MAN 336 Exam 3
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Trait theory of leadership
who? Identify common traits among successful leaders
intelligence, energy, honesty
problems with trait theory
assumes leaders are born not made
limited predictive validity
researchers realized that the search for universal leadership traits was futile/useless
behavioral theory of leadership
what? analyze the behaviors of what effective leaders “do”
task-oriented
productivity tends to be HIGHER
structing the roles of subordinates
providing them with clear instructions
outlining group and individual goals
relationship-oriented
showing concern/empathy for employee feeling
personal interest in employee well-being
people are more satisfied and react more
problems with behavioral theories
limited research supports that merely demonstrating these behaviors improves leaders effectiveness
neglected the role of the environment
contingency theory of leadership
when? understand when certain behaviors work and when they don’t
problems with contingency theory
better predictive validity but still low
too formulaic, leadership is not simple
missing an important part of leadership
inspiration theory (contemporary)
why? understand why followers follow certain leaders
five contemporary theories
transformational
leader-member exchange
servant
authentic
courage
learn all of these from Shackleton
transformational leadership
inspire and excite followers to high levels of performance
aligning employee goals with leader goals; charisma
servant leadership
self-sacrificing devotion to followers
employees first; focus on ethics, community development, self-sacrifice
leader-member exchange
focus on building strong relationships with subordinates
trust-based relationship between a leader and follower
authentic leadership
be who you are rather than who you think you should be; “be yourself”
requires understanding oneself
courage
willingness to be vulnerable in the face of uncertainty and doubt
Six leadership styles in leadership that gets results
Goleman’s leader styles
Coercive Style
Authoritative Style
Affiliative Style
Democratic Style
Pacesetting Style
Coaching Style
coercive style
directive, command and control
damaging effect on reward systems
works best in a crisis
“do what i tell you” (-)
Authoritative style
mobilizes people toward a vision
works best when changes require new vision
“come with me” (+)
Affiliative style
creates harmony and builds emotional bonds
works best to heal rifts in a team
“people come first” (+)
Democratic style
forges consensus through participation
collaboration
works best to build consensus
“what do you think?” (+)
Pacesetting style
sets high standards and lead by example
works best to get quick results from a high motivated team
“do as I do, now” (-)
Coaching style
develops people for the future
works best to help an employee improve performance
“try this” (+)
which leadership characteristic is universal and which vary across cultures?
democratic is the universal style
organizational culture
system of shared assumptions, values, and artifacts that show employees what is appropriate and inappropriate behavior
Three levels of organizational culture
surface level is artifacts
second level is value
deepest level is assumptions
assumptions
taken for granted and they reflect beliefs about human nature and reality
“its why we hold those values” / “its who we are”
the reason why people believe the value
values
shared principles. standards, and goals
guides to behavior
artifacts
visible and tangible aspects of organizational culture
behavior, language, decor, attire
expression of values
Disney’s culture
artifacts: uniform
Value: language
Assumptions: happy place on earth
Four ways cultures can be proactively maintained
Attraction-Selection-Attrition ASA
New employee onboarding
leadership
reward systems
Attraction-Selection-Attrition
ASA: who is apart of the org
attraction: who is attracted to the job
selection: pick though fits in the company’s culture
attrition: those who don’t fit in and leave company
New boarding/ onboarding
induction and newbie
new employees learn the attitudes and skills
leadership
role models / examples for others
Reward systems
reward behaviors or results
rewards performance or seniority
Disney culture maintenance
???
org culture and org outcome
????
organizational structure
defines how job tasks are formally divided, grouped, and coordinated
functional structure
grouping jobs based on similarity in functions
HIGH span of control, centralization, task specialization
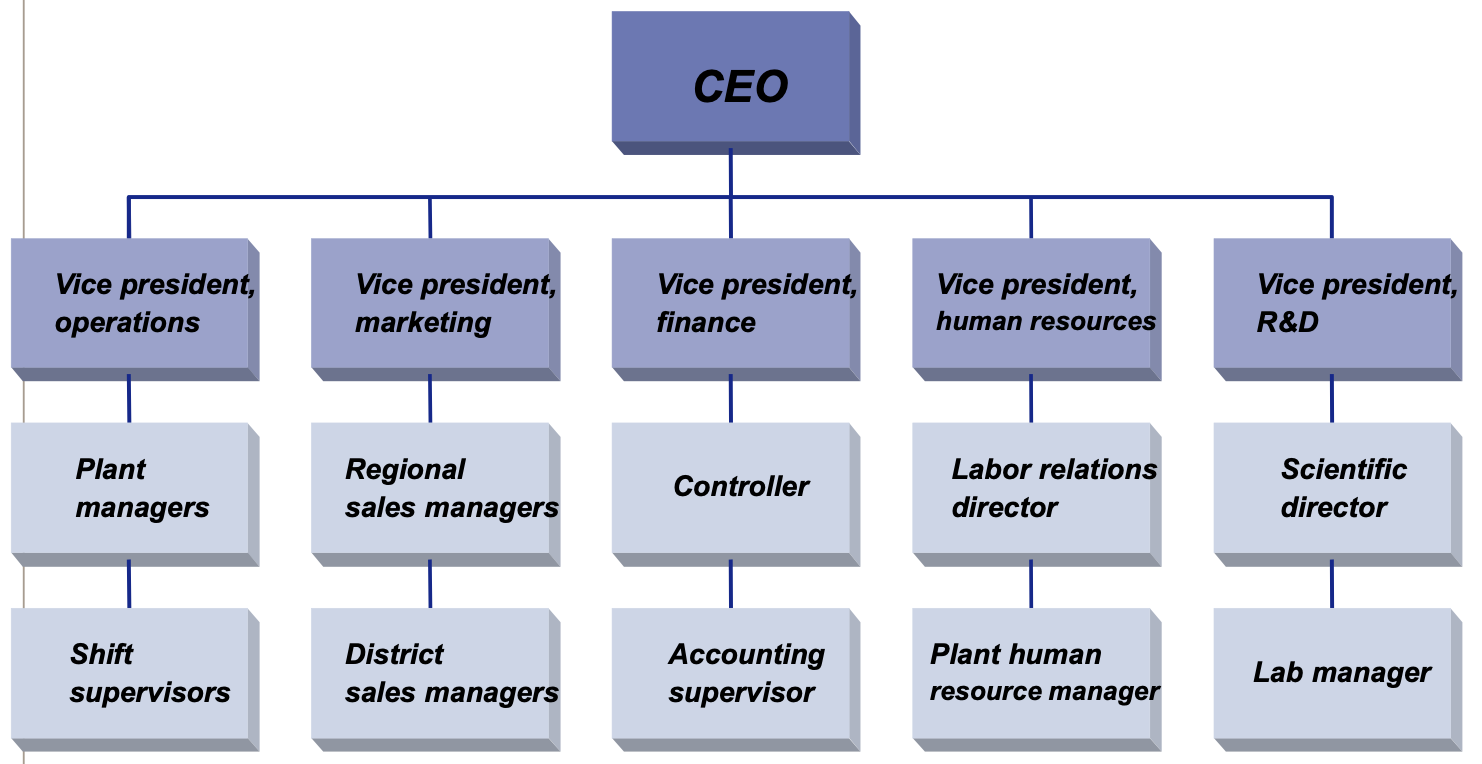
when to use functional structure
stable environment
small number and similar products
small to medium size organizations
advantages of functional
advantage
efficiency, quality
low cost
excellent coordination within function
disadvantage of functional
Disadvantage
difficult to adapt; little innovation
poor coordination across function
slow decisions
divisional structure
grouping of jobs based on the products, services, customers, or geographic locations product based
LOW span of control, centralization, task specialization
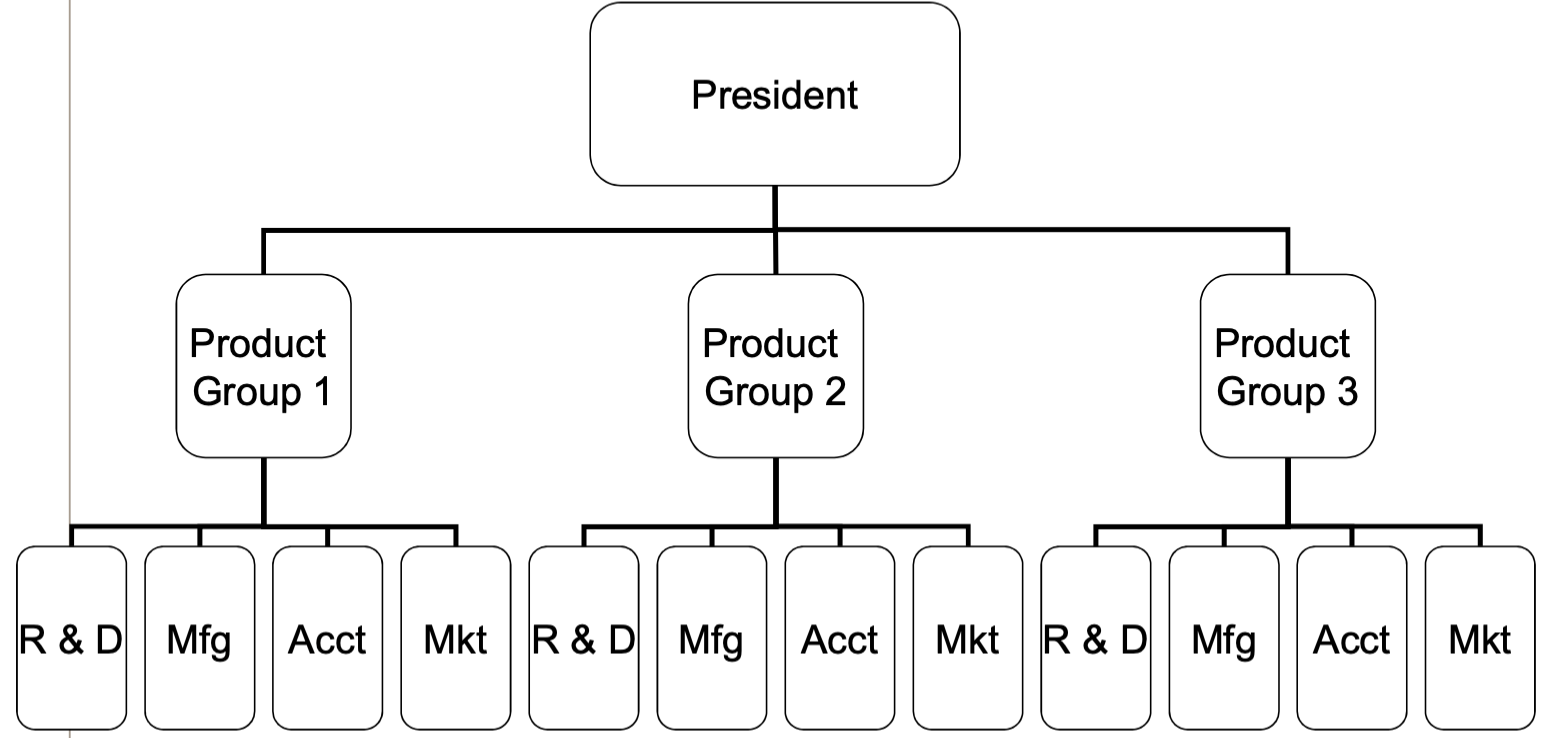
when to use divisional structure
unstable, uncertain environment
large size organization
goals of product specialization
advantage of divisional
Advantage
innovation; adaptable
product/customer focus
high coordination between function
disadvantage of divisional
Disadvantage
duplication of resources across divisions
less functional/ technical specialization
less top management control
Matrix structure
cross a traditional functional structure with a product structure
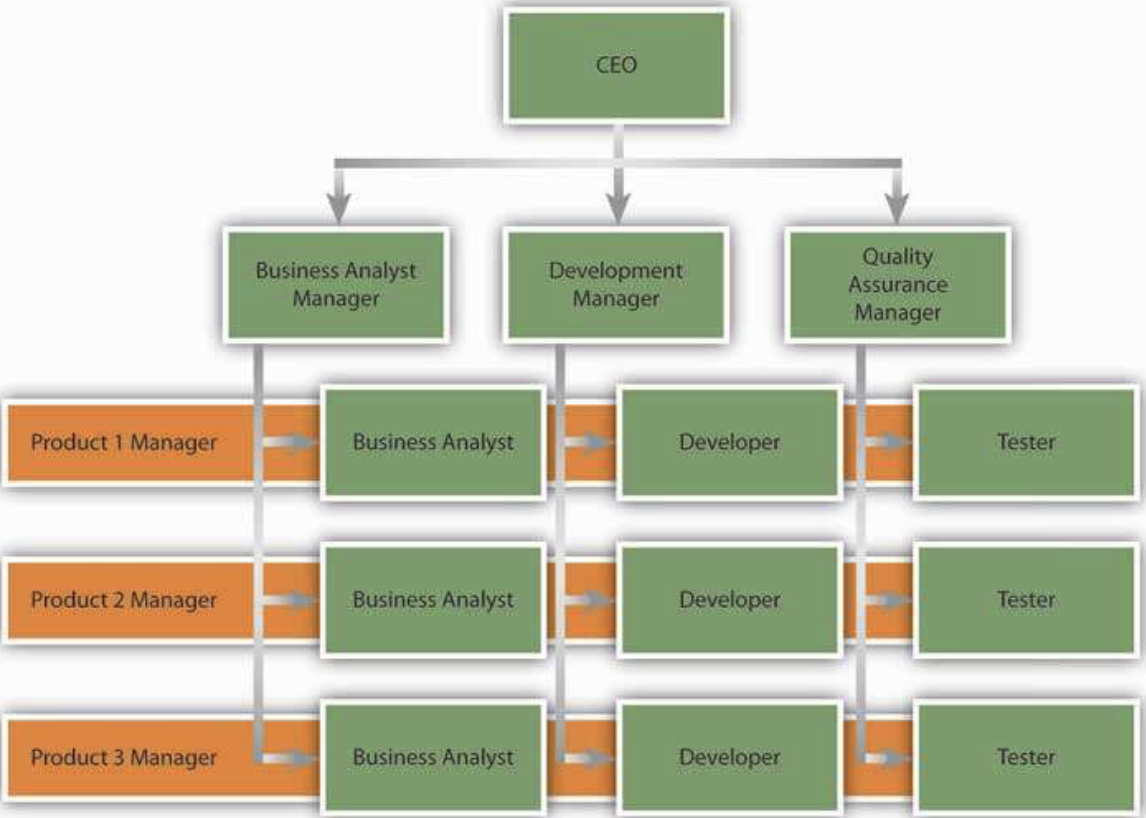
when to use matrix structure
dynamic, uncertain environments
large complex organizations
need to balance efficiency and innovation
advantages of matrix
advantage
can achieve best of both worlds
allows responsiveness and innovation
disadvantage of matrix
disadvantage
multiple lines of authority
can trigger conflicts between managers
requires coordination to reduce conflicts
centralization
decision making is concentrated at higher levels in an organization
greater demands on CEO and higher level managers
benefits and cost of centralization
leads to more efficient operations if company is stable
candidates are more likely to be attracted to decentralized organizations
enhances control but reduces innovation
task specialization
extent to which jobs are narrowly focused
benefits and costs of task specialization
improves quality but reduces coordination
span of control
number of employees reporting to a single manager
benefits and costs of span of control
high span is preferred when task complexity and task interdependence is low