Anxiety, Trauma, & OCD- Kruger
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
what is the common thread of all anxiety disorders?
excessive fear and anxiety and related behavioral disturbances
Fear
- emotional response to real or perceived threat
- associated with sympathomimetic symptoms
- Cognition= thoughts of immediate danger & escape behaviors
- symptoms of adrenaline are not pleasant but not dangerous either
for what type of patients is the fear response dangerous?
pts with cardiac issues due to symptoms of adrenaline
Anxiety
- associated muscle tensions, vigilance in preparation, cautious, apprehensive, avoidant
- anticipation of future threat, associated with physical symptoms
- certain amounts of anxiety is normal
- generally short lived
How do anxiety disorders differ from normal and/or transient states?
- anxiety disorders are persistent, out of proportion for the threat and must cause significant impairment
- causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
Selective mutism DSM criteria
- child consistently fails to speak in certain settings
- problem has lasted at least a month (not including 1st month of school)
- issue cannot be fully explained by a communication disorder
- the condition interferes with the child's education or social communication
- the child's silence cannot be attributed to an unfamiliarity with spoken language
Selective mutism facts
- onset usually before age 5, can persist into adulthood
- shy, timid, inhibited
- identified in preschool or kindergarten
- MC in girls
- more common in immigrant children
- high levels of social anxiety
- consistent failure to speak in social situations with expectation to speak despite speaking in other situations
what other disorders is selective mutism associated with ?
social phobia
social anxiety disorder
OCD
panic disorder
PTSD
Specific Phobia DSM criteria
- marked, persistent, and disproportionate fear of a specific object or situation, typically lasting 6 months or more
- immediate anxiety is usually produced by exposure to object
- avoidance of feared situation
- significant distress or impairment
Specific Phobia facts
- more common in women
- 75% of pts have multiple specific phobias
- may induce vasovagal response or hyperventilation
- generally, pt recognizes fear is excessive or unreasonable (a child cannot recognize this)
- most childhood phobias disappear
- those with phobias are 60X more likely to attempt suicide
what is the etiology of specific phobias?
- unconscious anxiety placed on neutral symbolic object
- personal or observed traumatic event
- parental modeling
- unexpected panic attack in the situation
- information transmission
- operant conditioning
Little Albert Experiment
A study in which a white rat was paired with a loud sudden noise in order to condition a fear response in an infant.
Infant would cry upon seeing the white rat even when the noise was not associated with it
name the animal type phobias
- arachnophobia (spiders)
- ophidlophobia (snakes, MC in US)
- cynophobia (dogs)
natural environment phobias
- acrophobia (heights)
- aqua phobia (water)
- astraphobia (thunderstorms)
situational phobias
- claustrophobia
- nyctophobia (dark)
- aviophobia (flying)
blood, injection, injury & other phobias
- triskaldekaphobia= #13
- coulrophobia = clowns
- dentophobia (dentist)
Social Anxiety Disorder DSM 5 criteria
A- a persistent fear of 1 or more social/performance situations in which the pt is exposed to unfamiliar people or possible scrutiny by others
B- exposure to the feared situation almost invariably provokes anxiety, may cause panic attack
C- recognizes the fear is unreasonable/excessive
D- feared situations are avoided or else endured with intense anxiety/distress
E- the avoidance, anxiety/distress in feared situation interferes significantly with normal routine
F- fear/anxiety/avoidance is persistent, lasting 6 months or more
Social Anxiety Disorder facts
- 75% cases occur in ages 8-15
- may fear that they may act in a way that is embarassing
- MC in women BUT more men seek treatment b/c it impacts their career
- in kids, the social anxiety must occur with peers, not just adults
explain the cognition aspect behind social. anxiety disorder
- negatively evaluated by others, embarrassed, humiliated, fear of being judged as anxious, weak, crazy, stupid, unlikeable
explain the etiology behind social anxiety disorder
- traumatic social experience
- social skills deficits that produce recurring negative expereinces
- childhood hx of shyness/bullying
- after life changes that require a new social role
T/F- social anxiety happens in all aspects of the pt's life
FALSE- it is only impacting the pt's performance , not ALL aspects of life
what is the most common social anxiety?
public speaking
social anxiety is associated with..
- school drop out
- unemployment
- lower SES
- no children
- lower QOL
- MDD and substance abuse
what disorder is comorbid and related to social anxiety disorder?
avoidant personality disorder
DSM 5 criteria for panic disorder
- Recurrent unexpected panic attacks
- At least 1 of the attacks has been followed by at least 1 or more of the following: persistent concern about more panic attacks, worry about implications of the attack, a significant change in behavior related to attacks
- presense/absence of agoraphobia
- panic attacks are not due to direct effects of a substance or medical condition
- panic attacks are not better accounted for by another mental disorder
panic attack specifiers
- palpitations
- sweating
- trembling
- shortness of breath
- feelings of choking
- chest pain or discomfort
- nausea or abdominal distress
- feeling dizzy, light headedness
- chills/heat sensations
- paresthesias
derealization or depersonalization
- fear of losing control or "going crazy"
- fear of dying
Panic Disorder & panic attack
- more common in women
- must have 2 unexpected panic attacks
- panic attacks are abrupt
- pt can have panic disorder +/- agoraphobia
-can last anywhere from 1 minute to an hour
define a panic attack
- abrupt surge of intense fear/discomfort
- peaks within minutes
- +/- physical or cognitive symptoms
define panic disorder
more than 1 unexpected panic attack
T/F- panic attack is used as a descriptive specifier
true b/c it occurs across a variety of anxiety and mood disorders
what disorder has the MOST medical visits?
panic disorder
panic disorder has the strongest association with?
agoraphobia (35% develop this)
impulsively suicidal
* note= in DSM5, panic disorder and agoraphobia are now unlinked
Agoraphobia: DSM-5 Criteria
1- marked, disproportionate & immediate fear about being in at least 2 of the following: public transportation, open spaces, shops, theaters, line/crowds, outside of home alone
2- fear is related to concern that escape might be hard or help unavailable
3- avoidance of agoraphobic situations
4- symptoms last 6 or more months
5- significant distress or impairment
agoraphobia facts
- initial onset <35yo, peak in late adolescence & early adulthood
- the avoidance is more influential of the disability than the disorder itself
- MC in women
->33% become completely home bound
- 50-75% have panic disorder
name the comorbidities of agoraphobia
- anxiety
- MDD
- PTSD
- substance abuse
explain the cognitive aspect behind agoraphobia
- does not feel safe
- escape might be difficult
- help may not be available
Generalized Anxiety Disorder DSM 5 Criteria
1- excessive anxiety and worry (apprehensive expectation) occurs most days for at least 6 months
2-difficult to control the worry
3- associated with 3+ of the following 6 symptoms:
-restlessness/feeling on edge.
-being easily fatigued.
-difficulty concentrating or mind going blank.
-irritability.
-muscle tension.
-sleep disturbance
4- clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning.
5- disturbance is not attributable to physiological effects of substance or another condition
6- disturbance is not explained by another mental disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder facts
- more common in women
- anxiety is shifting in various domains
- anxiety NOT focused on specific object or situation
- no avoidance behaviors with this, no escape
- may experience somatic symptoms
- free of panic
what is GAD associated with?
MDD
OCD
Agoraphobia
Late onset of GAD
about 60yo
poverty
recent adverse events
chronic physical and mental disorders
T/F- overall anxiety disorder are likely to coexist with anxiety and mood disorders such as depression, suicide, and substance abuse
TRUE
what remains the diagnosis cornerstone in the diagnosis and tx of anxiety disorders?
H&P
mental status examinations
fear network in the brain
amygdala, hypothalamus, brainstem
CNS mediators of anxiety
NE
serotonin
decreased inhibitory GABA sensitivity
why is recognizing anxiety level important?
for determining intervention and managing anxiety
mild anxiety
can motivate someone positively to perform at high level
moderate anxiety
- narrowing of perceptual field
- trouble attending to surroundings
- can follow firm, short and direct commands
- this is GAD level of anxiety
severe anxiety
- unable to attend to surroundings
- development of physical symptoms
- anxiety relief becomes the only goal
panic anxiety
this is terror
only concern is escape
treatment of anxiety disorders
- CBT
- SSRIs
- SNRIs
- exposure therapy for specific phobias
in general for anxiety disorders, the treatment is
SSRIs/SNRI in combo with CBT
T/F- beta blockers are given for performance anxiety or severe symptoms
TRUE
what is considered to be 2nd line agents for anxiety disorders?
benzodiazepines
- reserved for pts with refractory panic disorder
- clonazepam= outpatient drug of choice for 2-4 weeks at beginning of tx
what can you use to treat GAD?
SSRI/SNRI
buspirone (buspar)
what is the common thread for trauma and stressor related disorders?
psychological distress following exposure to event; develop in addition to fear/anxiety (normal)
dysphoria, anhedonia, aggressive, dissociative, etc
which 2 disorders happen in childhood and require social neglect?
1- reactive attachment disorder
2- disinhibited social engagement disorder
reactive attachment disorder
- Inhibited and emotionally-withdrawn behavior towards adult caregivers
- social and emotional disturbance
- this is internal, thinks adults are untrustworthy
- absent, grossly underdeveloped attachment; has capacity to form selective attachments
Disinhibited social engagement disorder
A- child actively approaches & interacts with unfamiliar adults & exhibits more than 2 of the following:· [1] reduced or absent reticence in approaching unfamiliar adults, [2] overly familiar verbal or physical behavior, [3] lack of checking back with adult caregiver after venturing away, even in unfamiliar settings, [4] willingness to go off with unfamiliar adult with minimal or no hesitation
B- behaviors not limited to impulsivity (ADHD)
explain the personality of those with Disinhibited social engagement disorder
- attention seeking behavior, inauthentic expression of emotions, external disinhibition, attention seeking behavior
- inauthentic expression of emotion, happier but inauthentic
- lack of boundaries
Both reactive attachment disorder and disinhibited social engagement disorder have what same criteria?
1- child experienced a pattern of insufficient care
2- the insufficient care is thought to cause the behavior
3- symptoms/behavior must be seen before age of 5 and child must be over 9 months old
PTSD prevalence
- more women develop PTSD, even though more men experience traumatic events
- increased rates in veterans, police, firefights, NYPD
- highest rates in rape, war, and genocide
- African Americans, hispanics, and native Americans have increased rate of PTSD vs. whites and Asians
T/F- there is a direct relationship between proximity, severity, and duration of trauma and risk of PTSD
TRUE
pathophysiology of PTSD
hippocampus- amygdala theory
- High-stress, high cortisol – produce traumatic long memories with vivid sensations & highly charged emotion reactions; ↓ hippocampal volume lose ability to distinguish past vs. present memory or correctly interpret environmental contexts; ↓ cortex lose regulation of emotional response triggered by amygdala
Physical changes of the brain due to PTSD
1) anterior cingulate cortex gets smaller (involved in rational decision making)
2) amygdala is overly responsive (processes memory & emotional reactions)
3) hippocampus is smaller (roles in long term memory formation)
the diagnosis criteria for PTSD requires what 4 categories?
1- intrusion
2- avoidance
3- negative cognition & mood
4- arousal & reactivity
what is at the center of clinical symptoms of PTSD?
pathological memory of the traumatic event
acute PTSD
symptoms last < 3 months
chronic PTSD
symptoms last more than 3 months
Delayed PTSD
symptoms start more than 6 months after trauma
what increases personal risk for PTSD?
- prior trauma
- less social support
- negativism
- pre-existing psychological disorders
- coping style
- lower IQ
- lower morale for soldiers
what determines whether we develop PTSD?
our personal history and vulnerability
what conditions are associated with PTSD?
- development regression in children
- paranoia
- MDD
- substance abuse
- somatization
- personality changes
- increased aggression/violence
what psychiatric disorders are associated with PTSD?
- MDD
- anxiety disorder
- social phobia, substance abuse
- impulsive behavior, suicide
what diagnosis comes before PTSD and is present the month before PTSD?
Acute stress disorder
what is the best predictor of PTSD?
the failure of acute symptoms to begin to resolve after 2 weeks
what class of meds is not considered to be 1st line therapy for PTSD?
SSRIs
what is the hallmark of acute stress disorder?
dissociative symptoms
treatment of trauma- stress related disorders
- exaggerated symptoms &social/occupational impairment must be brought within manageable limits before pt can begin to cope with stress
- crisis intervention theory
- prolonged exposures
- virtual reality exposure
- trauma narrative
Adjustment Disorder diagnostic criteria
- emotional/behavioral symptoms in response to & occurring within 3 months of identifiable stressor
- symptoms or behaviors are clinically significant
- once stressor or its consequences have terminated, symptoms don't persist for more than additional 6 months
Adjustment disorder facts
- there HAS to be a specific stressor/event but NON-TRAUMATIC EVENT
- frequent in adolescents
- diagnosis is somewhat overused b/c it doesnt carry the same stigma as something like MDD
- significant aspect= change!
acute adjustment disorder
stressor and symptoms last less than 6 months
chronic adjustment disorder
stressor and symptoms last more than 6 months
OCD diagnostic criteria
A. Presence of obsessions and/or compulsions.
B. Obsessions or compulsions are time-consuming (more than 1 hour per day)
OR cause significant distress or impairment
Obsessions are defined by
1) Recurrent & persistent thoughts, urges, or images that are experienced, at some time during the disturbance, as intrusive and unwanted, and that in most individuals cause marked anxiety or distress.
2) The individual attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts, urges, or images, or to neutralize them with some other thought or action (i.e., by performing a compulsion).
Compulsions are defined by
1) Repetitive behaviors that the individual feels driven to perform in response to an obsession or according to rules that must be applied rigidly.
2) aimed at preventing or reducing anxiety or distress, or preventing some dreaded event or situation;
OCD facts and stats
- not voluntary & not real life worries
- obsessions- compulsions must be greater than 1 hr a day
- typically starts in childhood or adolescence
- more common in females in adulthood but more common in males in childhood
- boys have earlier onset
what conditions are comorbid with OCD?
anxiety disorders (76%)
MDD (41%)
OCPD
Hoarding
Eating Disorders
Tourette's
Schizophrenia
T/F- there is not a strong link between OCD and suicidality
FALSE- there is a strong link - lifetime rates of suicidal ideation 64%, 46% for suicide attempts
Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS)
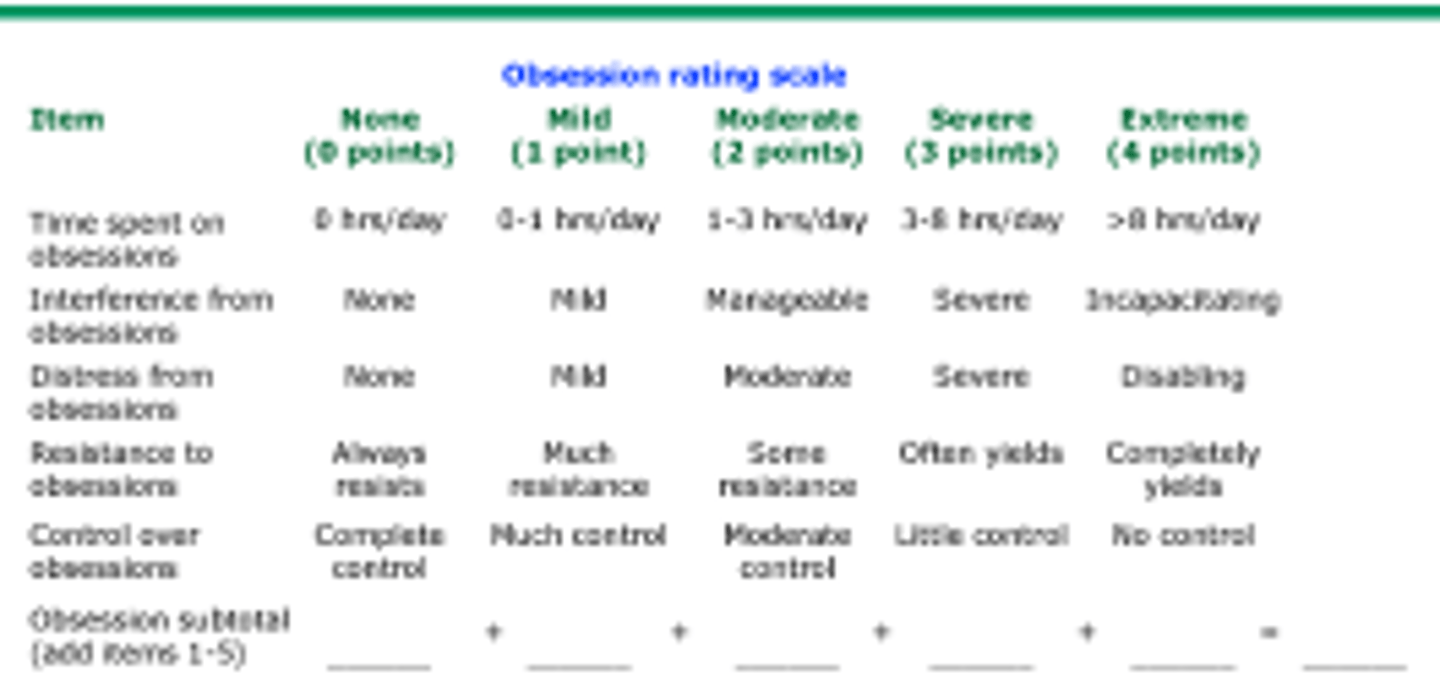
pathophysiology of OCD
- genetic and environmental factors
- research implicates cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) circuits
Treatment for OCD
high dose SSRI
+ CBT
different SSRI or Clomipramine (TCA) or Venlafaxine (SNRI)
body dysmorphic disorder diagnostic criteria
A- preoccupation with >1 perceived defects or flaws in physical appearance that are not observable to others
B- at some point, performed repetitive compulsive behaviors or mental acts in response to concerns
C- causes clinically significant distress & dysfunction
body dysmorphic disorder facts and stats
- mean onset is 17 yo
- MC in plastic surgery, dermatology, and dental clinics
- Comorbid: MDD (MC) , social anxiety disorder, personality disorders, OCD, substance abuse
Treatment for body dysmorphic disorder
SSRI or clomipramine (TCA) + CBT
Hoarding Disorder Diagnostic Criteria
A.Persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their value
B. This difficulty is due to perceived need to save items & to distress associated with discarding them
C. this difficulty discarding possessions results in the accumulation of possessions that congest and clutter living areas and substantially compromises their intended use
D. hoarding causes clinically significant distress in daily life activities
Hoarding Disorder facts and stats
- emerges 11-15yo
- interferes by 20s
- impairs by 30s
- MC in 55-94 yo
- usually older, unmarried/divorced, frequently unemployed
- Comorbid- GAD, MDD, OCD, social anxiety disorder
self study trichotillomania
- recurrent, irresistible urges to pull out hair
- can be focused (intentional) or automatic hair pulling
- cause= unknown, possibly genetic/environmental factors
Self study Excoriation
- chronic skin picking
- MC in women
- Tx= CBT & SSRIs