Stem Cells
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what are the 2 key characteristic of stem cells?
- ability to self-renew
- ability to differentiate into other specialized cell types
what is stem cell potency?
a measure of how many types of specialized cells a stem cell can make
what are the 3 types of stem cell potencies? describe
- totipotent: highest differentiation potential; able to form any cell type in the organism and extra-embryonic tissues like the placenta and yolk sac
- pluripotent: can differentiate into any cell type within the embryo but NOT extra-embryonic tissues (embryonic)
- multipotent: more limited ability, differentiating into a specific range of cell types within a tissue or organ (adult)
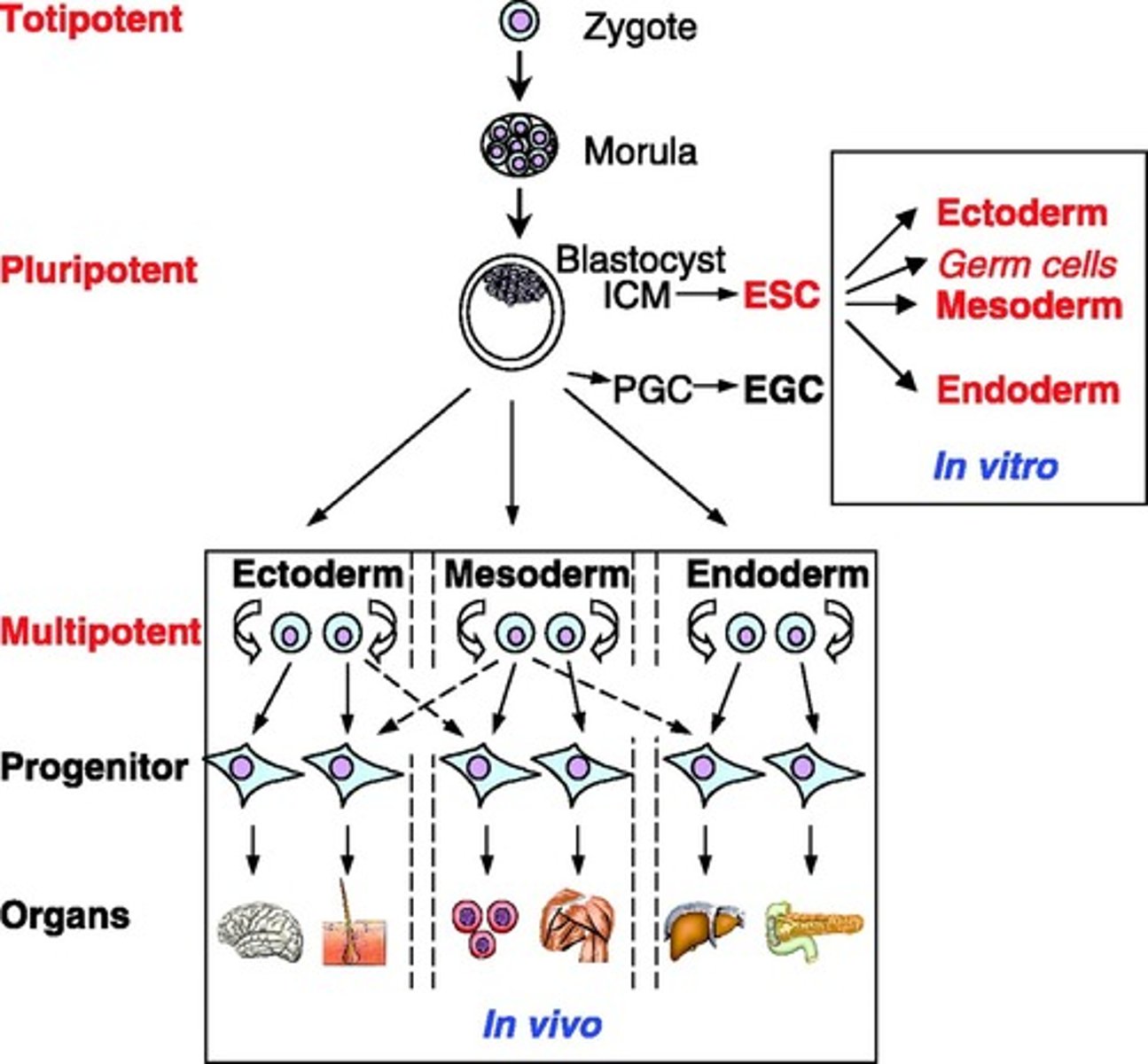
at what point during development do totipotent stem cells develop? pluripotent stem cells?
- totipotent: after 3 days of in vitro fertilization
- pluripotent: embryos that are 3-5 days old
embryonic stem cells are ___________ stem cells
pluripotent
- differentiate into different tissue cells under different conditions
adult and hematopoietic stem cells are ____________ stem cells
multipotent
- adult stem cells can form several kinds of specialized cells, but are more limited than embryonic stem cells
- hematopoietic stem cells can make all the different types of blood cells
what are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)? where do they come from?
adult stem cells (multipotent)
- originate from the CT or stroma that surrounds the body's organs and tissues
what cells do MSCs differentiate into?
osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondroblasts
- useful to make new body tissues (bone, cartilage, fat)
- considered as a promising option in tissue regeneration!
what is stem cell niche?
asymmetric self-renewal cell division
- both self-renewing and differentiating cells in a single cell division
- one daughter cell possesses stem cell properties and the other undergoes differentiation
T/F: cancer stem cells are naturally resistant to chemo or radiotherapy
TRUE
T/F: mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent
TRUE
- called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
- occurs via genetic reprogramming (adding transcription factors to the cell)
what reprogramming factors are added to mature cells to form iPSCs?
'OSKM' factors
- Oct-3/4
- Sox2
- KLF4
- c-Myc
hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantations are performed in ______________ patients; how does this work?
leukemia patients
- cells are derived from the umbilical cord (taken at birth and stored for years!)
- HPCs are given back to the patient and travel to the bone marrow, differentiate into RBCs, WBCs, or platelets
- the differentiated cells then enter the blood stream and help restore low blood counts in patients with blood disorderswhere
what are the 3 main sources of HPCs?
- cord blood
- bone marrow
- peripheral blood
what is an allogenic stem cell transplant?
the stem cells used for transplantation are from a donor
- serious risks and AEs (graft vs. host disease)
- preferred for young and healthy patients
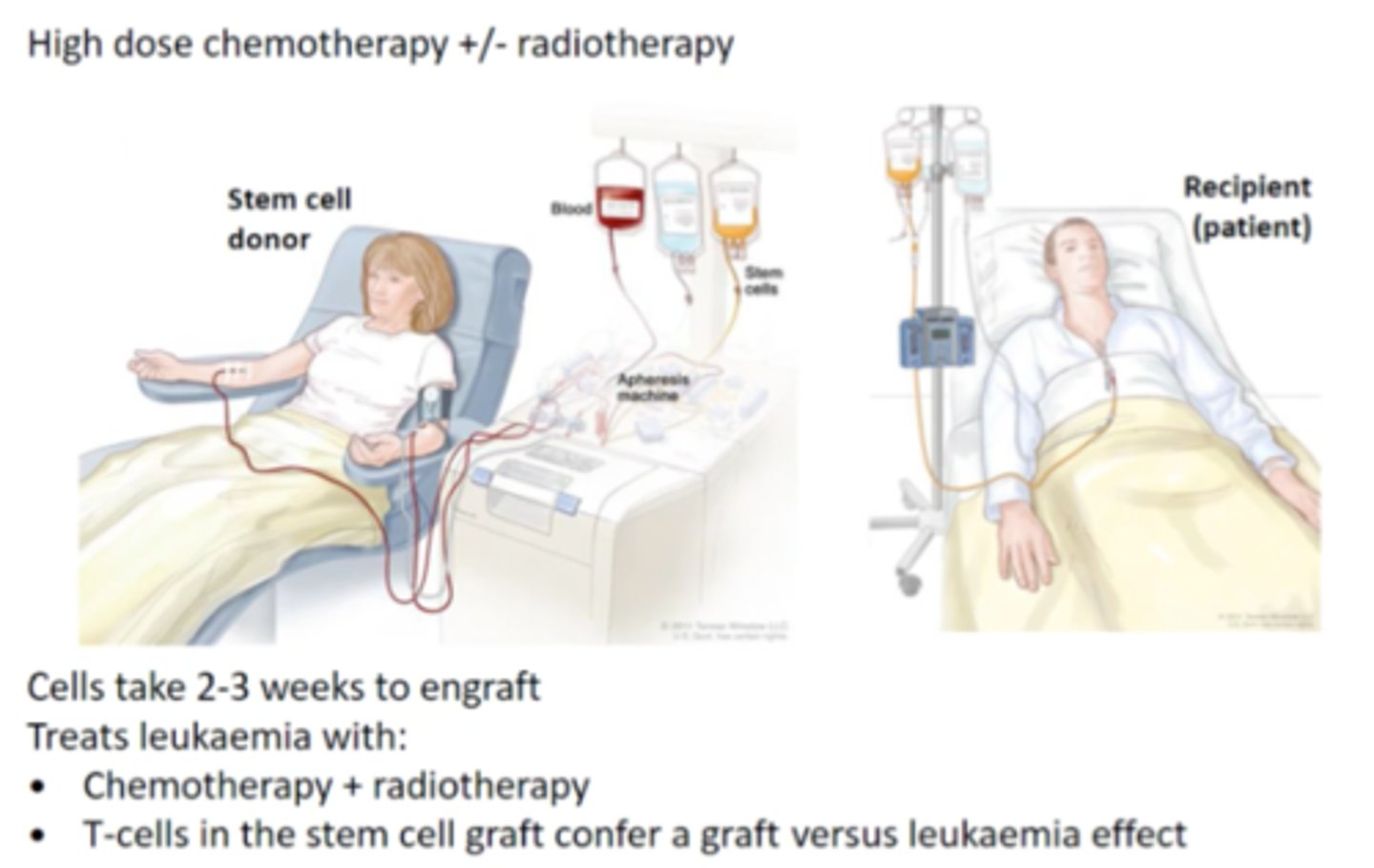
what is an autologous stem cell transplant?
the stem cells used for transplantation are from the patient themselves
- the patient's own stem cells are removed from their bone marrow or blood
- the stem cells are frozen and stored while the person gets treatment (high-dose chemo, radiation), then returned to body afterwards
what is an allogenic bone marrow transplant?
the bone marrow stem cells used for transplantation come from a donor
- used to treat patients with lymphoma, leukemia, and multiple myeloma
describe the 6 stages of allogenic bone marrow transplants
① stem cells are taken from a healthy host's blood/bone marrow
② stem cells are separated out and incubated with Abs
③ stem cells that bind with Abs are selected
④ reduce volume of fluid with stem cells
⑤ dilute stem cells
⑥ infuse stem cells into recipient
where are embryonic stem cells sources from for research?
- donated embryos from fertility clinics
- amniotic fluid
what are some of the applications of stem cells in research?
- tissue regeneration (muscle, skin, bone, cartilage)
- CVD treatment
- brain disease treatment
- cell deficiency therapy (pancreatic cells, liver cells)
- blood disease treatments
- donating or harvesting stem cells (BM, peripheral stem cells, umbilical cord blood)
how might iPSCs be used in regenerative medicine?
shows promise in treating muscular dystrophy, specifically Duchenne muscular dystrophy (gene mutation that produces dystrophin)