8 - Translation in Molecular and Cell Biology LF206
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Translation
Recodes the 4-letter nucleotide code of the mRNA template into the 20-letter amino acid code of the polypeptide product.
is this 4 letter code DNA or RNA?
GATC
DNA
is this 4 letter code DNA or RNA?
GAUC
RNA
20 letter code of all amino acids.
Ala, A Arg, R Asn, N Asp, D Cys, C Glu, E Gln, Q Gly, G His, H Ile, I Leu, L Lys, K Met, M Phe, F Pro, P Ser, S Thr, T Trp, W Tyr, Y Val, V
Gene
A sequence of DNA that is transcribed into mRNA.
Transcription
The process of synthesizing mRNA from a DNA template.
mRNA
Messenger RNA that carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome.
Polypeptide formation
The process by which amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain.
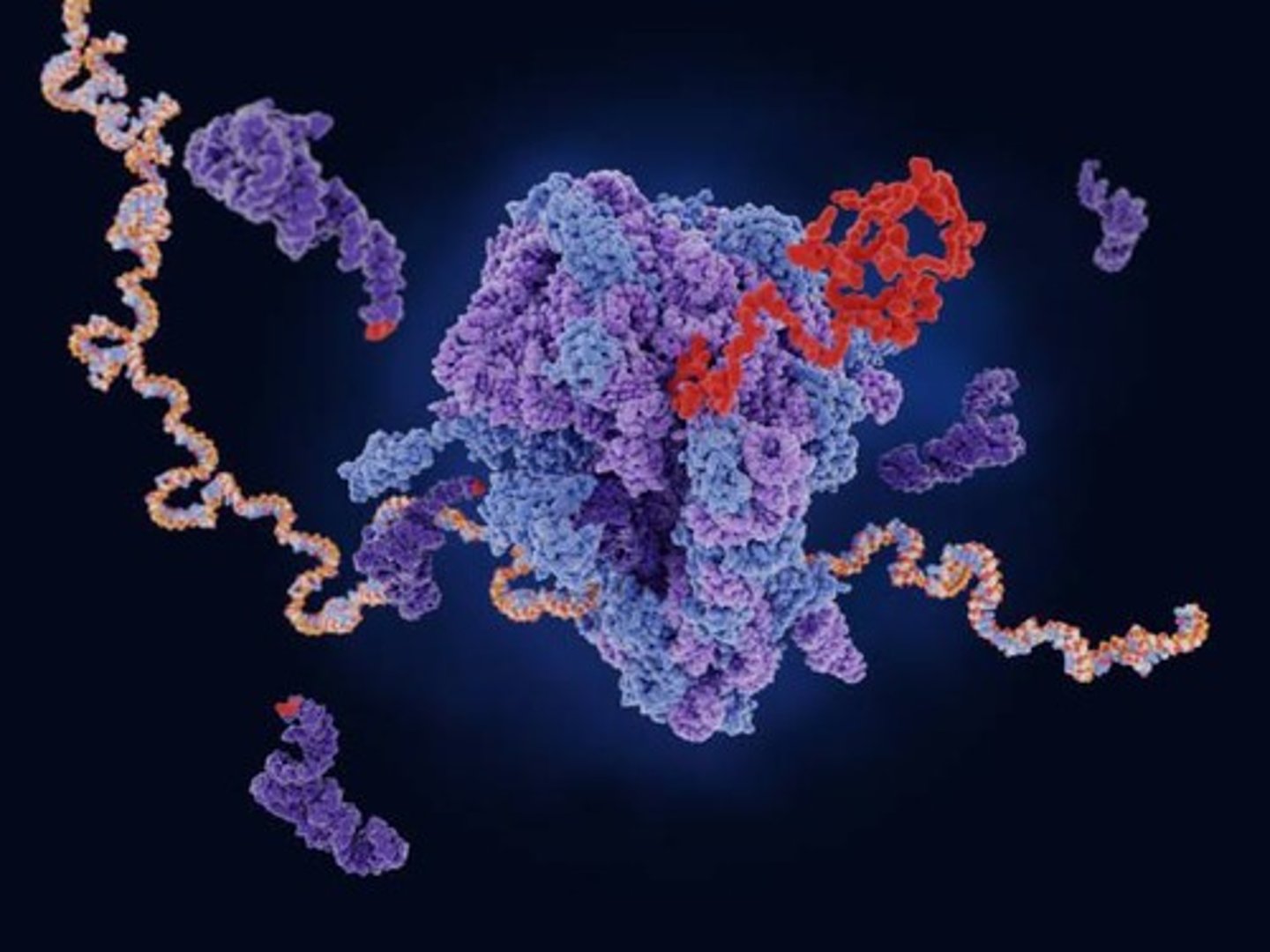
Ribosome
A molecular machine that catalyzes the formation of polypeptides from mRNA.
Aminoacyl tRNA
tRNA that is attached to its corresponding amino acid.
Peptide bonds
Covalent bonds that link amino acids together in a polypeptide.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA component of the ribosome, crucial for its structure and function.
Bacterial ribosome
Composed of 50S and 30S subunits, with specific rRNA and protein components.
Eukaryotic ribosome
Composed of 60S and 40S subunits, larger and more complex than bacterial ribosomes.
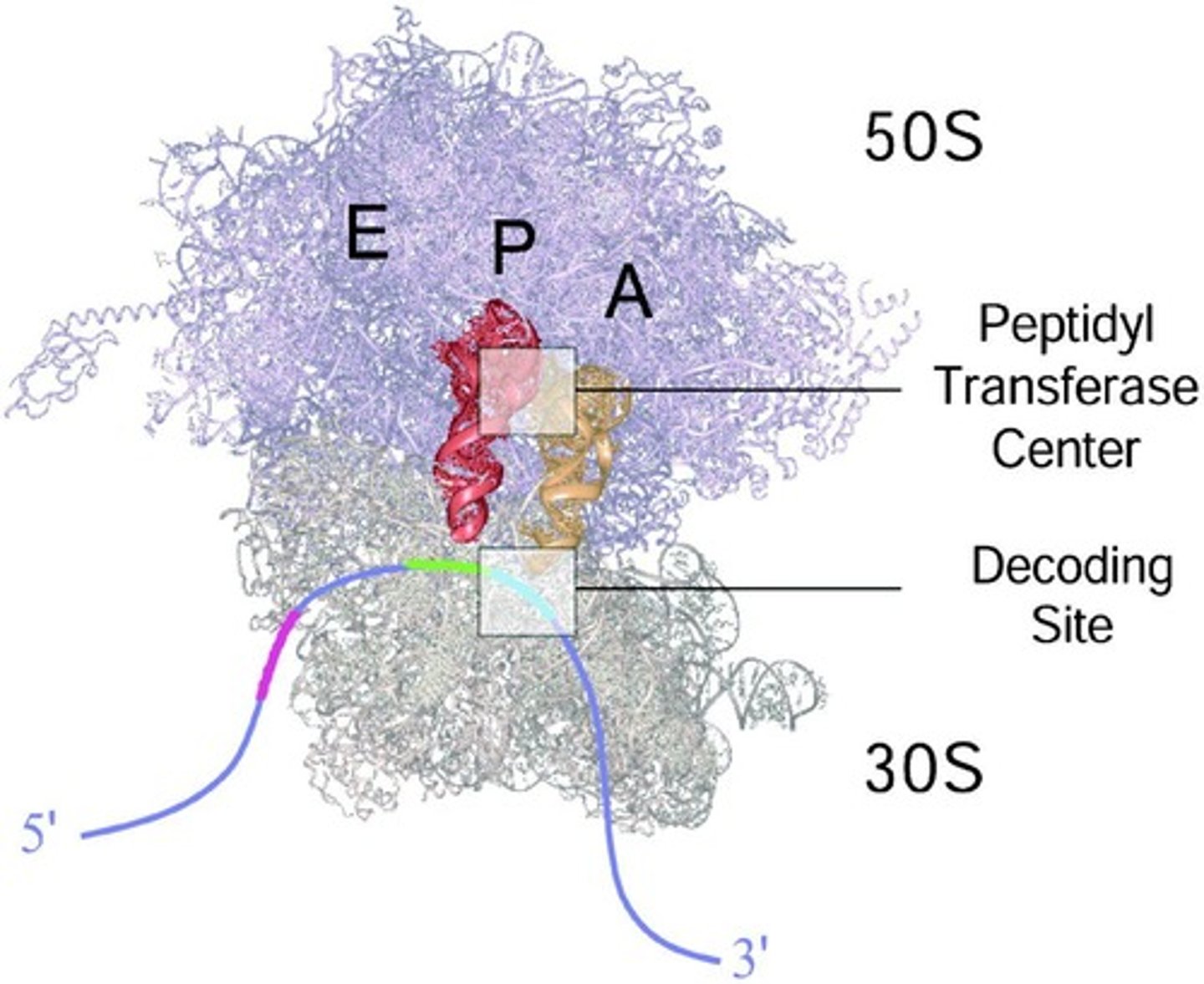
acronym for the 3 sites on a ribosome?
APE
a - acceptor
p - peptidyl
e - exit
Acceptor site (A site)
The site on the ribosome where incoming aminoacyl tRNA binds.
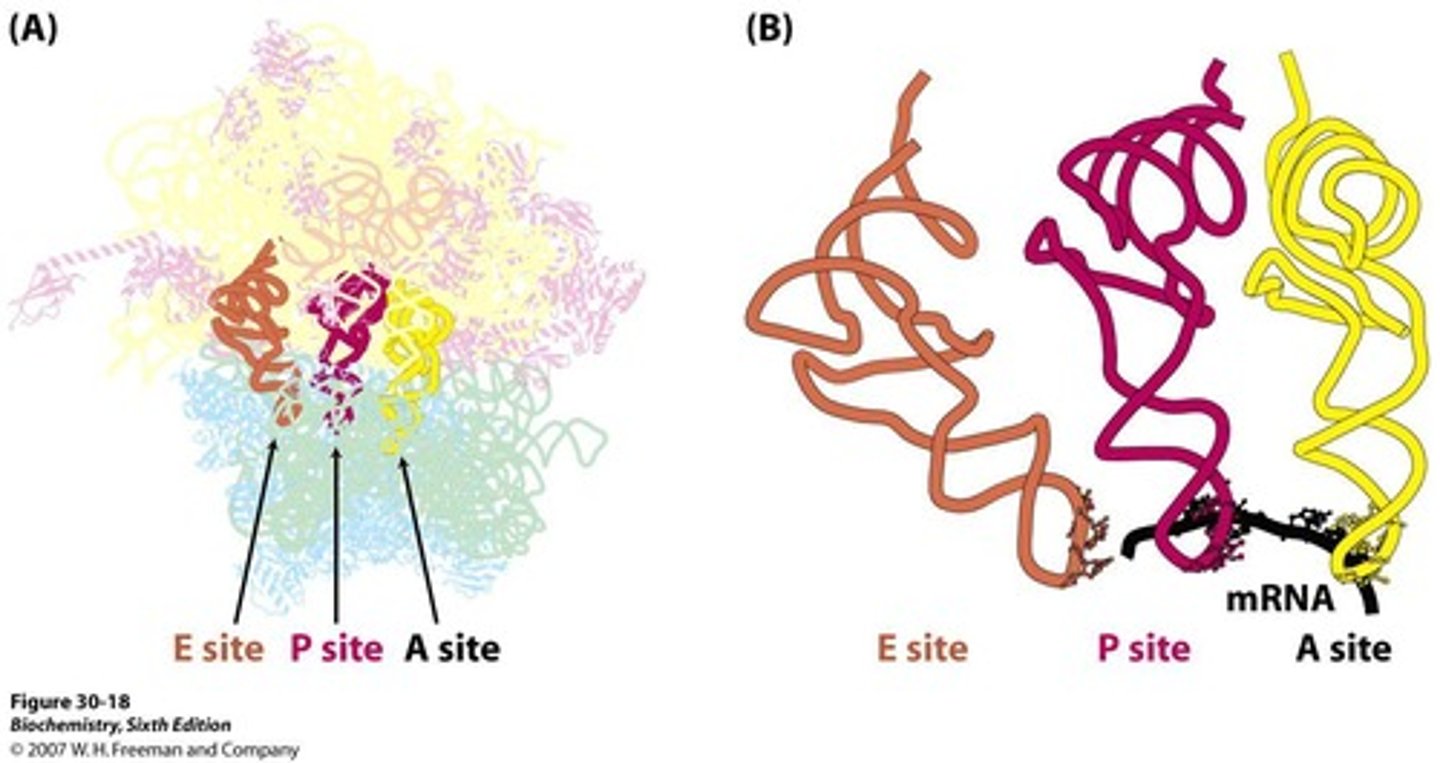
Peptidyl site (P site)
The site on the ribosome that holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain.
Exit site (E site)
The site on the ribosome where uncharged tRNA exits after delivering its amino acid.
Compensatory mechanism
A mutation that restores base pairing after a disruption caused by a previous mutation.
Watson-Crick base pairing
The specific pairing of nucleotides in DNA and RNA, maintaining structural integrity.
Structural conservation
The preservation of specific structures in rRNA across different species.
Secondary structures
The local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone.
Tertiary structures
The overall three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide, formed by the folding of secondary structures.
High energy cost to cell
The significant energy expenditure required for protein synthesis, involving over 150 proteins and ~ 40 tRNAs.
tRNA
Transfer RNA, a molecule that helps decode a messenger RNA sequence into a protein.
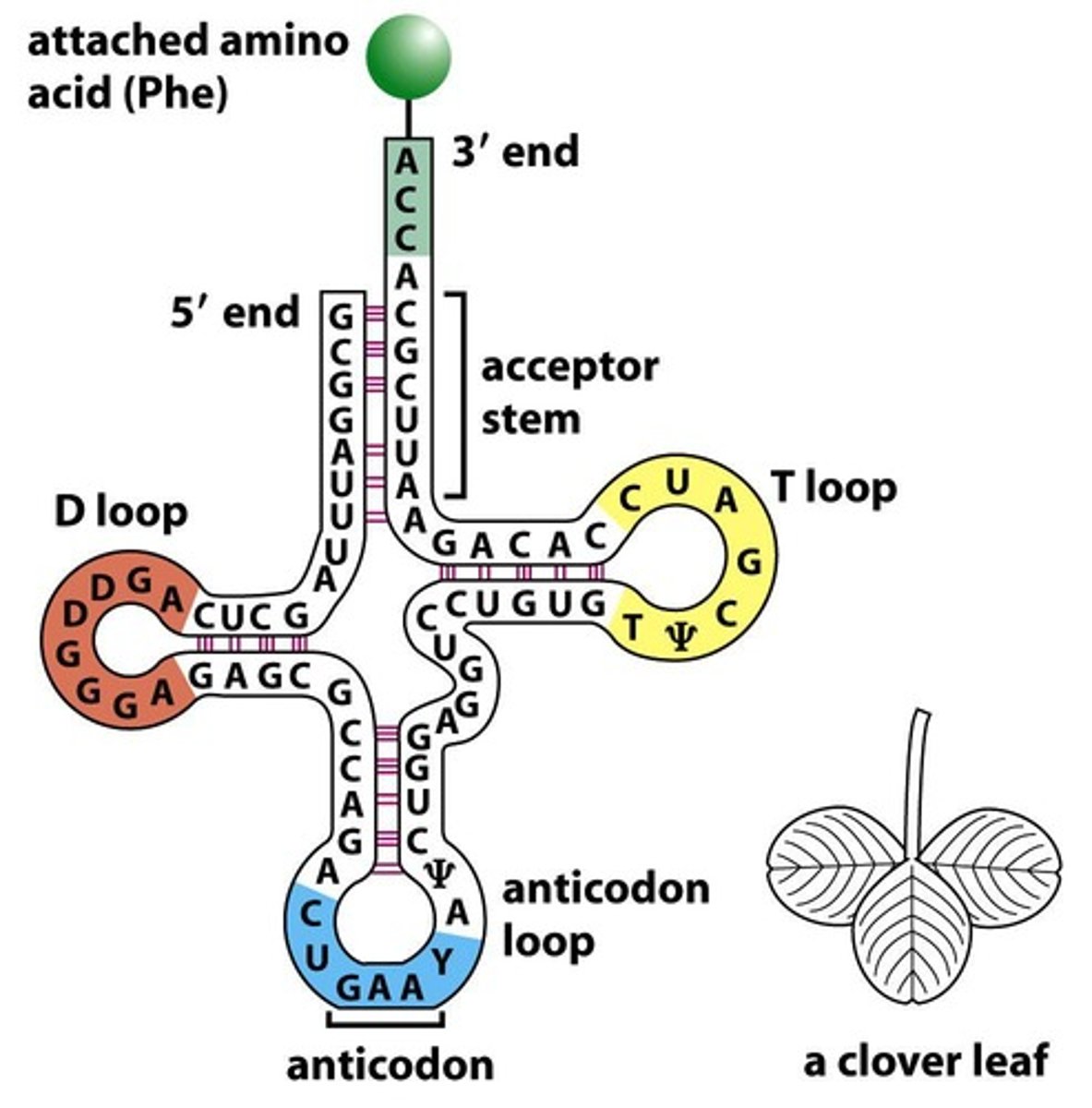
D loop
A loop in tRNA containing 8-12 unpaired bases and 2-3 dihydrouracil residues.
T-loop
A loop in tRNA that contains modified nucleotides including thymine.
CCA terminus
also known as?
The 3’ end of the tRNA molecule that is flexible and important for editing.
AKA acceptor stem
anticodon
A sequence of three bases in tRNA that pairs with the corresponding codon in mRNA.
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
An enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid to its corresponding tRNA.
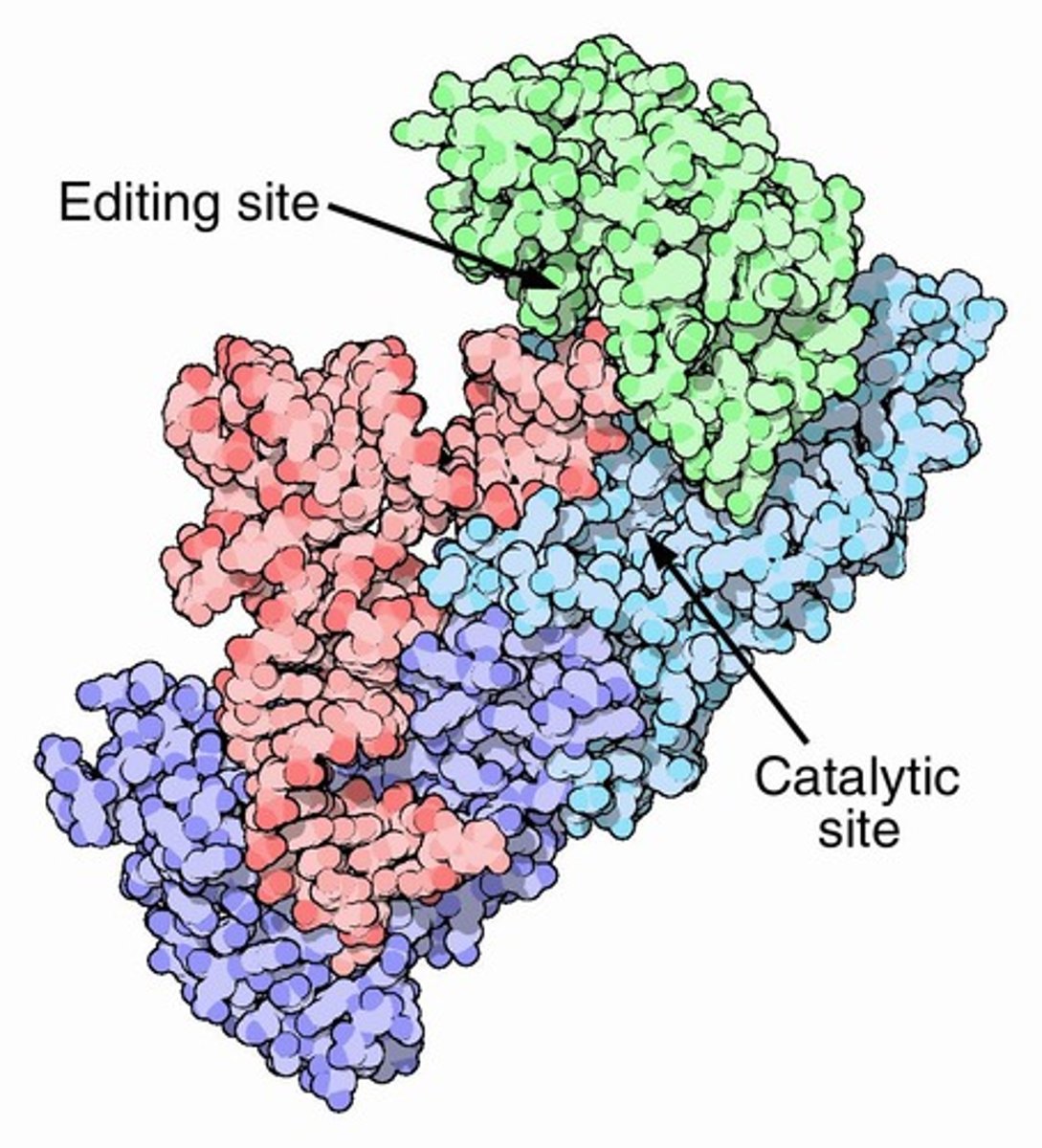
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase mechanism [4]
a specific amino acid and ATP binds to a specific amino acyl-tRNA synthetase
amino acid is activated by covalent binding of AMP - pyrophosphate is released
a specific tRNA binds to the enzyme, AMP is released as the amino acid covalently attaches to tRNA by an ester bond
charged tRNA is released
what is meant by charged tRNA?
amino acid is covalently attached to tRNA
Non-Canonical Base Pairs
Base pairs in tRNA that include non-conventional A-U and G-C pairs held together by multiple hydrogen bonds.
amino acylation
The process of attaching an amino acid to its corresponding tRNA by specific synthetases.
initiation factor
A protein that recognizes the initiator tRNA (fmet tRNA) during the initiation of translation.
transformylase
An enzyme that recognizes the initiator tRNA and modifies it.
Class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
Enzymes that approach/contact tRNA at the minor groove of the tRNA acceptor stem and the anticodon.
Class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
Enzymes that approach/contact tRNA at the major groove of the tRNA acceptor stem and the anticodon.
double sieve is a _________ mechanism that allows for the ________ of incorrect aminoacyl-___intermediates.
this can occur at which two stages?
proofreading
hydrolysis
AMP
hydrolysis of ester bond at incorrect aminoacyl-AMP
editing sites on most aminoacyl-tRNAs hydrolyse aminoacyl-tRNAs smaller than cognate aa
editing site
A site in aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that hydrolyzes aminoacyl-tRNAs which are smaller than the cognate amino acid.
ester bond
A type of covalent bond formed between an amino acid and tRNA during aminoacylation.
hydrolysis
The chemical process of breaking down a compound by reaction with water, used in proofreading.
charged tRNA
tRNA that has an amino acid covalently attached, ready for incorporation into a protein.
pyrophosphate
A byproduct released during the activation of the amino acid by binding to AMP.
specific amino acid binding site
A site on the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that ensures the correct amino acid is attached to the tRNA.
specific anticodon binding site
A site on the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that ensures the correct tRNA is selected based on its anticodon.
invariant modifications
Modifications to bases in tRNA that are consistent across all known tRNAs.
hydrolytic sites
Sites in aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that facilitate the breakdown of incorrect aminoacyl-tRNAs.
Overall fidelity of charging in vivo
99.99%
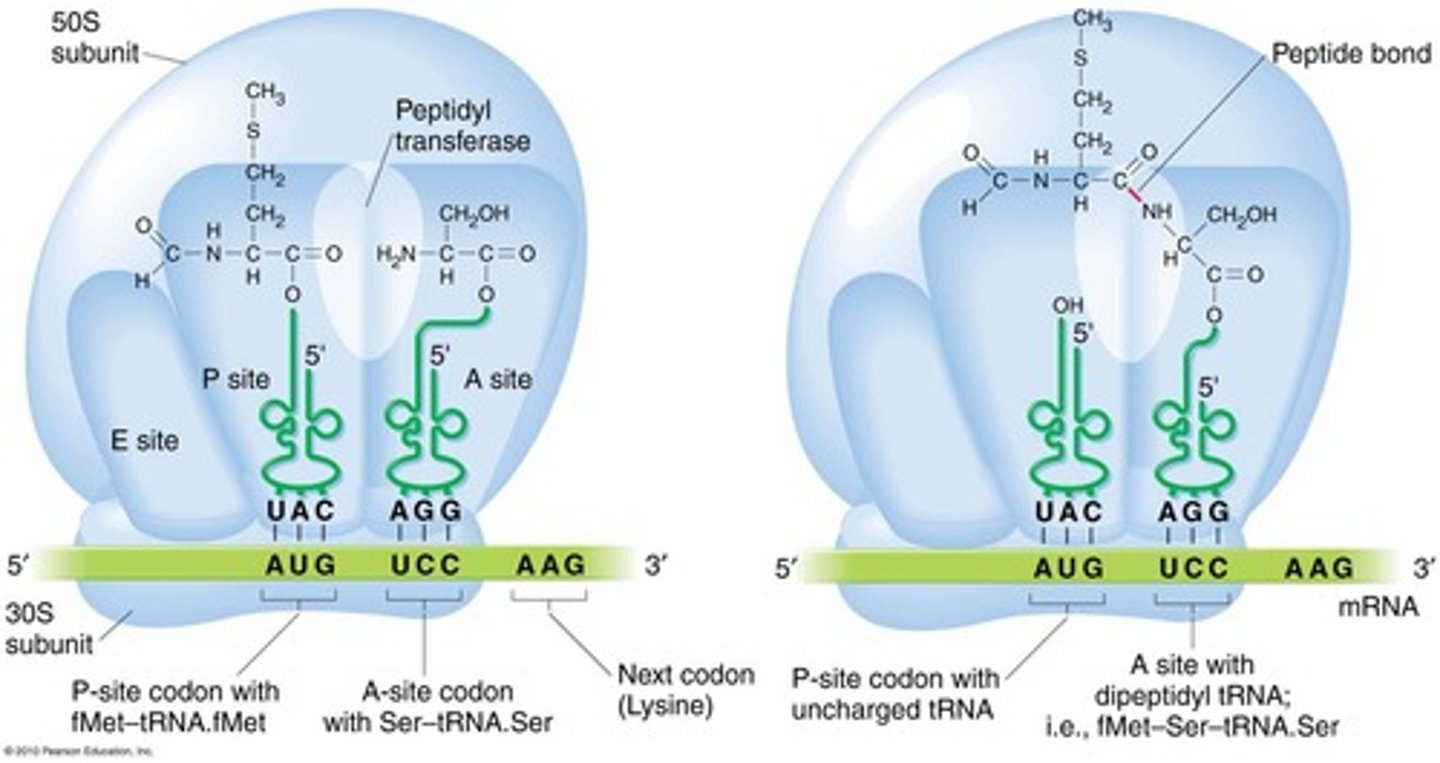
Ribosome binding sites for tRNA
Ribosomes have three binding sites for tRNA: A (Acceptor), P (Peptidyl), and E (Exit).
Peptide bond is built by which activity?
Requires a peptidyl synthase activity.
A site
Acceptor site of codon-directed binding of incoming aa tRNA.
P site
Peptidyl site; holds codon directed peptidyl tRNA.
E site
Exit site; not associated with mRNA.
Peptidyl transferase activity - is it RNA or enzyme activity? and why?
RNA
the closest protein of the growing polypeptide chain is 18.4Å from the active site
Provided by an invariant adenine residue A2451, which is provided by RNA, not protein.
Bacterial 70S ribosome
The ribosome is a giant ribozyme.
Protein folding starts where?
Starts in the ribosome polypeptide exit tunnel.
Erythromycin and other _______
target ______
it binds to the small 23S _____ of the ___S ribosomal subunit and inhibit elongation of the ______
they block the exit tunnel of ________ ribosomes
macrolides
elongation rRNA
50S
peptide
bacterial
Streptomycin inhibits _______ and causes _______
initiation
misreading.
Doxycycline and other _________
target ________
they bind to the ___ subunit and inhibit the binding of ______-tRNA to the _ site of the ribosome.
tetracyclines
elongation
30S
aminoacyl
A
Chloramphenicol and other ________
target _________
they inhibit ______ transferase activity of the ___ ribosomal subunit in ____karyotes
amphenicols
translocation
peptidyl
50S
prokaryotes
Diphtheria toxin
binds to a receptor with what domain? what follows?
Binds its receptor via its receptor-binding domain (R) followed by endocytosis.
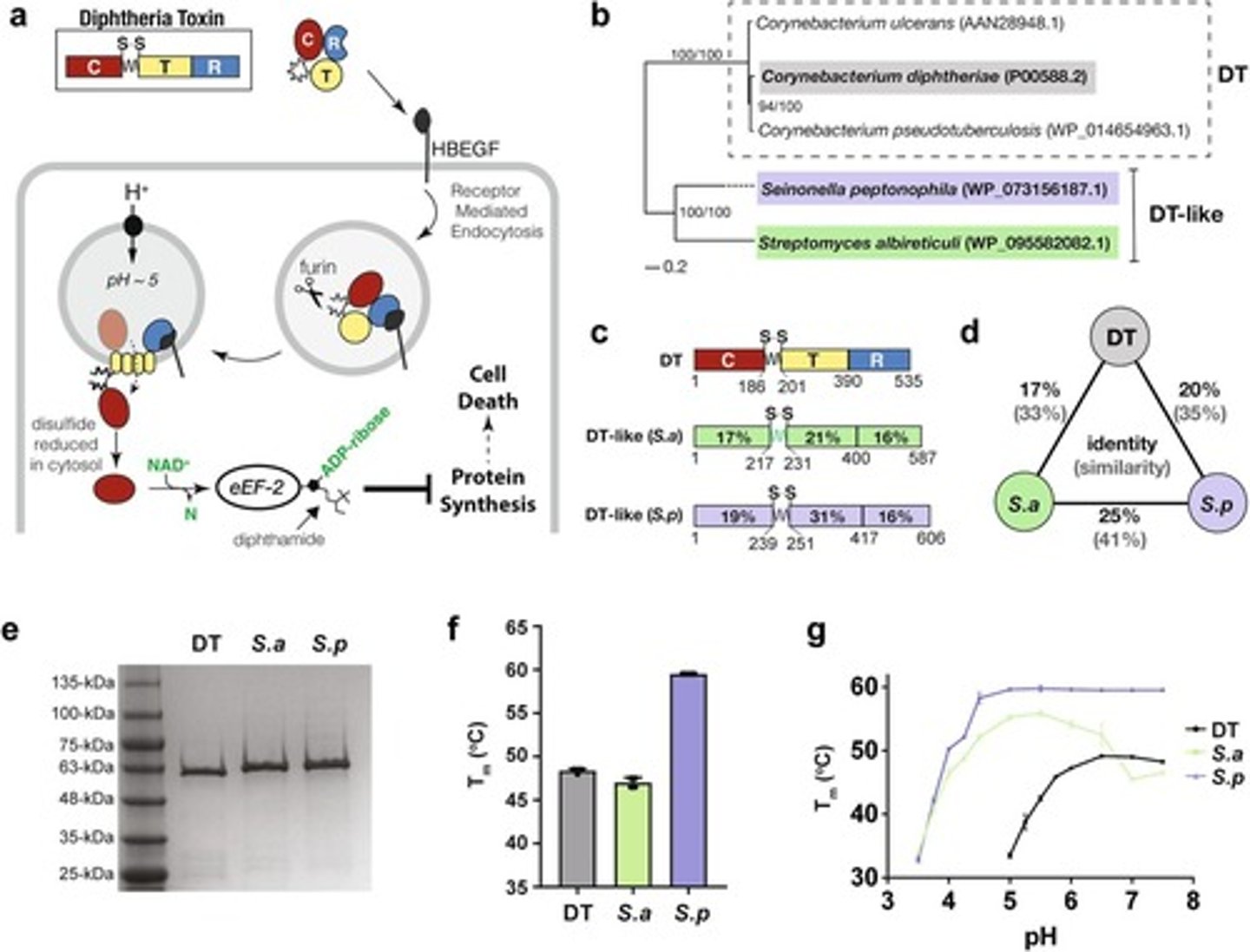
Furin cleavage
what does it process? what domains are still connected & by what?
The diphtheria toxin (DTx) is processed by furin cleavage, but the C and TR domains are still connected by a disulfide bridge.
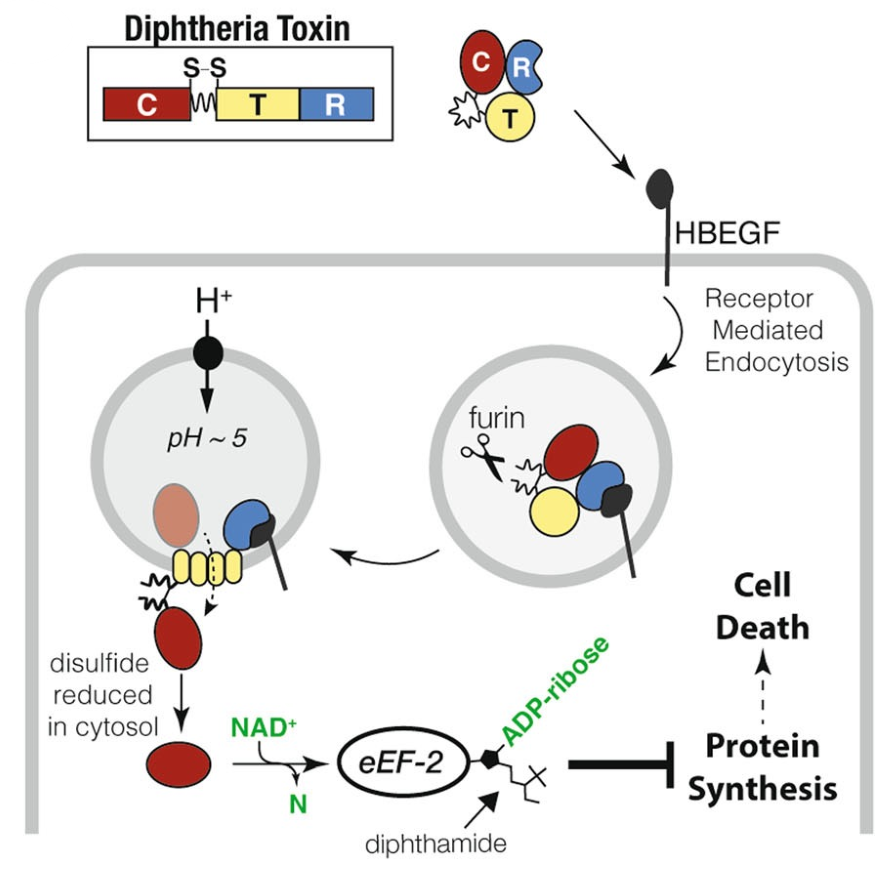
Translocation domain (T)
forms what? where?
of diphtheria toxin (DTx) forms a pore in the membrane of an acidified endosome.
Ricin
binds to a receptor with what? what follows?
Binds its receptor via its B chain (RTB) followed by endocytosis.
RTA
what is it?
what does it do?
Catalytic A chain of ricin that hydrolyses the N-glycosidic bond of adenine 4324 (A4324) within the 28S rRNA.
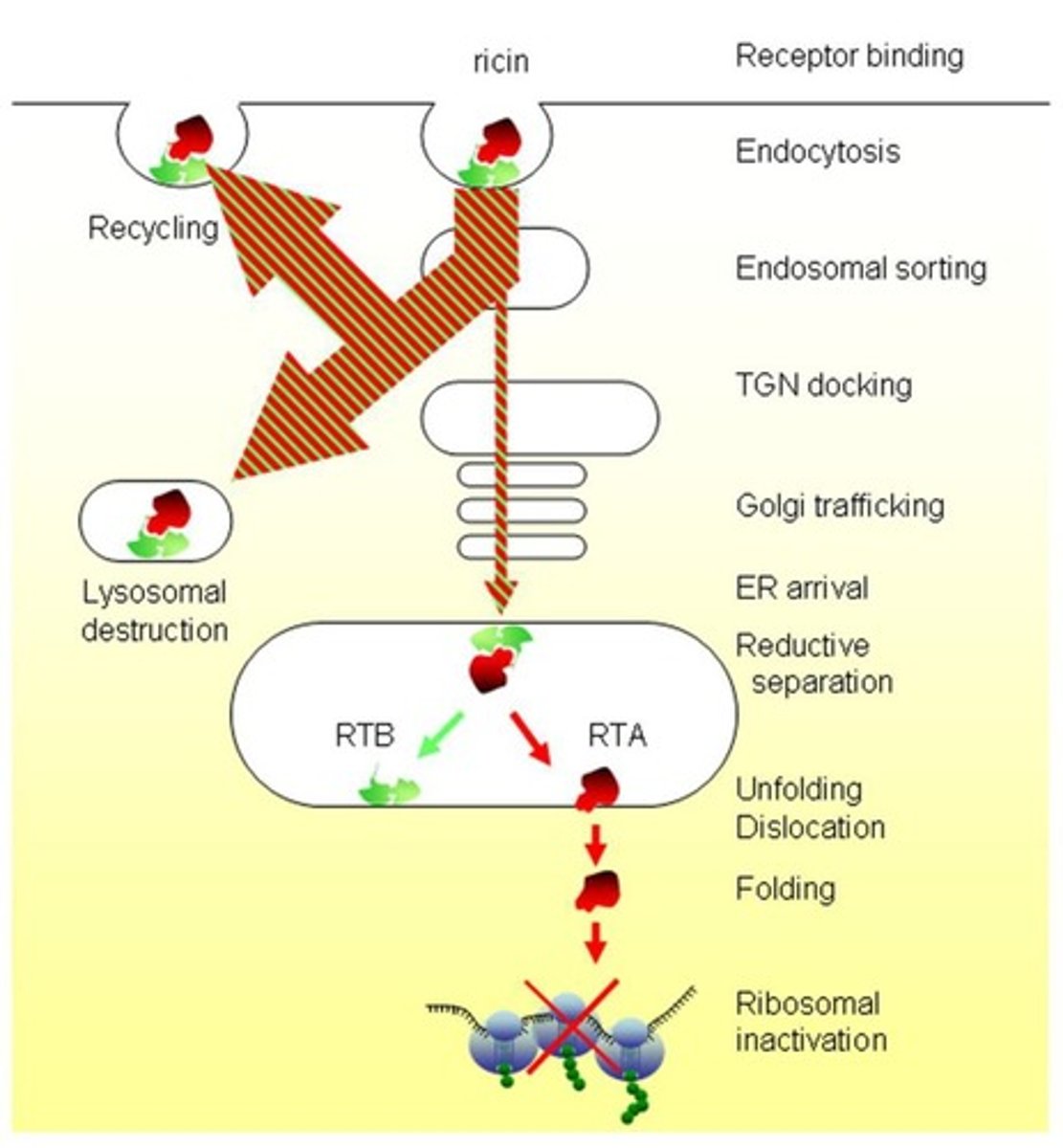
Protein synthesis inhibition by RTA
Active RTA irreversibly hydrolyses the N-glycosidic bond of A4324, stopping protein synthesis.
t-RNA structure
t-RNA forms an L shaped tertiary structure with a key CCA terminus for charging with an amino acid at one end and the anticodon at the other.
t-RNA synthetases
Most have both an activating domain and an editing domain to ensure correct charging of amino acids.
Secondary structures in polypeptides
Some can be formed by a polypeptide exiting the 50S ribosome subunit.
_______ synthesis can be used as a target for anti-microbial discovery
protein
mechanism of antibiotic streptomycin and other __________.
they target initiation.
they bind the small ___ rRNA of the 30S ribosomal ______ irreversibly, distorting it and interfering with the binding of _____-methionyl-tRNA to the ___ subunit.
aminoglycosides
16S
subunit
formyl
30S