PHYSIOLOGY OF SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS OF THE SPINAL CORD (Part 2)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
NOMENCLATURE IN THE DESCRIPTION OF PAIN AND ABNORMAL SENSATION
EEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE
Any abnormal sensation described as unpleasant
Dysesthesia
Exaggerated pain response from a normally painful stimulus
Usually includes aspects of summation c repeated stimulus of constant intensity and after sensation
Increased sensitivity and lowered threshold to painful stimuli
Hyperalgesia
Ex. inflammation or burns
Exaggerated perception of touch stimulus
Heightened cutaneous sensitivity
Hyperesthesia (hypesthesia)
Abnormal perception of pain from a normally non-painful mechanical or thermal stimulus
Usually has elements of delay in perception and of aftersensation
Allodynia
Ex. Trigeminal neuralgia
Decreased sensitivity and raised threshold to painful stimuli
Hypoalgesia (hypalgesia)
Reduced perception of all sensation
Anesthesia
Spontaneous positive, pricking sensation that is not unpleasant
“Pins and needles”
Parasthesia
Burning pain in distribution of one or more peripheral nerves
Causalgia
PAIN SENSATIONS
SKIN AND DEEP PAIN
SKIN PAIN
Two types:
Pricking pain → evoked immediately on penetration of skin by needle
Followed by stinging or burning pain
“Double response” → pricking followed by stinging or burning
DEEP PAIN
From visceral and skeletomuscular structures
Aching; can be sharp, knife-like, burning
Diffuse, purely localized
Pain at location other than site of stimulus
Deep pain → has infinite boundaries and location is distant from the visceral structures involved
Tends to be referred to other areas innervated by the same spinal segments of the viscera affected
REFERRED PAIN
Possible explanation:
Small-caliber pain afferents from deep structures and cutaneous afferents project to a wide range of lamina V neurons in the dorsal horn
Convergence of deep and cutaneous afferents on the same dorsal horn cells, and the fact that there are a lot more cutaneous afferents than visceral afferents and have direct connections with the thalamus, is probably the reason for the phenomenon
Unmyelinated sprouts of A-delta and C fibers of an injured nerve become capable of spontaneous ectopic excitation and afterdischarge and are susceptible to ephatic activation
Injured nerves are also sensitive to locally applied or intravenously administered catecholamines because of an overabundance of adrenergic receptors on regenerating fibers
CHRONIC PAIN
Sensory neurons in dorsal horns of SC or thalamus, if chronically bombarded with pain impulses, may become autonomously overactive (being maintained in this state perhaps by excitatory amino acids) and may remain so even after the peripheral pathways have been interrupted
MOTOR EXAMINATION
Observation, Inspection, Palpation, Muscle Tone Testing, Functional Testing, Strength Testing of Individual Muscle Groups
MUSCLE STRENGTH
Muscle strength → rated on a scale of 0/5 to 5/5
0/5: no contraction
1/5: muscle flicker, but no movement
2/5: movement possible, but not against gravity (test joint in its horizontal plane
3/5: movement possible against gravity, but not against resistance by examiner
4/5: movement possible against some resistance by the examiner (subdivided into 4-/5, 4/5, 4+/4)
5/5: normal strength
FUNCTIONAL TESTING
Rhythmic thumb and index finger tapping
Rhythmic heel tapping
Closed eyes, forward flex arms, maintain
SENSORY EXAMINATION
Sensory examination → performed in all extremities, including face and trunk; eyes closed
correlate and recheck to improve objectivity
Light touch → cotton tipped swab or fine light touch
Pain → Sharp or dull end of safety pin or broken wooden swab
Ask patient to identify sharp or dull
Temperature Sense - Cold metal i.e. end of a tuning fork
Vibration Sense - Low frequency tuning fork 128 Hz on ball of large toes or fingers
Joint Position Sense - Moving toe or finger up or done
Two-Point Discrimination -Special calipers or bent paper clip or Alternately touching with one or two points
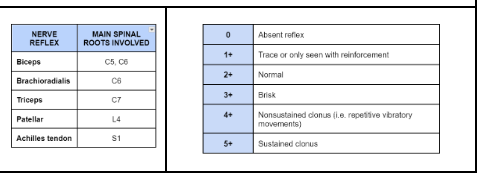
DEEP TENDON REFLEX