S&P chapter 16
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
3 components of chemical senses
taste - food enters the mouth which stimulates receptors on the tongue
olfaction - molecules enter the nose which stimulate receptor neurons in the olfactory mucosa
flavor - combo of taste and olfaction
length of time for receptors to undergo a cycle of birth, development, and death for olfactory receptors
5-7 weeks
length of time for receptors to undergo a cycle of birth, development, and death for taste receptors
1-2 weeks
neurogenesis
constant renewal of receptors
5 basic taste qualities
salty, sour, sweet, bitter, Umami (meaty, brothy, savory, associated with monosodium glutamate). spicy isn’t on this list because its somatosensory
papillae
ridges and valleys on the tongue, some of which contain taste buds
filiform
Shaped like cones and are found over the entire surface of the tongue, giving it its rough appearance
fungiform
Shaped like mushrooms and are found at the tip and sides of the tongue
foliate
Series of folds along the back of the tongue on the sides
circumvallate
Shaped like flat mounds surrounded by a trench and are found at the back of the tongue
amount of taste cells in each taste bud
50 to 100
taste pore
tips of taste cells that protrude into the taste pore
signals from taste cells travel along a set of pathways:
•Chorda tympani nerve from front and
sides of tongue
•Glossopharyngeal nerve from back
of tongue
•Vagus nerve from mouth and throat
•Superficial petronasal nerve from soft palate
these pathways make connections in
nucleus of the solitary tract in medulla
then, they travel to the… Followed by areas in the frontal lobe…
thalamus. insula, frontal opervulum cortex, orbital frontal cortex.
population coding for taste experiment
-different taste stimuli presented to rats, recordings were made from the chorda tympani
-showed that 2 substances (ammonium chloride and potassium chloride) are similar to each other but different from sodium chloride.
specificity coding for taste
-mouse: PTC + Cyx chemicals
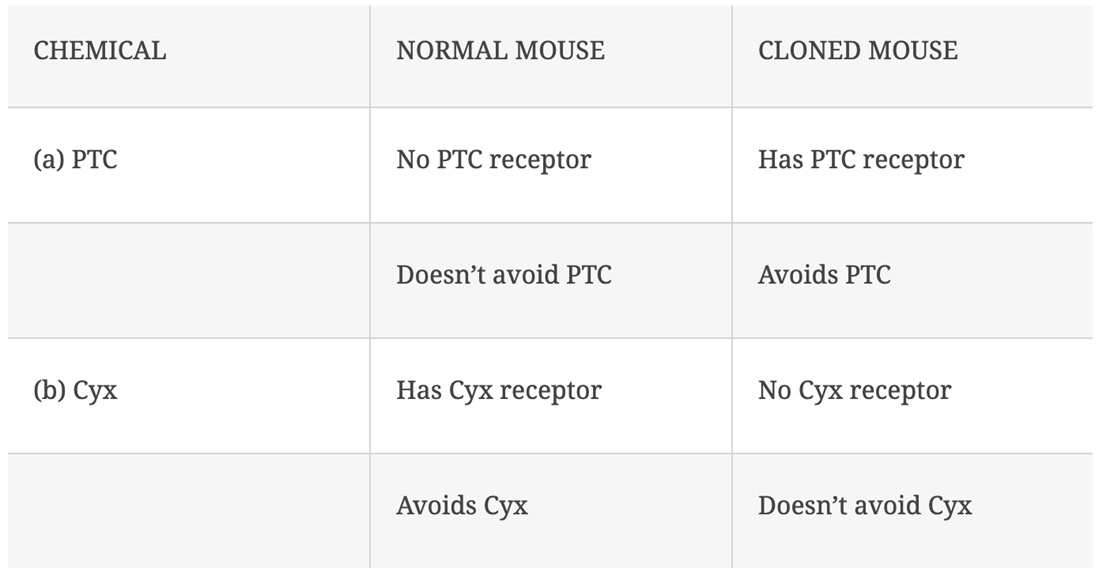
tasters
people who can taste PTC. 2//3 can taste PROP
nontasters
those who can’t taste PTC. 1/3 can’t taste PROP
people who can taste PROP have ____
higher densities of taste buds than those who can’t taste it
supertasters are more
sensitive to bitter substances than tasters.
microsomatic
having a poor sense of smell that is not crucial for survival
macrosomatic
having a well-developed sense of smell
detection thresold
the lowest concentration at which an odorant can be detected
forced-choice method
-participants presented with blocks of two trials– one trial contains a weak odorant, the other, no odorant
-Task = indicate which trial has a stronger smell
-threshold determined by measuring the concentration that results in a correct response on 75% of the trials
rats are ___ more senstivive to odors than humans
8 to 50 times
dogs are ___ more sensitive to odors than humans
300 to 10,000 times more sensitive
humans have ___ olfactory receptors and dogs have ____ olfactory receptors
10 million, 1 billion
humans can discriminate more than ____ different odors
1 trillion
COVID molecules attach to
any enzyme
ACE2 is found in
intestines, lungs, arteries, heart, nose. also found on surface of sustentacular cells
sustentacular cells can provide
metabolic and structural support to the olfactory sensory neurons
COVID causes loss of smell by
affecting their supporting cells
alzheimers disease
serious loss of memory and cognitive functions that come before mild cognitive impairment. loss of smell comes decades before other symptoms
olfactory mucosa
Dime-sized region located on the roof of the nasal cavity below the olfactory bulb
olfactory receptor neurons
Receptors in the olfactory mucosa (colored circles, tan part = supporting cells)
glomeruli
where olfactory neurons synapse onto the olfactory bulb
2 main olfactory areas
piriform cortex, orbitofrontal cortex
piriform cortex
primary olfactory area
orbitofrontal cortex
second olfactory area
amygdala is involved in
determining emotional reactions to smell
odor stimuli from food in the mouth reaches the olfactory mucosa through the ___
retronasal route
____is not influenced by olfaction
monosodium glutamate (savory taste)
responses from taste and smell are first combined in the
orbital frontal cortex
bimodalneurons
neurons that respond to 2 types of information (taste and smell, taste and vision)
____ is impacted by how hungry we are
firing rate
flavor being influenced by a persons expectations
participants couldn’t tell the difference in wine when the price was hidden. when the price was revealed, the participants said they were more satisfied with the expense wine.
flavor being influenced by hunger
when hungry and before consuming food, the pleasantness for both banana and vanilla were high. after consuming food, both pleasantness ratings decreased