Chapter 10: Photosynthesis (no Calvin Cycle)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Organisms that photosynthesize
Photosynthetic Bacteria (cyanobacteria)
Photosynthetic Protists (Euglena)
Algae and Seaweeds
Plants
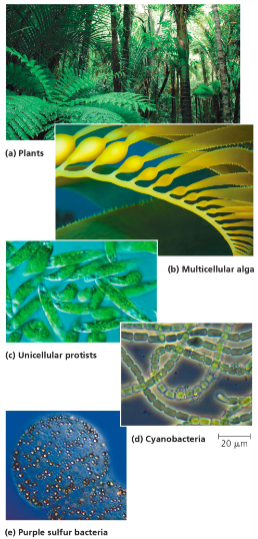
Where does photosynthesis occur (environments)?
freshwater and marine environments
terrestrial plants
Diatoms and Phytoplankton
main, general point of photosynthesis
capture light energy to drive synthesis of organic molecules
Solar energy → Chemical energy
Photosynthesis requires
CO2 + Water (H2O) + Light
Cellular Respiration produces
CO2 + Water (H2O)
Chloroplasts are mainly found in
Mesophyll cells
Mesophyll cells
the primary photosynthetic cells found within a plant leaf
Xylem and Phloem
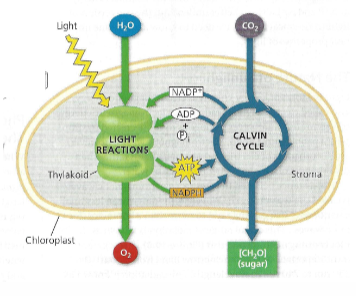
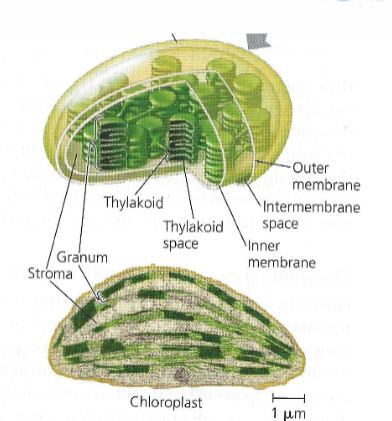
Stroma
the fluid-filled space inside chloroplasts; light-independent reactions / Calvin Cycle occurs here
Thylakoids
a flattened, membrane-bound sac located inside chloroplasts of plant cells; light-dependent reactions occur here
Granum
stacks of thylakoid
Basic leaf structure (top → bottom)
Cuticle→Upper Epidermis→Mesophyll→Lower Epidermis→Stomata
Cuticle
waxy covering of leaves
made of Cutin
non-polar, repels water
Upper epidermis
produces cuticle
protects the leaf by aiding in preventing water loss and providing an extra layer between the outside and inside of the leaf
Xylem
transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant, through the stem, and up to the leaves
Phloem
transport sugars (carbohydrates) produced during photosynthesis from the leaves ("source tissues") to other parts of the plant
Lower epidermis
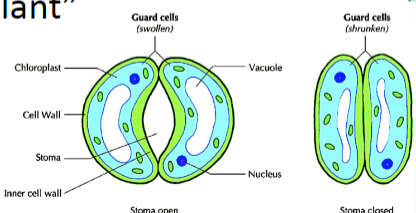
facilitate gas exchange through tiny pores called stomata, allowing carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and oxygen to exit, while also regulating water loss by opening and closing these stomata with the help of guard cells
Stomata
primary means for gas exchange via opening and closing via Guard Cells
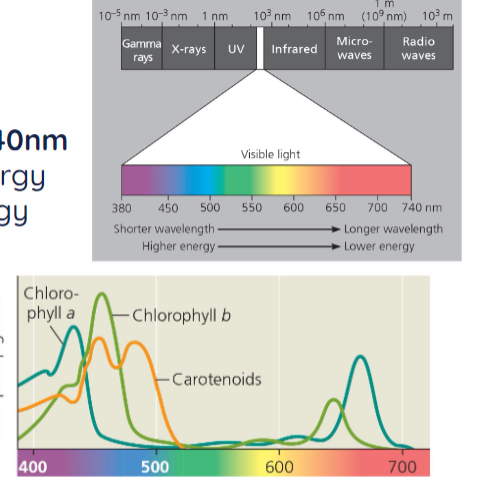
Electromagnetic Spectrum
visible light from 380nm-740nm
small wavelength = more energy
large/long wavelength = less energy
Photons
discrete unit of light
Chlorophyll a
green pigment b/c absorbs blue and red light
absorbs light energy for photosynthesis (main)
Chlorophyll b
abosrbs light at wavelengths where Chlorophyll a is less efficient
absorbs blue and red light (but at lower wavelengths than Chlorophyll a)
Carotenoids
absorbs light where Chlorophyll a/b cannot (blue-green light)
appears red, yellow, orange
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Light/Hill Reaction
occurs on Thylakoid Membrane
Photosystems II/I: have Light Harvesting (Antenna pigments) and Reaction Center Complexes (Chlorophyll a)
P680 (PSII) / P700 (PSI)
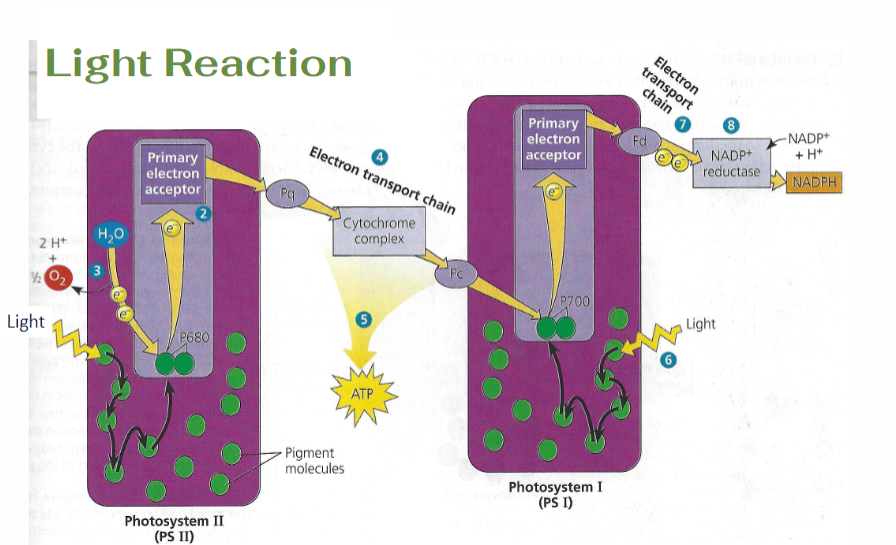
Photolysis
splitting of water molecules
H2O → 2H+, 2e-, 1/2O2
H+ = gradient (thylakoid space)
e- = replacement
O2 = released
Products of the Light Reaction
O2, ATP, NADPH
Path of Light Reaction
Light→P680→Primary e- Acceptor→Pq→Cytochrome Complex→Pc→P700→Primary e- Acceptor→Fd→NADP+ Reductase→NADPH