Cardiac Action Potential and Heart Physiology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the primary function of the sinoatrial (SA) node?
It generates impulses about 75 times per minute.
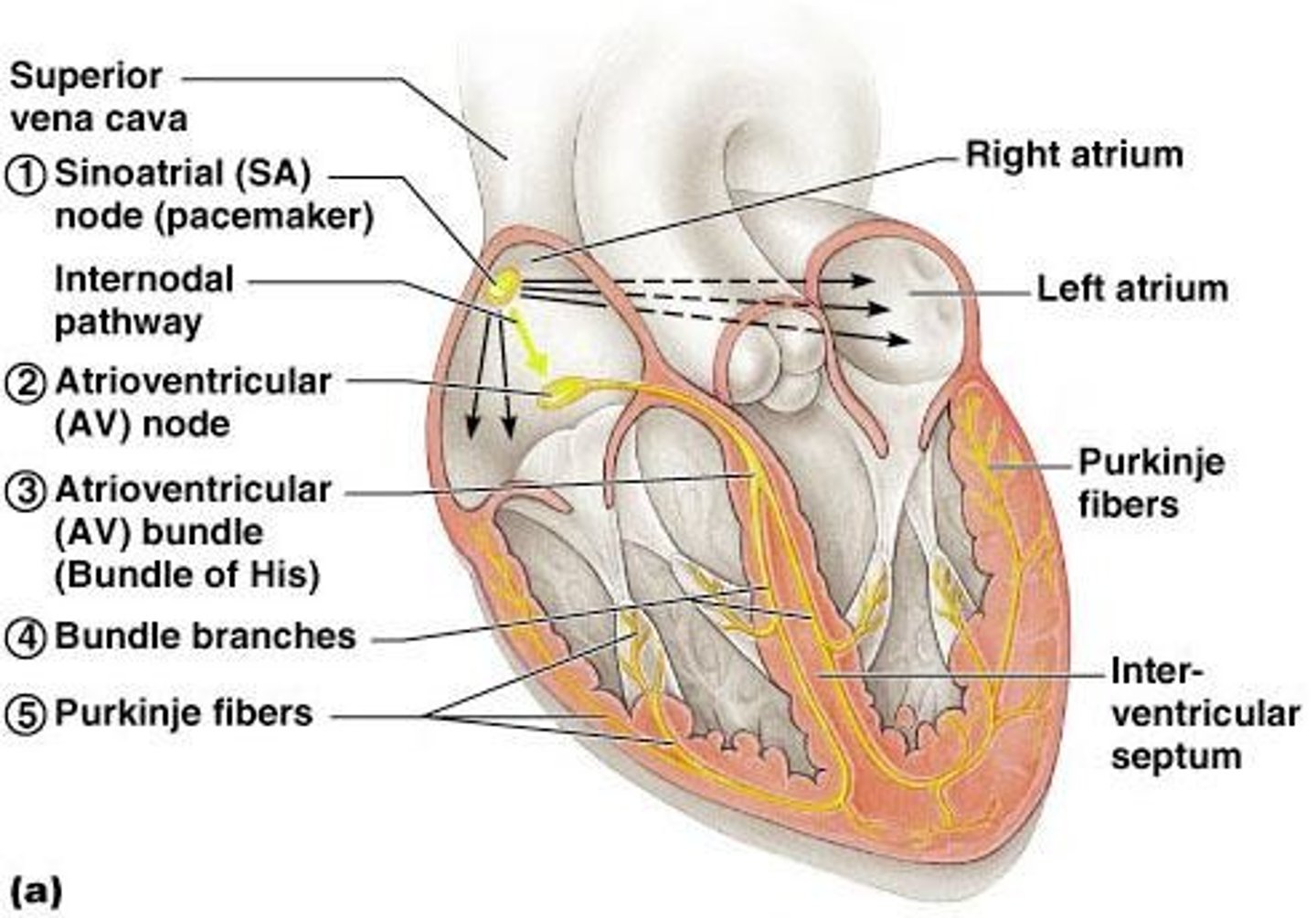
What is the role of the atrioventricular (AV) node in heart physiology?
It delays the impulse approximately 0.1 second.
How does cardiac muscle contraction differ from skeletal muscle contraction?
Cardiac muscle contraction is similar to skeletal muscle contraction but is self-excitable and contracts as a unit.
What is the absolute refractory period of cardiac muscle contraction?
It is long, lasting about 250 ms.
What are autorhythmic cells responsible for in the heart?
They initiate action potentials and have unstable resting potentials called pacemaker potentials.
What ion influx is primarily used during the rising phase of the cardiac action potential?
Calcium influx is used rather than sodium.
Describe the sequence of excitation in the heart starting from the SA node.
The impulse generated by the SA node passes to the AV node, then to the bundle of His, which splits into bundle branches, and finally to the Purkinje fibers.
What happens during Phase 0 of the cardiac action potential?
Depolarization occurs.
What occurs during Phase 1 of the cardiac action potential?
Early repolarization phase.
What is the characteristic of Phase 2 in the cardiac action potential?
It is known as the plateau phase.
What occurs during Phase 3 of the cardiac action potential?
Rapid repolarization.
How does the depolarization phase of the action potential relate to the electrocardiogram (ECG)?
It coincides with the QRS complex.
What does the repolarization of the action potential coincide with on the ECG?
It coincides with the T wave.
What is the typical rate of action potentials generated by the heart per minute?
Approximately 75-80 action potentials.
What is the role of the sympathetic cardioacceleratory center?
It stimulates the heart.
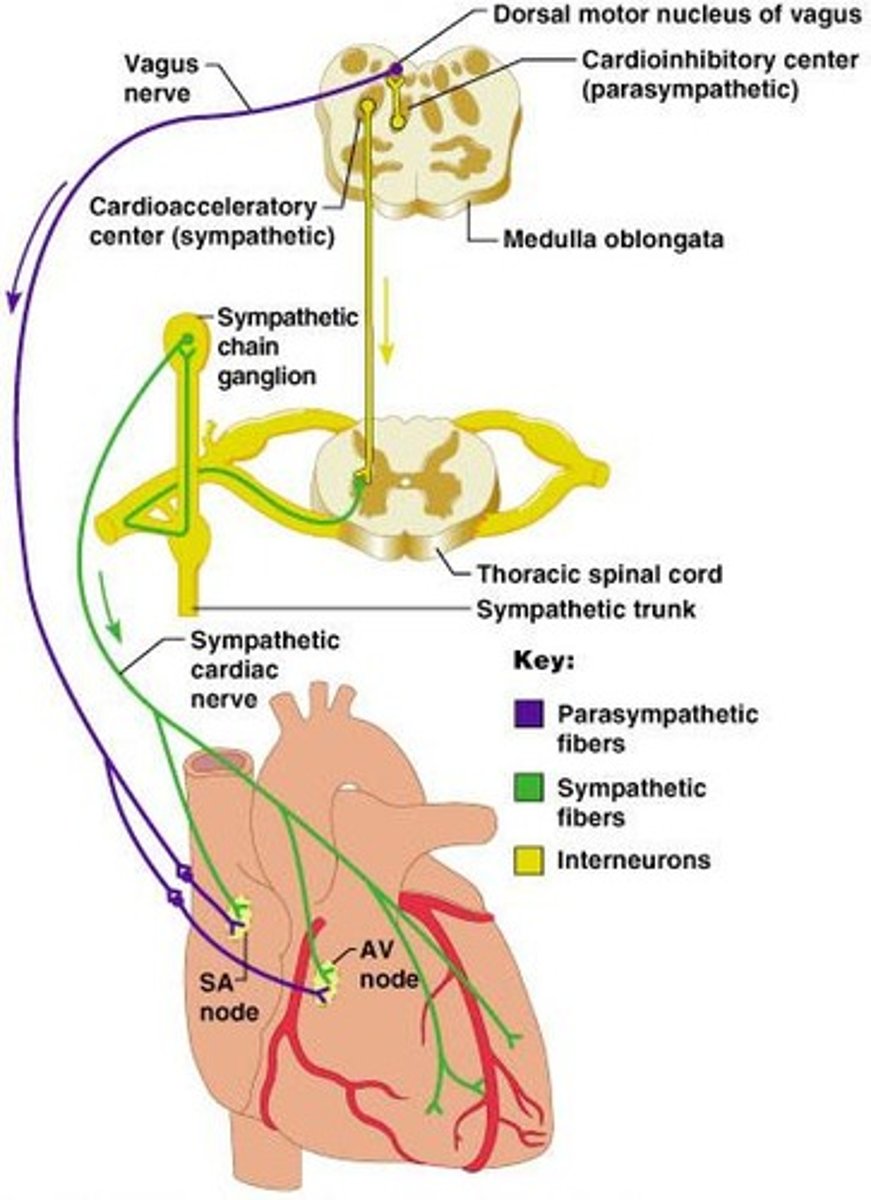
What is the role of the parasympathetic cardioinhibitory center?
It inhibits the heart.
Can the nervous system elicit cardiac action potentials?
No, cardiac action potentials can only be initiated by the SA node.
What is the significance of the bundle branches in heart physiology?
They carry the impulse toward the apex of the heart.
What do Purkinje fibers do in the heart?
They carry the impulse to the heart apex and ventricular walls.
What is the resting potential of cardiac muscle cells?
It is the electrical potential of the cells when they are not actively conducting an impulse.
What is the importance of the long absolute refractory period in cardiac muscle?
It prevents tetanus and allows the heart to fill with blood between contractions.