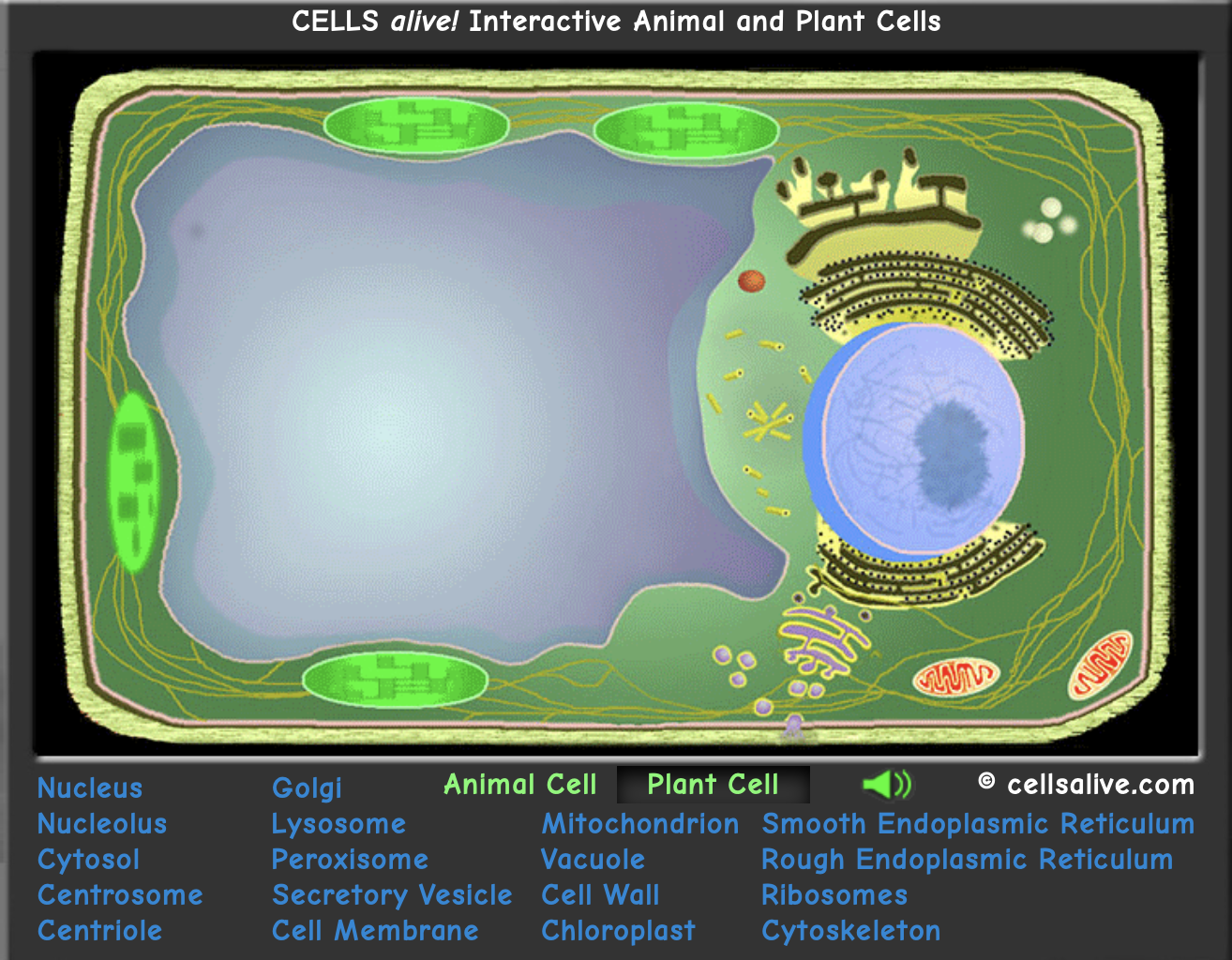
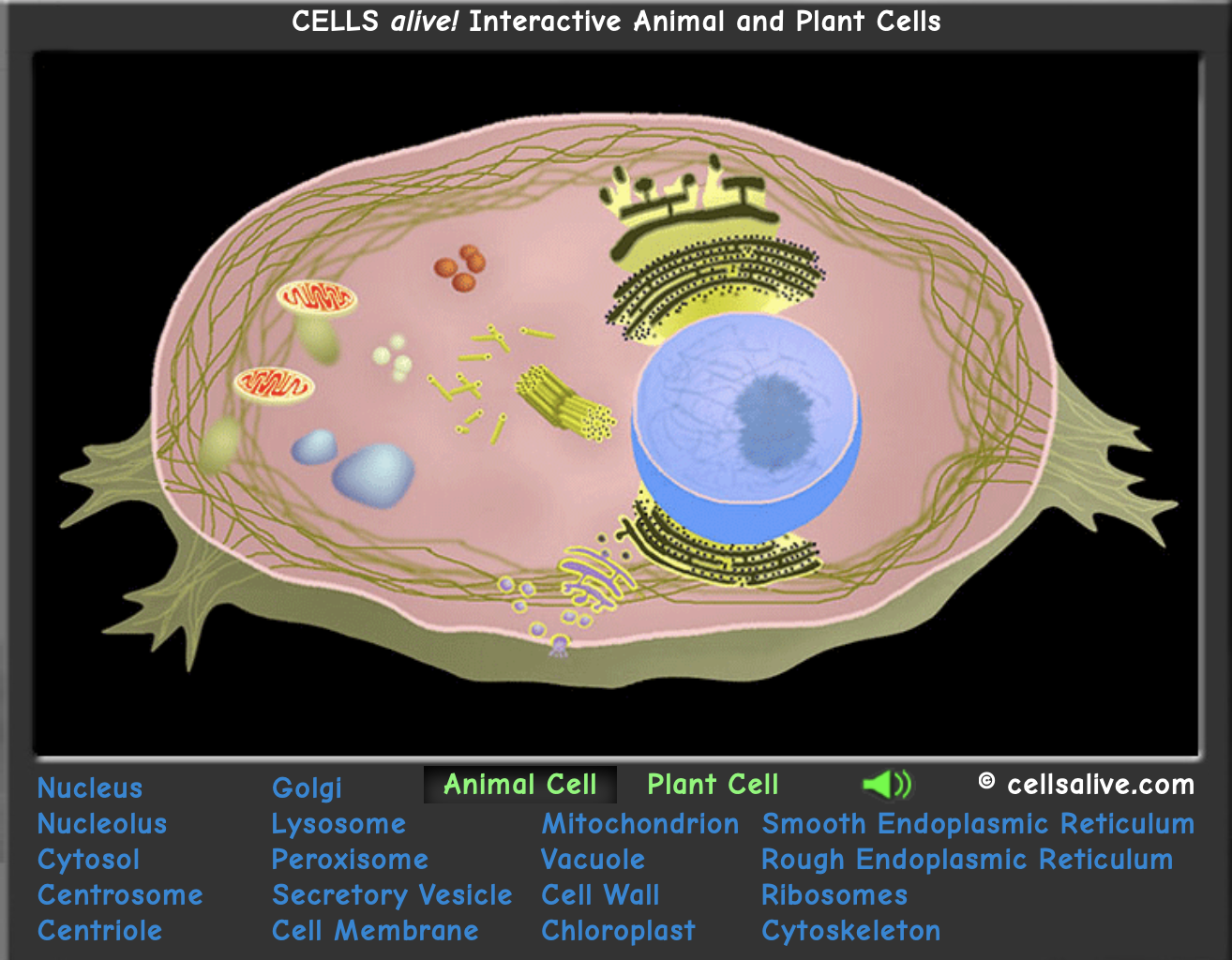
cell anatomy
Describe the difference between an organelle and the rest of the
structures in a cell.
==Organelles==: are cell structures that have their own membrane surrounding them.
==Cells==: are the structural and functional unit of all living things.
Describe the function of each structure in a cell.
Basic Structures
- ==Plasma Membrane==: Surrounds the cell as a barrier, keeping the contents of the cell inside the cell.Regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell(Do not call this the cell membrane as it is too easily confused with the cell wall.)
- ==Cell Wall==: Rigid outer covering of some cells that keeps the cell from over-inflating with water and bursting. It is also used for support in plants. (Animal cells do not have cell walls. Let me say that again, animal cells do not have cell walls.)
- ==Ribosomes==: Site for protein synthesis (making of proteins).The ribosome is an elaborate enzyme that builds proteins from individual amino acids.
- ==Cilia==:Tiny hair-like structures for movement.They move like oars on a boat. (Not shown in animation.)
- ==Flagella==: Longer whip-like structure also for movement. (Not shown in animation.)
- ==Chromosomes== (Chromatin):The cell's DNA and the proteins that organize the DNA to prevent it from becoming tangled.(Think of the DNA as an extension cord and the proteins as the reel you wrap it on.)
- ==Cytoskeleton==: The support beams for the cell that give it shape.Also act as a railroad network for moving packages throughout the cell.
organelles
- ==Nucleus==: Surrounded by the nuclear envelope, this is the location of the DNA in the cell.Remember that DNA contains the recipes for making every protein of the cell. For this reason, it is often thought of as the control center of the cell.
- ==Nucleolus==: A specific region inside the nucleus where the instructions (DNA) for making ribosomes are found.Since the cell makes lots of ribosomes, this area is very busy and stands out from the rest of the nucleus.
- ==Mitochondria==: Produces energy during cellular respiration (burning sugar)."Power House" of the cell.
- ==Chloroplasts==: Uses sunlight energy to build sugar during photosynthesis.
- ==Vesicles==: Storage sacs of cells.Can contain digestive enzymes, proteins for export, or anything else the cell wishes to store in small quantities.Vesicles can move about the cell by "walking" along the cytoskeleton. (Lysosomes in animation are an example of vesicles.)
- ==Vacuole==: Larger storage sacs for food, water, and wastes.Plants have a large central vacuole for storing water and providing support to the cell.(As plant cells lose water, the central vacuole deflates like a balloon. This is why the plant "wilts.")
- ==Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)==: A long, flat tube with ribosomes attached to the membrane.It starts at the nuclear envelope then extends into the cytoplasm.Functions in protein synthesis and processing.Also synthesizes phospholipids that become the cell membrane and membrane of other organelles.(There are many free-floating ribosomes as well, so do not assume all proteins are made on the rough ER.)
- ==Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER)==:This part of the ER does not have ribosomes attached.Synthesizes phospholipids, steroids, and fats.
- ==Golgi Complex (or Body)==: Modifies proteins and lipids by adding sugar groups and also packages them for export from the cell.
- ==Centrioles==:Produce spindles in animals cells and used in the movement of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis (cell division).Produces cilia and flagella used for cellular movement.Found near the nucleus. \n
Describe and recognize the visual appearance of each structure in a cell that can be seen through your microscope.
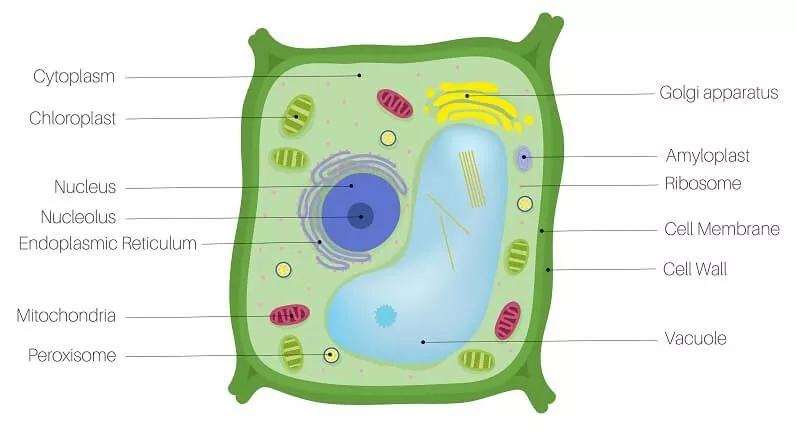
plant cell
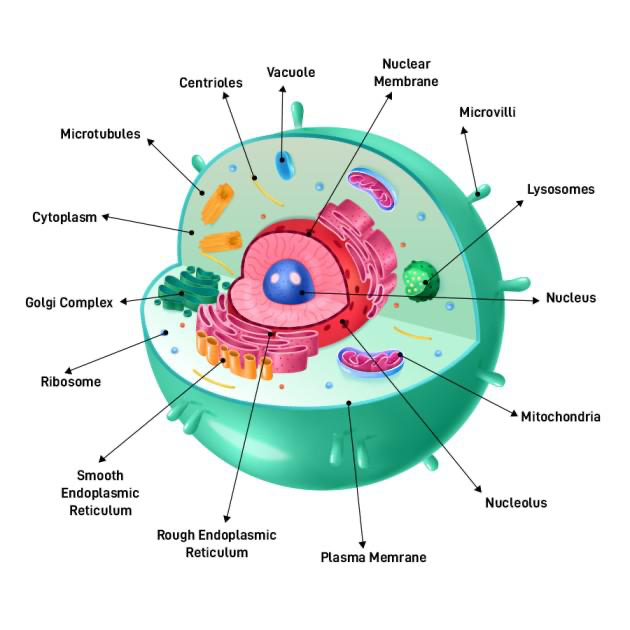
animal cell
List structures and organelles found in plant cells, but not found in animal cells.
animals
- nucleus
- nucleolus
- cytosol
- centrosome
- what structure is found in animals cells only and not plant cells: ==centriole==
- Golgi
- lysosome
- peroxisome
- secretory vesicle
- cell membrane
- mitochondria
- vacuole
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- rough endoplasmic reticulum
- ribosomes
- cytoskeleton
plants
- what two organelles are only found in plants: the ==cell wall== and ==chloroplast== are only found in plant cells
List organelles found in eukaryotic cells, but not found in prokaryotic cells
==Prokaryotic== cells: have ^^no membranes^^ other than the plasma membrane.This means that they ^^lack all organelles^^, including the nucleus. (Prokaryotic means "before the nucleus.")
Prokaryotic cells still contain DNA and still do jobs such as respiration or photosynthesis, but: they do not do them in as organized a fashion.
- %%Bacteria%% have what kind of cell: prokaryotic cells.
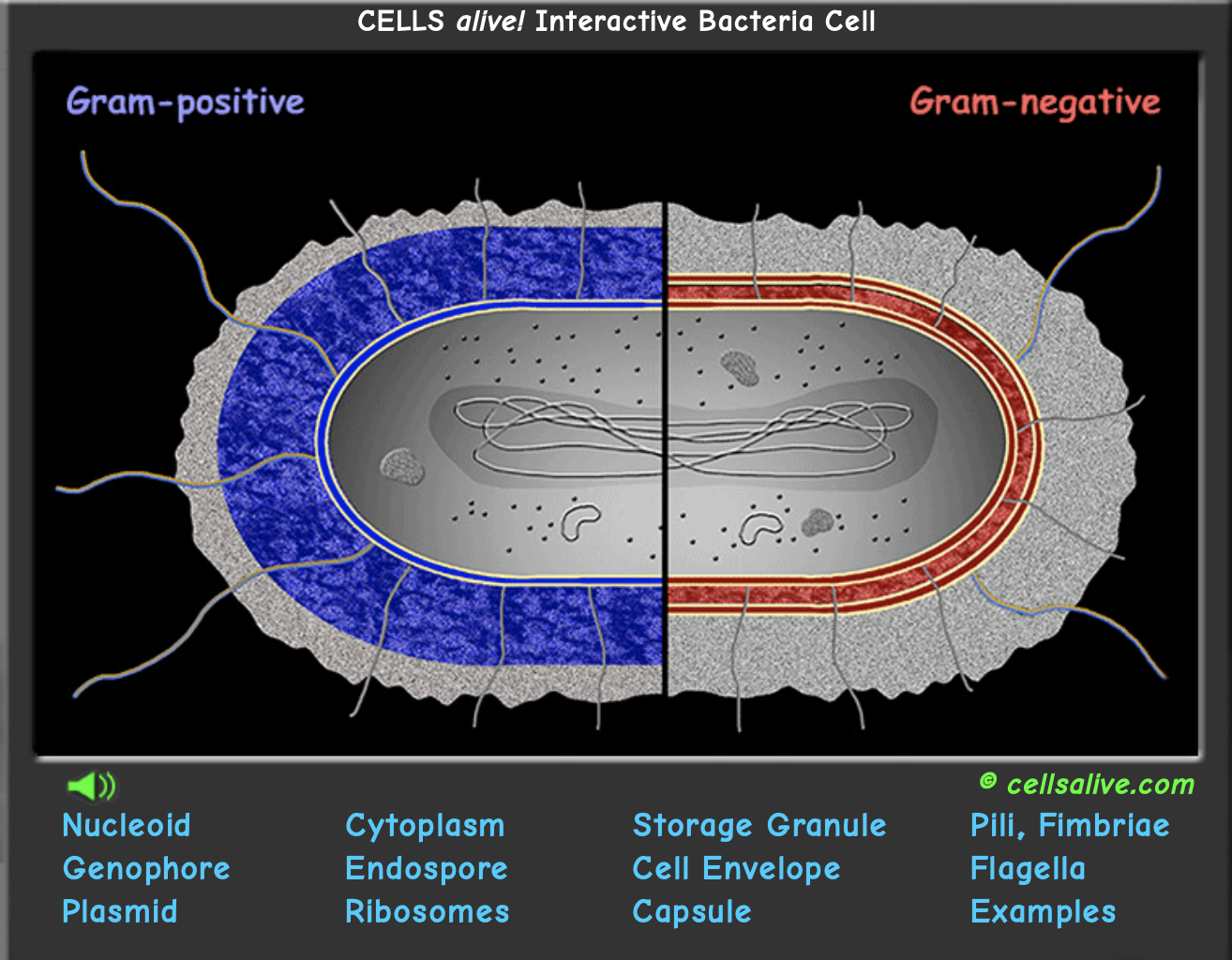
==Eukaryotic== cells:have ^^organelles^^, including the nucleus.
- Eukaryotic means: "true nucleus."
%%Animals, plants, fungi, and protists%% all have what kind of cell: all have eukaryotic cells.
- animal:
- plant: