BIO topic 4: systematics and phylogenys
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
systematics
Discipline focused on classifying organisms based on their evolutionary relationships/ history.
phylogenetics
field of systematics focused on evolutionary relationships among organisms
phylogenetic tree
an evolutionary hypothesis of a group of relationships among organisms
depicts lineages descending from common ancestors
organize biological data
visualize evolutionary patterns
facilitate classification
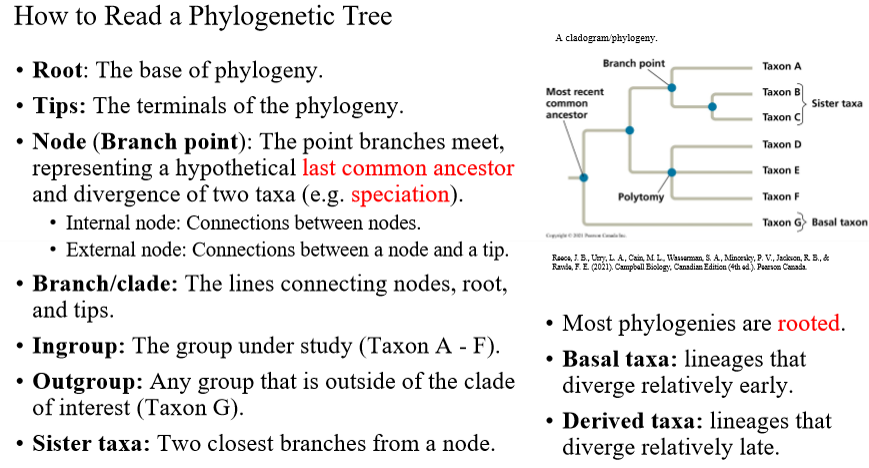
how to read a Phylogenetic tree
plylograms versus cladograms
p: include measures of time, depicts hypothesis of evolutionary history, fossil is required
c: only hypothesis on the relative relationships among taxa(is A closer to B than C?)
identify clades and groups
Monophyletic: Clade that includes most recent common ancestor and all of its descendants
Paraphyletic group: a group that includes the most recent common ancestor and some of its decedents
Polyphyletic group: group that includes some of its descendants without its common ancestor
How are branches connected
Dichotomy: only two branches diverge from a common ancestor (node)
Polytomy: more than 2 branches diverge from a node
soft versus hard polytomy
s: represents uncertainty about which taxa arise from the mode are most related to each other
h: represents a hypothesis that more than 2 taxa arose from the same CA
morphological data
anatomical Features, Qual: color shape, Quant: measurements, widly used in fissils
molecular data
Genomic(DNA sequence), protein strucure, ect. organisms grouped together based on shared traits
homology
character traits that evolved from a common ancestral structure
analogy
character traits that independently evolved from convergence evolution
synapomorphy
derived feature shared by more than 2 taxa and their last common ancestor
autapomorphy
derived feature found only in ONE taxa
symplesiomorphy
ancestral feature shared by at least some members of a taxonomic group
parsimony
of all possible cladograms the one with the fewest evolutionary changes is considered the most likely(=best)
distiguishing between basal and derived character traits can be difficuls
a possible remedy: von baer’s law: the more general(basal) characteristics appear earlier in the embryo than more specialized ones.
fossil evidence: indisputable existence of a taxa in a time long past