Exam 3 PATHO
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
The Common Cold:
Viral infection of upper
No ANAs needed
2-3 colds/year (adult); 6-8 colds/year (child)
Single “cold virus” or more:
Rhinovirus: most common
early fall → late spring
Parainfluenza: < 3 yrs
Adeno/coronavirus
Winter & spring
RSV: < 3 yrs
winter & spring
linked to asthma *
Transmission of Common Cold:
Fingers, cough, sneeze
nasal mucosa + conjunctival surface: common portal of entry for viruses
s/s & t/x of Common cold:
s/s:
Dryness & stuffiness
Rhinitis
Clear & watery secretions
Post nasal drip → cough + sore throat
Headaches
Chills & fevers
t/x:
Rest
Antipyretic drugs
Decongestants
Rhinosinusitis/Sinusitis:
Rhinitis: nasal mucosa inflammation
Sinusitis: paranasal sinuses inflammation
You can have both
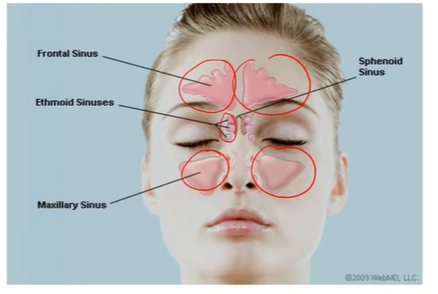
Sinuses Types:
Paranasal Sinuses
Air-filled spaces connected to the nasal cavity by small openings (ostia).
Linked with the nasal turbinates (superior, middle, inferior).
1. Maxillary Sinus
Located below the eyes (orbit) and above the hard palate.
Drainage opening is high (superior & medial) → makes drainage difficult.
2. Frontal Sinus
Located in the forehead area.
Opens into the middle meatus of the nasal cavity.
3. Ethmoidal Sinuses
3–15 small air cells on each side.
Found between the eyes.
Each has its own drainage path to the nasal chamber.
4. Sphenoidal Sinus
Located behind the eyes, in front of the pituitary gland.
Drains into the sphenoethmoidal recess (top of nasal cavity).
Rhinosinusitis classifications, d/x, t/x:
Acute: viral, bacterial, mixed
5-7 days; 4 weeks
Subacute: 4-12 weeks
Chronic: >12 weeks
D/x:
physical examination
Pain in head or when bent over or coughing/sneezing
MRI for SEVERE cases
rules out neoplasm
T/x:
Viral → rest for 1 week → >7days → ANA
Antipyretics
Mucolytic agents
Influenza:
Most common cause of upper
direct contact/ aerosols (cough/sneeze)
targets respiratory epithelium
Highest death rate
Types: can have lots of mutations
A: most common
infects animals
most severe
divides into
Hemagglutinin (H)
Neuraminidase (N)
B: only humans
Less severe
No subtypes
t/x:
fluids
Antiemetics
Antiviral drugs: <48 hrs; shortens time of flu
Amantadine
Rimantadine
Zanamivir
Oseltamivir
Acute Bronchitis:
Acute infection/inflammation of bronchi
follows viral illness
Pneumonia symptoms
EXCEPT pulmonary consolidation and chest infiltrates
Pneumonia:
Lower infection; happens more with pts who are virulent
leading cause of death in uncs
PJP (opportunistic infections) in immunocompromised/AIDS
c/x:
Bacteria, virus, fungi, parasites
streptococcus/pneumococcal pneumonia
gastric secretions aspirated → lungs
“aspiration pneumonia”
Source → Community or hospital acquired
Agent type → Typical/Atypical
Typical: infection → inflammation → productive cough
Infection Distribution → Lobar or Broncho
Community-Acquired Pneumonia:
Patient admitted → <48 hours → pneumonia s/s → infected facility → cooked
(Hospital would be >48 hours & 20-50% mortality rate)
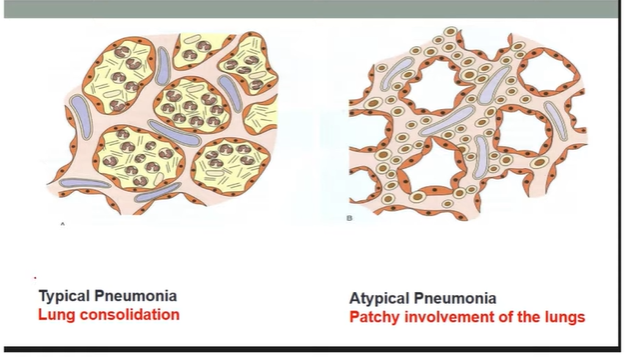
Typical vs Atypical Pneumonia:
Typical:
death in uncs
Pneumococcal pneumoniae
Marked inflammation of lungs
Exudate (fluid + debris) fills alveoli → lung consolidation (clear 99)
s/s:
Purulent (thick/yellow-green) sputum
Severe fever, chills, malaise, pleuritic pain
Egophony → aaa instead of eee
Seen clearly on chest X-ray
Atypical (Walking):
from viruses or Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Patchy lung involvement → mainly affects alveolar septa & interstitium
No alveolar exudate → No lung consolidation
Symptoms:
Mild/moderate sputum
Mild fever, less severe illness (“walking”)
Moderate increase in white blood cell count
Pneumonia s/s, a/x, d/x:
Sensorium changes
Cyanosis
Diaphoresis
Dyspnea
Fevers/chills
Headache
Malaise
Nausea/vomiting
Pleuritic chest pain
Productive cough
URI
Typical Assessment:
Dullness in percussion
^ tactile fremitus in palpation
Bronchophony, egophony, whispered pectoriloquy (not supposed to hear) in auscultation
d/x:
CBC for WBC
Gram stain
Blood cultures BEFORE ANAs
ABG values
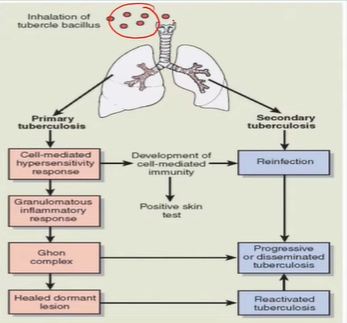
TB:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis → affects lungs & other systems
t/x of HIV → v TB
Disseminated/Miliary TB: from lungs → brain, bones, GU, heart
Primary: first infection; airborne droplets
- psi room
report to nurse before entering
N95 mask
Attacks macrophages → cell-mediated response
Screen testing:
Mantoux test
TST (intradermal) → check for induration
positive signs
5,10,15mm induration
Immigrants, IV drug users, working in shelters, [HIV + ppl, organ transplant, contact with TB + ppl (5mm)]
d/x:
PPD
Sputum & Blood culture
CXR
t/x:
Isoniazid (INH): 6 months if latent TB;
Rifampin (RIF)
Pyrazinamide (PZA)
Ethambutol (EMB)
NORMAL would be all for 2 months → 4 months of INH & RIF
TB pathogenesis:
Granuloma: ghon focus; macrophages that eat TB → dead tissue
+ LN = Ghon complex
Active TB s/s:
Low grade fvere
Night sweats
Anorexia
Hemoptysis
Dyspnea → SOB
Gas Exchange:
Dissolved Oxygen (PaO2/PO2)
80 -100
Oxyhemoglobin
95-100 sat
PaCO2: 35-45
carbaminohemoglobin (10%)
CO2 traveled in bicarbonate or CO2
Use of Chemoreceptors (O2, CO2, pH levels) and Lung receptors (monitors breathing patterns)
central chemoreceptors: in brainstem; ^ RR due to v pH
peripheral chemoreceptors: carotid & aortic bodies; measures PO2 & CO2 → ^ RR if PO2 < 60 mmHg
Insufficient O2 terms:
🔵 Hypoxemia
↓ Oxygen in arterial blood → PaO₂ < 80 mmHg
Causes:
Hypoventilation
Diffusion problems (gas exchange issue)
Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch
Right-to-left shunt
Often leads to ↑ CO₂ (hypercapnia)
🩸 Hypoxia (Ischemia)
↓ Oxygen in body tissues/cells
Can result from hypoxemia or poor blood flow
🔴 Hypercapnia
↑ Carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO₂ > 45 mmHg)
Dead space: Good ventilation; blocked perfusion
Silent: Blocked ventilation & blocked perfusion
Shunt: Blocked ventilation; Good perfusion
Types of Pleural Effusions:
Transudate (Hydrothorax)
Clear, watery fluid
Causes: Congestive heart failure (CHF), renal failure, liver failure
Exudate
Creamy fluid with proteins and white blood cells
Specific gravity > 1.020
Contains inflammatory cells and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Causes: Bacterial pneumonia, malignancies
Empyema
Pus-filled fluid with glucose, proteins, leukocytes, and cell debris
Causes: Bacterial pneumonia, rupture of lung abscess
Chylothorax
Lymphatic fluid in pleural cavity
Milky appearance (contains chylomicrons)
Causes: Trauma or inflammation of lymphatic vessels
Hemothorax
Blood in the pleural cavity
Pleural pain effusion s/s, d/x, t/x:
Sudden onset, Unilateral, made worse w/chest movement
d/x:
CXR, US, CT
t/x:
Thoracentesis
Fluid drainage
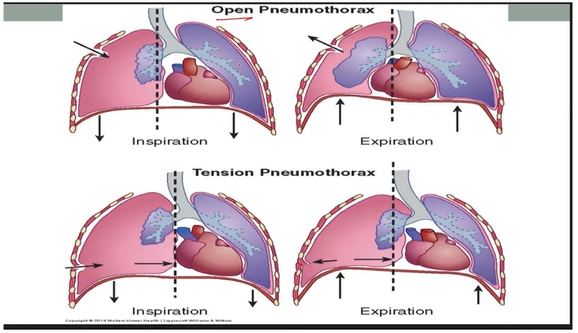
Pneumothorax:
Air accumulation in pleural space → partial or complete collapse
Types:
Spontaneous Pneumothorax (Primary)
Air blister (bleb) on lung surface bursts
young, healthy, tall ppl
Traumatic Pneumothorax (Secondary)
Chest injury (rib fracture, stab, or gunshot wound)
Open Pneumothorax (Communicating)
Air moves in and out of pleural space
Pressure inside = outside air pressure
Tension Pneumothorax
Air enters but cannot escape
Pressure builds up in pleural space → compresses lung
Tracheal deviated to the unaffected side & mediastinal shift
s/s:
Pain, SOB, Tachypnea, Hyperresonance, absent breath sounds
d/x: CXR, CT, O2, ABGs
t/x:
chest tube or large bore needle
Atelectasis:
Collapsed lung → deflation
Surgery, obstruction, pneumonia
GET OUT OF BED
s/s:
SOB, cough, fever, leukocytosis
d/x: CXR, CT
Prevention: deep breathing exercises, spirometer, ambulation
T/x: inflate & reduce obstruction
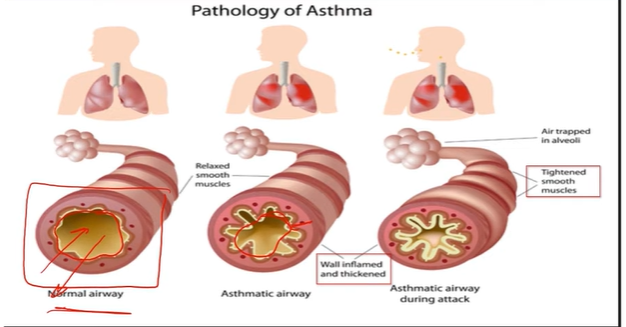
Asthma:
Chronic inflammatory disorder → inflammation & constriction of airways
Airway remodels → structure changed
SABA (albuterol) → opens airways; used for asthma attacks
LABA: prevents attacks
s/s:
chest constriction, wheezing, non productive coughing, tachypnea, tachycardia
t/x:
SABA for Bronchospasms
Theophylline: sim to caffeine → opens airways
Inflammation:
Inhaled corticosteroids
Montelukast (leukotriene antagonists)
Mast cell stabilizers
Anti-Ige Antibodies
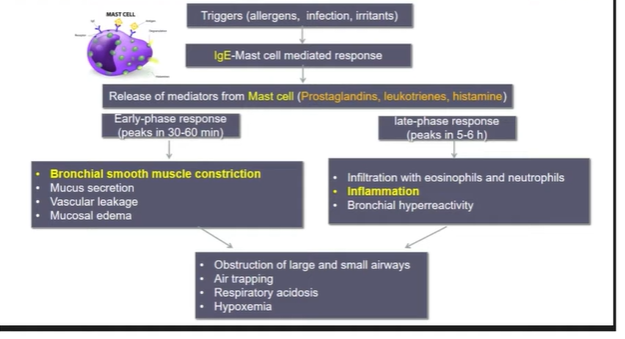
Asthma triggers:
Allergens, infections, exercise, drugs, hormonal changes, stress, smoke, cold air
IgE Type 1 Hypersensitivity
Asthma Severity:
Step 1: Mild intermittent
Uses inhaler <2x/week day
<2/month night
Step 2: Mild persistent
>2 weekly but not daily day
>2/month night
Step 3: Moderate persistent
Daily during day
>1/week night
Step 4-6: Severe persistent
Symptoms are constant day
more than once a week night
COPD:
Chronic bronchitis: obstruction from mucus
Emphysema: obstruction from destroyed alveoli
Emphysema:
Destruction of elastin → enlargement of airways
elastin helps for alveoli recoil → v alpha 1 antitrypsin → elastase → elastin broken down
can be genetic of alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency or from smoking
s/s:
40-50
barrel chest
Weight loss
v breath sounds
normal ABG till late disease progression
Cor pulmonale: RHF
d/x:
pulmonary function test
CXR
t/x:
X smoking, avoid pollutants
Bronchodilators
v O2 Flow
Anticholinergics
Steroids for last measure
Pursed lip breathing teaching
Surgery, transplant
Chronic Bronchitis:
Mucus hypersecretion & chronic productive cough > 3monhts or 2 consecutive years
Dramatic cyanosis
Hypercapnia & hypoxemia
SMOKING
s/s:
dyspnea, productive coughing, HTN, wheezing, SOB
d/x:
Pulmonary function test
t/x:
Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, X smoking, vaccination
Emphysema vs Bronchitis:
Emphysema (Pink Puffers)
Breathe faster to keep oxygen levels normal
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Use of accessory muscles and pursed-lip breathing
Skin usually pink due to adequate oxygen
Bronchitis (Blue Bloaters)
Cannot breathe fast enough to maintain oxygen levels
Cyanosis (bluish skin) and polycythemia (high RBC count)
Often develop cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure)
Pulmonary Embolis:
Blockage of pulmonary vessels by embolus
Types:
Thrombus – from DVT (most common)
Fat – after bone fracture or fat injury
Amniotic fluid – enters blood after membrane rupture during delivery
VIRCHOWS TRIAD
Hypercoagulability: Estrogen, Testosterones, smoking, obese
Venous Stasis: A fib, immobilized, paralysis, long flight
Endothelial injury: HTN, trauma, surgery
s/s:
chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia
d/x:
CT, MRI, VQ, D-dimer, EKG
t/x:
Prevent DVT, TPA for thrombus, Anticoagulants prevent, IVC filter for Inferior vena cavae for thrombus collection
Pulmonary Hypertension
^ psi in pulmonary arteries
c/x:
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (unknown, genetic, drugs)
LHF
Lung diseases
s/s:
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Fatigue, chest discomfort
Tachypnea
SOB when exercising
Thickened/hypertensive pulmonary arteries
Cor Pulmonale
Right ventricular enlargement due to pulmonary hypertension
Pressure overload → RV works harder → hypertrophy → dilation → RV failure
Effects:
v lung ventilation
Pulmonary vasoconstriction
RV hypertrophy → increased heart workload
Low oxygen levels → kidney makes more erythropoietin → more RBCs → polycythemia → thicker blood
Overall increased strain on the heart
s/s:
EKG shows right ventricle hypertrophy
Chest pain
Pulmonic & Tricuspid valves murmur
t/x:
v workload of RV → lowering pulmonary arterial psi
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) – Simplified Notes
Fluid fills the alveoli → lungs can’t expand fully → less oxygen enters blood
Caused by various conditions that injure the lungs
Key Lung Changes:
Damage to alveolar epithelial cells → leaky alveolar-capillary membrane
Protein-rich fluid in alveoli
Sloughing of type I alveolar cells
Dysfunction of type II cells → surfactant inactivated
Inflammation: neutrophils, macrophages, platelets, oxidants, proteases
Edematous interstitium, fibrin, hyaline membranes, and cellular debris
Causes: drowning, pneumonia, sepsis, stroke, massive burns, DIC, fat embolism
Progressive ARDS Manifestations:
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) and low blood oxygen (hypoxemia)
Rapid breathing → respiratory alkalosis
Poor tissue oxygen → metabolic acidosis
Increased WOB
Slow/shallow breathing → high CO₂ (hypercapnia) → respiratory acidosis
Respiratory failure
WHITE LUNGS from protein fluids
Acute Diarrhea:
>3 stool/day; loose & watery stool
not bloody, purulent, greasy
<14 (acute); >4 weeks (Chronic)
Infection or poison
Types:
Large Volume: excessive water/secretions
Viral/Bacterial in large or distal s.i.
Small Volume: excessive motility
frequent loss of small stools
Other s/s:
Fever, headache, vomit, abd pain, malaise
Constipation:
Change of frequency, size, consistency, ease of stool; <once every 3 days
Very subjective
c/x:
Dehydrated, delayed GI motility, sedentary, low fiber/residue diet, Psychogenic, Drug side effects
t/x:
^ fluid (>6 8oz/day), ^ fiber, exercise, bowel training
If lifestyle changes dont work:
Laxatives, stool softeners, enemas, suppository
Check for impaction in uncs → bowel obstruction
Anorexia:
Loss of appetite to eat despite feeling of hunger
from other GI issues, drug side effects, cancer s/s
Nausea
Unpleasant sensation preceding vomiting
subjective
Irritation/distention in GI tract
Simulated by higher brain center (traumatic injury)
Vomiting (Emesis)
Forceful emptying via mouth; complex reflex from medulla oblongata (vomiting center); nausea, tachycardia, diaphoresis cause this
Excessive distention, chemical stimulation, pain
Projectile Vomiting: from stimulation of vomiting center; ^ ICP
Abdominal Pain Types:
Parietal: stimulation of pain receptors in parietal peritoneum/abd wall
localized, sharp, intense, & lateralized (one-sided)
Visceral: stimulation of abd organs; inflammation
Vague, diffused (non-localized), dull
Referred: localized at some point along afferent nerve pathway of organ/tissue
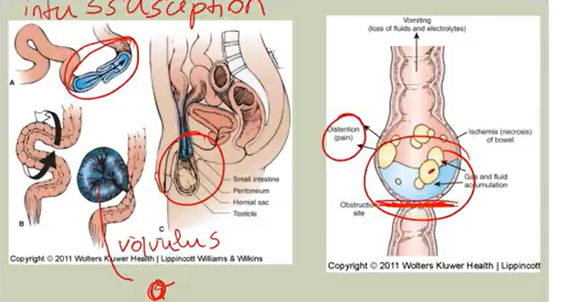
Intestinal Obstruction:
Mechanical: problem of bowel lumen movement patency → distention & electrolyte imbalances → bowel ischemia, acidosis, perforation shock, sepsis
Tumor, scar/adhesion tissue, constipation
intussusception, volvulus
s/s:
nausea/vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea, fever, colicky pain
reduced bowel sounds or borborygmus (hyper active sounds)
Peritonitis: fluid escape → peritoneal cavity → board-like rigidity; EMERGENCY
Nonmechanical (Ileus): complete stop of intestinal movement; no blockage (48-72hrs)
Abd surgeries, blood supply disruption there, narcotics/morphine
s/s:
Abd cramping/distention
Nausea/Vomiting
Failure of gas/stool passage
No bowel sounds
t/x:
NPO & NG tube (to decompress)
Acute Abdomen:
Episode of sudden/severe abd pain (hours or longer)
Causes:
Surgical, diagnose early
Gynecological: Lower Q, PID, Fibroids, ovarian cyst
Medical: pneumonia, acute MI, DKA, Hepatitis
Appendicitis: triad of RLQ pain, anorexia, leukocytosis
Peritonitis:
Peritoneum inflammation
c/x:
after perforation of gut/organ → cavity
Ulcer, appendix rupture, diverticulum, PID
s/s:
Pain (inflamed & rebound)
Nausea/Vomiting
Board-like rigidity of abdomen
Tachycardia, fever, ^ WBC
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD):
Break/ulceration in mucosal lining of esophagus/stomach/duodenum
Gastric protective mechanism & irritating factors (acid-pepsin, NSAIDs, H. pylori) imbalances
v PG → v bicarb production → ulcer
Acid= 2pH; ^ production after meal
c/x:
H pylori (gram -): lives in stomach → inflammation, dmg, bleeding
Excessing NSAIDs (aspirin) usage
X PG synthesis
Zollinger-Ellison (idiopathic disease): Acid hypersecretion from tumors
Too much acid delivery in duodenum → v protective layer here
r/x: Age, warfarin & NSAIDs, corticosteroids, smoking
Types:
Duodenal ulcer: Epigastric burning 2-3 hrs after eating;
4x more common > GU; in younger ppl
Relieved with food or antacids (buffer)
^ Weight; symptoms at 1-2am
Gastric ulcer:
in NSAIDS users and uncs
Pain after meal
v Weight
s/s:
Dyspepsia
Pain when stomach empty (duodenal)
Pain after meal (gastric)
Hematemesis (Upper GI bleed)
Melena: black tarry stools
Perforation & Hemorrhage
d/x:
Endoscopy (gold standard test)
Blood → H. Pylori
t/x:
Avoids ^ acid secretion foods
X alcohol, caffeine, NSAIDS, smoking
v Stress
Antacids (PPI), Antihistamines (H2 blockers) → ^ bicarb; antibiotics
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
Reflux → esophagus w/w/out inflammation
HCl acid/pepsin
c/x:
Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter (LES): relaxes and cannot put psi → esophagus → backflow
due to CCB, narcotics, ETOH, nicotine, chocolate, peppermint
v esophageal peristalsis & gastric emptying
s/s:
Heartburn (75-80%)
Regurgitation of food/fluid
Chronic cough
Barret Esophagus → metaplasia → dysplasia; indication of major issue
d/x:
Rule out neoplasm with dysphagia, orophagia, weight loss, occult blood loss
Endoscopy: gold-standard test, more specific
t/x:
Weight loss, small frequent meals
X high-fat, chocolate, alcohol, peppermint, caffeine, onions, garlic, citrus, tomatoes, smoking
X tight clothes
Sleep with head of bed elevated (not pillows)
H2 Blockers, PPI, surgery
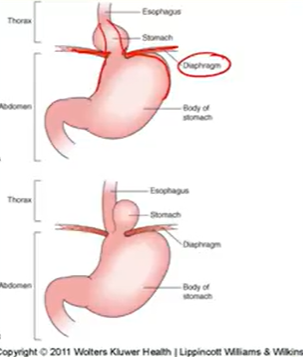
Hiatal Hernia:
Stomach protrude through diaphragm
GERD or asymptomatic
d/x: Barium swallow/endoscopy
t/x: Same as GERD and surgery if large
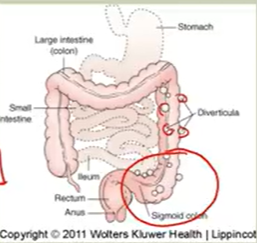
Diverticulosis:
Herniation outpouchings of mucosa/submucosa layers; sigmoid colon
Asymptomatic
^ in pts w/v fiber diet & uncs
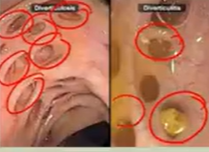
Diverticulisis:
Inflammation of diverticula in bowel wall
perforation & abscess formation
LLQ pain in uncs lasting several days
Low grade fever, nausea/vomiting, anorexia
D/x:
CBC: slight leukocytosis
SER is high
Urine normal
CT scan, abdominal films
NO Barium enema or Colonoscopy
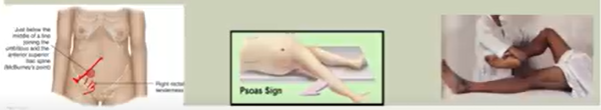
Appendicitis:
Inflammation of vermiform appendix
obstruction w/fecalith, stricture, neoplasm
Common with younger ppl; leading cause of abdominal surgery
s/s: umbilicus pain → RLQ pain; anorexia & N/V & low grade fever
Maximal pain at McBurney’s point
Rovsing’s sign: RLQ pain → LLQ palpation
Psoas sign: pain w/R thigh extension
Obturator sign: pain w/internal rotation of flexed R thigh
>24 hours → perforation → peritonitis → board-like abdomen & its s/s
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
abd pain w/ defecation/change in bowel habits → disorted defecation & distention
common PCP visits; in women
Altered gut motility & secretion & flora; hypersensitivity & hyperalgia
d/x: Rome III Diagnosis Criteria → defecation improvement & stool characteristics
t/x:
Mild symptoms
v Stress
Warmth → abdomen
^ laxatives, fibers, prebiotics; X obvious foods
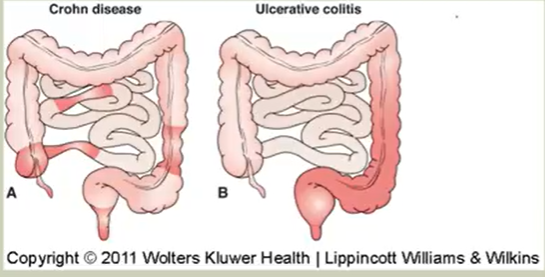
Inflammatory Bowel Disease:
Ulcerative Colitis: Chronic → affects colonic mucosa (rectum & sigmoid); AI disease → inflammatory ulceration
15-30 years; >60 years
Hyperemic Mucosa → mucosal destruction → bleedings, pain, urge to defecate & passage of blood
10-20 stools/day (exacerbation); crampy abd pain & dehydration & anemia
Risk for colon cancer
D/x: colonoscopy
T/x:
Anti-inflammatory meds, removal of colon parts
Chron’s Disease: Patchy inflammation of all GI layers (mucosa & submucosa); from mouth → anus
Young adults & teens; familial
Slowly w/remissions & exacerbations (stress-induced)
Fissures, granulomas (cobblestone), fistulae in perianal area, strictures (narrowed intestine area) → obstruction
Inflammatory lesions → granuloma formation → malabsorption (v weight)/ obstruction/ fistula & abscess formation → diarrhea & malnutrition
3-5 semisolid foul smelling stools/pain; nonbloody stool; urgent to defecate at night, IDA
Perianal abscesses & fistulas (opening in rectum)
c/x: unknown; theories
d/x: CT scan, ^ WBC v RBC, ^ ESR, Sigmoidoscopy
t/x: ^ calorie & protein diet, v fiber/residue
stress management
Anti-inflammatory drugs, ANAs, Vitamins, electrolytes
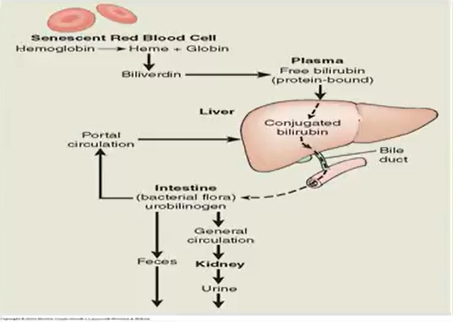
Jaundice:
Excessive destruction of RBCs; impaired bilirubin uptake via liver → v bilirubin conjugation
Bile flow obstruction from liver → gallbladder → duodenum
Liver functions
Production of bile salts
Elimination of bilirubin
Metabolism of steroid hormones
Metabolism of drugs
Carbohydrate metabolism
Fat metabolism
Protein metabolism
Storage of mineral and vitamins
Filtration of blood and removal of bacteria
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of gallbladder; 2ndary to previous cholelithiasis (gallstones)
either bile or calculi
Stones impacts cyctic duct → inflammation behind obstruction → ^ psi → distention, ischemia, gangrene, perforation
Acute:
RUQ pain & tenderness → back/shoulder
Biliary colic: pain starts from mild → severe
N/V
Recurrent attack after fatty meals
+ Murphy Sign: tenderness in RUQ & ^ breathing
Common duct stones from jaundice or F/S
Chronic:
Asymptomatic → 15-20yrs → symptomatic (20%) → mild dyspepsia after fatty meals
D/x: US (gold-standard test)
Liver function tests → ^ AST & ALT & alkaline phosphatase
T/x:
Cholecystectomy
Asymptomatic → conservative treatments
Avoid foods w/^ fat
Antacids
Viral Hepatitis Periods:
Prodomal/Preicterus period: X jaundice but flu-like symptoms (malaise, fatigue)
Anorexia, N/V, fatigue
Headache, aches
^ AST & ALT
Icterus Period: Jaundice (in HAV); RUQ tenderness
Pruritus, brown urine, light/clay colored stools, spider angioma, v prodomal s/s
Recovery period: v Jaundice → normal urine & stool
Enzyme lvs return normal; v pain
Hepatitis Types:
A: Caused by HAV; fecal-water/food (shell-fish, fresh fruits)
v mortality rate
Vaccine: dead virus; 2 injections 6 months apart
Water. food, & hygiene safety
B: Exchange of body fluids (sex, IV, health care workers)
Symptomatic (mild→ life-threatening)
Clean needles, immunization, safe-sex
Vaccine: recombinant HBV (not live virus)
Hepatomegaly → RUQ tenderness; splenomegaly; X jaundice;
2-3 weeks of illness → chronic
C: Exchange of blood & body fluids
IVDU via needle sharing
Uncommon with sex & maternal-fetal
Incubation period → 6-7 weeks
No vaccine
D: always comes w/Hepatitis B
D/x: Check for antibodies
A: Anti-HAV IgM → acute infection
Anti-HAV IgG → cured from HAV
B: HBs-Ag → acute infection
HBsAb (Antibody) → cured from HBV
C: Anti-HCV → acute infection
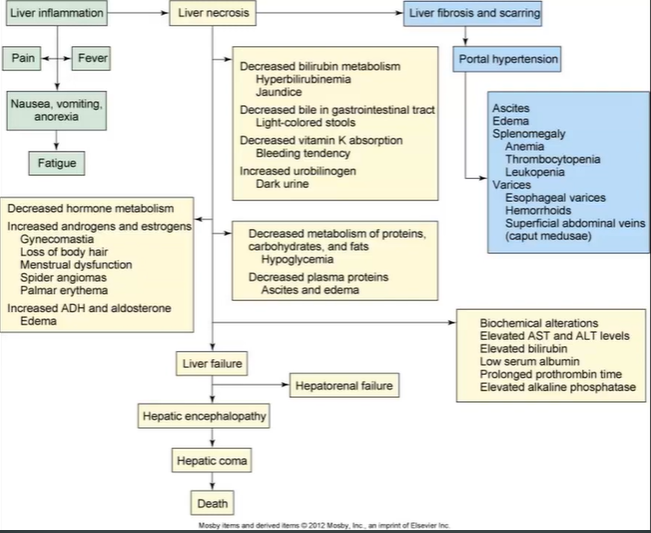
Cirrhosis:
Liver tissue replaced w/fibrous/scar tissue
ETOH, Viral Hepatitis, Biliary Disease
Scarring → liver flow disruption → portal HTN → liver failure
Portal vein: transport blood from stomach, intestines, spleen, & pancreas → liver
s/s:
Weight loss, Ascites (v albumin)
Hepatomegaly & Splenomegaly
Jaundice
Caput Medusae: enlarged veins around umbilicus
Esophageal Varices → GI bleeding
Hepatic Encephalopathy → v LOC from ^ ammonia
Clay-stool & dark urine
v weight, weakness,
d/x:
Liver function test
Coag studies, CBC, CT. ^ ammonia lvs
t/x:
TIPS (Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt)
Lactulose ammonia
Prevent infection
Liver Transplantation
Acute Pancreatitis:
Inflamed pancreas & surrounding tissue
Enzymes auto-digest pancreas
Alcohol, biliary tract disease, hyperlipidemia, infections, surgery, drugs
s/s:
epigastric & abd intense pain → refractory to narcotics; radiates to back
from activity
N/V, tachycardic, kussmaul, ^ temp, high/low BP
d/x:
Check ^ lipase levels
Check ^ serum amylase (3x more)
C-reactive protein ^ → ^ ESR
Gallstone pancreatitis → US
t/x:
IV fluids
Pain control
NPO & NG tube
clear fluids when no pain & enzyme levels return normal
Advanced diet
Estrogens
Made from cholesterol
Sexual maturation
Ovulation
Development and maintenance of female accessory organs
Cell division in breasts and endometrium
. Maintaining skin and blood vessels
Decreasing bone resorption
Increased HDL levels, decreased LDL and cholesterol
Moving fluid into tissues
Progesterone
Maintaining pregnancy
Endometrium and myometrium thickened
Promote growth of breast for lactation
Smooth muscle relaxation
. Prevent maturation of other follicles by suppressing FSH and LH
. Provide immune modulation (tolerance against fetal antigens)
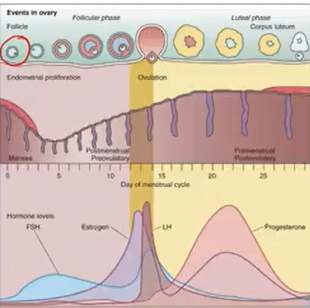
Menstrual Cycle:
GnRh: begins cycle → Anterior P → FSH & LH secretion (secreted at different times)
FSH → matures ovarian follicles → strongest survives → estrogen
LH → induces ovulation → oocyte released to fallopian tube & follicle cells → corpus luteum → progesterone ^ (luteal phase) → drop → restarts cycle
Then estrogen produced → X FSH → Activates LH
Alterations:
Puberty:
2nd sex characteristics, rapid growth, reproduction; 8-13
Delayed Puberty: (13 girls/14 boys); 95% is normal; 5% is X hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad axis or systemic disease
Precocious Puberty: (<7 girls/<9 boys)
Obese, ^ protein consumption, household products, CNS tumors
Abnormal uterine bleeding: irregular menstrual cycle & bleeding
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)
No organic disease, unpredictable, lack of ovulation, perimenopausal
IDA
T/x: NSAIDs → v PG → vasoconstriction
contraceptives, levonorgestrel, intrauterine device (IUD), ablation, hysterectomy
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
STD induced from vagina → uterus → fallopian tube → ovary → peritoneal cavity
Chlamydia & Gonorrhea
R/x: previous STD NOT treated, many sexual partners, douches, IUD → birth control
s/s: lower abd & cervix pain, ^ WBC & C-reactive protein & ESR, purulent discharge, fever
Chandelier sign: severe cervical motion tenderness
t/x: ANAs, if IUD → remove it
External Genitalia Disorders:
Bartholin: cyst & abscess; fluid-filled sac → occlusion of duct
from bacterial, chlamydial or gonococcal infection
tender & pain
t/x: moist heat, ANAs, I & D
Vulvodynia: chronic pain syndrome → vulvar area
Vulvar Carcinoma:
younger women: before vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia or HPV infection
Older women: before non-neoplastic disorders
Lesions → itching & repeated injury
Healing cells mutate
NOT HPV
Vaginitis:
s/s: Discharge, redness, swelling, pain urinating, intercourse, ^ WBC
Normal vagina pH (4-4.5) → protects against infection
Disruption through:
Abnormal estrogen lvs, STDs, ^ Glycogen (DM, pregnant)
Douching, soap, spermicides, tampons
ANAs
Cervicitis:
Acute/chronic; purulent discharge os/endocervical bleeding
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis
Abnormal flora ← v Estrogen
Anatomic female Abnormalities:
Pelvic organs
Cystocele: herniation of bladder → vagina; dropped
Weak supporting muscles
s/s: bearing down, difficulty emptying bladder, frequent urination
Rectocele: herniation of rectum → vagina
s/s: difficulty defecating
Uterine Prolapse: bulging uterus → vagina
t/x: surgery, pessary (plates to provide support), Kegel, estrogen therapy (menopausal women only)
Endometrial Disorders:
PID
Endometritis: uncommon but from infection
Abortion, delivery, instrumentation
Vagina bleeding, tender, foul-smelling discharge
ANAs
Endometriosis: Ectopic Endometrial Implants outside of uterus
unknown
R/x: early menarches, longer duration & flow, menstrual pain (cue to abnormal hormone cycle); retrograde menstruation (goes up instead of down)
Can occur anywhere; very painful
Infertility
t/x: stop cycle, remove implants,
Uterine Leiomyomas: myomas/uterine fibroids; smooth muscle benign tumors
Asymptomatic → enlarge → vaginal bleeding, pain, pressure
t/x myomectomy/hysterectomy
Endometrial Cancer
Ovarian Disorder:
Cysts: common form of tumors (benign)
Functional: follicle/luteum
→ enlarged → dull aching pain
Fluid-filled
Corpus luteum cyst: cells left behind from ovulation
PCOS: most common endocrine disorder
Anovulatory menstrual cycles; ^ androgens (male) & polycystic ovaries
Follicles do NOT ovulate after ^ LH → immature follicles ^/Amenorrhea (no menses)
Primary Amenorrhea: never menstruated in life or 15/13 (no sex characteristics)
Congenital/h-p-o- axis
Secondary: had menses → stopped (>6 months)
Pregnancy, PCOS, Fat-muscle ration alteration: exercise/anorexia nervosa
H-p-o axis; infection
Hyperinsulinemia, Obese, DM, HTN, Hyperlipidemia, Menstrual irregularities, Hirsutism, acne, infertile
t/x oral contraceptives; lock in
Dysmenorrhea:
Painful menstruation:
Primary: ^ PG
T/x w/NSAIDs
Secondary: structural problems throughout cycle
Premenstrual Syndrome:
Physical, emotional, behavioral changes associated w/cycle → v relationships & affects ADLs
mild (PMS) → regular (PMS)→ PMDD ( premenstrual dysphoric disorder)
PMS: >300 s/s:
Swollen breasts, bloat abd pain, headache, backache
Depression, anger, fatigue → SSRIs
Menopause:
X ovarian function; vv estrogen
v Breast tissue, body hair, elasticity, SQ fat, Ovaries & uterus
Friable cervix & vagina
Hot flashes, palpitations, dizzy, headache
Insomnia, Irritability, anxiety, & depression
HTR if NEEDED → osteoporosis
Male Anatomy
Androgens:
Testosterones: from Leydig ← ^ LH
Dihydrotestosterone: → peripheral tissues; produced by enzyme 5-alpha reductase
FSH → Sertoli cells → Spermatogenesis
Erection: when corpus cavernosum + spongiosum → filled w/blood
Veins constrict to maintain erection
even start with baby
Erectile Dysfunction: v sexual satisfaction
Organic:
Neurogenic: stroke, Parkinson’s
Hormonal: v Testosterones
Vascular: DM, atherosclerosis
Drug induced (SSRIs & BB (v BP))
Psychogenic
Mix

Penile Disorders:
Inflammation based
Balanitis: inflammation of penis gland
Poor hygiene & phimosis (cannot retract foreskin) & DM
Peyronie Disease: fibrous scar tissue → pain and curvature during erection
localized + progressive; palpable
50% goes away
Inflammation happens after plaque formation
Priapism: involuntary, prolonged penile erection (4-6 hrs)
painful; X sexual arousal
Emergency
Any age; 60% → idiopathic; 40% → spinal cord trauma, sickle cell disease, leukemia, infections, trauma
Impaired blood flow → corpora cavernosa
t/x: analgesics, sedation, hydration (sickle cell), needle aspiration
Penile cancer
Testicular Disorders
Disorders of the Testicular Tunica
Hydrocele: excess fluid → tunica vaginalis
congenital, infection, trauma, testicle torsion
smooth, tense, transilluminates
Hematocele: accumulation of blood → tunica vaginalis
Dark red/purple skin
Spermatocele: painless sperm containing cyst epididymis ←> testis
solitary/multiple
Small
Varicocele: abnormal enlargement of testicular vein draining testis
Bag of worms like
Blood pools in veins → venous system → v b.f. in testis → X spermatogenesis → infertile
Testicular torsion: twisting of spermatic cord
exercise, trauma
testicular pain, N/V, tachycardia
large & tender; X cremasteric reflex
surgery ← <6 hrs > → loss of testis
Inflammations
Epididymitis: inflammation of epididymis
Primary: nonsexual infection; congenital
Secondary: Anal sex; STIs
s/s:
Unilateral pain
Inflammation
similar to torsion
+ reflex
^ WBC
t/x: scrotal elevation & support (phren’s sign); ANAs, Analgesics, Antipyretics
Orchitis: inflammation of the testis
Precipitated from primary UTI → reach testes via blood, lymph, urethra
Mumps Orchitis: most common cause
Sudden onset
3-4 days after onset of parotitis
High fever, erythema, edema, tenderness of scrotum & leukocytosis
Risk for sterility if both testicles involved
Testicular Cancer: 15-35
Excellent prognosis
Unknown cause
R/x: undescended testes
First sign: slight testicle enlargment
D/x: physical examinations, U/S, CT scans, MRI, Tumor markers
Prostate Disorders:
Prostatitis:
Different kinds
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): compresses urethra; accelerate and nonmalignant
Nodules → compressed → urethra → narrow slit
UTI, retention → incontinence; nocturia
can be treated
DO NOT TAKE anticoligernic meds
Prostate cancer: most common male cancer
second to lung cancer
Screening: PSA & digital rectal exam
Unclear, r/x → Age & high fat diet
s/s: asymptomatic → similar BPH s/s → metastasis
Childhood Disorders:
Hypospadias: opening of urethra → ventral penis surface
Undescended 10%
Epispadias: opening on dorsal sides
Less common
Phimosis: tightening of prepuce → X retraction
Erections help remove adhesions → if not → surgery
Paraphimosis: foreskin is retracted and cannot go back
Restricts glans blood supply → ischemia & necrosis
Cryptorchidism (Undescended Testes)
1 + testes fail to move down into sac
R/x: premature babies
Infertility malignancy
Skin Lesion Types
Macule: circumscribed flat skin areas
Different in color
<1cm
Petechiae, flat nevi
Patch: Large macule; >1 cm
cade au lait spot, mongolian spot
Papule: small, solid, elevated lesion
<1cm
Elevated nevus (mole), wart, bug bite
Plaque: skin elevation
>1cm
silvery/scaly
Psoriasis
Pustule: visible purulent fluid below skin
<1cm
Acne, impetigo
Vesicle: circumscribed skin elevation; serous fluid
<1cm
Herpes simplex, Varicella, zoster
Nodule: solid skin mass
>1 cm
Palpable (epi → dermis)
Dermatofibroma, Xanthoma
Bulla: elevation w/fluid
>1 cm
only to epidermis
Burns, Blisters
Wheal: Elevated pink/white area with papule/plaque
Following allergic response
Red; axon-mediated
PPD test; urticaria
Cyst: closed cavity/scar
Semisolid + fluid
Sebaceous cyst cystic acne
Pressure Ulcers:
Ischemic ulcers from unrelieved skin psi → dmg
Decubitus ulcer: pressure interrupts normal skin b.f.
Psi, Shearing force (friction + gravity), friction, moisture
prone in sacrum, heels, ischia, trochanters
Do frequent skin assessment; reposition every 2 hours; educate; v moisture, ^ nutrition & hydration
There are stages:
Intact but erythema
Partial-thickness loss (epi, dermi)
Full thickness loss → subcut fat
Full loss → exposure of bone, muscle; irrevirsible
Deep tissue injury: discolored (purple/maroon) intact skin/blood filled blister
Unstageable: full-thickness loss w/ulcer & slough/eschar or both
Skin disorders:
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Type 1 Hypersensitivity
Inflammatory process → erythema
Severe pruritus, lesions w/indistinct borders; epidermal changes
Chronic → skin thickens → leather → hyperpigmented → scratching & itching → lichenification
IgE AXAs
h/x of asthma or high fever
Contact Dermatitis: allergic & irritant; Type 4 hypersensitivity
inflmmatory on CD4 & CD8 → alergen → skin → carrier protein → non-IgE antigen
Allergic agents:
Antimicrobials, hair dyes, latex, plant adhesives
Irritant agents: soap, detergents, organic solvents
s/s: Erythema, swelling, pruritus, vesicular lesions; poison ivy
Papulosquamous Disorders:
Psoriasis: Chronic, relapsing, proliferative, inflammatory disorder
complex interactions between → macrophages, fibroblasts, dendritic cells, NK cells, CD4, CD8
Dermal & epidermal thickening
Scalp, knees, ass, back, elbow
Turnover from 14-20 days → 3-4 days
No time to mature/keratinize
Erythematous plaques → thick/silvery scales → hard to remove → bleed when removed/Auspitz’s sign
T cells activated → growth facts → papule creations & neutrophil/monocyte attraction → inflammatory process
Pityriasis Rosea: benign, self-limiting inflammatory disorder from virus
Herald patch: circular, demarcated, salmon-pink; 3-10 cm → 14-21 days → secondary lesion (smaller) → trunk & upper extremities
Winter month
Skin Infections:
Fungal:
Tinea: superficial; dermatophytes
Ringworm, athlete’s food → attack dead cells
Candidiasis: attacks living tissue; on skin, mucous membranes, vagina, GI tract; NOT an STD
Mycoses → dermatophytes → termed tinea
Tinea capitis → scalp
Manus → hand
Pedis → foot; athlete’s foot
Corporis → ringworm
Cruris → groin, jack itch
Unguium → nails/onychomycosis (ugly ass nails; systemic treatment)
Bacterial
Cellulitis: infection of dermis & subcut tissue
Impetigo: superficial skin infection; staphylococcus/Streptococci
Highly contagious; honey-colored crust; moist erythematous base
Viral:
HPV: common warts (1 & 2); children on fingers; plantar warts (bottom of feet)
Condylomata acuminata: Anogenital wars (6 & 11); sexual transmitted
16 & 18 → 70% of cervical cancer causes
Herpes Simplex virus (HSV):
1 → oral infection or cornea, mouth, orolablast
2 → genital infections
Herpes zoster (shingles) & Varicells (chicken pox)
Same virus
Primary infection followed years after activation (shingles)
Latent virus & dorsal root ganglia
Benign Tumor:
Actinic Keratosis: premalignant lesion of aberrant proliferations of epidermal keratinocytes
Nevi (mole/birthmarks)
Skin Cancer:
Basal Cell carcinoma: most common cancer in world
Red macule/papule → depressed cancer
Grows slowly → ulcerates & crust
rare metastasis
Squamous cell carcinoma: sun exposure induced; 2nd common skin cancer
in site/invasive
Result of actinic keratosis → premalignant lesions → proliferations → epidermal keratinocytes
Malignant melanoma: malignant tumor of skin
Most serious
ABCD(>6mm)E
Changing nevi, new swelling, redness, scaling, oozing
Sun exposure: ^ r/x for basal or squamous cell carcinoma
severe → malignant melanoma
Burns:
Injury resulting from contact/thermal exposure, radiation, chemical, electrical agents
Cardiovascular response: fluid evaporation → ^ WBC, hematocrit, & hypoproteinemia
Cellular response:
Transmembrane potential X: impairs Na-K pump → ^ intracellular Na & H20 v K
Metabolic response: hypermetabolic state → needs ^ energy
Immunologic: immunosuppressant state
Control airway, fluids adequate, control airway, nutrition (^ protein, fat, Cals)
Wound management, grafting
Infection & sepsis t/x
Thermoregulate
Monitor circumferential burns for COMPARTMENT SYNDROME: ^ muscle psi → nerve & b.v. damage → swelling & edema
hypoxia → dearth
Intense pain in arms & legs
t/x: escharotomy/fasciotomy: open the skin → v psi
First degree:
Superficial (epidermis)
Local pain & erythema & blanches w/psi
No blisters; 3-6 day heals
Mild → moderate sunburnt
Superficial partial thickness: epidermis & some dermis
Blisters & heals in 10-21 days
Second Degree:
Deep partial thickness: epidermis & deeper dermis
Blisters & heals → 2-6 weeks; w/out scars
Do NOT remove blisters
Wet/waxy dry
MOST PAINFUL
Third Degree:
Full thickness: epidemis + dermis + subcut
Wound dry & leathery → eschar
W/out blister; painless
Escharotomies → releases psi & prevents compartment syndrome
Flames, explosions
4th degree: full thickness & deeper tissue (muscles & burns)
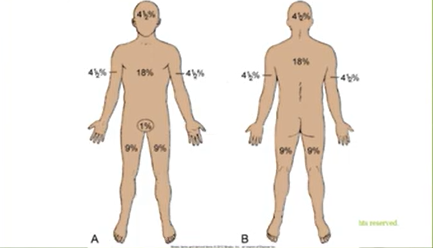
Rule of Nines: look at image
>20% = major burn injuries
Massive evaporative water loss & large # of fluid, ^ blood concentration
Lund & Broward chart is another way to estimate burn injury
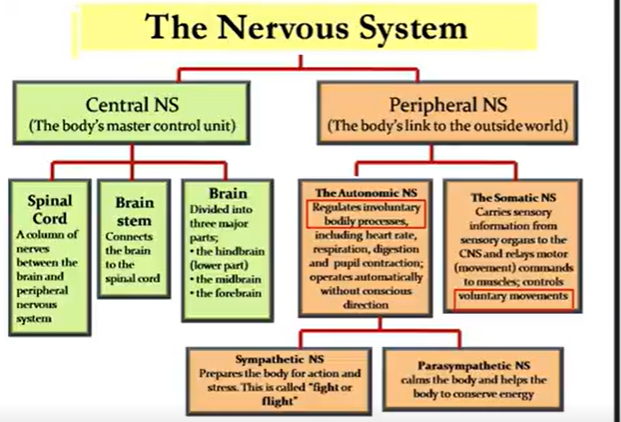
Nervous System
SNS: catecholamines (epi, norepi, dopamine) connected → adrenergic receptors (a1 a 2 b1 b2 b3)
PNS: Acetylcholine; connected → cholinergic receptors (muscarinic & nicotinic)
Dendrites ← stimuli → axons
Schwann cells: myelin/white matter (^ speed)
Cell firing:
stimulus → Na channels → threshold → ^ Na channels → Na enters cell → depolarization → K channels open → K diffuses out → repolarization
Meninges:
Dura: venous drainage
subdural space
Arachnoid: waterproof
subarachnoid space (w/CSF)
Pia: Holds cerebral arteries
CSF: sim to blood plasma
600ml/day produced from choroid plexuses
Inside brain ventricles → s.c.
leaks → out capillaries → arachnoid villi → venous circulation
-plegia: stoke/paralysis
Paresis: weakness
Hemi: both limbs on 1 side
Di/para: both limbs
Quadri: all limbs
Pain
Gate Control Theory: non-painful input closes gait → reduces pain → CNS
Pain threshold: lowest pain # one can feel
Pain Tolerance: greatest pain # on can endure
Nociceptive Pain: injury → tissue; visceral (cavity lining & organs), somatic/ (skin, joints, muscles)referred
Many pain types
Neuropathic/non-nociceptive pain: chronic (>6 months) pain from primary lesion → leads to long term pain pathway changes → abnormal sensory info processing
Central/peripheral
Tingling, numbing, burning
Headaches:
Migraine: episodic & repeated lasting 4-72 hrs
Familial
Women 22-55
D/x: unilateral, throbbing, worse w/movement, N/V, photophobia or phonophobia
Phases:
Premonitory (few days; feeling u gonna get it)
Aura (smth right before)
Headache
Recovery
R/x: altered sleep, overexertion, weather, skipping meals, before period, alcohol/nitrates
Cluster: period of days → spontaneous remission for long period
minute → hours
Men 20-50
Autonomic X & trigeminal activation
D/x: unilateral, severe pain
Ipsilateral eye, red eye, stuff nose
Tension-type: most common; bilateral headache like a tight band around head
Gradual pain; 2nd decade
Episodes (hours → days)
D/x: 15 days/month; 3 months
Myasthenia Gravis:
AI; type II hypersensitivity (xtra AcH AXAs)
Gradual destruction of AcH receptors (only striated muscles)
Nerve impulse transmission defect in neuromuscular junction
Thymus tumor/Hyperplasia
Women 3x > men
Gradual weakness (proximal → distal)
s/s: Insidious onset, progressive weakness, ptosis (dropping eyelids), diplopia, dysphagia
Crisis: Diaphragmatic involvement → difficulty breathing → intubation → myasthenia crisis → quadriplegia → vvv dysphagia & respiratory failure arrest
vs Cholinergic Crisis: too much anticholinesterase drug → toxicity → ^^^ AcH
^ GI, SMC contraction, salivation; v CV, v RR
D/x: Tensilon test: provide meds → if improved quickly → positive
T/x:
Anticholinesterase inhibitors: builds up AcH in nerve ending
Corticosteroids
Guilliain-Barre Syndrome:
Demyelinating disorder →peripheral & cranial nerves
ascending motor paralysis (feet → up)
Resp/GI infection precedes 1-4 weeks before
C/x: Infection, surgery, vaccination
s/s: muscle weakness, paresthesia, resp. arrest/ cardiovascular collapse
recovery possible
severe when it reaches diaphragm
t/x: supportive care, ventilator, plasmapheresis, Immunoglobin
Parkinsons:
Chronic & progressive; degenerative & debilitating
basal ganglia & substantia nigra affected → loss of dopamine producing neurons & intracellular inclusions (Lewy bodies) → X dopamine (normal AcH & v dopamine)
Genetic + environment; 40 → peaks 58-62 years; males
s/s: TRAP
Tremors at rest
Rigidity
Bradykinesia/akinesia
Postural disturbance (flexed, forward leaning)
Pill-rolling, dementia, depression, shuffling steps
D/x: H & P
T/x: replace dopamine & anticholinergic drugs (lowers AcH)
Dosage ^ after 5 years
Deep brain stimulation
X AntiHTN, Neuroleptics, Antiemetics
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Neurodegenerative → lower & upper MOTOR neurones
Sensory & ANS NOT INVOLVED
Progressive muscle weakness → atrophy, splasciticy
Excessive glutamate; X inflammation
Men (3:2) Women
s/s: weakness in any or all; paralysis (progressive atrophy)
Normal intellectual & sensory function sustained till death
d/x: H & P
T/x: little t/x available
Riluzole
Rehab
2-5 years life expectancy
MS:
Demyelinating; CNS associated (myelin); AI
T & B cells cross blood brain barrier → myelin become foreign → inflammation triggered → Myelin producing cells (oligodendrocytes) destroyed
20-40; Male (1:2) Female; white ppl
s/s: crisis & remission; paresthesia, weakness, impaired gait
Optic neuritis; motor ocular nerves X
Dysphagia
d/x: lesions in CNS, CT, CSF (^ IgG)
T/x: anti-inflammatory & immunosuppresantws
treat pain, depressions, GI problems
Avoid EXTREME temps
Plasma exchange
Spinal Cord Injury & Shock:
Motorcycle crashes, sports, penetrating, elderly falls
16-30
Vertebral injuries (flexion, extension, compression) → compresses tissue
Spinal/Neurogenic Shock:
normal s.c. activity ceases → below level of injury
Complete reflex, motor, sensory, ANS activity
X bladder/rectal control
Ends when reflexes are regained
7-20 days; 3 months
ER
Autonomic Dysreflexia/Hyperreflexia:
Injury above T6
After shock → X bladder/rectum emptying → SNS activation → ^BP (arteriolar spasms) & v HR → life threatening → stroke
s/s: headache, blurred vision, distended rectum/bladder, sweating & flushed skin
^ICP:
normal 5-15
Due to blood, CSF, brain tissue → arteries collapse → X blood flow
C/x: brain swelling, hydrocephalus, Tumors
Hydrocephalus: too much CSF in ventricles
C/x: ^ production, obstruction, defective reabsorption
Children is noncommunication (obstruction of ventricle system) whilst Adults is communicating (v reabsorption)
Monroe-Kelli Hypothesis: theory where volume and pressure are balanced
s/s: >2 years of age; headaches, v LOC, sluggish & dilated pupils
Cushing’s Triad: ^ SBP, bradycardia, irregular respirations
Brain Herniation against bone, dura matter → oculomotor nerve compression
Traumatic brain injury (Hematoma-related):
Whiplash: stopping too quickly
COUP injury: directly in injury site
Counter COUP: opposite injury site
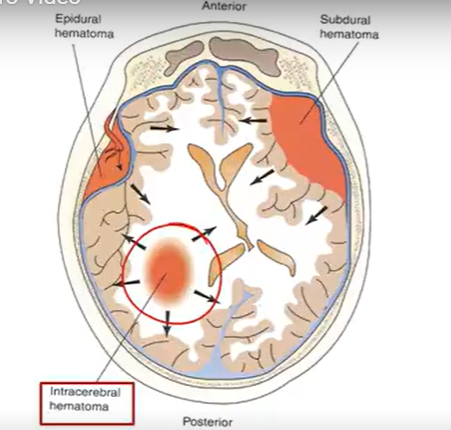
BRAIN HEMATOMEAS: collection of blood
Epidural: between skull & dura mater; rapid bleeding (meningeal artery tearing) → unconscious → lucid period
Brain compression; good prognosis
HA, V, confusion, drowsy
Subdural: dmg in bridging veins (dura -arachnoid mater)
Bleeding progresses quickly → ^^^ ICP → high mortality
Intracerebral: anywhere in brain (trauma or hemorrhagic stroke)
size & location → Vomiting
resolves by itself of through surgery
Subarachnoid: (arachnoid-pia mater)
From cerebral aneurysm/trauma; rapid onset
R/xL intracranial aneurysm, HTN, smoking, ETOH, cocaine
s/s: vomiting, AMS, fever, seizure
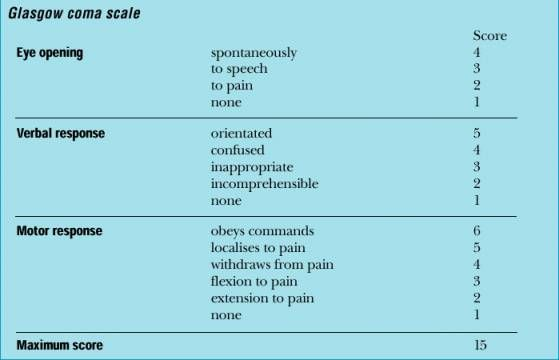
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Describes injury severity; 3-15
8 = intubation
decorticate flexion: 3 points
decerebrate flexion: 2 points
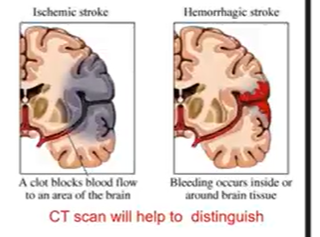
CBA-stroke:
Sudden loss of brain function from X blood supply to part of brain
Ischemic: clot blockage → vO2; thrombotic/embolic
Thrombotic: Thrombus ← arterial occlusion ← brain vessel blood clot
TIA: clots causes intermittent blockage (24 hrs)
Embolic: clot travels TO brain → blocks brain supply
Hemorrhagic: bleeding inside or around (cerebral artery)
C/x: HTN, ruptured aneurysm
r/x:
age, sex, genes, race
HTN, Hyperlipidemia, Smoking, ETOH, DM, a-fib, obese, cocaine
Stroke s/s:
Hemiparesis, hemisensory loss
LOC, Headache, slurred speech
ALWAYS OPP SIDE OF BODY
Intracranial Aneurysm:
From HTN, arteriosclerosis, cocaine, birth; 50-59
s/s: Asymptomatic, Dizzy, HA, CN (3, 4, 5, 6) compression
Berry (saccular) or Giant (fusiform)

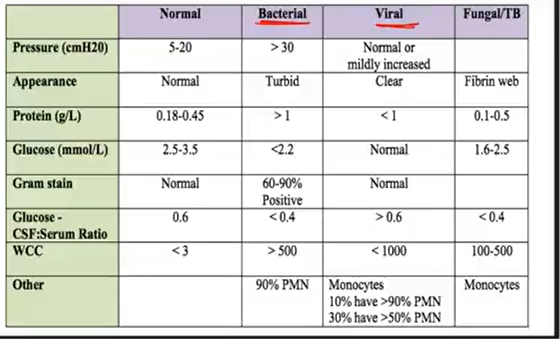
Meningitis:
Inflammation of meninges; stiff neck
Bacterial: Meningococci/pneumococci → CSF or Resp infection (sinusitis, otitis media)
s/s: fever, ^HR, chills, petechiae
Nuchal rigidity, HA, photophobia
Brudzinski sign: reflex when moving neck above → flexes knees
Kerning sign: 90 degree leg elevation → unable to do it from pain
Check CSF: Turbid appearance, >1 protein; <2.2 glucose
t/x: ANAs; aseptic treated w/ antivirals/steroids
Vaccination (ppl that live in dorms)
virus
Clear appearance; <1 protein; normal glucose
fungi, parasites, toxins
Seizures:
Sudden/explosive discharge of cerebral neurons
Epilepsy: periodic & unpredictable seizure occurrences
Seizure: disorders, synchronized, rhythmic brain neuron firing; types:
Focal: specific neural focus; simple/complex (vLOC, bad senses, psychomotor phenomena “chewing movements”) partial
Generalized: entire cerebral cortex
Absence: staring at smth for few seconds → then lock back in
Mistaken for ADHD
Tonic-Clonic: tonic (stiff) → clonic (limb jerking) → post-ictal (body limps)
Myoclonic: brief shock-like contraction (face, trunk)
Myoclonus: falling in ur sleep
Atonic: sudden muscle tone loss; limb & head dropping
1-2 seconds; LOC v; no postictal confusion
Secondary: Focal → Generalized
Status Epilepticus: Seizures lasting > 5mins
^ Hypoxia & v glucose; acidosis
ER
Common in jits/uncs
t/x: diazepam, lorazepa, life support, prognosis
Convulsion: jerky, contract–relax (tonic-clonic) movements seen in some seizures.
Epilepsy: seizures with no correctable underlying cause.
Prevalence: affects 5–10 people per 1,000.
Aura: a warning sign that appears right before a seizure.
Prodrome: early signs (malaise, headache) occurring hours to days before a seizure.
Postictal phase: period after the seizure; person feels fatigued and has no memory recall.
Alzheimer Disease:
neuritic plaques + Amyloid plaques + neurofibrillary tangles; can only see after u die
most are dementia; >65 & 2x/5 years; gradual
cortical atrophy & neural loss (parietal + temporal)
v ACH → cholinergic deficit
s/s: impaired short-term memory; retrieve distant memories better
Sundown syndrome: later stages; worse during the evening
Death from pneumonia & Pulmonary embolism
d/x: 10 warning signs
t/x: ACH precursors (little benefit); AChE inhibitors
