Muscular System Notes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
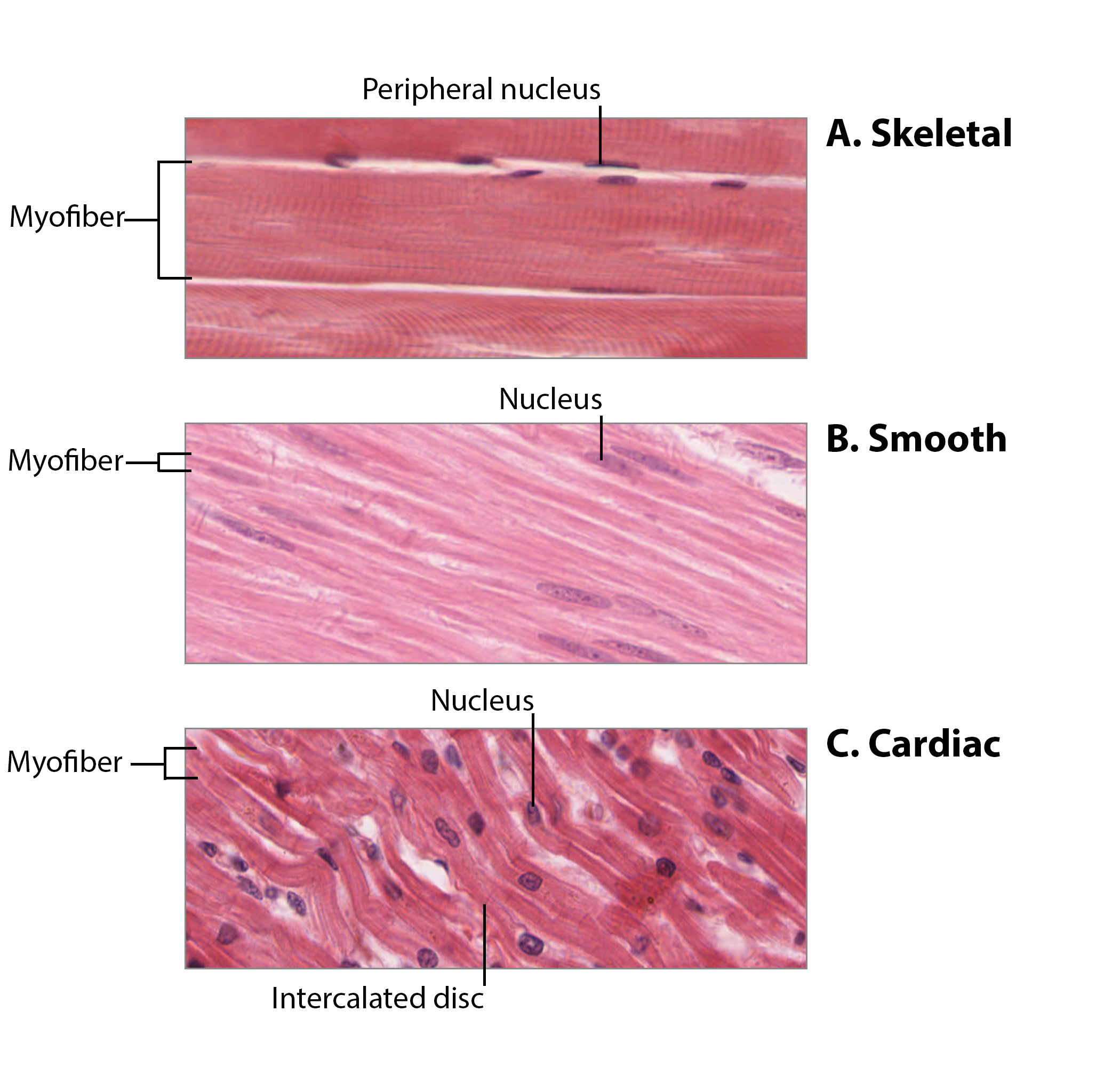
Cardiac Muscle
Found in the heart, involuntary.
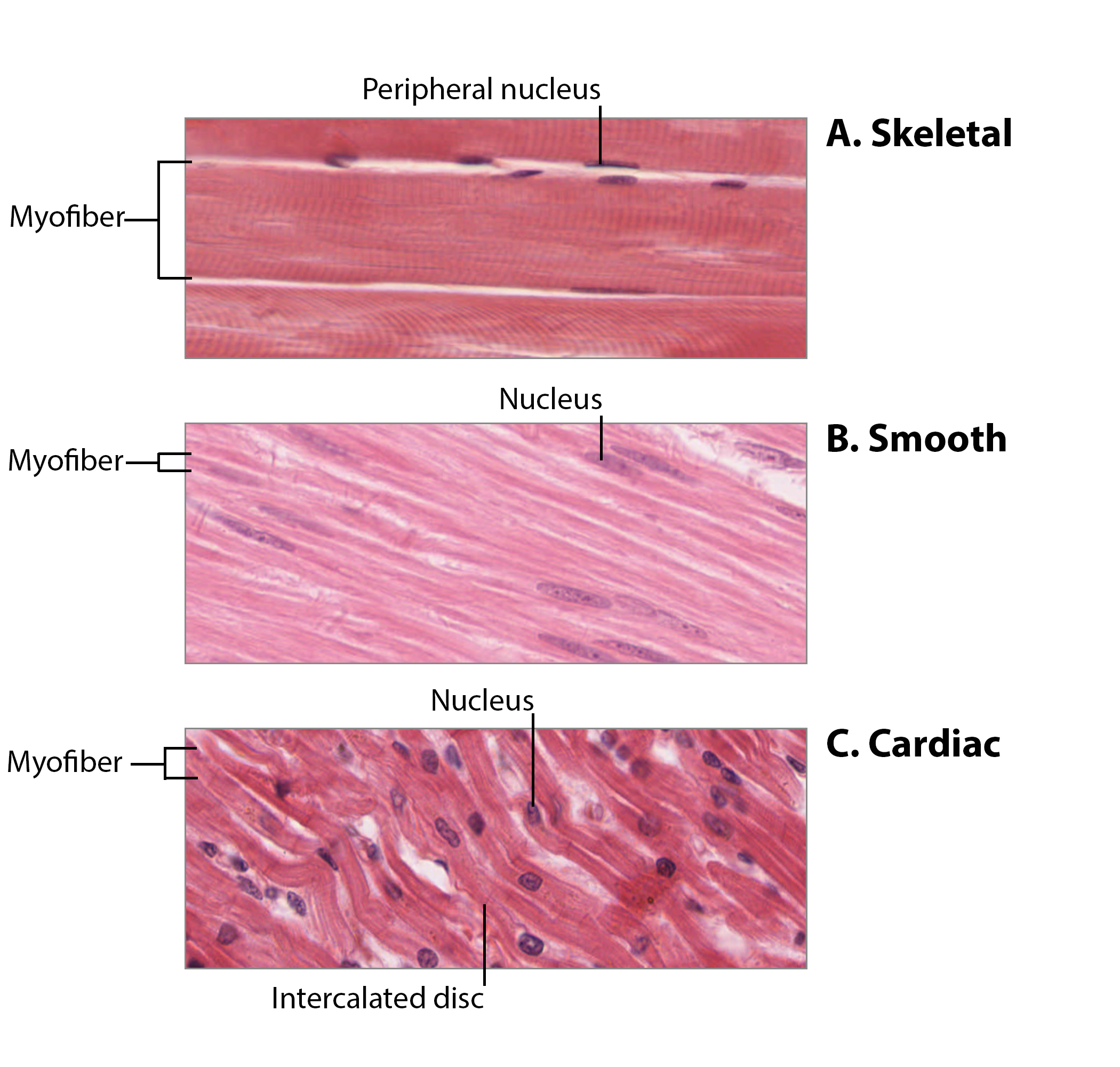
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary, striated, primarily responsible for movement.
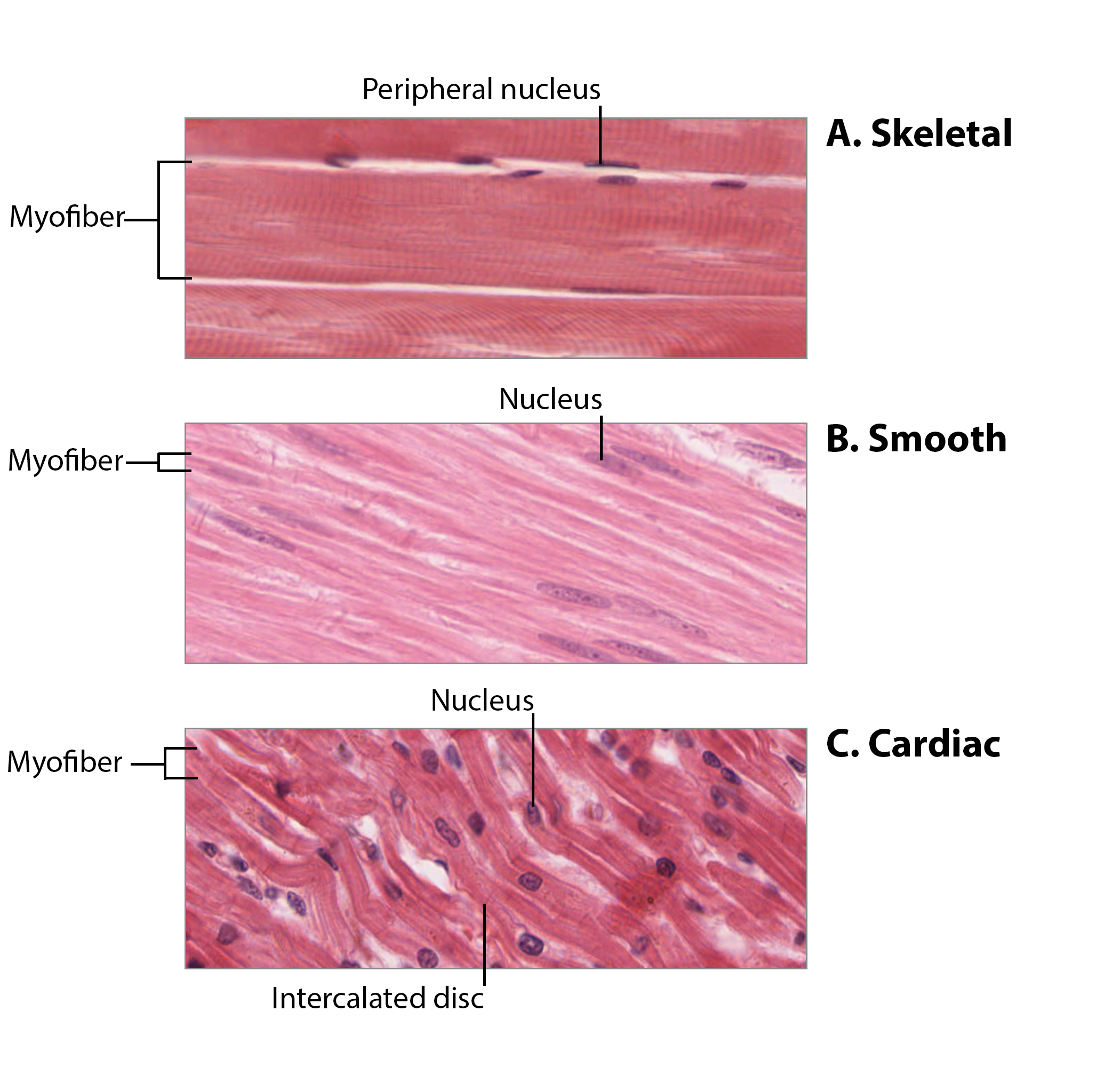
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary, found in walls of hollow organs.
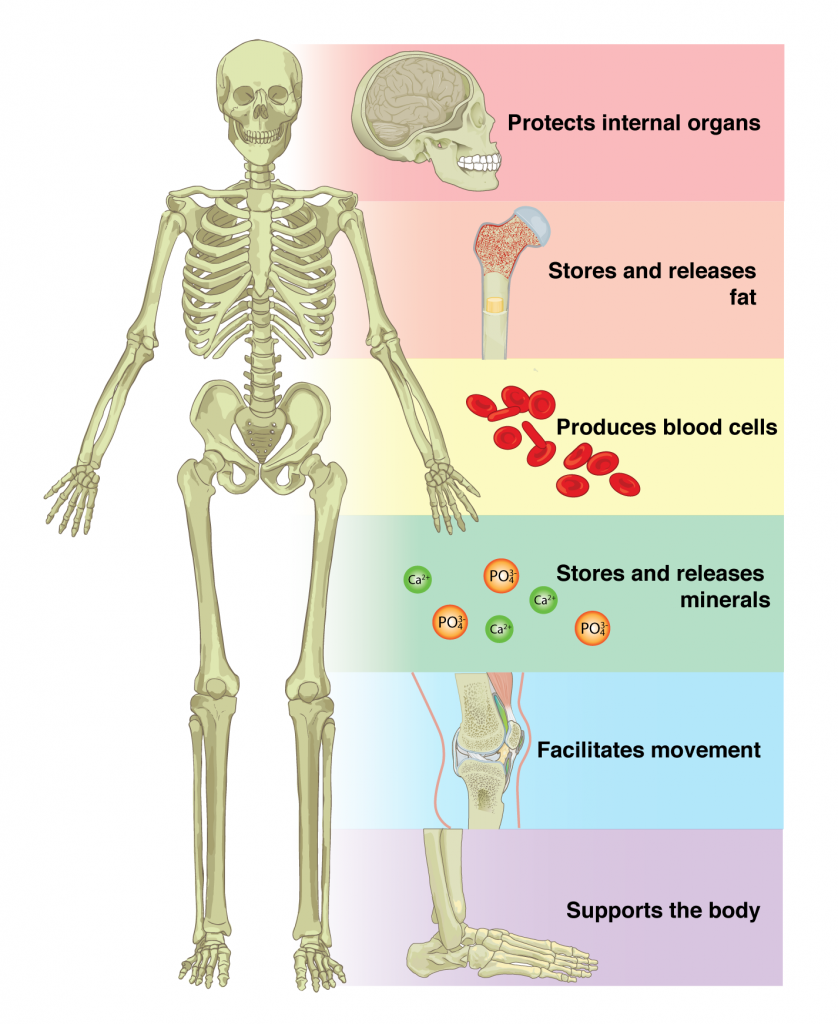
Movement
Involves both voluntary (e.g., lifting an arm) and involuntary actions (e.g., digestion, blood pumping).
Stability
Maintains posture and prevents undesired movements.
Control of Body Openings and Passages
Sphincter muscles regulate movement (e.g., in the digestive tract).
Heat Generation
Skeletal muscles produce significant body heat (up to 30% at rest, 40x during exercise).
Glycemic Control
Regulates blood glucose levels by absorbing sugar.
Skeletal Muscle Voluntariness
Skeletal muscle operates under conscious control.
Striations
Visible light and dark bands due to internal proteins that allow contraction.
Muscle Structure
Skeletal muscle cells are known as muscle fibers, characterized by long slender shapes, multiple nuclei, and bundled contractile proteins (myofibrils).
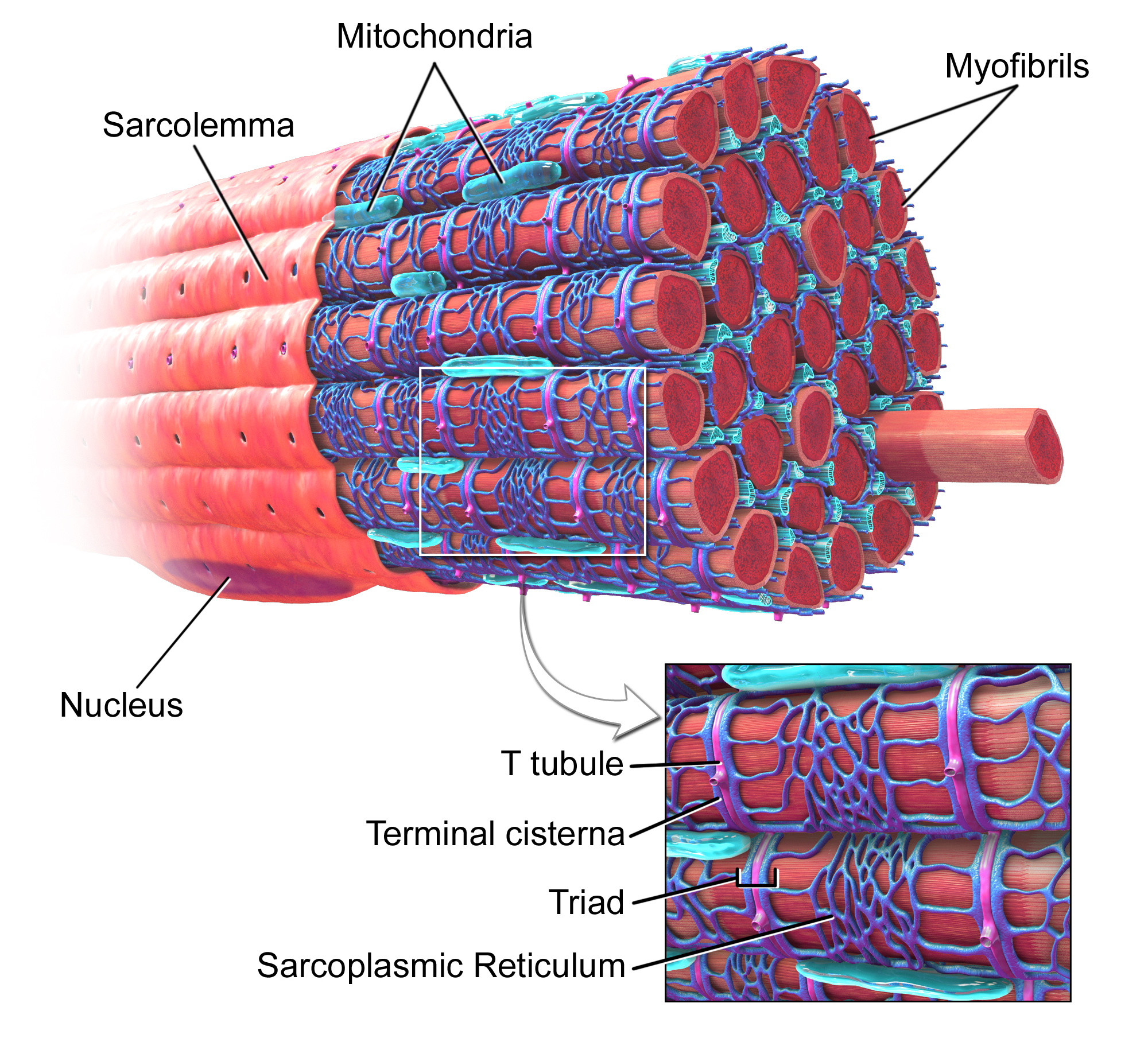
Components of Muscle Fibers
Includes membrane (sarcolemma) with T tubules for electrical conduction and sarcoplasmic reticulum for calcium storage.
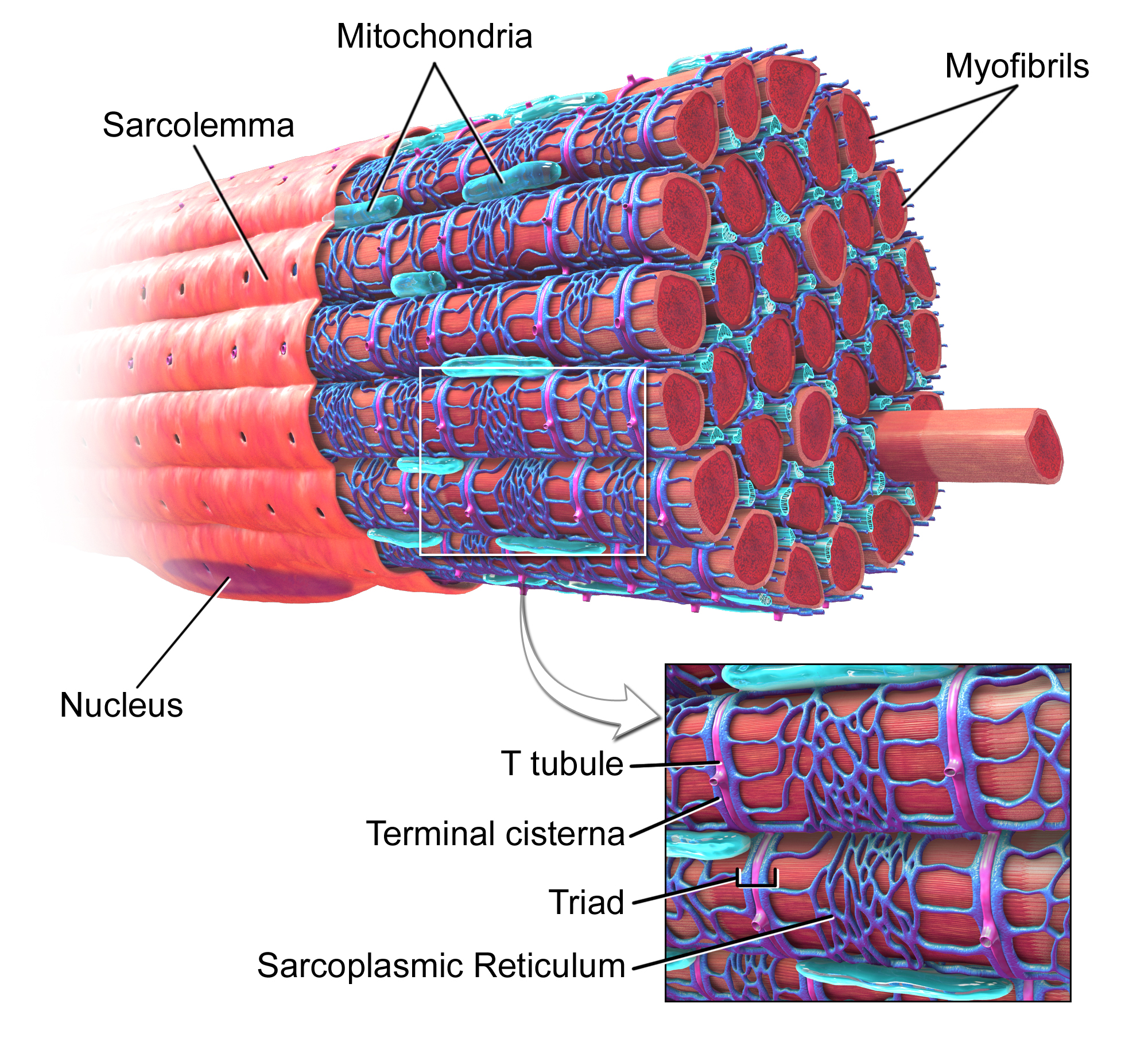
Myofibrils
Packed with contractile proteins: Thick filaments (myosin) and thin filaments (actin strands intertwined with tropomyosin and troponin).
A Bands
Dark bands where both thick and thin filaments overlap.
I Bands
Light bands consisting of only thin filaments.
Z Disks
Proteins anchoring thin filaments, marking the borders of myofibrils (sarcomeres).
Neural Stimulation
Skeletal muscles contract only when stimulated by motor neurons in the brain/spinal cord.
Neuromuscular Junction
Site of axon terminal and muscle fiber connection, separated by synaptic cleft.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Released neurotransmitter that binds to receptors on the muscle fiber, triggering contraction.
AChE
Acetylcholinesterase enzyme that breaks down ACh to halt stimulation and allow muscle relaxation.
Excitation
Electrical nerve signal triggers muscle fiber activation via ACh release.
Steps of Excitation
- Nerve signal leads to ACh release. 2. ACh binds to receptors. 3. Ion influx initiates action potential.
Contraction
Involves sliding filament model leading to muscle shortening through cross-bridge formation.
Steps of Contraction
- Myosin binds to ATP, hydrolyzing it. 2. Myosin head binds to actin. 3. Power stroke pulling actin filaments. 4. New ATP binding resets myosin.
Relaxation Process
- End of ACh release. 2. Breakdown of ACh. 3. Reabsorption of calcium. 4. Troponin-tropomyosin blocks myosin attachment sites.
Isometric Contraction
Muscle tension without shortening (e.g., holding a weight).
Isotonic Contraction
Muscle tension changes while maintaining contraction.
Concentric Contraction
Muscle shortens while maintaining tension (e.g., lifting).
Eccentric Contraction
Muscle lengthens while maintaining tension (e.g., lowering weight).
ATP Generation
Essential for muscle contraction via anaerobic fermentation (2 ATP) and aerobic respiration (30 ATP).
Fatigue and Endurance Factors
Includes glycogen depletion, calcium leakage, K+ buildup; endurance influenced by mitochondrial density.
Slow-twitch Fibers
Aerobic, resistant to fatigue, contain many mitochondria.
Fast-twitch Fibers
Anaerobic, quick to contract, fatigue rapidly, rich in anaerobic enzymes.
Resistance Training
Increases muscle fiber size, improves strength but not endurance.
Endurance Exercises
Improve fatigue resistance, enhance efficiency in ATP production.
Cross-training
Combines resistance and endurance training for maximized performance.
What are thick filaments composed of?
Thick filaments are primarily composed of myosin.
What are thin filaments comprised of?
Thin filaments are composed of actin strands, which are intertwined with tropomyosin and troponin.