Bio 115 - WVU EXAM 2
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
5, 6, 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
A new flower species has a unique photosynthetic pigment. The leaves of this plant appear to be reddish yellow. What wavelengths of visible light are not being absorbed by this pigment?
Red and Yellow
Where do the majority of the atoms for a plant's macromolecules, such as carbohydrates, come from?
Air
The Calvin Cycle occurs in the ______.
stroma
Which of the following best describes the function of the Calvin Cycle?
convert chemical energy (ATP and NADPH) to chemical energy (glucose)
Increasing the amount of carbon dioxide available will _______ the rate of the Calvin Cycle.
increase
Which photosynthetic process is associated with the most ATP production?
reactions at Photosystem II
reactions at Photosystem I
Calvin Cycle
reactions at Photosystem II
Endocytosis is the process by which ___.
the plasma membrane pinches off to take up material from the outside of the cell.
Which of the following is an example of autophagy?
A membrane encloses a peroxisome which is then delivered to a lysosome.
Phagocytosis is a way for cells to ___.
Transport a food particle or smaller cell into the from the outside of the cell into the cell.
In _____ inhibition, the inhibitor binds a region of the enzyme different from the active site. In _____ inhibition, the inhibitor binds the active site.
allosteric
competitive
Muscle cells in oxygen deprivation convert pyruvate to ______ and in this step gain ______.
Lactate, NAD+
Select all that apply. What are the products of glycolysis?
ATP, NADH, 2 pyruvate
Which of the following would be the last effect of blocking the last step in the electron transport chain in the mitochondria of one of your cells?
ATP synthase production of ATP would stop.
What are features shared by ALL cells?
1. Cell Membrane
2. Ribosomes
3. Biological Molecules (DNA, Protein, Carbohydrates)
4. Cytosol (Cytoplasm)
True or False? Prokaryotic cells do not contain membrane-bound organelles.
false
Which of these characteristics are shared by all living things?
cell membrane
cell wall
vacuole
deoxyribonucleic acid
nucleus
ribosomes
cell membrane
deoxyribonucleic acid
ribosomes
Select all that apply. Which of these organelles / molecules are involved in some way in building proteins?
rough E. R.
ribosome
golgi apparatus
nucleus
DNA
mRNA
What happens to the atoms that make up fat molecules that your body catabolizes?
They are released as CO2 and H2O.
During aerobic cellular respiration, a proton gradient in mitochondria will be generated by ______ and used primarily for _____ .
the electron transport chain, ATP synthesis
Which step in cellular respiration produces ATP? Select all that apply
electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
Pyruvate Processing
glycolysis
citric acid cycle
electron transport chain and chemiosmosis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle
The immediate source of energy that allows ATP synthase to make ATP is
proton gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane
Which of the following statements is true of both lactic acid fermentation and ethanol fermentation?
They directly produce NADH
They use oxygen
They directly produce NAD+
They directly produce ATP
They directly produce NAD+
Which one of the steps produces the most ATP when glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
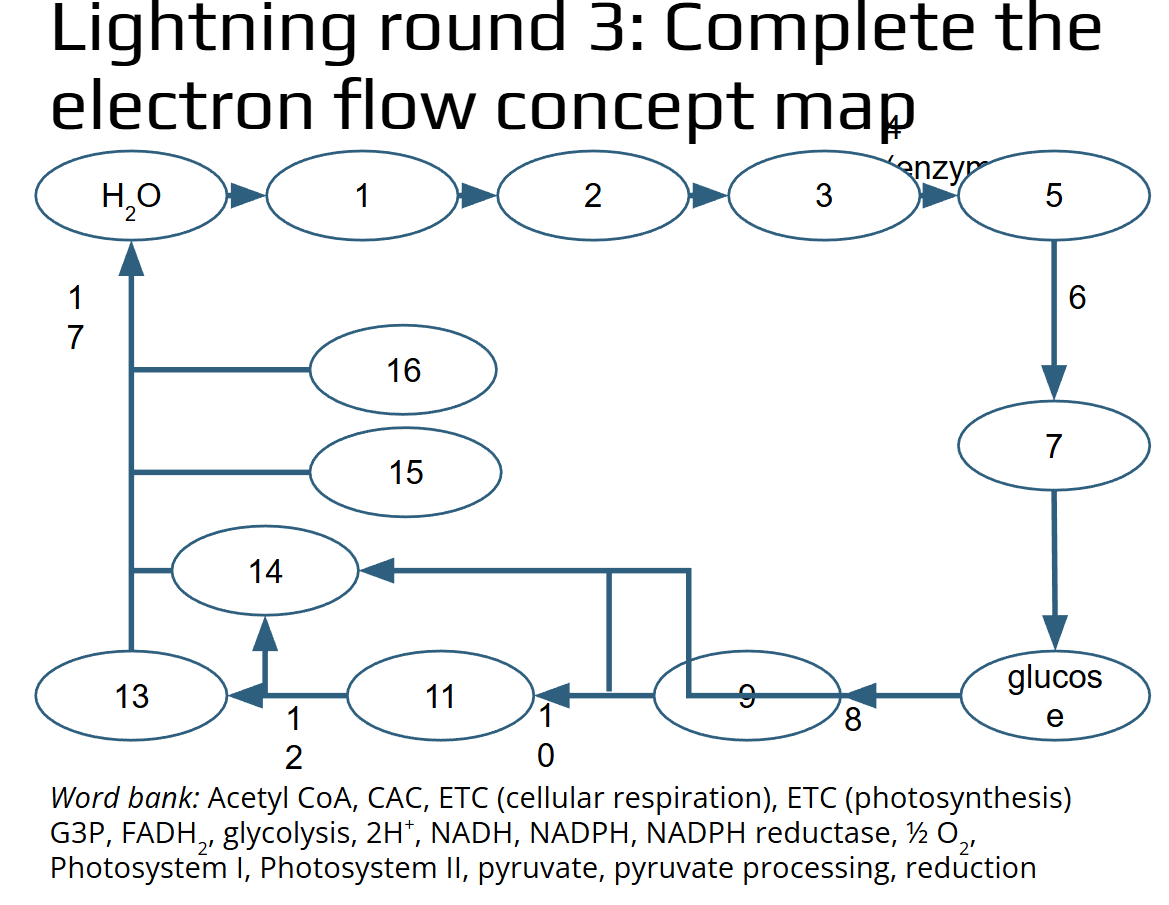
Complete the electron flow concept map.
Word bank: Acetyl CoA, CAC, ETC (cellular respiration), ETC (photosynthesis) G3P, FADH2, glycolysis, 2H+, NADH, NADPH, NADPH reductase, ½ O2, Photosystem I, Photosystem II, pyruvate, pyruvate processing, reduction
Questions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1. Photosystem II
2. ETC (Photosynthesis)
3. Photosystem I
4. NADPH Reductase
5. NADPH
6. Reduction
7. G3P
8. Glycolysis
9. Pyruvate
10. Pyruvate Processing
11. Acetyl CoA
12. CAC
13. FADH2
14. NADH
15. 2 H+
16. ½ O2
ETC (Cellular Respiration)
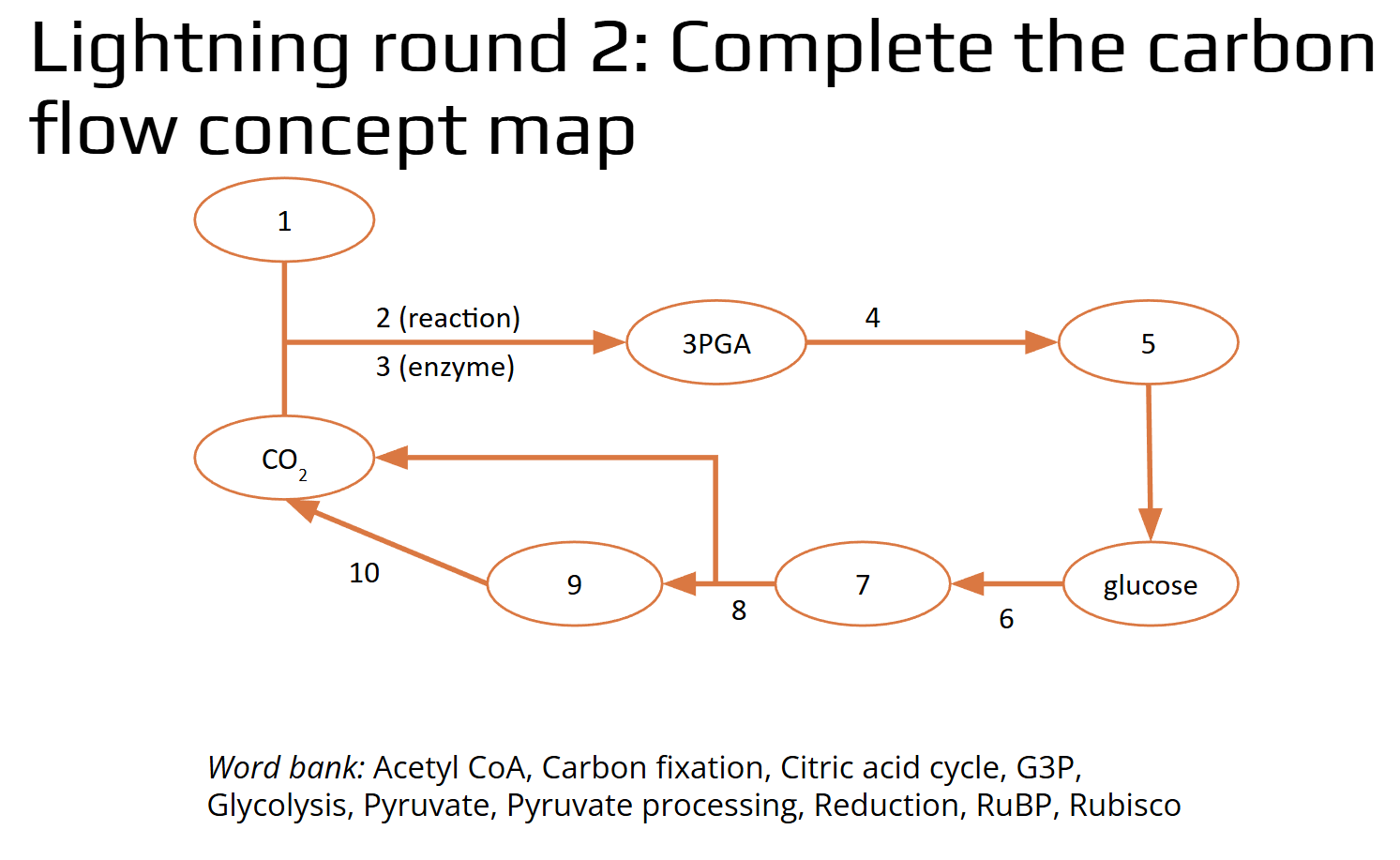
Complete the carbon flow concept map.
Word bank: Acetyl CoA, Carbon fixation, Citric acid cycle, G3P, Glycolysis, Pyruvate, Pyruvate processing, Reduction, RuBP, Rubisco
Questions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1. RuBP
2. Carbon Fixation
3. Rubisco
4. Reduction
5. G3P
6. Glycolysis
7. Pyruvate
8. Pyruvate Processing
9. Acetyl CoA
10. Citric Acid Cycle
What are the outputs and inputs of glycolysis?
inputs: glucose, NAD+H+, ADP+P outputs: NADH, pyruvate, ATP
What are the inputs and outputs of pyruvate processing?
inputs: pyruvate→ CoA, NAD+ + H+
outputs: CO2 + acetyl CoA, NADH
What are the inputs and outputs of CAC?
inputs: acetyl CoA, FAD + H+, NAD + H+, ADP+P outputs: CO2, FADH2, NADH, ATP
What are the inputs and outputs of the ETC?
inputs: NADH, FADH2, ADP+P, O2+H+
outputs: NAD+ + H+, FAD+2H+, ATP, H2O
what are the inputs and outputs of the light-dependent reactions?
inputs: sunlight, NADP + H+, ADP+P, water
outputs: ATP, NADPH, O2 + H+
What are the inputs and outputs of the Calvin Cycle?
inputs: CO2, NADPH, ATP,
outputs: ADP, NADP + H+, sugar
What is chemiosmosis?
The process by which hydrogen ions (protons) diffuse to the other side of the biological membrane from high to low concentration.
What’s the function of the CAC?
Finish break down of carbon
What’s the function of pyruvate processing?
transfer carbon containing molecule to mitochondria
Select all that apply. Which of the following are found in plant cells?
chloroplasts
cell wall
lysosome
mitochondria
cell membrane
centromere
chloroplasts 2. cell wall 3. mitochondria 4. cell membrane
Which of the following reactions is the correct description of the beginning of the Citric Acid Cycle?
Acetyl CoA + citrate = oxaloacetate
Pyruvate + citrate = oxaloacetate
Acetyl CoA + oxaloacetate = citrate
Pyruvate + oxaloacetate = citrate
Acetyl CoA + oxaloacetate = citrate
For each of the following processes listed, determine if the process occurs during cellular respiration, photosynthesis, both, or neither.
1
oxygen is the final electron acceptor
2
Reduction of NADP+
3
water is an electron donor
4
chemiosmosis occurs
5
Generation of proton gradients
Respiration
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
BOTH
BOTH
For each of the following processes listed, determine if the process occurs during cellular respiration, photosynthesis, or both.
All reactions can occur in the dark or light
2
reactions that involve chemiosmosis
3
Reactions that can occur in all eukaryotic cells
4
reactions that need enzymes
5
reactions that involve NADPH
6
Reactions that can occur in sunlight
7
reactions that produce water
8
reactions that use carbon dioxide
9
reactions where ATP is the FINAL product
10
reactions that occur in cells that contain chloroplasts
ONLY cellular respiration
BOTH
ONLY cellular respiration
BOTH
ONLY photosynthesis
BOTH
ONLY cellular respiration
ONLY photosynthesis
ONLY cellular respiration
ONLY photosynthesis
Which of the following structures listed below have a circular chromosome? Select all that apply.
A.
Eukaryotic Cells
B.
Mitochondria
C.
Lysosomes
D.
Chloroplasts
E.
Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic Cells
Chloroplasts
Lysosomes
Mitochondria
A photosynthesizing plant is moved from light to dark. Which of the following describes the correct order in which these processes will stop?
ATP formation, carbon dioxide fixation, oxygen release
ATP formation, oxygen release, carbon dioxide fixation
oxygen release, ATP formation, carbon dioxide fixation
carbon dioxide fixation, ATP formation, oxygen release
oxygen release, ATP formation, carbon dioxide fixation