BIO 202: Chapter 10.1 - 10.6 Male Reproduction
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
reproductive system
only system in the body that produces new cells genetically different from the rest of the body’s cells
mitosis
process where daughter cells are identical to the parent cell for the purpose of growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues
produces two diploid cells identical to parent cell (46 chromosomes)
prophase
first phase of mitosis in which chromatin condenses into chromosomes, spindle fibers form, and nuclear envelope breaks down
metaphase
second phase of mitosis in which chromosomes align at the cell’s equator, attached to spindle fibers at the centromeres
anaphase
third phase of mitosis in which sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
telophase
fourth phase of mitosis in which chromosomes uncoil into chromatin, nuclear envelopes reform, and cytokinesis completes the division
cytokinesis
final step of cell division in which the cytoplasm splits to create two separate daughter cells
meiosis
process that reduces the number of chromosomes by half to produce four genetically unique haploid gametes (23 chromosomes)
meiosis I: separation of homologous chromosomes
meiosis II: separation of sister chromatids
homologous chromosomes
matching chromosome pairs
one from each parent
same size, shape, and gene sequence but may carry different versions of those genes
s phase
phase before meiosis I in which DNA replicates to form pair of sister chromatids
prophase I
first phase of meiosis I in which chromatin condenses, homologous chromosomes pair to form tetrads and cross over at chiasmata to exchange DNA, spindle fibers form, and nuclear envelope breaks down
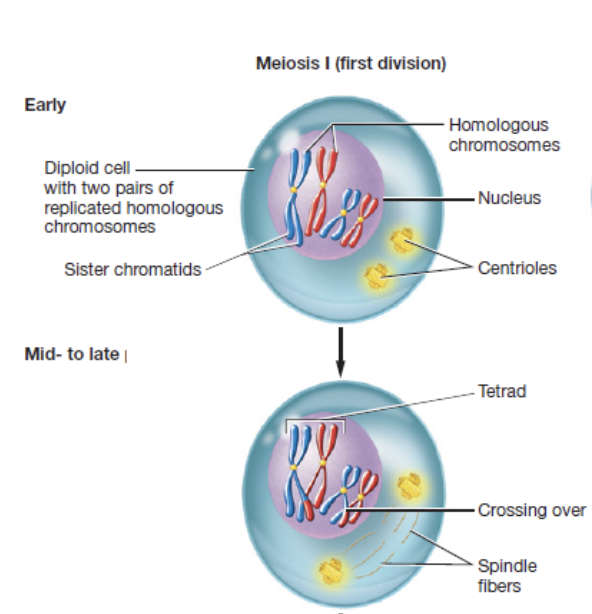
chisamata
points where homologous chromosomes physically connect during meiosis to allow segments of genetic material to be exchanged
metaphase I
second phase of meiosis I in which tetrads align at the equator
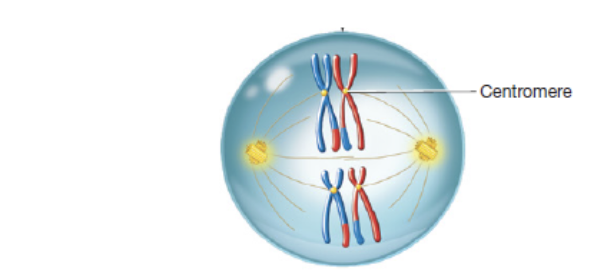
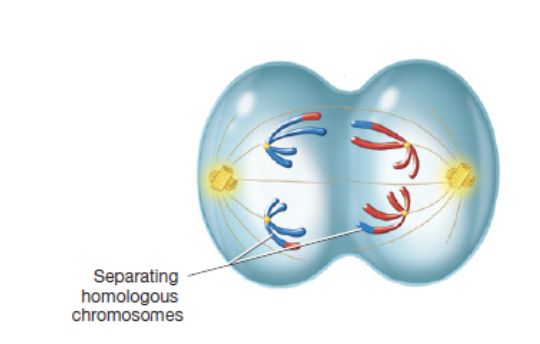
anaphase I
third phase of meiosis I in which homologous chromosomes separate
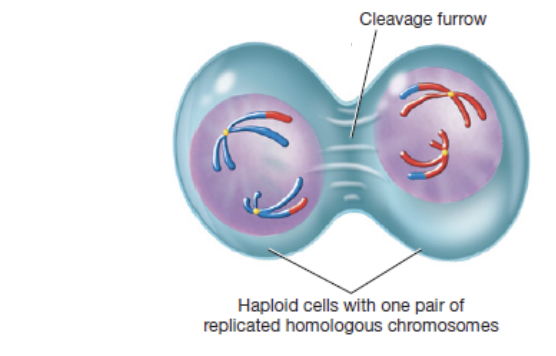
telophase I and cytokinesis
fourth phase in meiosis I in which two haploid cells form, each with 23 chromosomes
prophase II
first phase of meiosis II in which chromosomes condense and spindle fibers reforn
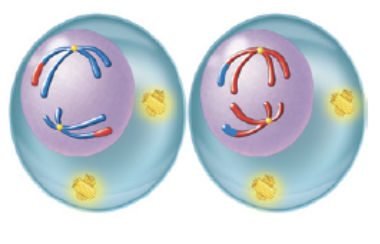
metaphase II
second phase of meiosis II in which chromosome align at the equator
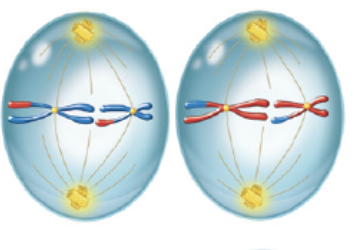
anaphase II
third phase of meiosis II in which sister chromatids separate to opposite poles
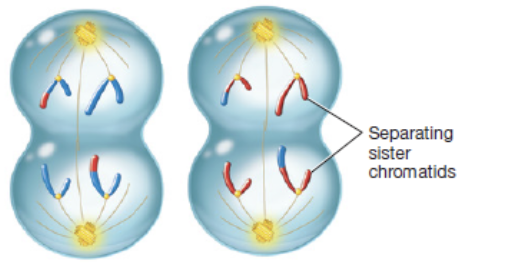
telophase II and cytokinesis
fourth phase of meiosis II in which four haploid gametes form that each have 23 single-stranded chromosomes
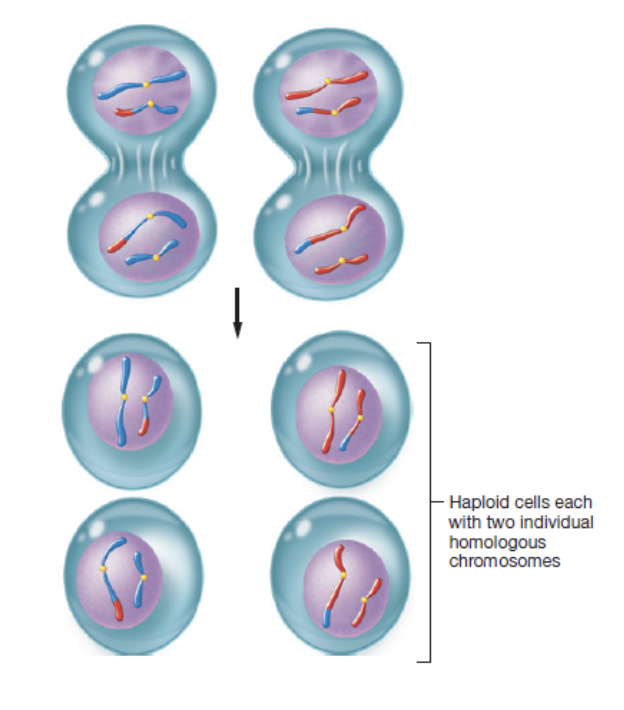
zygote
fertilized egg that forms when male and female gametes combine
has full set of 46 chromosomes
gonads
primary reproductive organs that produce gametes
testes in males
ovaries in females
gametogenesis
process of forming new gametes through meiosis
external reproductive organs
located in the perineum in both males and females
perineum
diamond shaped area between the thighs in males and females
bordered by pubic symphysis, coccyx, and left and right ischial tuberosities
divided into anterior triangle and posterior triangle
chromatid
one half of a duplicated chromosome
sister chromatids
identical copies joined after DNA replication
centromere
region where sister chromatids are held together and spindle fibers attach during cell division
short arm (p)
shorter section of the chromosome above the centromere
long arm (q)
longer section of the chromosome below the centromere
telomeres
repetitive DNA sequences at the chromosome ends that protect genetic material
kinetochore
protein structure on the centromere where spindle fibers attach
gene
sequence of deoxyribonucleic acid that contains instructions for making a protein or RNA molecule
has a specific locus on a chromosome
alleles
variations of a gene that may produce different traits
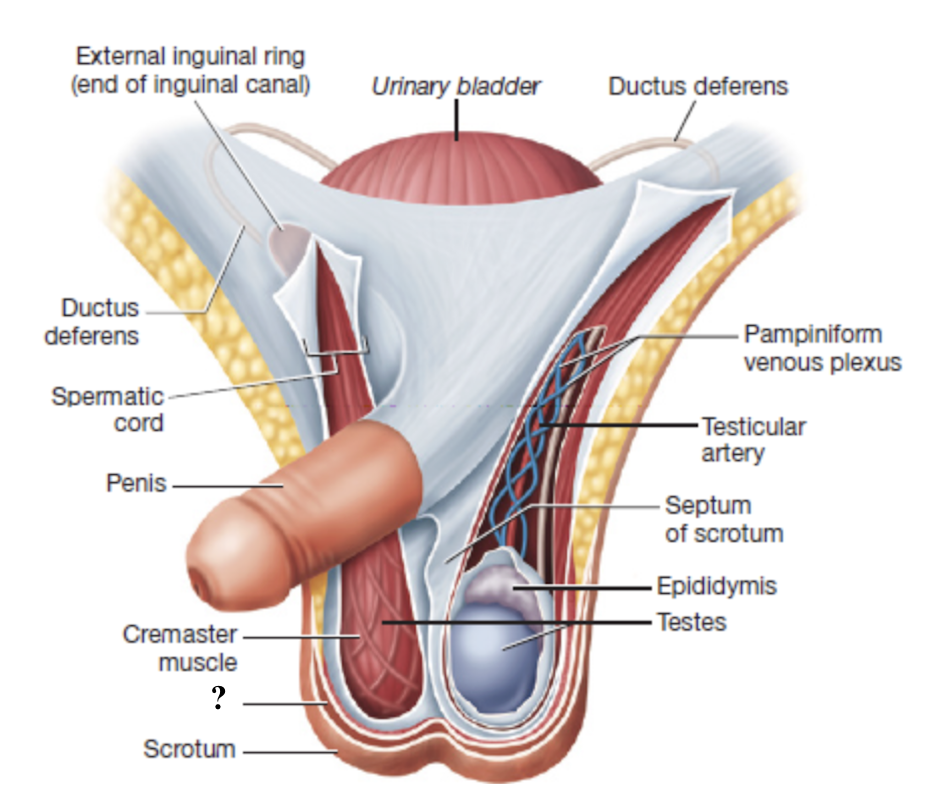
scrotum
external sac that houses the testes
composed of skin, connective tissue, and subcutaneous layer of smooth muscle
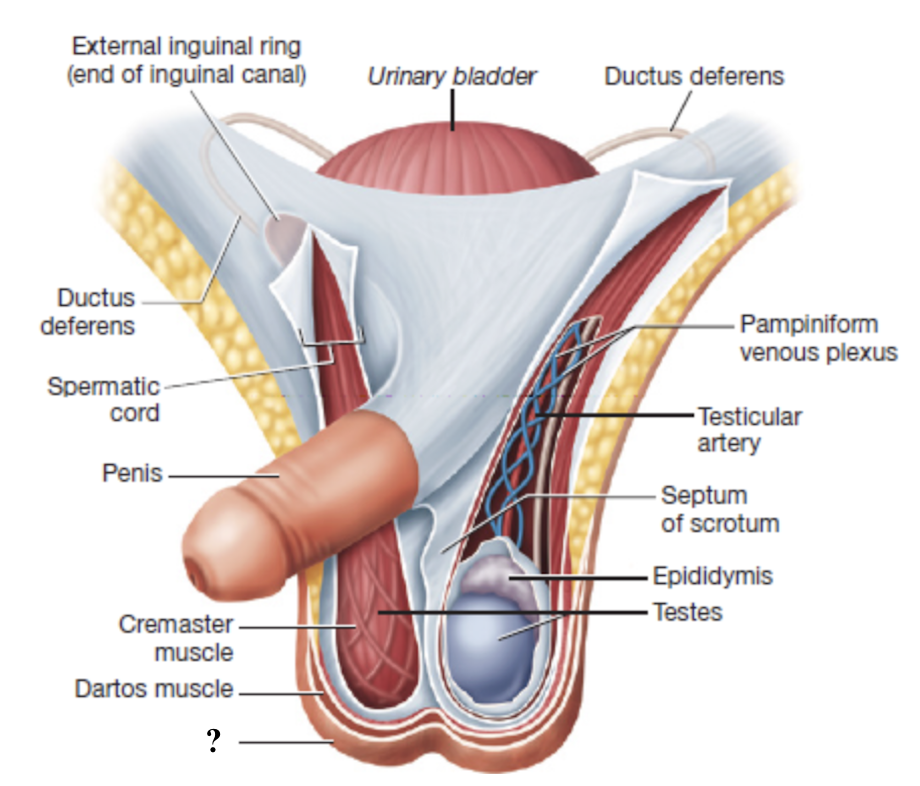
dartos muscle
smooth muscle in the scrotum that contracts in response to cold temperatures to help converse heat
94 F
sperm production requires a temperature of about ____
connective tissue septum
runs along the midline to divide the scrotum into two chambers that each contain one testis
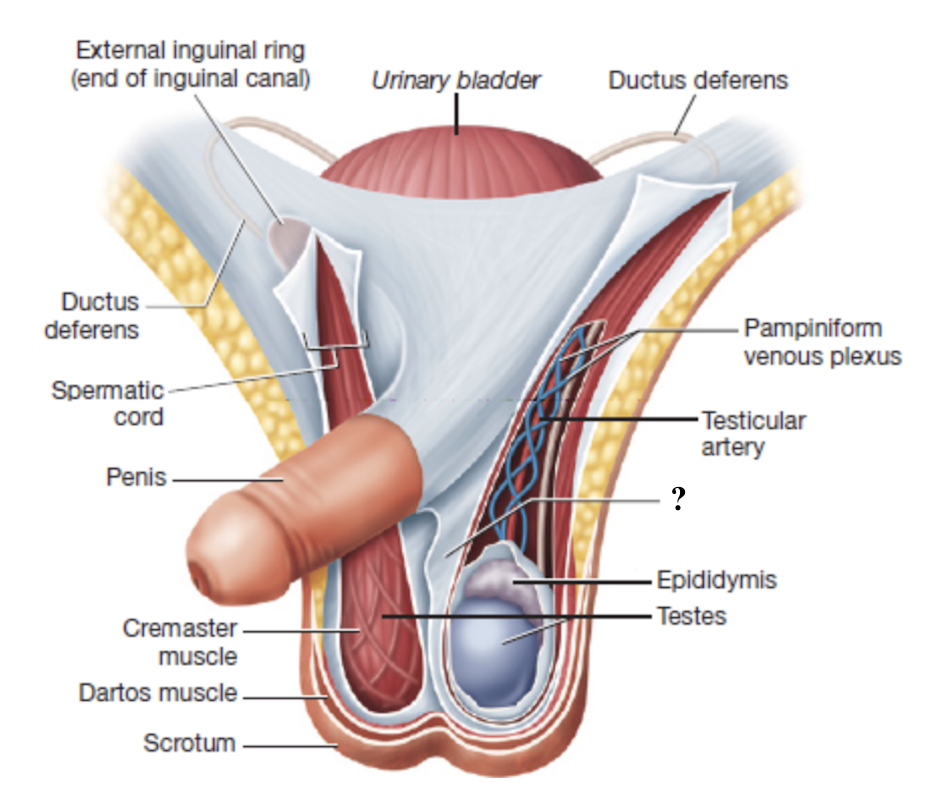
spermatic cord
serves as a passageway for structures that support the testes and passes through the inguinal canal
deep to scrotum
layer of connective tissue
inguinal canal
narrow tube about 4 cm long with two openings
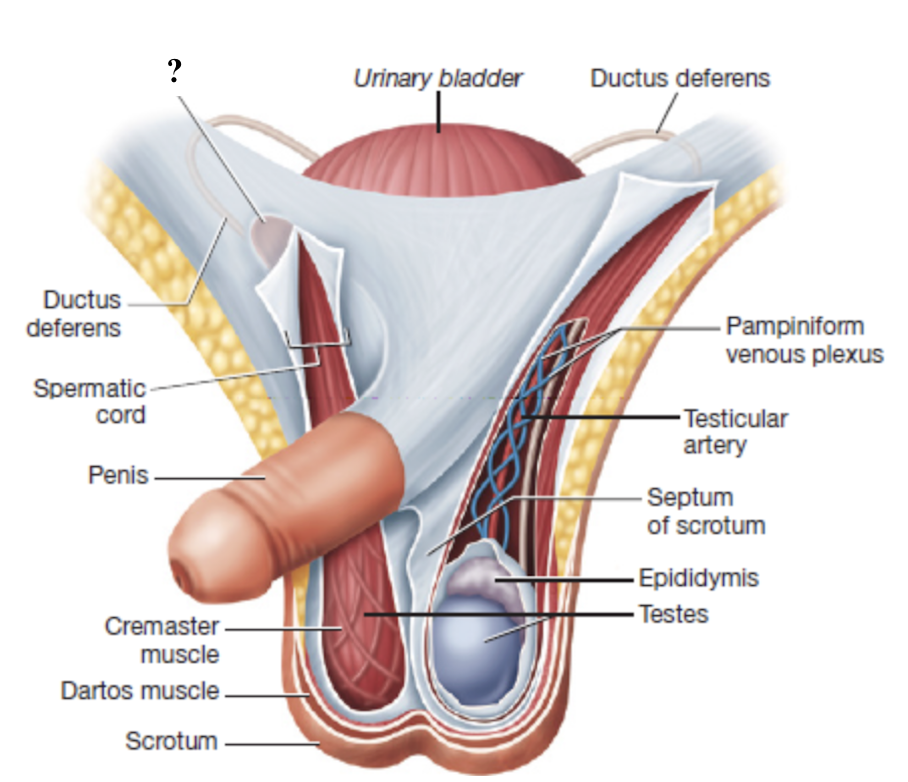
external inguinal ring
internal inguinal ring
external inguinal ring
inferior opening from the scrotum into the inguinal canal
internal inguinal ring
superior opening from the inguinal canal into the pelvic cavity
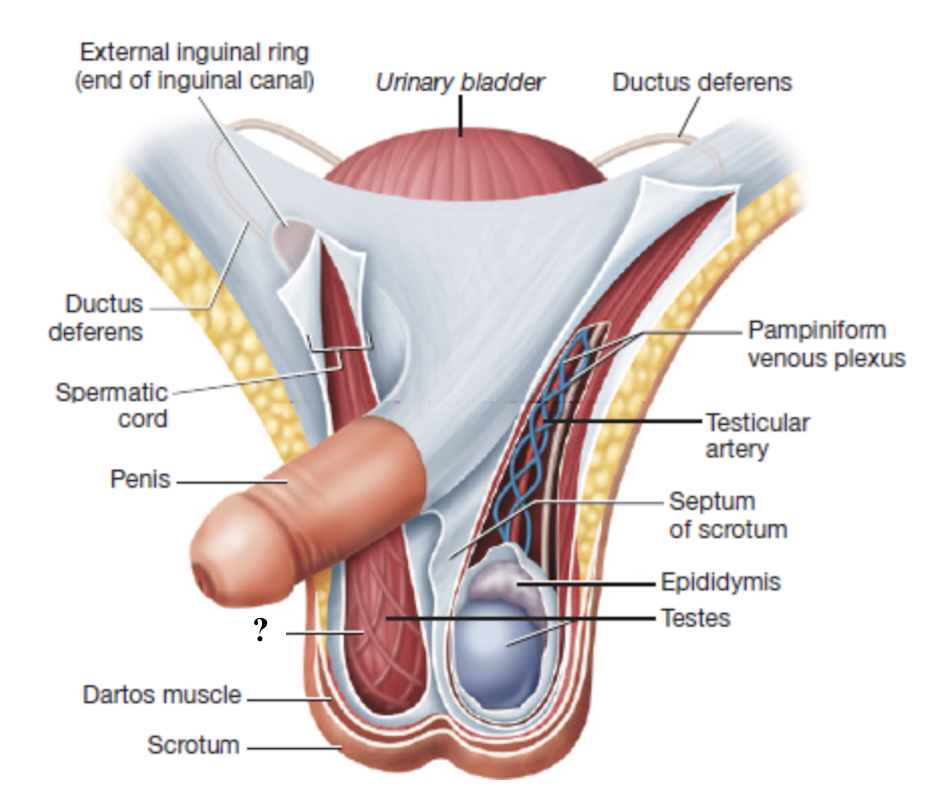
cremaster muscle
smooth muscle fibers interwoven with the spermatic cord that contract to move the testes closer or farther from the body
regulate temperature for optimal sperm production
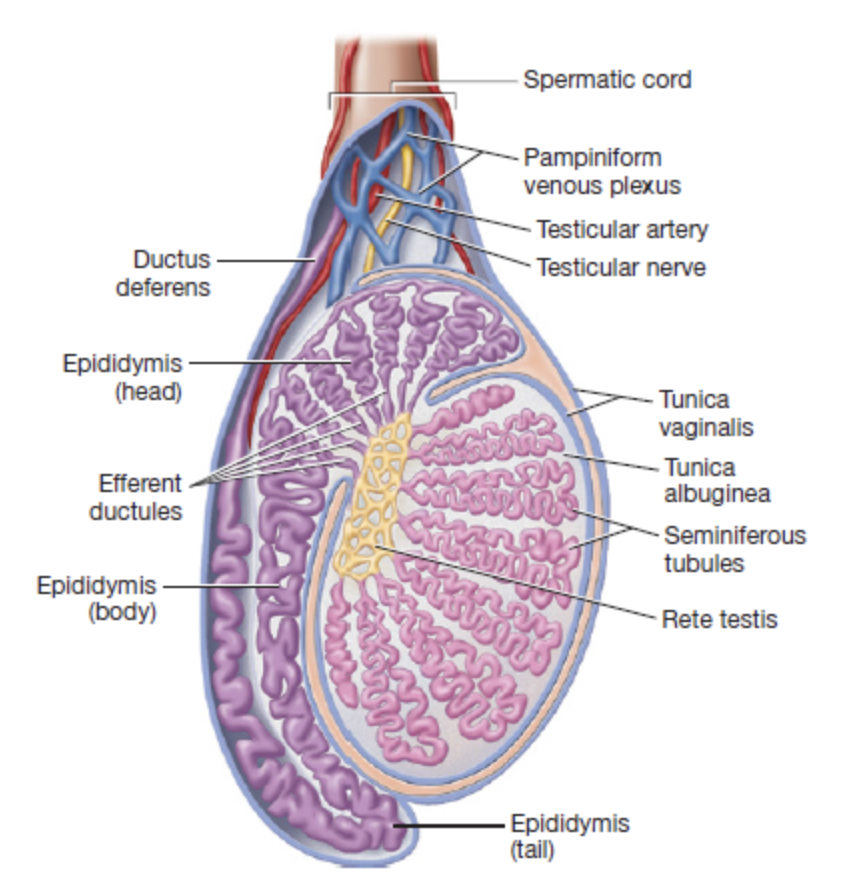
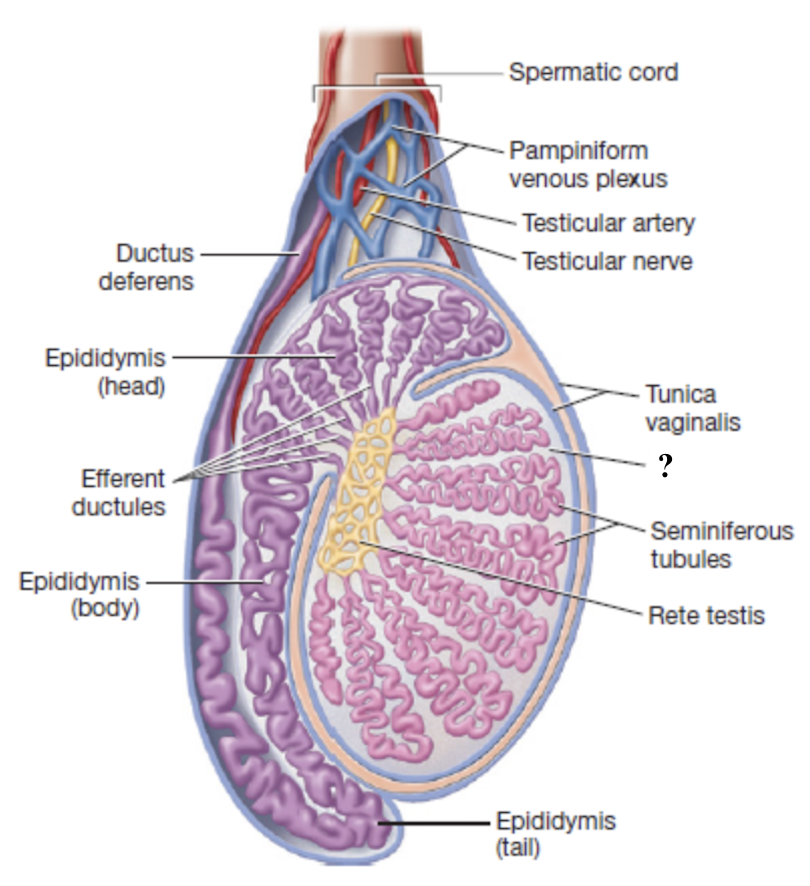
tunica vaginalis
superficial serous membrane producing fluid to reduce friction
one of the coverings of the testes deep to the cremaster muscle
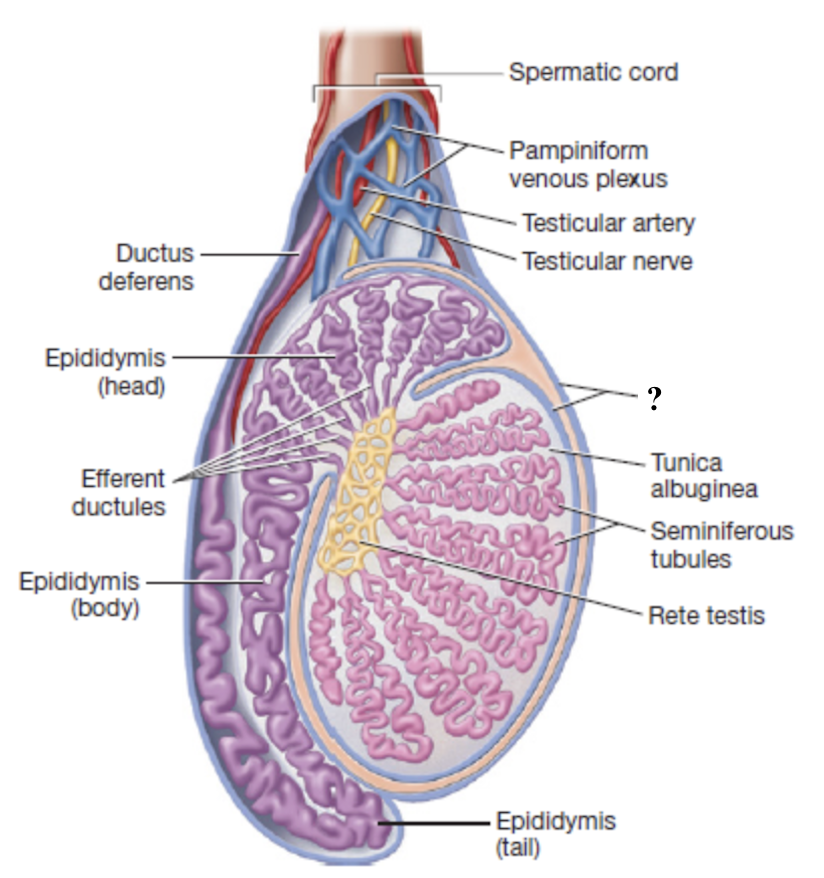
tunica albuginea
deep, dense connective tissue layer that divides each testis into 250-300 wedge shaped lobules
one of the coverings of the testes deep to the cremaster muscle
testicular artery
supplies oxygenated blood to the testes
originates from the abdominal aorta
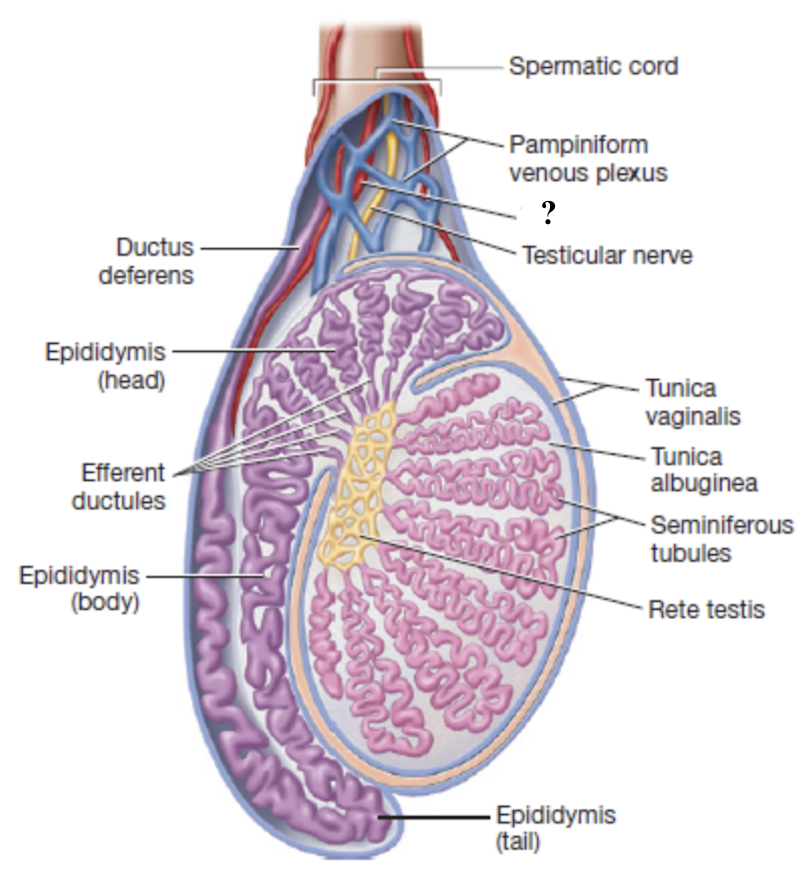
pampiniform venous plexus
network of slender veins surrounding the testicular artery
drains deoxygenated blood from the testes
acts as countercurrent heat exchanger
lowers arterial blood temperature
testicular vein
after passing through the inguinal canals, the pampiniform venous plexus merge to form this vein
right drains into inferior vena cava
left drains into left renal vein
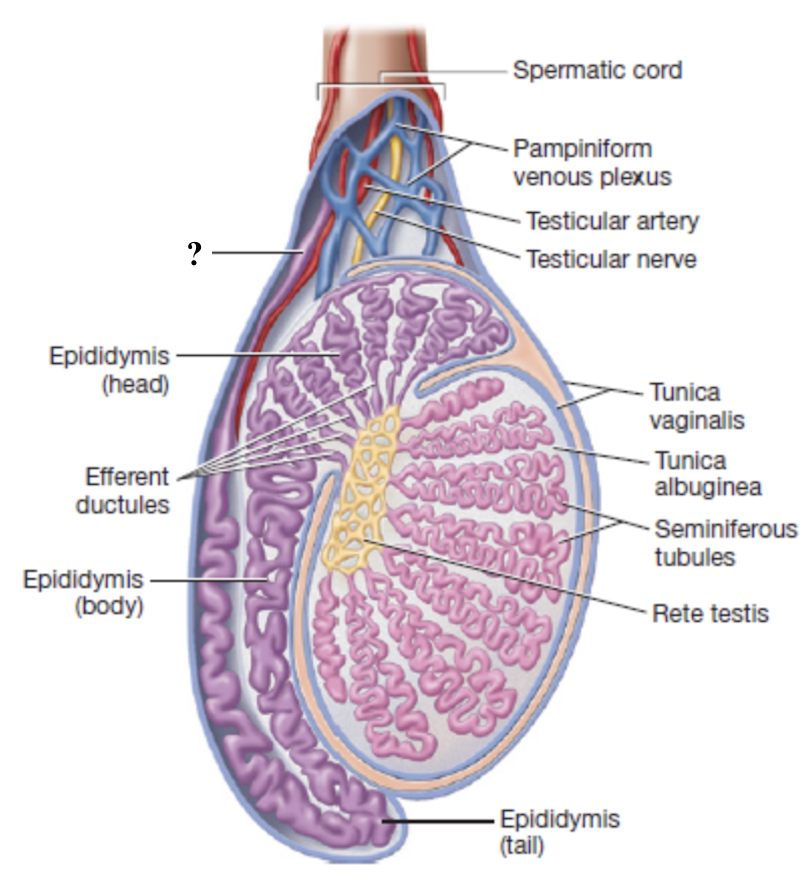
ductus vas deferens
muscular tube that transports sperm from the epididymis toward the ejaculatory duct
loops posteriorly and superiorly around the urinary bladder
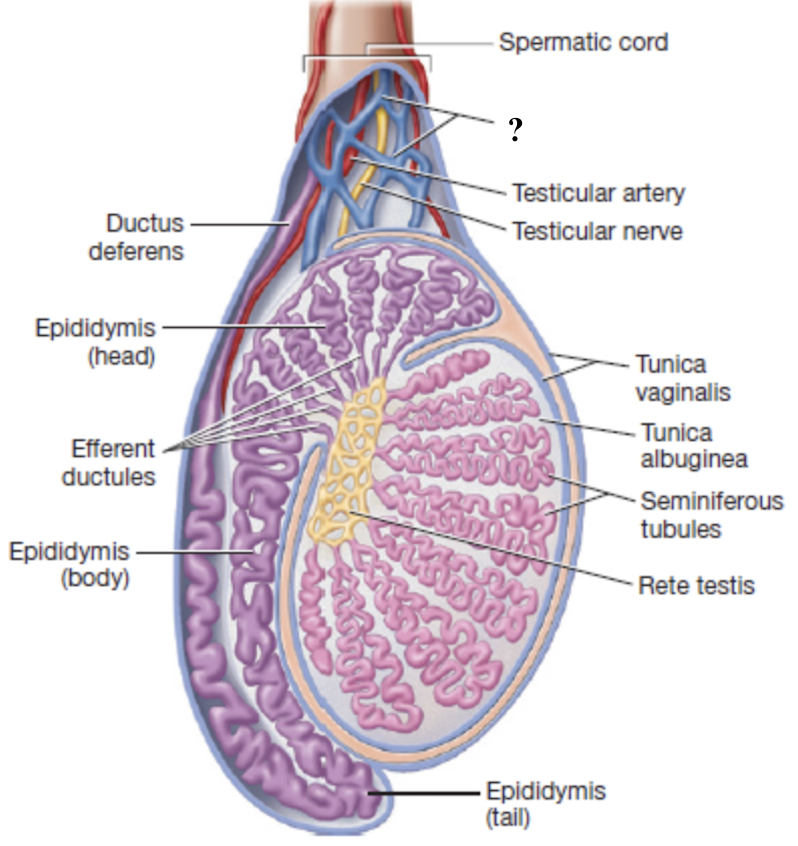
testicular nerves
mixed sensory and motor fibers that innervate the testes
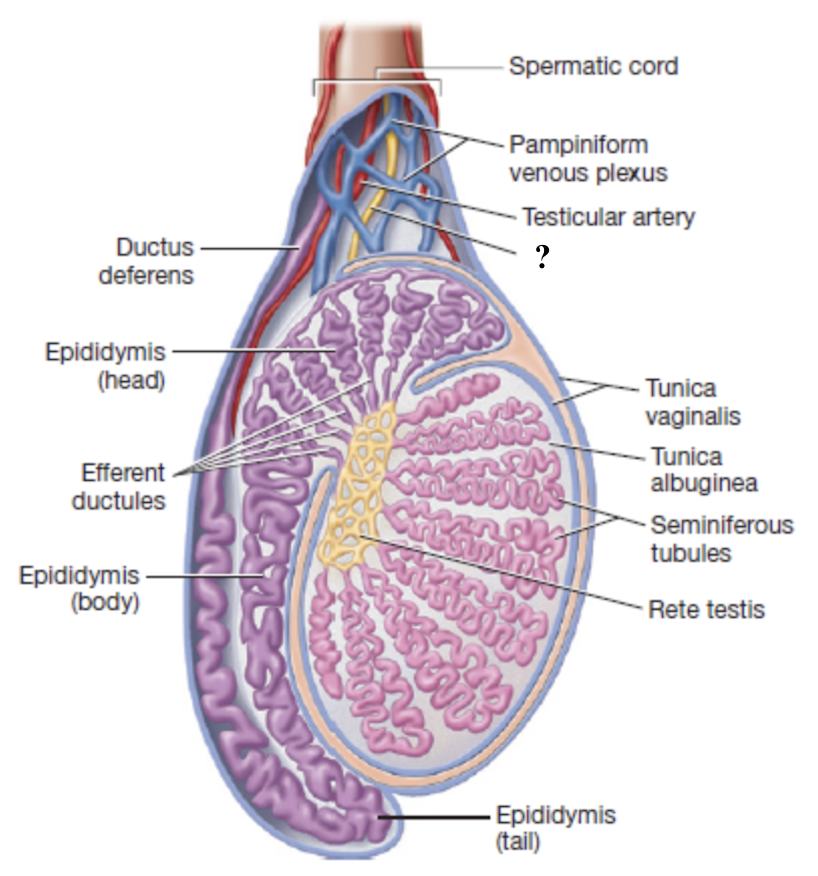
lymphatic vessels
drain excess fluid and help maintain tissue health
testicular torsion
condition in which the spermatic cord can twist and cut off blood supply to the testis
can cause permanent testicular damage and often requires surgical intervention to untwist and secure the testis
seminiferous tubules
tightly coiled within each testicular lobule
converge into the rete testis
rete testis
network near the superior portion of the testis that serves as an initial site where sperm cells begin partial maturation
exits via 12 small efferent ductules
efferent ductules
contain clusters of ciliated cells that help propel sperm toward the next structure
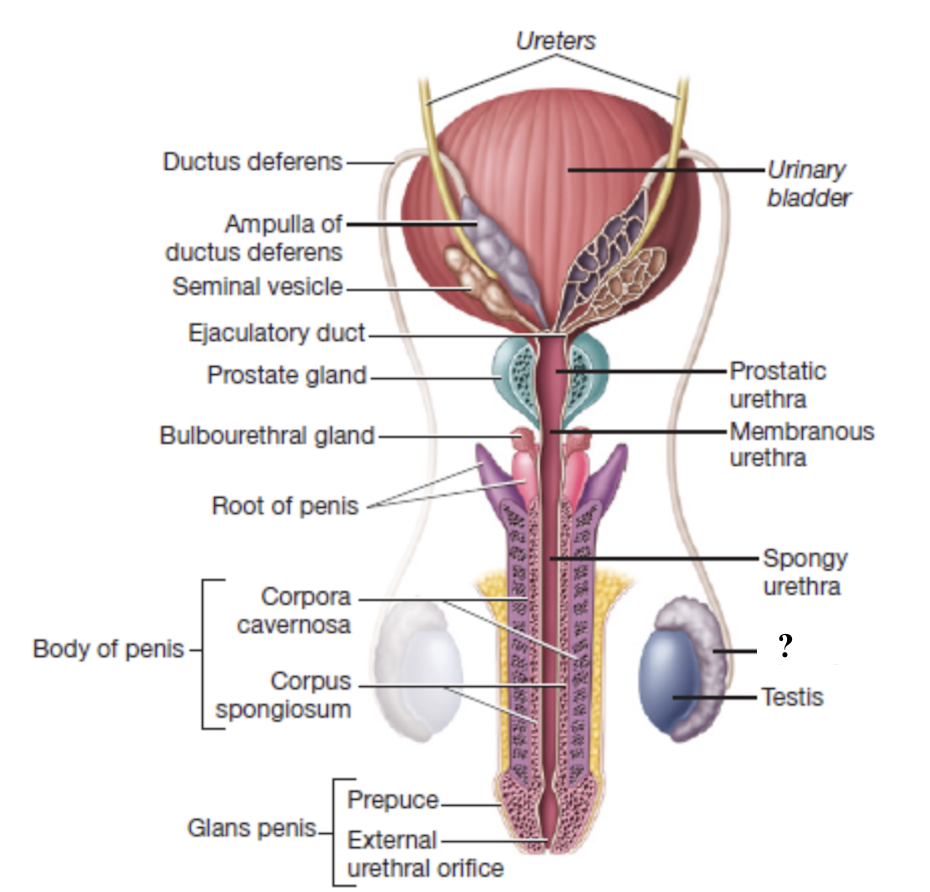
epididymis
primary site of sperm maturation and storage
had three regions (head, body, tail) that immature sperm migrate through to complete maturation before moving into the ductus deferens
vasectomy
surgical method of male contraception in which a short segment of the ductus is cut and sealed
interrupts the passage of sperm from the epididymis to the urethra so semen no longer contains sperm but other components are still present
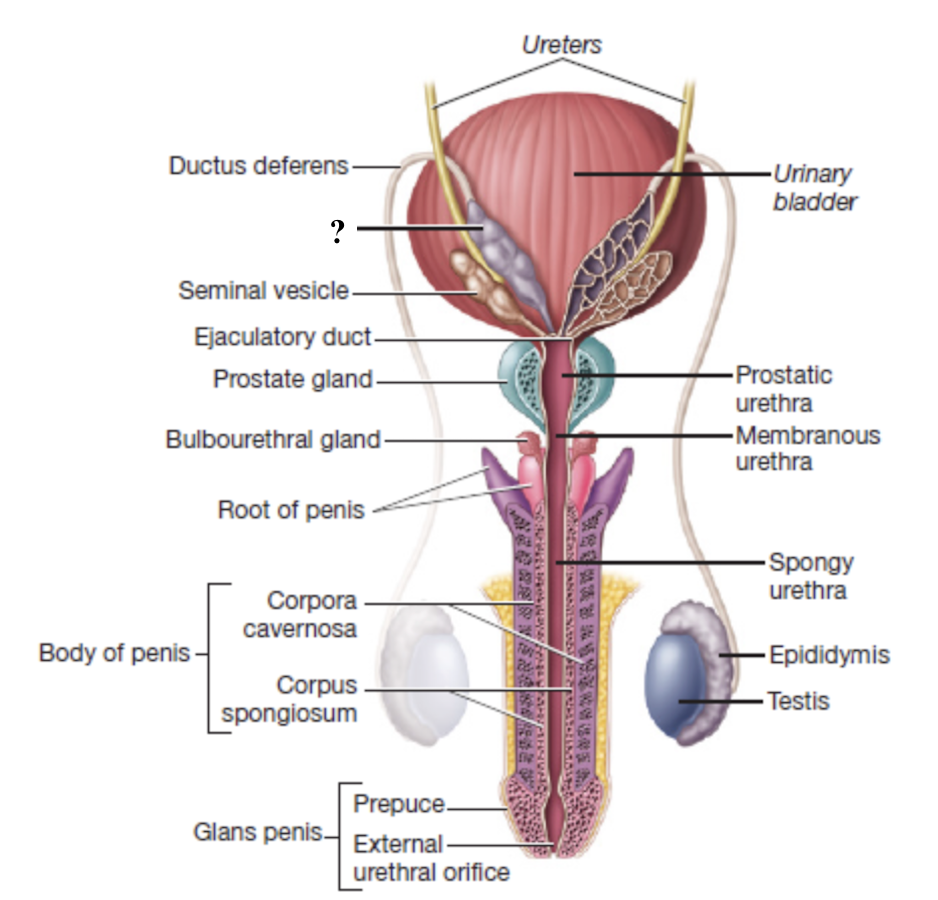
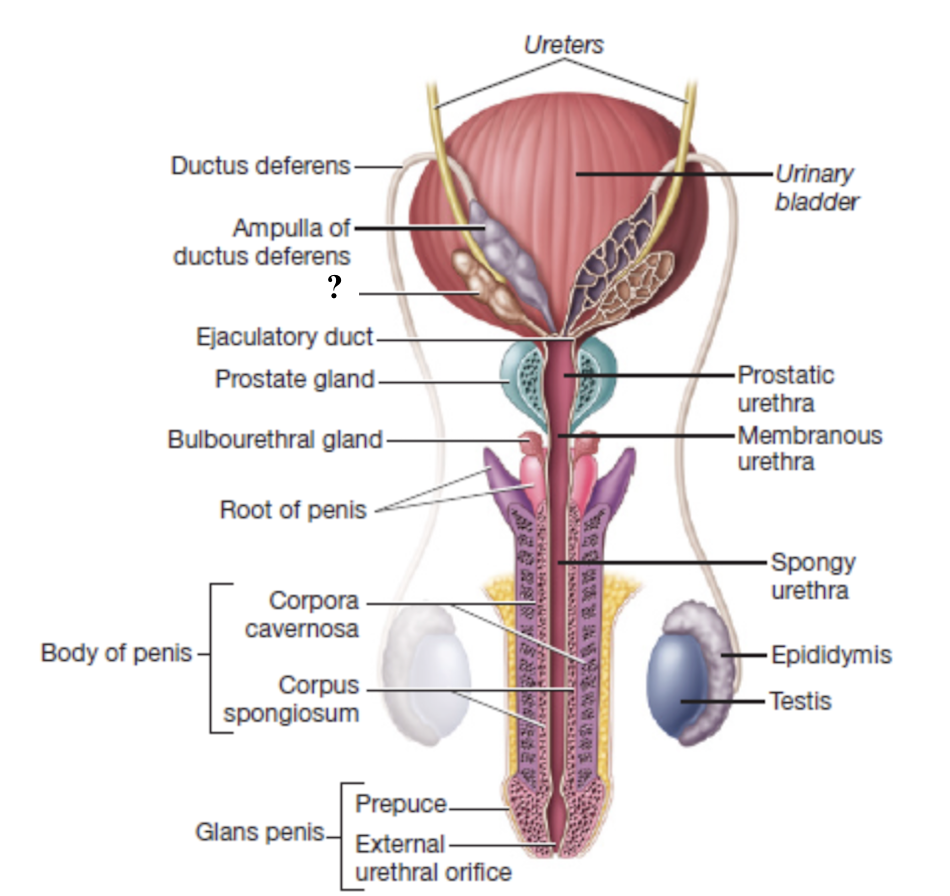
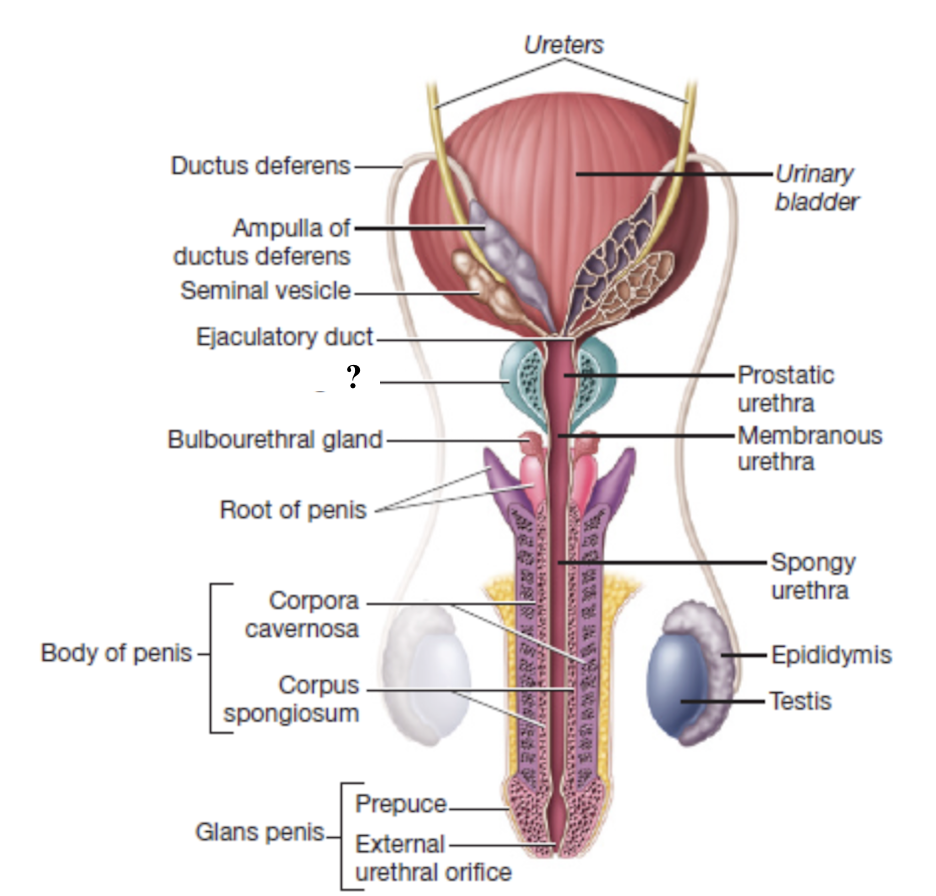
ampulla of ductus deferens
widen, enlarged terminal region of the ductus deferens on the posterior surface of the bladder
serves as a reservoir for sperm
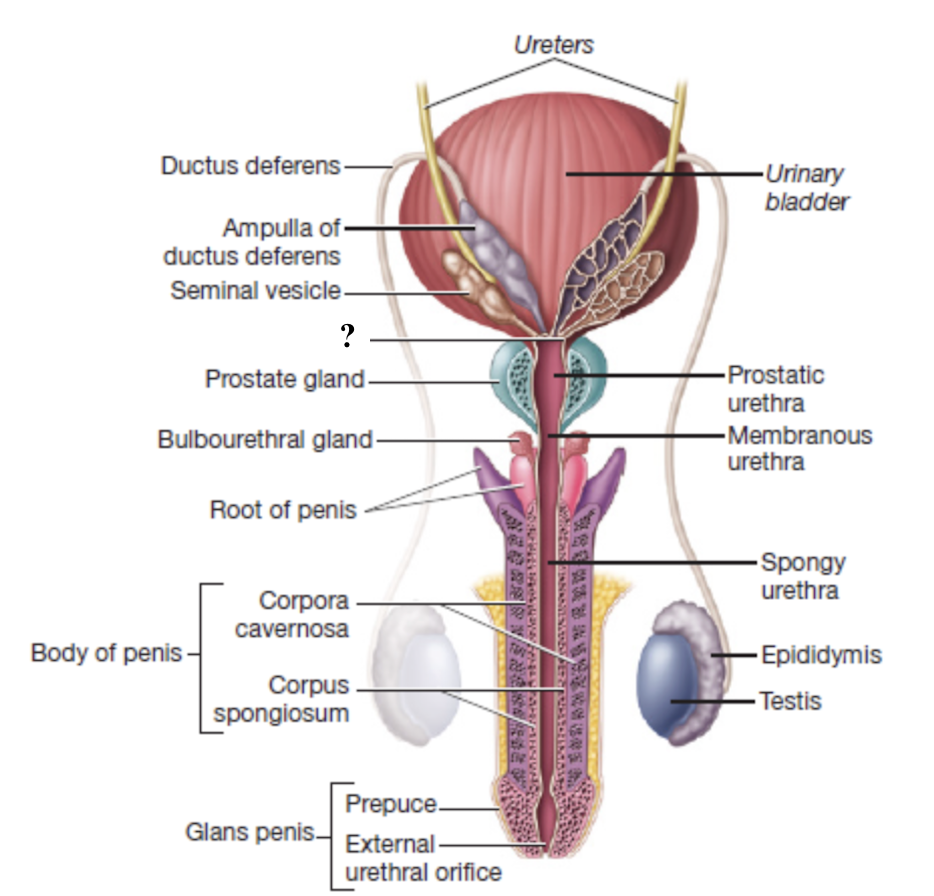
ejaculatory duct
formed by the union of the ampulla of the ductus deferens and the seminal vesicle duct
passes through the prostate gland and empties into the prostatic urethra
male urethra
prostatic urethra → membranous urethra → spongy urethra
enters the corpus spongiosum of penis
terminates at the external urethral orifice at tip of penis
seminiferous tubule → rete testis → efferent ductules → epididymis → ductus deferens → ampulla of ductus vas deferens → ejaculatory duct → urethra → external urethral orifice
pathway of spermatic ducts
seminal vesicles
paired exocrine glands posterior to the urinary bladder
empty into the ejaculatory ducts
secretion is rich in fructose to nourish sperm and substances that enhance sperm motility
prostate gland
single exocrine gland that surrounds the prostatic urethra and ejaculatory ducts
empties into the prostatic urethra
thin, milky secretion contains enzymes, citric acid, and antimicrobial agents to help activate and protect sperm
benign prostatic hypertrophy
noncancerous enlargement of the prostate that is common in older men
can compress the urethra and obstruct urine flow
90%
seminal vesicles and prostate gland together produce about ___ of semen volume which supply nutrients, maintain optimal pH, and help propel sperm
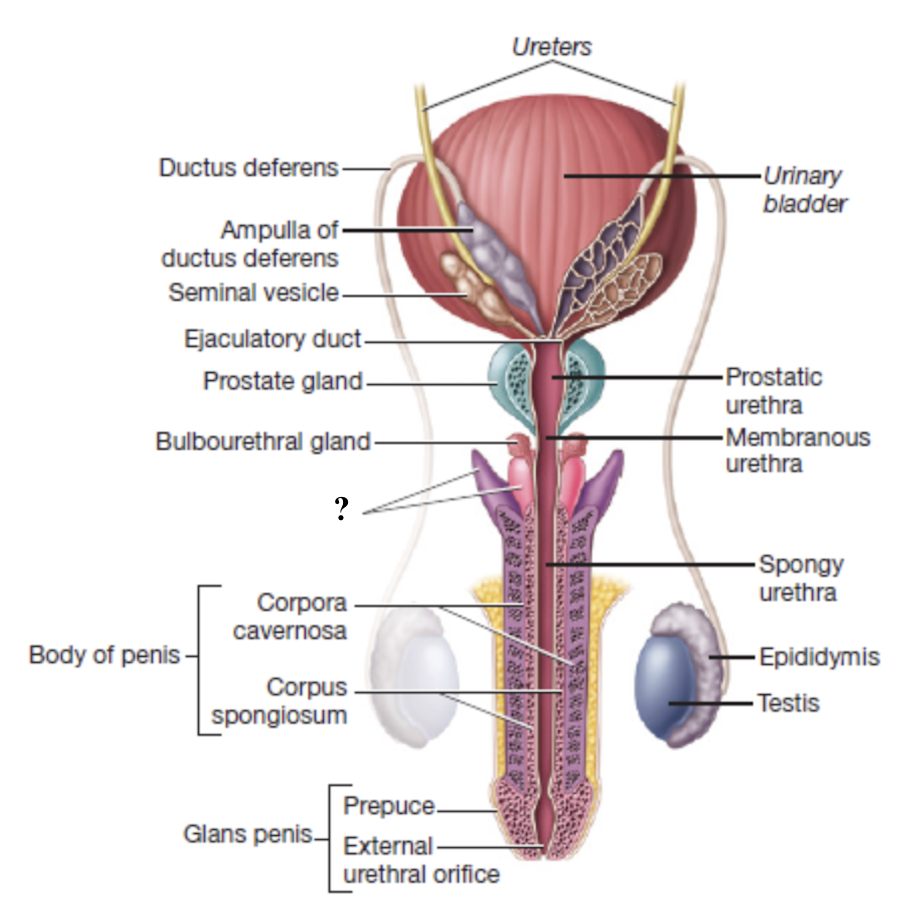
bulbourethral glands
pair of small, brownish glands at the root of the penis
empty into the membranous urethra
secrete alkaline fluid before ejaculation to neutralize acidity
secrete clear fluid that lubricates head of penis before intercourse
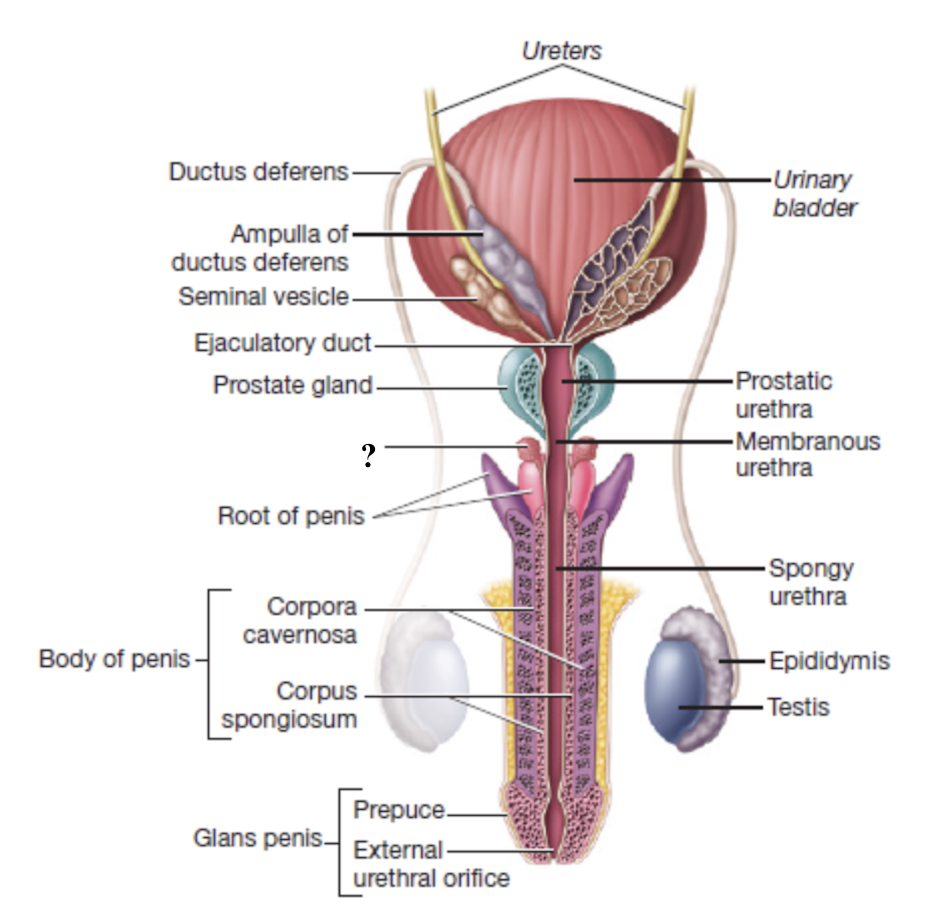
root of penis
internal portion of the penis that anchors it to the pubic arch
glans penis
external portion of the penis
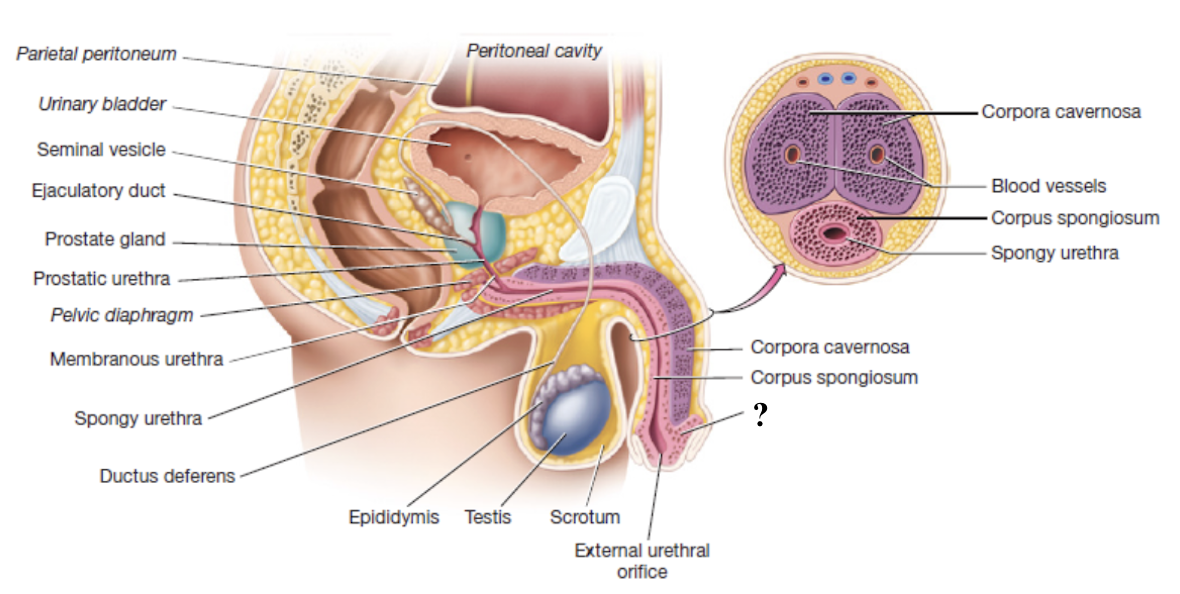
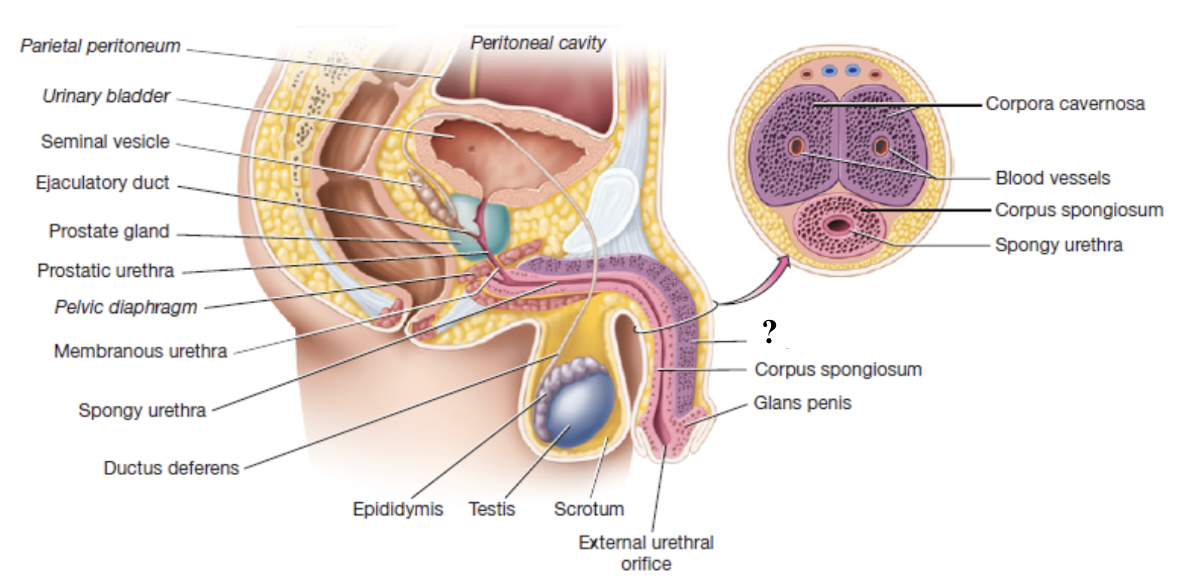
corpus spongiosum
unpaired erectile body of penis that surrounds the spongy urethra and enlarges to form the glans penis
composed of vascular spaces that fill with blood during erection
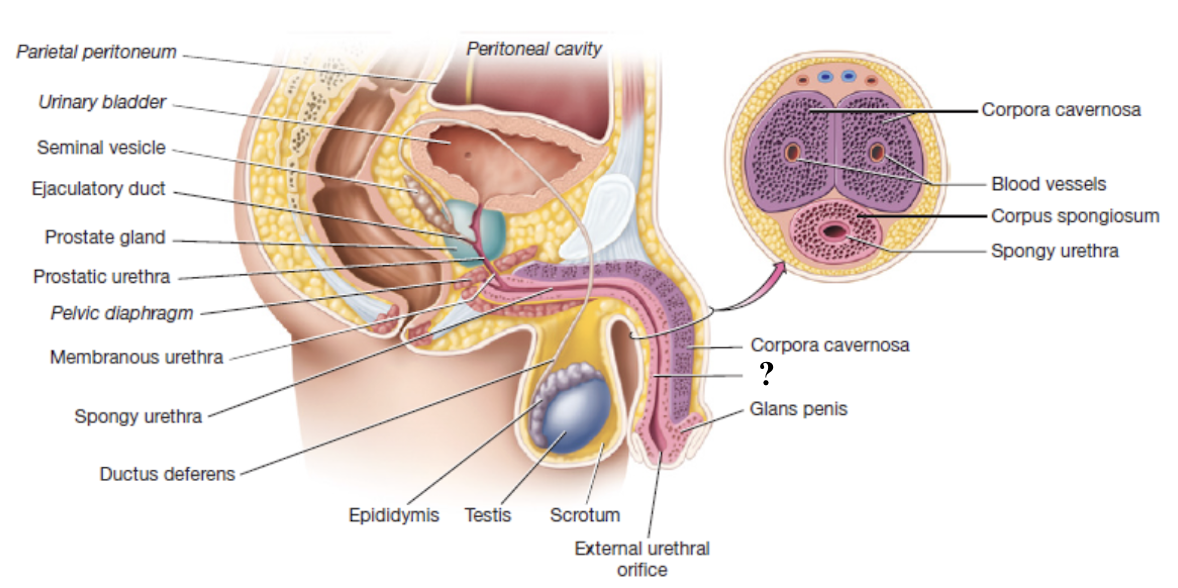
corpora cavernosa
paired erectile bodies of penis that are positioned side-by-side along the dorsal aspect of the penis
composed of vascular spaces that fill with blood during erection
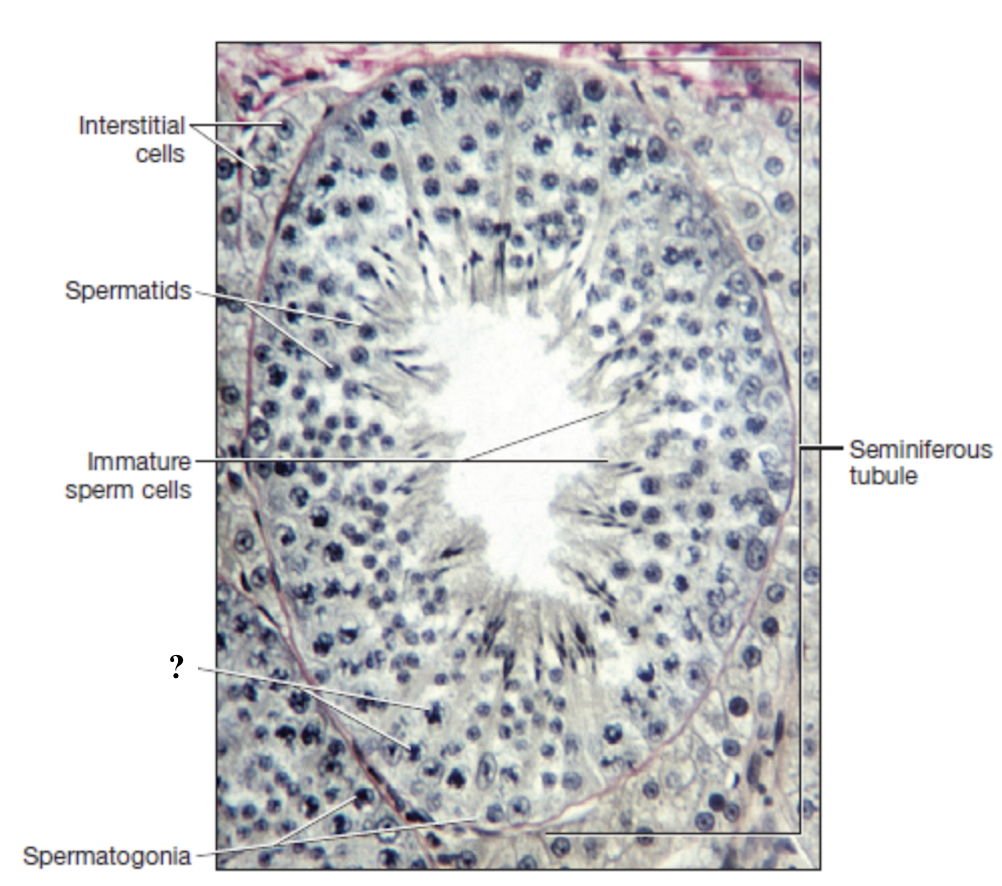
spermatogenesis
process of developing spermatozoa within the seminiferous tubules of the male testis
begins at puberty and continues throughout adulthood
each cycle takes about 70 days to complete
testosterone (cells of leydig)
secreted by interstitial cells located between the seminiferous tubules to play key role in regulating spermatogenesis
sustentacular (sertoli) cells
cells that form the walls of the seminiferous tubules and are connected by tight junctions
support, nourish, and control movement of developing sperm cells
remove waste
produce fluid filling lumen of seminiferous tubules
blood-testis barrier
formed by the tight junctions of sustentacular cells
protects developing sperm from harmful substances in the blood
protects immune system exposure to sperm cell antigens to avoid production of antisperm antibodies
spermatogonium
spermatogonia (stem cell) in outer wall of the seminiferous tubule undergoes mitotic division
one cell remains a spermatogonium
other cell becomes primary spermatocyte
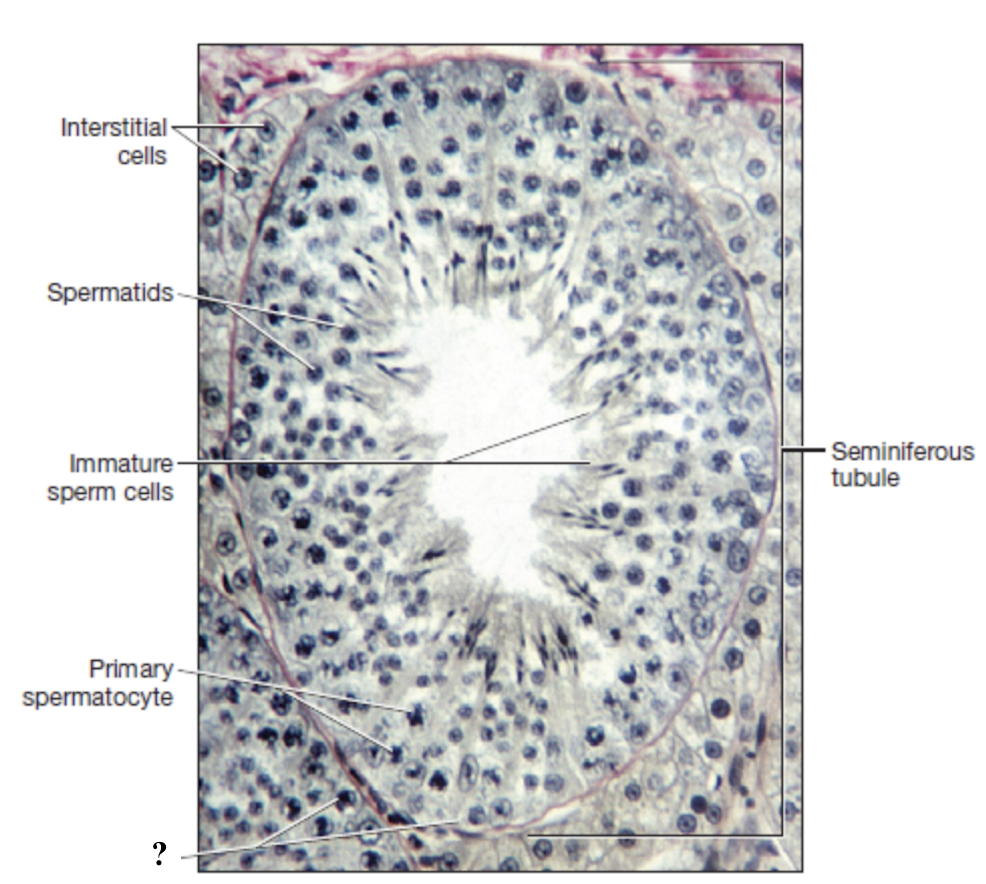
primary spermatocyte
diploid with 46 chromosomes enters meiosis
secondary spermatocytes
produced after meiosis I
haploid with 23 replicated chromosomes
spermatids
produced after meiosis II
haploid with 23 single-stranded chromosomes
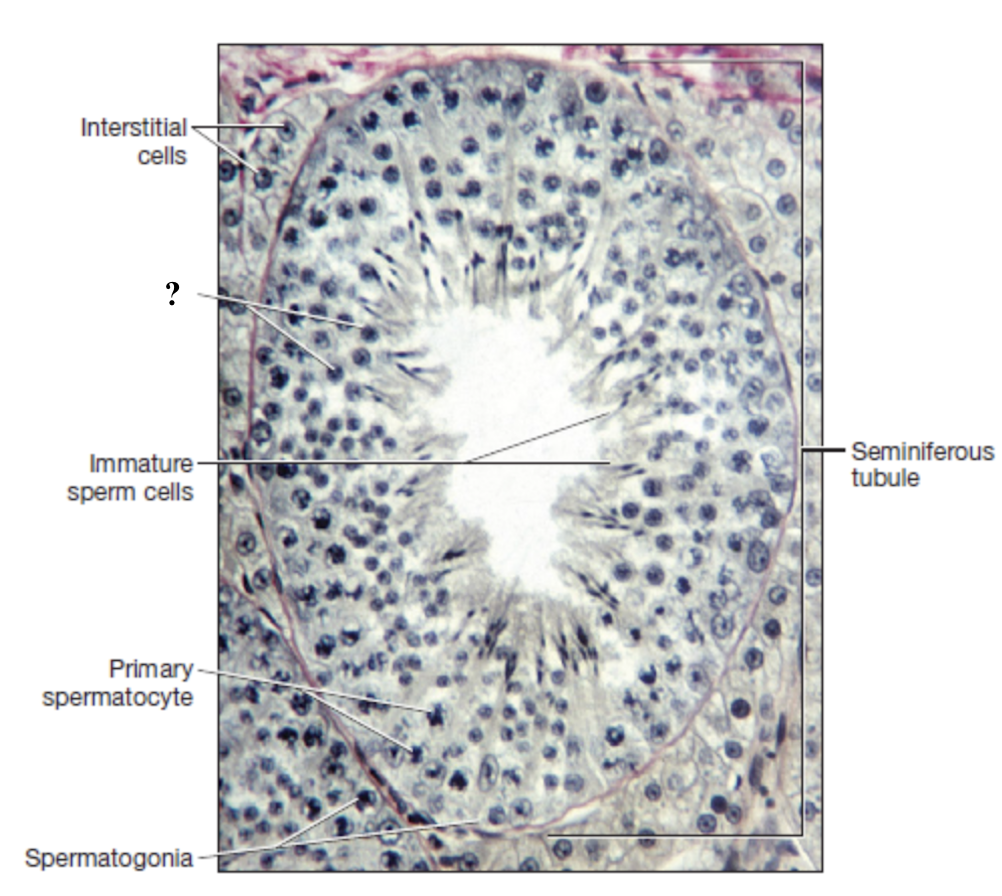
spermatozoa
result from spermiogenesis and is the final transformation stage
acrosome of spermatozoa
cap-like sac covering the head of the sperm
contains digestive enzymes that help penetrate outer layer of ovum during fertilization
mitochondria of spermatozoa
multiply and coil tighly in the midpiece
produce large amounts of ATP for tail movement
flagellum of spermatozoa
enable motility of the sperm cell
its microtubules are formed by centrioles
pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
epididymis mucosal lining
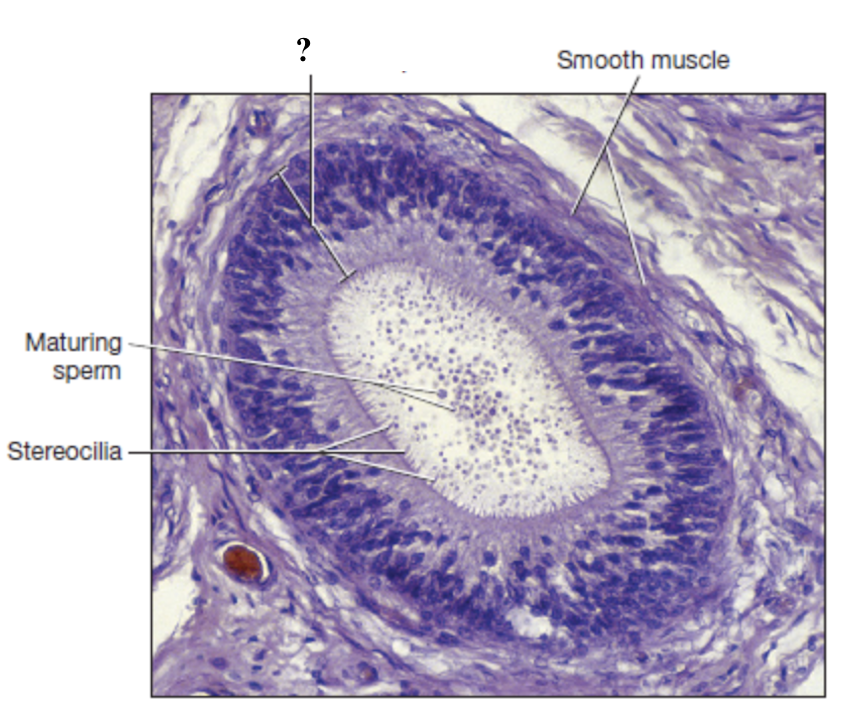
sterocilia
nonmotile microvilli that function to …
complete spermiogenesis
absorb excess fluid
pass nutrients to developing sperm cells
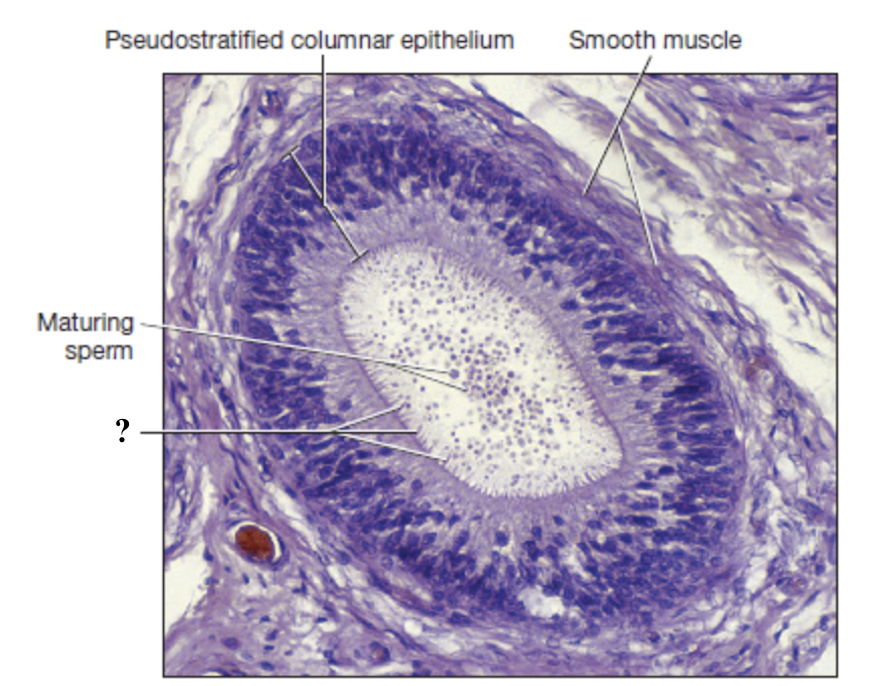
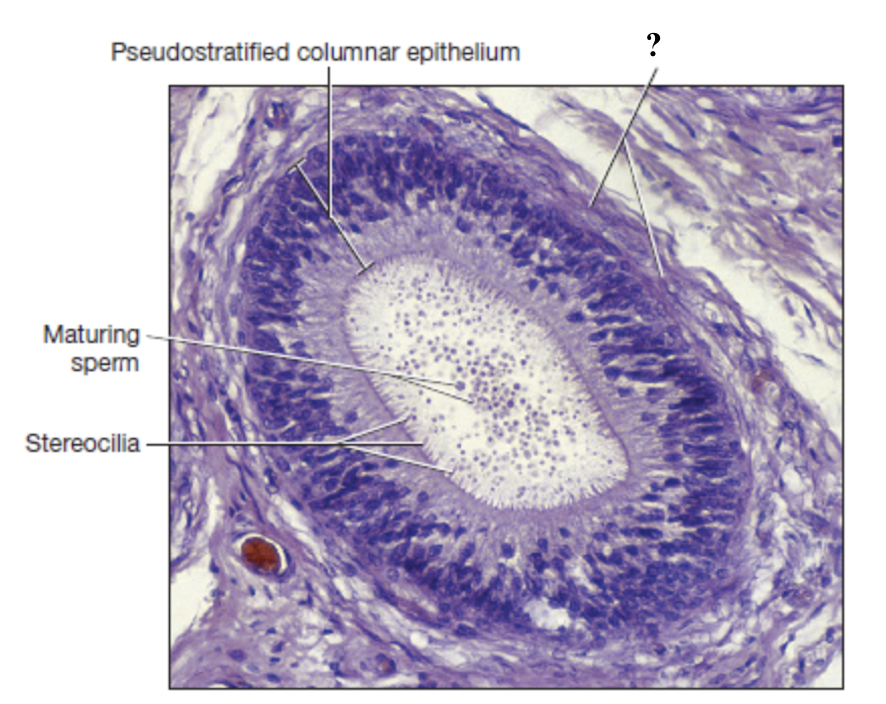
smooth muscle of epididymis
surrounds the epididymal tubules and propels sperm toward the tail
hypothalamus releases gonadotropin releasing hormone → anterior lobe of pituitary gland → follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone released → spermatogenesis activation
hormonal pathway of sperm cell production
follicle stimulating hormone
binds to sustentacular cells in walls of seminiferous tubules to stimulate them to produce androgen binding protein and inhibin
luteinizing hormone
binds to interstitial cells between seminiferous tubules to stimulate them to produce testosterone
testosterone binds to androgen binding protein to form a complex that stimulates spermatogenic cells to mature into sperm cells
negative feedback control
maintains a steady, normal range of testosterone production in adult males
rising testosterone levels: inhibit both the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
inhibin: enhances negative feedback inhibition by also targeting the hypothalamus and pituitary gland