Environmental and Socioeconomic Impacts of Food Production and Agriculture
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are the objectives of the Food and Agriculture module?
Students will be able to identify ecological impacts of food production, the impact of climate change on food production, compare agricultural production methods, and evaluate their merits and demerits.
What does the phrase 'I am what I eat' imply in the context of food?
It suggests that food reflects culture, builds the body, and contributes to one's ecological footprint.
What has changed the American relationship to food since 1958?
The rise of fast food has contributed to an unhealthy American diet.
What is the Slow Food movement?
A movement that promotes local food and traditional cooking as a response to fast food culture.
What is the carbon footprint of food?
The amount of carbon dioxide emissions associated with the production and transportation of food.
How much water does one almond require?
One almond requires one gallon of water.
What is the CO2 footprint for shipping food?
Ship transportation emits 30 kg CO2 per mile.
What is California Senate Bill 1383?
A mandatory food waste diversion program that also recovers surplus food products to address food insecurity.
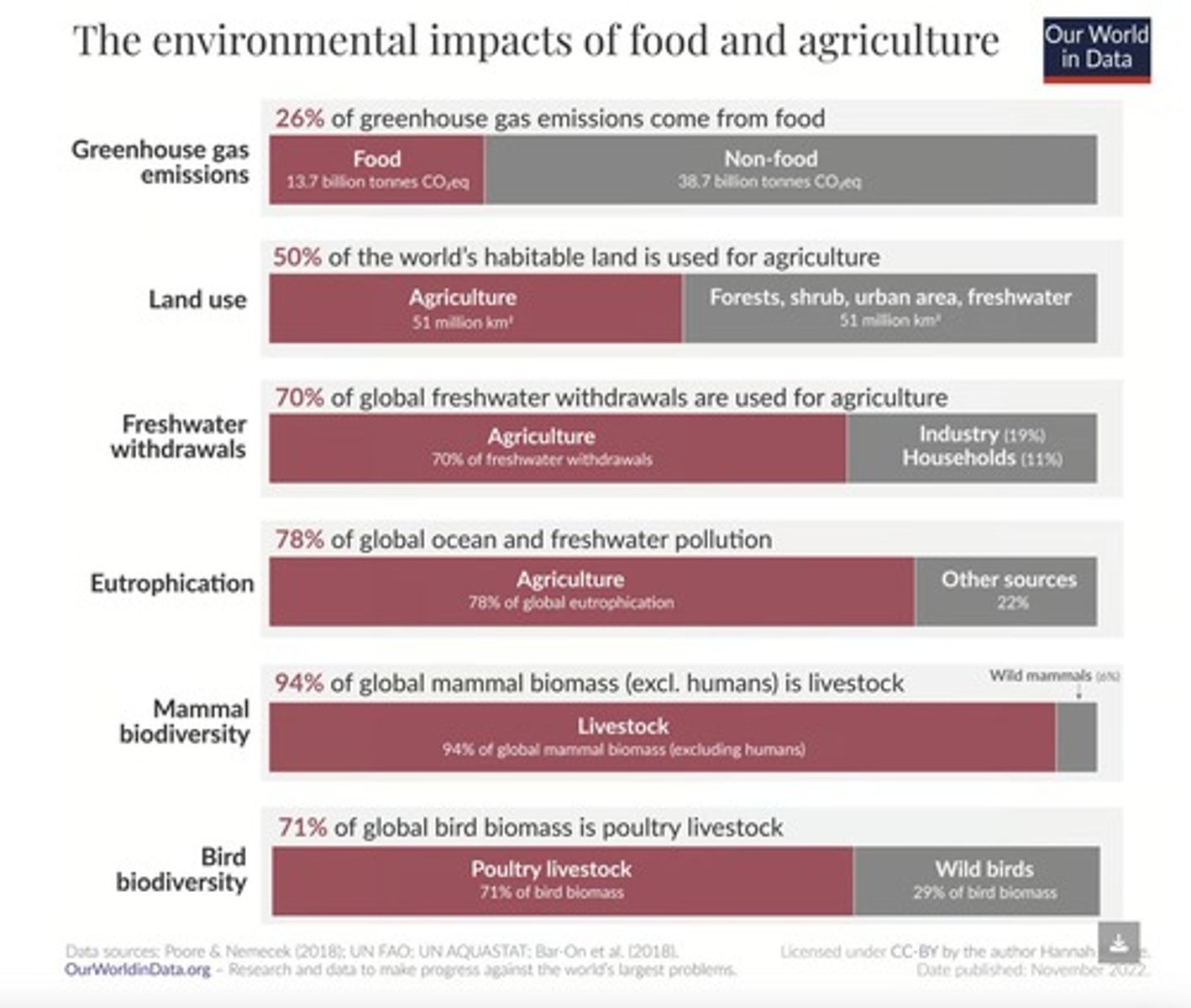
What are the ecological impacts of livestock farming?
Livestock farming has extensive ecological footprints including greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, and ecological disturbances.

How does aquaculture's ecological footprint compare to livestock?
Aquaculture generally has a smaller ecological footprint than livestock but can still spread diseases to wild fish.
What are the ecological impacts of crop production?
Crop production involves greenhouse gas emissions from fertilizers and pesticides, as well as water consumption and ecological disturbances.
What is the significance of intercropping or companion planting?
It maximizes agricultural efficiency by allowing plants like corn, beans, and squash to support each other's growth.
What is subsistence agriculture?
A small-scale farming method where food is grown primarily for family consumption.
What role do women play in traditional agriculture?
Women are often responsible for labor-intensive tasks and managing resources like firewood, clean water, and food production.
What are the two main principles contrasted in agriculture?
Traditional agriculture based on the feminine principle versus industrialized agriculture based on masculinist science.
What are the benefits of traditional agriculture?
It promotes ecological sustainability by maximizing nature's regenerative abilities and supporting local communities.
What are the main components of livestock ecological footprints?
Manure management, greenhouse gas emissions, water use, and land use.
What is the impact of food waste on the environment?
Food waste contributes to methane emissions and represents a significant loss of resources.

What are the ecological disturbances caused by fisheries?
Fisheries can cause ecological disturbances depending on the methods used for catching fish.
What are lentils known for in traditional Indian farming?
Lentils are a source of protein and deposit nitrogen in the soil, providing critical nutrients to companion plants.
What benefits do mustard plants provide?
Mustard plants provide greens, seeds, and oil.
What is the nutritional advantage of traditional grains over milled wheat or rice?
Traditional grains have higher nutritional content, including protein, minerals, calcium, and iron.
What is the 'Green Revolution'?
refers to the introduction of industrial agriculture and scientific methods that disrupted traditional farming practices.
What are the key differences between traditional and industrialized agriculture?
small scale, polyculture, and ecologically sustainable vs large scale, monoculture, and ecologically unsustainable.
What are High Yielding Variety (HYV) crops designed for?
HYV crops are designed for industrial agriculture, requiring high inputs of fertilizers and water to achieve high yields.
What are some environmental impacts of industrialized agriculture?
Biodiversity loss, soil degradation, air pollution, water contamination, and negative human health effects.
What are Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)?
organisms whose DNA has been altered to create desired traits, such as herbicide tolerance or pest resistance.
What are some concerns associated with GMOs?
Concerns include potential health risks, the emergence of superweeds, and contamination of local varieties.
How does climate change impact agriculture?
Climate change leads to rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased pests and diseases, which can reduce crop yields.
What are some adaptations for sustainable food production in response to climate change?
Adaptations include organic agriculture, sustainable fisheries, and regenerative agriculture practices.
What practices are involved in organic agriculture?
Organic agriculture avoids synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, uses organic soil enrichment, crop rotation, and promotes biodiversity.
What is regenerative agriculture?
restoring soil health and increasing biodiversity through sustainable practices.
What can consumers do to support sustainable food production?
Consumers can make sustainable choices, look at labels, eat less meat, support sustainable animal products, and choose sustainable seafood.
What is the role of international treaties in sustainable fisheries?
International treaties aim to prevent overfishing, stop harmful fishing methods, and expand marine protected areas.
What is the impact of climate change on fisheries?
Climate change threatens fish populations and yields, affecting food security and livelihoods.
What is the significance of the phrase 'working with nature' in agriculture?
It emphasizes sustainable practices that align agricultural methods with natural ecosystems rather than forcing nature.
What is the ecological footprint of High Yielding Variety crops?
HYV crops have a high ecological footprint due to their reliance on chemical inputs and intensive resource use.
What is the relationship between industrial agriculture and mega corporations?
Industrial agriculture is often controlled by a few mega corporations that sell seeds and agricultural inputs, limiting farmer autonomy.
What are 'superbugs' in the context of GMOs?
Superbugs are pests that develop resistance to the pesticides produced by Bt crops, potentially leading to increased pest problems.
What is the impact of climate change on crop nutrition?
Rising CO2 levels and fast growth can dilute nutrients in crops, leading to less nutritious food.