Biol 190 Unit 2 Chapter 9
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
1
New cards
What are organelles?
"Little organs" usually enclosed within their own lipid bilayer; specialized unit in a cell that has its own specific function; only found in eukaryotic cells
2
New cards
What are the two main roles of an organelle’s lipid bilayer?
1. Separate different chemical reactions within the cells (especially incompatible reactions)
2. Increase efficiency of reactions or transport of molecules
3
New cards
What is the nucleus?
\-"Cell's control center"
\-Largest organelle inside cell
\-contains the genetic material (DNA/the blueprint of life)
\-DNA is complexed with proteins (i.e. chromatin or chromosomes)
\-site of DNA replication and transcription
\-Largest organelle inside cell
\-contains the genetic material (DNA/the blueprint of life)
\-DNA is complexed with proteins (i.e. chromatin or chromosomes)
\-site of DNA replication and transcription
4
New cards
What is the nucleolus?
\-Center of nucleus
\-location for ribosome assembly
\-location for ribosome assembly
5
New cards
What is the nuclear envelope?
Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus (protection)
6
New cards
What is the nuclear pore?
Channels in the nuclear envelope (allows things in & out)
7
New cards
Does DNA leave through the nuclear pore?
No, DNA stays within the pore, but RNA and ribosome do to the cytoplasm
8
New cards
Are ribosomes considered organelles?
No, it lacks a phospholipid bilayer and found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
9
New cards
What are ribosomes?
The site of translation/ protein synthesis; found in two locations:
\-in the cytosol (free ribosomes= no organelle is needed)
\-Endoplasmic reticulum (bound to ER)
\-in the cytosol (free ribosomes= no organelle is needed)
\-Endoplasmic reticulum (bound to ER)
10
New cards
What is the structure of ribosomes?
Large subunit bound to small subunit
11
New cards
What is the function of ribosomes?
Gene expression-\> (more specifically) the step of translation
12
New cards
What is the endomembrane system?
Series of physically connected or vesicle-connected membranes that work together in protein synthesis, protein enfolding, and protein transportation.
13
New cards
What is the function of the endomembrane system?
\-Regulates protein traffic
\-Performs metabolic functions
\-Performs metabolic functions
14
New cards
What membranes are involved in the endomembrane system?
1. Nuclear envelope
2. endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
3. Golgi apparatus
4. lysosomes
5. vacuoles
6. plasma membrane
15
New cards
What are vesicles?
Sacs made of membrane
16
New cards
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
"Biosynthetic Factory" ; the ER membrane is continuous with the nuclear envelope; two regions
17
New cards
What are the two distinct regions of ER?
\-Smooth ER: lacks ribosomes
\-Rough ER: surface is studded with ribosomes
\-Rough ER: surface is studded with ribosomes
18
New cards
What is the function of the smooth ER?
1. Site of lipid synthesis (name some lipids)
2. Metabolizes and stores glycogen
3. Toxin and poison breakdown (particularly in the liver)
4. An internal storage site for ions (e.g. Ca2+ in muscle)
19
New cards
What is the function of the rough ER?
\-Has bound ribosomes, which secrete glycoproteins
\-distributes transport vesicles
\-a membrane factory for the cell
\-distributes transport vesicles
\-a membrane factory for the cell
20
New cards
What are glycoproteins?
Proteins covalently bonded to carbohydrates
21
New cards
What are transport vesicles?
Secretory proteins surrounded by membranes
22
New cards
What is the lumen?
Space between membrane within rough ER
23
New cards
What are the steps performed in the rough ER?
1. Polypeptide synthesized by ribosome
2. Polypeptide folds into protein and is modified
3. Transport vesicle "buds off"
4. Receptor proteins tell the cell where to ship the contents
24
New cards
What happens to the transport vesicle?
Transport vesicles leave the ER and reach the Golgi
25
New cards
What is the Golgi apparatus?
A stack of single membranes (cisternae)
26
New cards
Define cisternae.
Flattened membranous sacs
27
New cards
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
An assembly line:
1\. Modifies products of the ER
a. Packages, stores, and distributes proteins for their final destination
b. Adds protein modifications, like carbohydrate groups
\
2\. Creates lysosomes
3\. Makes polysaccharides for plant cell walls
1\. Modifies products of the ER
a. Packages, stores, and distributes proteins for their final destination
b. Adds protein modifications, like carbohydrate groups
\
2\. Creates lysosomes
3\. Makes polysaccharides for plant cell walls
28
New cards
What is the receiving side of the Golgi apparatus?
Cis face
29
New cards
What is the shipping side of the Golgi apparatus?
Trans face
30
New cards
Where does the functional protein from the Golgi apparatus go?
The functional protein (inside a transport vesicle) stay within the cytoplasm of the creating cell, creates a lysosome, or transport vesicle fuses with cell membrane to release the protein out (secretion)
31
New cards
What are lysosomes?
Membranous sacs filled with digestive enzymes; inactive until they fuse with another vesicle
32
New cards
What can a lysosome hydrolyze?
Lysosome enzymes hydrolyze all 4 macromolecules
33
New cards
What is the function of lysosomes?
Cleanup and recycle- both of cellular and foreign materials: two ideas-\> phagocytosis and autophagy
34
New cards
What is the first function (idea) of lysosomes?
Phagocytosis: eating extracellular items
\-Protection from bacteria
\-Food metabolism by forming food vacuoles
\-Protection from bacteria
\-Food metabolism by forming food vacuoles
35
New cards
What is the second function (idea) of lysosomes?
Autophagy (self-eating) -Recycles organelles and macromolecules
36
New cards
What is the function of peroxisomes?
Breakdown of long chain fatty acids through beta-oxidation; metabolism creates H2O2 (toxic peroxides), so converts them to water
37
New cards
What are peroxisomes important in?
Metabolism of fatty acids
38
New cards
Where do peroxisomes come from?
Buds off the ER instead of the Golgi (like lysosomes); found in most eukaryotic cells
39
New cards
What are glyoxysomes?
Specialized peroxisomes found only in plants, aid breakdown of lipids into carbohydrates in growing seedlings
40
New cards
What organelles harvest energy?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts harvest energy and contain their own DNA and ribosomes
41
New cards
What is mitochondria?
All eukaryotic cells, is the site of cellular respiration
42
New cards
What are chloroplasts in?
Plants and other photosynthesizers
43
New cards
What is the theory of endosymbiosis?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved after a prokaryotic cell was engulfed by a larger cell and lived inside; engulfed cell provided its host with advantages because of its special metabolic activities
44
New cards
Define selective advantage.
The characteristic of an organism that enables it to survive better than other neighboring organisms
45
New cards
What is the evidence for the endosymbiont theory?
1. Circular DNA molecules
2. Contain free ribosomes with similar subunit
3. Enveloped by a double membrane
4. Grow and reproduce somewhat independently in cells
46
New cards
What is the mitochondria?
"Powerhouse of the cell" for energy production (ATP)
47
New cards
What are the characteristics of DNA?
Can divide independently-\> own DNA and ribosomes; \# in a cell can vary, 1-10,000; important for energy metabolism
48
New cards
What is the structure of the mitochondria?
Has 2 membranes inner highly folded
49
New cards
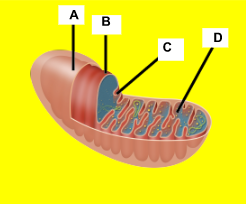
Label the mitochondria.
A. Outer membrane B. Inner membrane C. Intermembrane space D. Matrix
50
New cards
What is mitochondrial disease (MD)?
Commonly linked to diseases of aging
51
New cards
What is the primary cause of mitochondrial disease (MD)?
A defect in nuclear DNA (nDNA) encoding for protein or in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
52
New cards
Where does mtDNA come from?
Primarily inherited from the mother's egg, expressing ~30 proteins not expressed
53
New cards
How many individuals have mitochondrial disease (MD)?
1 in 200 individuals have a mitochondrial DNA mutation that may lead to disease
54
New cards
What are chloroplasts?
Site of photosynthesis; have ribosomes-\> can divide independently
55
New cards
What is the function of chloroplasts?
Convert light energy to chemical through photosynthesis, involving the green pigment chlorophyll
56
New cards
What type of kingdoms have chloroplasts?
Plantae and protista (never animalia of fungi-\> decomposers)
57
New cards
Are prokaryotes photosynthetic?
Yes, only need chlorophyll to perform photosynthesis
58
New cards
What are vacuoles?
Storage organelle
59
New cards
What is the function of vacuoles?
Store pigment attracting pollinators and storage of toxins and chemicals (opium)
60
New cards
What are food vacuoles formed by?
Phagocytosis
61
New cards
Where are vacuoles found?
Mostly in plants, but some animal and protists cells have vacuoles
62
New cards
What are contractile vacuoles?
Found in many freshwater protists, pump excess water out of cells
63
New cards
What are central vacuoles?
Found in many mature plant cells; holds organic compounds and water; store toxins and waste; water creates turgor pressure, helps to physically support plants
64
New cards
What organelles are found in animal and plant cells?
1. Nucleus (nuclear envelope, nucleolus, chromatin)
2. Rough ER
3. Smooth ER
4. Golgi apparatus
5. Ribosomes
6. Microfilaments
7. Cytoskeleton (microtubules and mitochondrion)
8. Peroxisome
9. Plasma membrane
65
New cards
What organelles are found in plant cells but not animal cells?
1. Central vacuole
2. Chloroplasts
3. Cell wall
4. Plasmodesmata
5. Glyoxysome
66
New cards
What are the functions of the cytoskeleton?
\-supports the cell and maintains its shape
\-keeps organelles anchored in place
\-cell movement
+interacts with motor proteins
+cytoplasmic movement, streaming -transport of materials throughout cell
\-keeps organelles anchored in place
\-cell movement
+interacts with motor proteins
+cytoplasmic movement, streaming -transport of materials throughout cell
67
New cards
What are the three primary fibers to the cytoskeleton?
Intermediate filaments, microtubule, microfilaments
68
New cards
What is the first primary fiber to the cytoskeleton?
Intermediate filaments: tough, woven cables of proteins. Provide structure and strength. Anchors organelles; intermediate in diameter; made of protein subunit: keratin
69
New cards
What is the structure of the first primary fiber to the cytoskeleton?
Fibrous proteins coiled into cables
70
New cards
What is the second primary fiber to the cytoskeleton?
Microtubule: largest cytoskeletal element
\-can lengthen and shorten rapidly
\-used in cell division; broadest in diameter; made of protein subunit: tubulin (bead-like)
\-can lengthen and shorten rapidly
\-used in cell division; broadest in diameter; made of protein subunit: tubulin (bead-like)
71
New cards
What is the structure of the second primary fiber to the cytoskeleton?
Hollow tubes
72
New cards
What is the third primary fiber to the cytoskeleton?
Microfilament: long, slender filaments. Move the cell or change its shape by shortening and elongating; smallest in diameter; made of protein subunit: actin (bead-like)
73
New cards
What is the structure of the third primary fiber to the cytoskeleton?
Two intertwined strands of actin
74
New cards
Define dynamic instability.
A fiber's ability to switch between growing and shrinking
75
New cards
Which fibers have dynamic instability?
Microtubules and microfilaments
76
New cards
Where are microtubules found?
Cilia, flagella, and centrosomes; microtubules control the beating of cilia and flagella
77
New cards
What are cilia and flagella?
Cellular appendages that help cells move in their environment (locomotion); similar structure-\> different functions
78
New cards
What is the structure of microtubules in cilia and flagella?
9 fused pairs on the outside, 2 un-fused microtubules inside
79
New cards
Define flagella.
Long appendages, used to propel the cell through fluid. Allow locomotion; present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
80
New cards
Define cilia.
Short appendages, used for movement or moving fluid past the cell; present only in eukaryotes
81
New cards
What are motor proteins?
Proteins that use energy to physically walk along microtubule tracks
82
New cards
What are centrosomes?
"Microtubule-organizing center" an organelle that consists of a pair of centrioles made from microtubules
83
New cards
What is the function of centrosomes?
Organize microtubules that are needed for cellular division
84
New cards
Where are microfilaments found?
Microvilli (made from microfilaments), pseudopod, and muscle fibers
85
New cards
What is the structural role of microfilaments for microvilli?
To bear tension, resisting pulling forces within the cell
86
New cards
What is the role microfilaments play in some cells?
Increase the membrane's surface area
87
New cards
How does the pseudopod movement occur?
Through actin polymerization
88
New cards
Muscle fibers are made of...
Actin (microfilament) and myosin (motor protein)
89
New cards
What does myosin do for muscle fibers?
Myosin uses ATP-\> closes or elongates the gap between the microfilaments/ muscle fiber (allowing your muscles to contract and body to move)