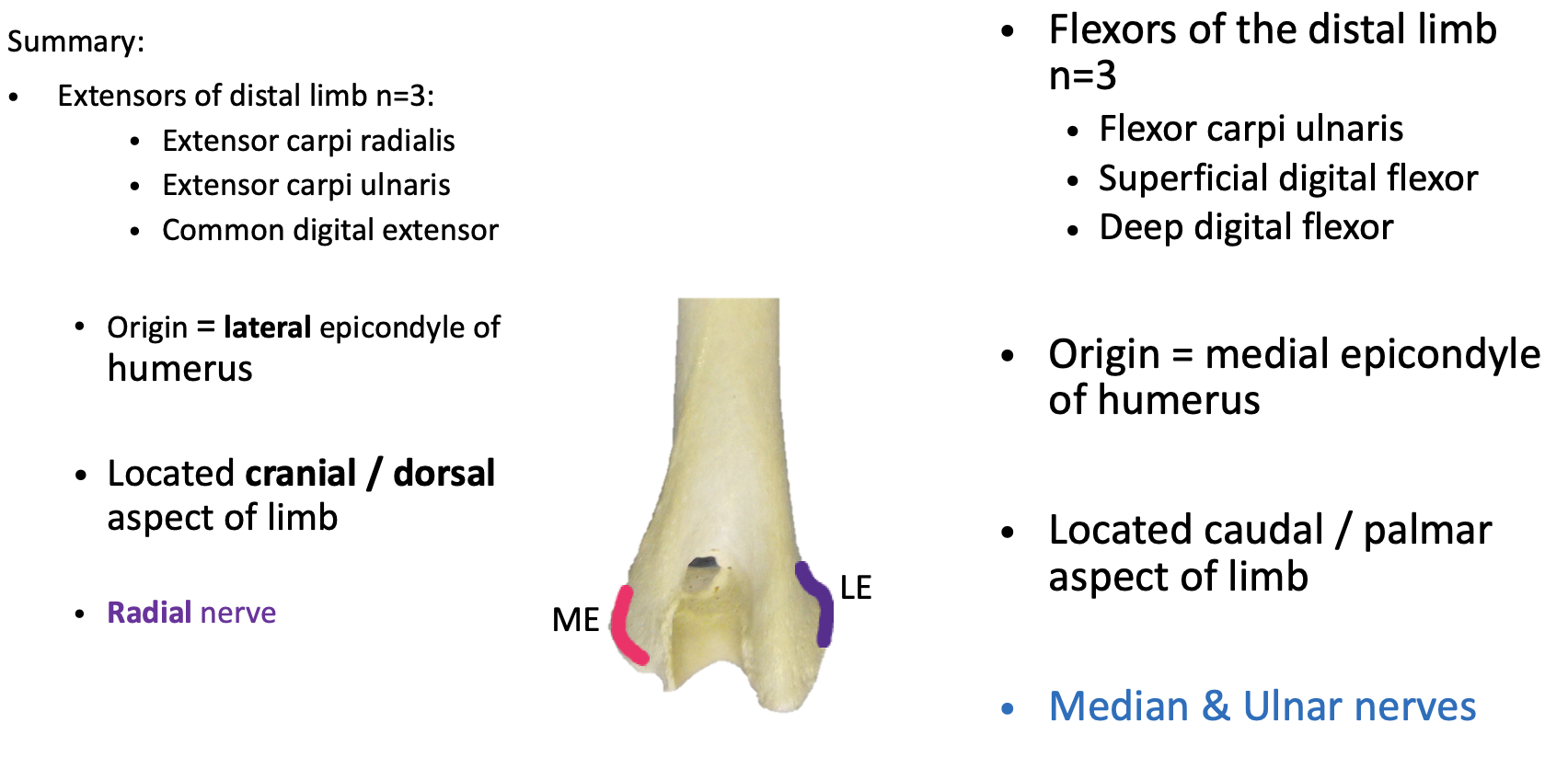
What are some general features of the muscles of the antebrachium? Keep these in mind as you go along, as these will remain constant (there are 5)
1) Will affect the joints of the carpus and digits
2) Origin - epidcondyles of the humerus
3) Muscle belly located in the antebrachium ; extend as tendons to the carpus and digits
4) Tendon of insertion → distal to carpus
5) EXTENSOR = DORSAL ASPECT OF CARPUS
FLEXOR = PALMAR ASPECT OF CARPUS
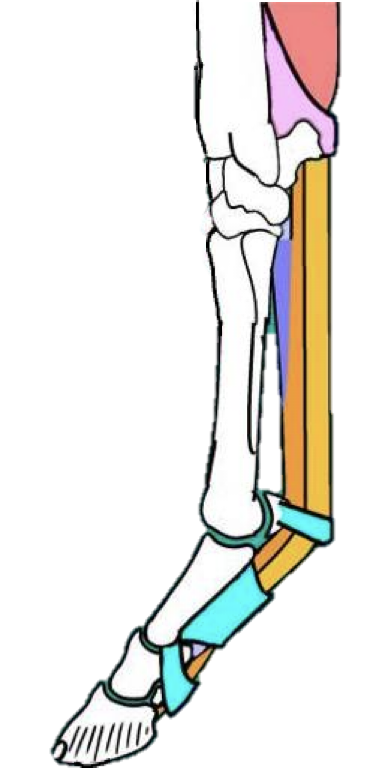
Describe the extensor carpi radialis muscle… origin, insertion, location, function, nerve supply, and any unique characteristics for identification
Origin - Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion - the metacarpal bones
Location - CRANIAL aspect of antebrachium, becomes a tendon once reaching the carpus
Function - in the name… extensor carpi = CARPAL EXTENSOR
Nerve supply - also in the name; Radial nerve
Unique feature - has a small, oblique muscle that runs over the tendon portion of the carpi radialis (see image)

Describe the common digital extensor muscle… origin, insertion, location, function, nerve supply, and any unique characteristics for identification
IS THE MOST IMPORTANT EXTENSOR MUSCLE
Origin - lat epicondyle of humerus
Insertion - ALL DIGITS (at the distal phalanx, splits and inserts at each digit)
In the horse, is one single branch down to the distal phalanx
Protected by dorsal bursas from the associated joint capsules
RECEIVES suspensory ligament branches (see previous notecard set)
Location - Cranio - lateral aspect of antebrachium (see images); crosses over DORSAL carpus and DORSALLY over metacarpo-phalangeal and interphalangeal joints
Function - Carpal AND digital EXTENSOR
Nerve supply - Radial nerve
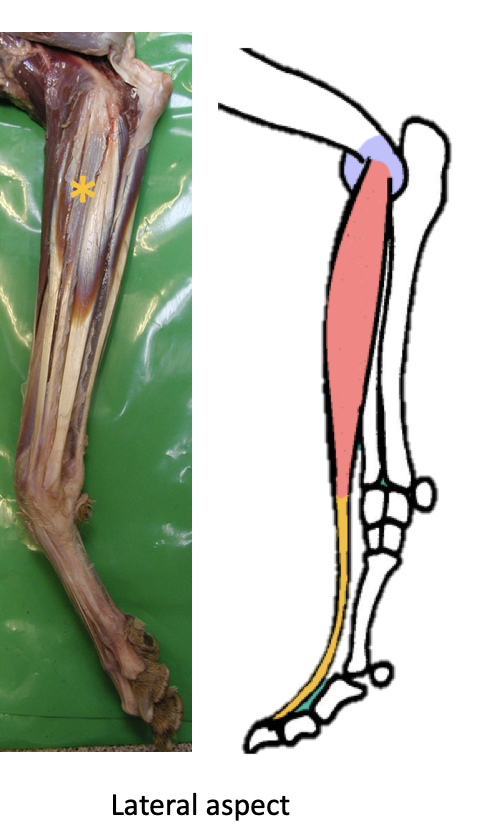
Describe the extensor carpi ulnaris / ulnaris lateralis muscle… origin, insertion, location, function, nerve supply, and any unique characteristics for identification
Origin - Lat epicondyle
Insertion - 5th Metacarpal bone + accessory carpal bone
Location - LATERAL aspect of antebrachium (say ulnaris lateralis… gives location better);
crosses over the LATERAL aspect of the CARPUS
Function - DEPENDS ON LIMB POSITION
Supports both extension AND flexion, depending on limb positioning
When limb is already EXTENDED, muscle SUPPORTS that extension
When limb is FLEXED, helps produce + maintain flexion via attachment to ACB (the “lever” of the carpal bones")
Nerve supply - Radial nerve
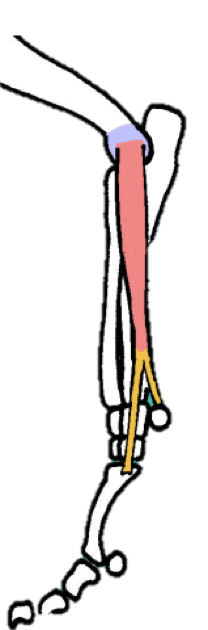
Describe the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle… origin, insertion, location, function, nerve supply, and any unique characteristics for identification
Origin - HAS 2 ORIGINS
MEDIAL epicondyle
Olecranon process of ulna
Insertion - ACB
Location - CAUDAL aspect of the antebrachium; crosses caudal aspect of carpus
Function - in the name: flexor carpi = FLEX CARPUS
Nerve supply - Median + Ulnar nerves
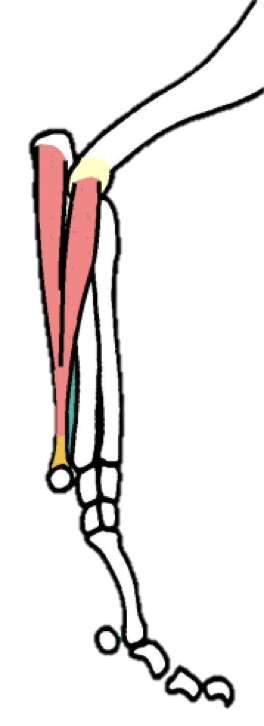
Describe the superficial digital flexor muscle muscle… origin, insertion, location, function, nerve supply, and any unique characteristics for identification
REALLY IMPORTANT
Origin - medial epicondyle
Insertion - ALL digits (MIDDLE PHALANX)
Location - caudal aspect of limb; crosses over PALMAR aspect of carpus, metacarpo-phalangeal, and interphalangeal joints
Function - is a carpal AND digital FLEXOR
Nerve supply - Median + Ulnar nerves
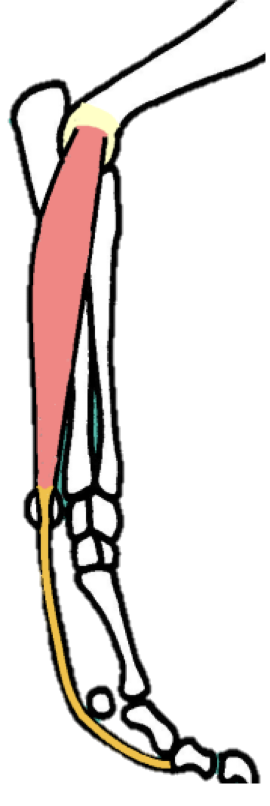
How does the SDFT muscle of the canine differ from that of the HORSE?
In the horse:
SDFT is only ONE branch
Receives an Accessory Check Ligament (ACL) from the radius
Found PROXIMAL to carpus
Limits the length of the tendon, and protects the muscle belly from overstretching
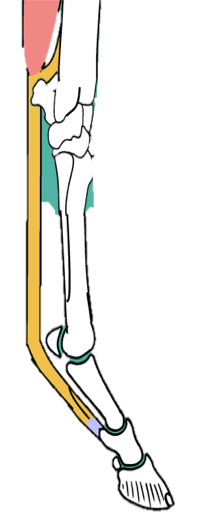
How are the SDFT of the canine and horse SIMILAR? Think of 3 things
Both are VERY close to the surface; are almost palpable
Both split distally to allow passage of the deep digital flexor tendon
Both insert at the middle phalanx
Describe the deep digital flexor tendon muscle… origin, insertion, location, function, nerve supply, and any unique characteristics for identification
Origin - HAS 3 ORIGINS
Medial epicondyle
Radius
Ulna
Insertion - ALL digits (palmar aspect of DISTAL phalanx; this is why SDFT has to split)
Location - caudal aspect of limb; crosses PALMAR aspect of CARPUS and all other joints
In the HORSE: runs over distal sesamoid (navicular bone)
Function - Carpal AND digital FLEXOR
Nerve supply - Median + Ulnar nerves
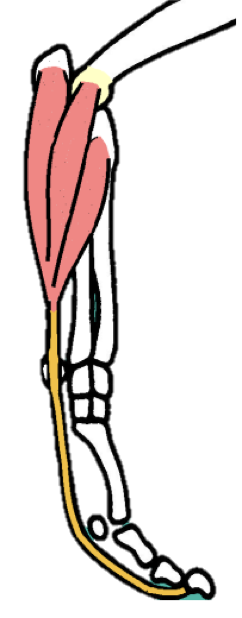
How is the DDFT SIMILAR to the SDFT in the horse?
Is 1 branch as well
ALSO HAS AN ACCESSORY CHECK LIGAMENT
This one comes from the DISTAL portion of the carpus… is an extension of the carpal joint capsule (see images)
Has the same function as the proximal ACL for the SDFT
Summary slide
TIME FOR EQUINE VARIATIONS
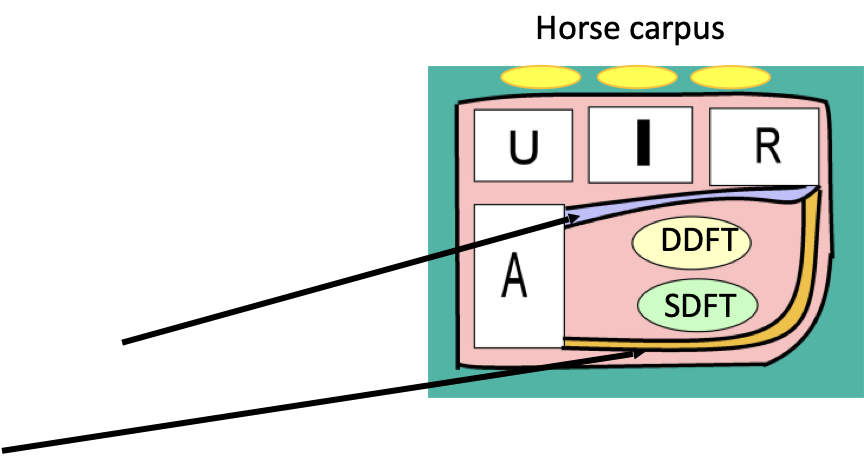
What is the carpal canal? What are its contents, and what makes up its boundaries?
The carpal canal, or “carpal tunnel”, is a passageway on the PALMAR aspect of the carpus…
The SDFT and DDFT run through here, along with blood vessels and nerves
Boundaries:
Dorsally - palmar aspect of carpal joint capsule (purple line)
Laterally - the accessory carpal bone
Palmar - the flexor retinaculum
In orange; is a sleeve of fibrous tissue that encases the limb, like a compression sock
In the dog, the SDFT runs OUTSIDE of this
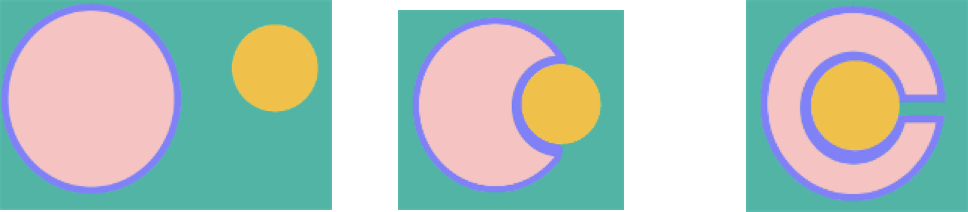
What is a “tendon sheath”, and what is its function?
Is a fluid filled tissue that surrounds the tendon, protecting it where it passes through confined spaces
Doesn’t completely wrap around, more like absorbs it (see images)
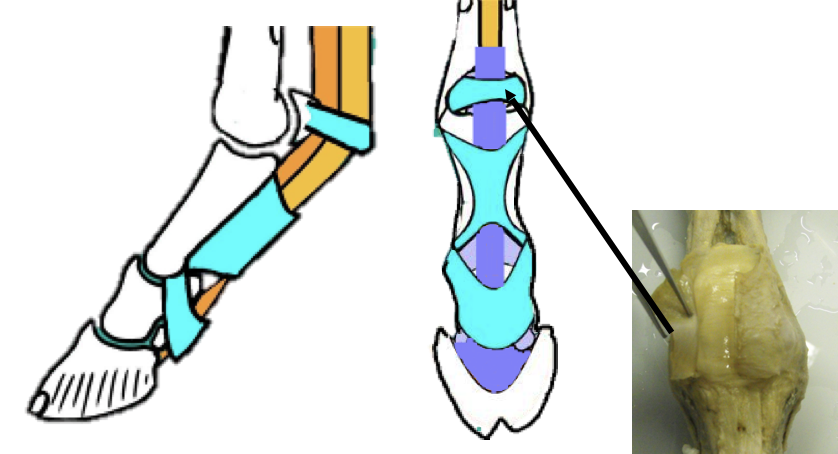
Describe how the tendons on BOTH the dorsal aspect and palmar aspect of the equine distal limb are stabilized… what particular ligaments can be found on the palmar aspect?
Dorsally -
Only CDE is found here… held in place by retinaculum
Palmar -
SDFT and DDFT are held in place by:
Carpal canal
ANNULAR LIGAMENTS (in blue)
Found in the fetlock and pastern regions
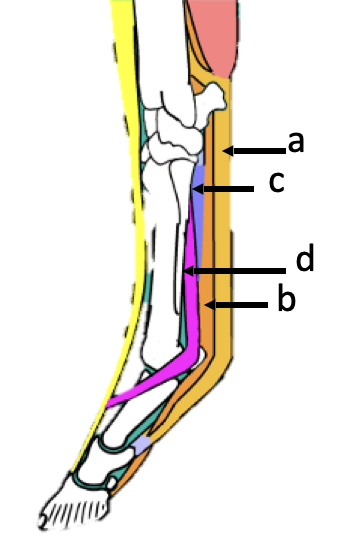
What is the order of tendons on the palmar aspect of the distal equine limb, starting from the skin:
Skin -
a) SDFT
b) DDFT
c) ACL / Check ligament (fused with DDFT)
d) Suspensory ligament (branches in 2)
Describe the concept of the “equine stay apparatus”… what needs to be done in order for this to work?
Most of the horse’s weight is borne on the forelimb… so a mechanism is needed to allow for passive weight-bearing, which lets a horse sleep standing up.
This requires MAINTENANCE OF EXTENSION; this is done by:
Proximal limb joints → prevention of flexion
Carpus → prevention of flexion and hyperextension
Distal limb joints → prevention of hyperextension
What muscles and ligaments of the proximal limb joints help to prevent flexion in the equine stay apparatus?
Scapula → Serratus ventralis muscle
Suspends weight of the body between the forelimbs
Prevention of flexion:
Shoulder → biceps brachii
Elbow → caudal collateral ligaments + the alignment of the bones
Carpus → lacertus fibrosis (fibrous tendon that attaches biceps brachii to metacarpals)
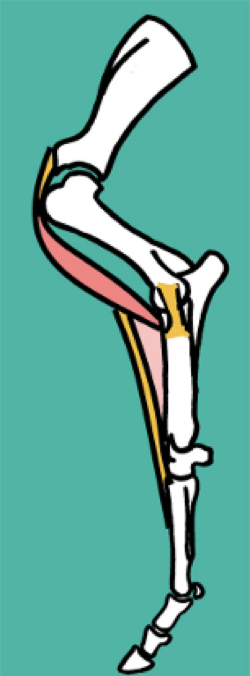
What muscles and ligaments of the carpus and distal limb joints help to prevent hyperextension in the equine stay apparatus?
Carpus:
Palmar fibrocartilage joint reinforcement (in blue)
SDFT and check ligament
Retinaculum
MCP / Fetlock joint :
Suspensory ligament
Common digital extensor
Proximal sesamoids
Distal sesamoidean ligaments
(short, cruciate, oblique & straight)
MCP, PIP, and DIP joints
DDFT & SDFT
Check ligaments
Annular ligaments